果桑是以收获桑椹为主或果叶兼用的一类桑树品种。桑椹营养丰富,风味独特,富含花青素、白藜芦醇、黄酮、生物碱、多糖等多种功能活性成分,还含有丰富的氨基酸、维生素等,具有补肝、养肾、降血糖、黑发乌须、增强免疫力、抗衰老等药理作用和保健功效[1]。原国家卫生部把桑椹列为“既是食品又是药品”的农产品之一,桑椹被誉为“21世纪的最佳保健果品”[2]。随着全民崇尚天然、绿色食品的大健康时代到来,桑椹及其加工产品受到越来越多消费者的喜爱,果桑产业的发展前景十分广阔。
重庆市蚕业科学技术研究院桑树育种团队联合资源昆虫高效养殖与利用全国重点实验室(西南大学)的科研人员,经过多年的选育试验,成功培育出桑椹产量高、抗性强、观赏性强、便于采摘的果叶兼用桑树新品种渝果1号。2021年,新品种通过重庆市蚕桑品种审定委员会审定(审定编号:渝蚕桑品审202101)。
1 选育经过
2009年5月,从原西里蚕种场(重庆市北碚区蔡家岗街道)地坎桑园的优良野生桑收集种子并播种繁育成品系。2011年5月,初步选定优良单株并标记;2011年12月,将选定的优良单株苗木移栽到重庆市蚕业科学技术研究院(原重庆市北碚蚕种场)桑园进一步进行比较试验。2012年在田间继续观察调查,从中筛选出了1株叶片大、叶肉厚、节间密、生长势旺盛、桑椹产量高、品质好的优良单株,暂定名为渝果1号。2012年12月,采用冬季简易芽接技术繁育建立了母种园。2013—2015年开展新品种的生物学特性调查,并建立品种比较试验桑园,以红果2号和湖桑32号作为对照品种。2016年向重庆市蚕桑品种审定委员会提出审定申请,并于2016—2019年在重庆市蚕业科学研究院以及重庆市合川区、江津区、涪陵区、万州区的共5个区域试验点开展区域鉴定试验。
2 主要性状
2.1 遗传学特征
为分析渝果1号的亲缘关系,资源昆虫高效养殖与利用国家重点实验室(西南大学)对渝果1号的ITS序列进行测定,并将测序结果与重庆市作物种质北碚桑树圃保存的38个品种进行比对。结果显示,渝果1号的ITS序列长度为611 bp,基于ITS序列标记数据构建的系统发生树表明,渝果1号与白桑(Morus alba)聚为一支(图1)。
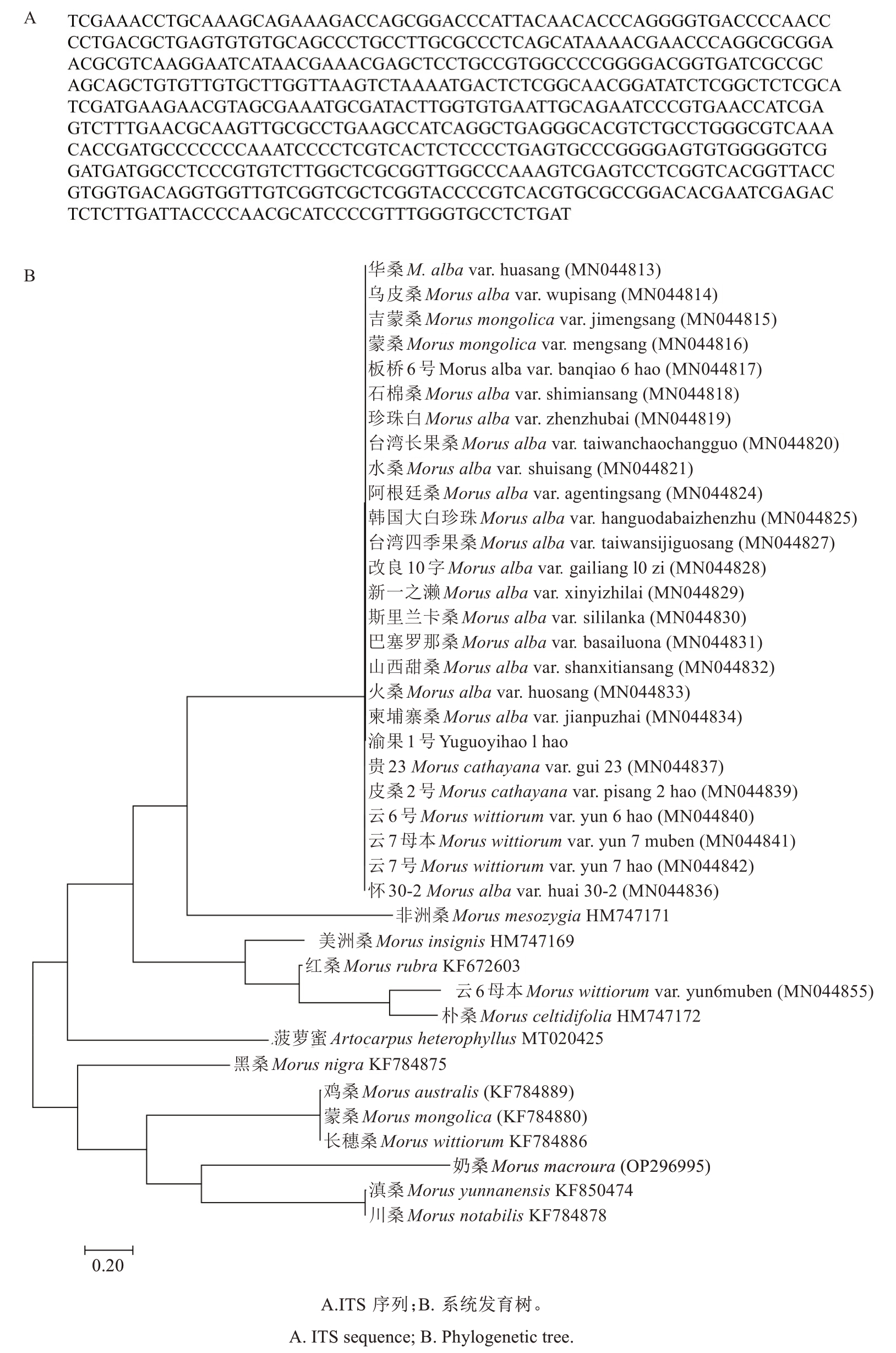
图1 果叶兼用桑品种渝果1号的ITS序列及系统发育树
Fig. 1 ITS sequence and phylogenetic tree of the fruit and leaf dual-purpose mulberry cultivar Yuguo 1
2.2 生物学特性
渝果1号树形高大开展,枝条粗壮直立,侧枝多,发条力强,节间距4.07 cm(图2-A)。枝条皮色为灰色,皮孔小,圆形或椭圆形,黄褐色,均匀突出,28个·cm-2。冬芽长三角形,紫褐色,饱满,芽尖歪向一侧;鳞片红褐色紧凑、无小毛;副芽大且多,左生或右生(偶有左右对生);芽褥高,叶痕半圆形、陷入浅(图2-B)。叶呈心脏形,叶形较大,叶长21.5 cm,叶幅15.2 cm,叶序为3/8,叶肉质地中等,叶面光滑平展,叶色深绿,光泽强,叶缘为锯齿,叶基深心形,叶尖尾状(2-C)。果实为圆筒形,纵径3.16 cm,横径1.63 cm,果实紫黑色,枝条结果部位果实多、叶片少(图2-D~F),果实成熟期较集中,便于采收。

图2 果叶兼用桑品种渝果1号的形态特征
Fig. 2 Morphological characteristics of the fruit and leaf dual-purpose mulberry cultivar Yuguo 1
由表1可知,渝果1号较红果2号具有更好的产叶性能。渝果1号为中熟品种,在育成地(重庆市北碚区)的发芽期为2月18日—3月2日,两年平均发芽率为91.60%,对照品种红果2号为94.12%,湖桑32号为90.48%(表2)。
表1 果叶兼用桑品种渝果1号与两个对照品种枝叶性状比较
Table 1 Comparison of branch and leaf traits between the fruit and leaf dual-purpose mulberry cultivar Yuguo 1 and two control cultivars
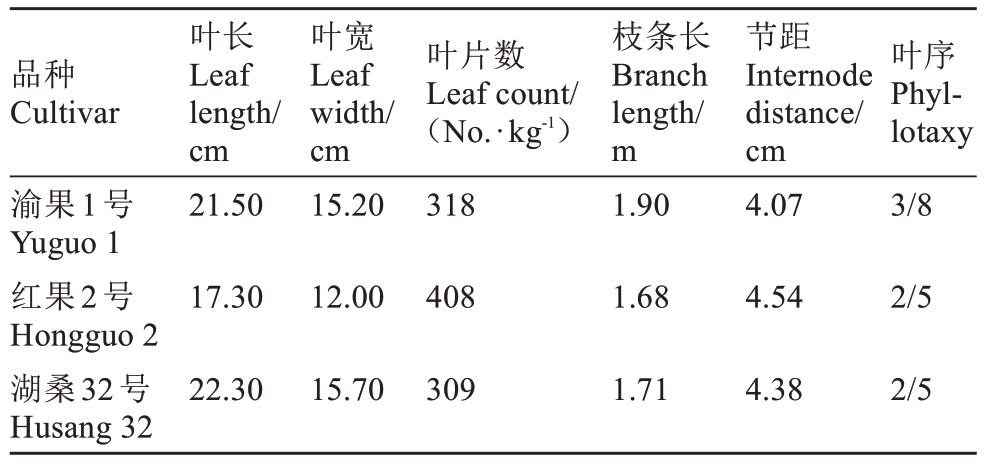
注:数据为2018—2019年重庆市蚕业科学技术研究院及重庆市江津区、涪陵区、合川区、万州区5个区试点调查的平均值。表3同。
Note:The data represent the average values from surveys conducted in 2018—2019 at five pilot sites in Chongqing Sericulture Science and Technology Research Institute, Jiangjin District, Fuling District, Hechuan District, and Wanzhou District. The same Table 3.
品种Cultivar叶片数Leaf count/(No.·kg-1)渝果1号Yuguo 1红果2号Hongguo 2湖桑32号Husang 32叶长Leaf length/cm 21.50叶宽Leaf width/cm 15.20318枝条长Branch length/m 1.90节距Internode distance/cm 4.07叶序Phyllotaxy 3/8 17.3012.004081.684.542/5 22.3015.703091.714.382/5
表2 果叶兼用桑品种渝果1号与两个对照品种发芽期调查
Table 2 Investigation of the budding period of the fruit and leaf dual-purpose mulberry cultivar Yuguo 1 and two control cultivars
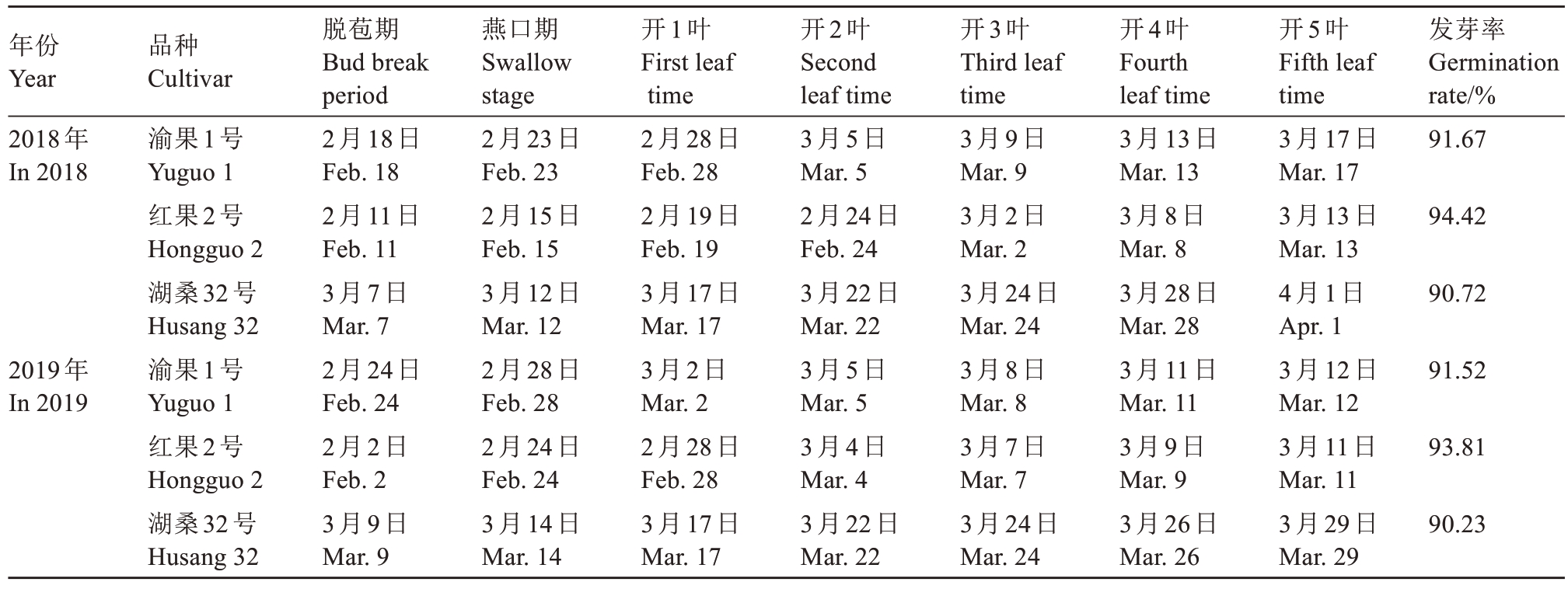
注:调查地点为重庆市蚕业科学技术研究院桑园。
Note:The survey was conducted at the mulberry garden of the Chongqing Sericulture Science and Technology Research Institute.
年份Year 2018年In 2018开1叶First leaf time发芽率Germination rate/%91.67 94.42 90.72 2019年In 2019品种Cultivar渝果1号Yuguo 1红果2号Hongguo 2湖桑32号Husang 32渝果1号Yuguo 1红果2号Hongguo 2湖桑32号Husang 32脱苞期Bud break period 2月18日Feb. 18 2月11日Feb. 11 3月7日Mar. 7 2月24日Feb. 24 2月2日Feb. 2 3月9日Mar. 9燕口期Swallow stage 2月23日Feb. 23 2月15日Feb. 15 3月12日Mar. 12 2月28日Feb. 28 2月24日Feb. 24 3月14日Mar. 14 2月28日Feb. 28 2月19日Feb. 19 3月17日Mar. 17 3月2日Mar. 2 2月28日Feb. 28 3月17日Mar. 17开2叶Second leaf time 3月5日Mar. 5 2月24日Feb. 24 3月22日Mar. 22 3月5日Mar. 5 3月4日Mar. 4 3月22日Mar. 22开3叶Third leaf time 3月9日Mar. 9 3月2日Mar. 2 3月24日Mar. 24 3月8日Mar. 8 3月7日Mar. 7 3月24日Mar. 24开4叶Fourth leaf time 3月13日Mar. 13 3月8日Mar. 8 3月28日Mar. 28 3月11日Mar. 11 3月9日Mar. 9 3月26日Mar. 26开5叶Fifth leaf time 3月17日Mar. 17 3月13日Mar. 13 4月1日Apr. 1 3月12日Mar. 12 3月11日Mar. 11 3月29日Mar. 29 91.52 93.81 90.23
2018—2019年调查显示,重庆市蚕业科学技术研究院桑园内渝果1号的花期为3月10—30日,其中初花期在3月10—17日,盛花期在3月15—24日,末花期在3月22—30日;桑椹成熟期为4月11日至5月5日,盛熟期为4月19—26日。
2.3 经济性状
2.3.1 果实产量 与红果2号比较,渝果1号的果实产量性状更优(表3),坐果率91.01%,平均单芽坐果数6.18粒,平均单果质量3.96 g,1 hm2桑园的平均年产果量为39.38 t,比对照品种红果2号高25.63%(表3)。
表3 果叶兼用桑品种渝果1号与对照品种红果2号的果实产量性状调查
Table 3 Investigation of fruit yield traits of the fruit and leaf dual-purpose mulberry cultivar Yuguo 1 and the control cultivar Hongguo 2
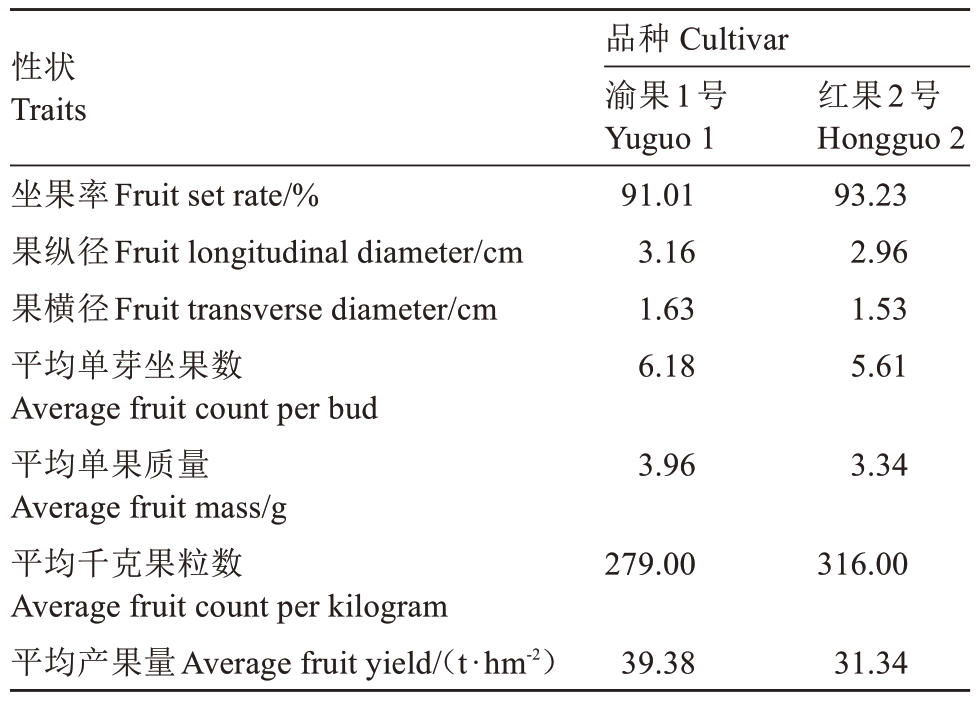
性状Traits坐果率Fruit set rate/%果纵径Fruit longitudinal diameter/cm果横径Fruit transverse diameter/cm平均单芽坐果数Average fruit count per bud平均单果质量Average fruit mass/g平均千克果粒数Average fruit count per kilogram平均产果量Average fruit yield/(t·hm-2)品种 Cultivar渝果1号Yuguo 1 91.01 3.16 1.63 6.18红果2号Hongguo 2 93.23 2.96 1.53 5.61 3.963.34 279.00316.00 39.3831.34
2.3.2 桑叶产量及养蚕成绩 2018—2019年两年的区域试验调查结果显示,渝果1号桑叶年均产量为20.84 t·hm-2,较对照品种湖桑32号降低1.38%,但比对照品种红果2号提高13.20%(表4)。
表4 果叶兼用桑品种渝果1号与两个对照桑品种的桑叶产量调查
Table 4 Investigation of leaf yield of the fruit and leaf dual-purpose mulberry cultivar Yuguo 1 and two control mulberry cultivars
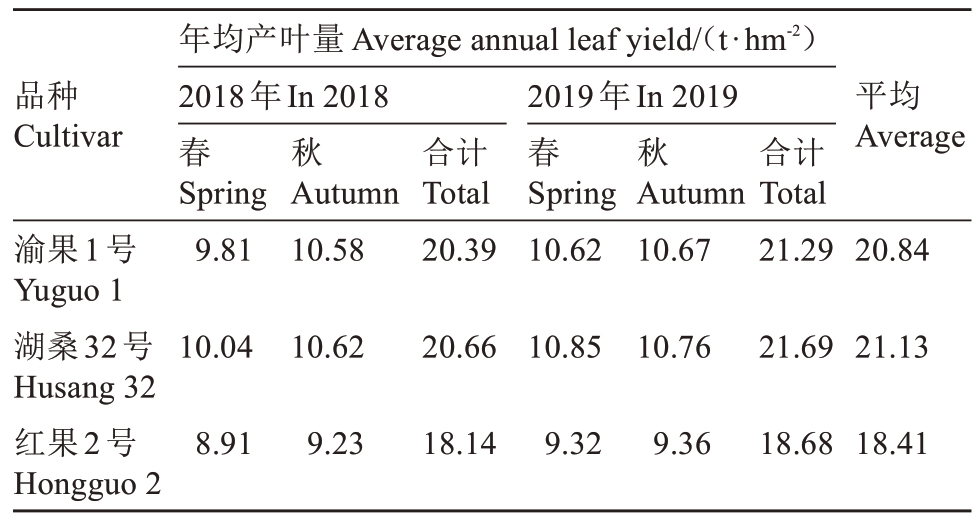
品种Cultivar年均产叶量 Average annual leaf yield/(t·hm-2)2018年In 2018春Spring 9.81秋秋平均Average渝果1号Yuguo 1湖桑32号Husang 32红果2号Hongguo 2 Autumn 10.58合计Total 20.39 2019年In 2019春Spring 10.62 Autumn 10.67合计Total 21.2920.84 10.0410.6220.6610.8510.7621.6921.13 8.919.2318.149.329.3618.6818.41
2018—2019年,利用区域试验中渝果1号及两个对照品种春季收获的桑叶进行养蚕叶质鉴定试验,调查结果见表5。渝果1号桑叶养蚕的万蚕平均产茧量为19.13 kg,较叶用对照品种湖桑32号的产量提高0.58%,较果用对照品种红果2号的产量提高5.98%;渝果1号桑叶养蚕的万蚕平均茧层产量为4.37 kg,较湖桑32号的产量提高0.23%,较红果2号的产量提高8.17%;使用渝果1号的桑叶饲养4~5龄蚕,每100 kg桑叶的平均产茧量为4.93 kg,与湖桑32号的产量相当,较红果2号的产量提高4.23%。
表5 果叶兼用桑品种渝果1号与两个对照桑品种桑叶养蚕试验成绩
Table 5 Performance of sericulture using leaves from the fruit and leaf dual-purpose mulberry cultivar Yuguo 1 and two control mulberry cultivars
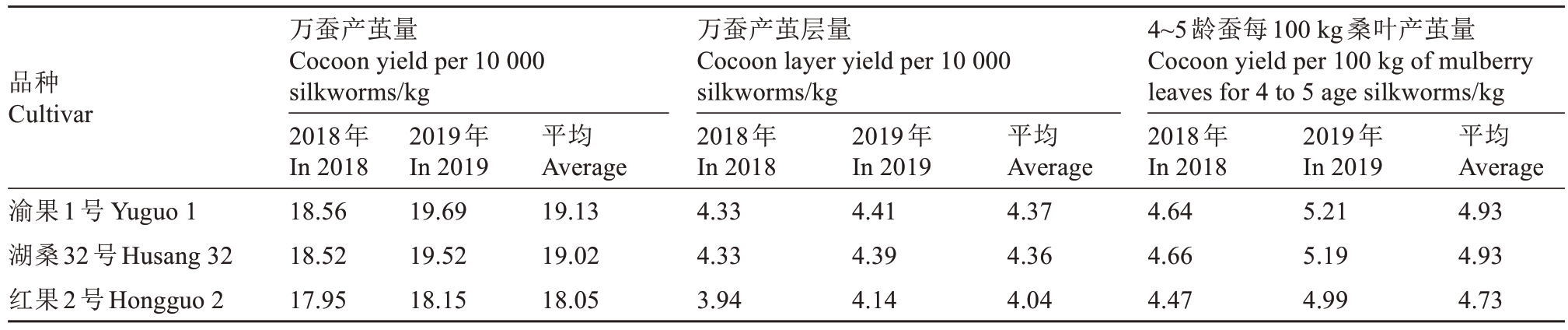
注:数据为2018—2019年春季重庆市蚕业科学技术研究院及重庆市江津区、涪陵区、合川区、万州区5个区试点桑叶养蚕成绩的平均值;供试家蚕品种为871×872。
Note:The data represent the average sericulture performance using mulberry leaves collected in spring 2018—2019 from five pilot sites in Chongqing Sericultural Science and Technology Research Institute, Jiangjin District, Fuling District, Hechuan District, and Wanzhou District. The silkworm cultivar used in the trials was 871×872.
品种Cultivar 平均Average 4.93 4.93 4.73渝果1号 Yuguo 1湖桑32号Husang 32红果2号Hongguo 2万蚕产茧量Cocoon yield per 10 000 silkworms/kg 2018年In 2018 18.56 18.52 17.95 2019年In 2019 19.69 19.52 18.15平均Average 19.13 19.02 18.05万蚕产茧层量Cocoon layer yield per 10 000 silkworms/kg 2018年In 2018 4.33 4.33 3.94 2019年In 2019 4.41 4.39 4.14平均Average 4.37 4.36 4.04 4~5龄蚕每100 kg桑叶产茧量Cocoon yield per 100 kg of mulberry leaves for 4 to 5 age silkworms/kg 2018年In 2018 4.64 4.66 4.47 2019年In 2019 5.21 5.19 4.99
2.4 桑椹理化性状
渝果1号糖度和花色苷含量测定参照赵珮等[3]的方法;多酚含量测定参照李巨秀等[4]的方法;总黄酮含量测定参照黄金枝等[5]的方法;pH测定参照赵玉生等[6]的方法;榨汁率测定参照梁彬等[7]的方法;还原糖含量测定参照NY/T 2742—2015[8];总酸含量测定参照GB 12456—2021[9];多糖含量测定参照SN/T 4260—2015[10];粗蛋白含量测定参照GB 5009.5—2016[11]。对重庆市蚕业科学技术研究院2018—2019年连续两年试验收获的渝果1号和红果2号的成熟桑椹进行理化性状检测分析,结果见表6。渝果1号桑椹的糖度、总酸含量、多糖含量、蛋白质含量、pH值和榨汁率较对照品种红果2号分别提高11.76%、19.26%、32.64%、8.50%、1.88%和1.91%,但还原糖、花色苷、多酚、总黄酮含量较红果2号分别降低25.23%、62.26%、44.66%和24.39%。
表6 果叶兼用桑品种渝果1号与对照品种红果2号的桑椹理化性状比较
Table 6 Comparison of physical and chemical properties of mulberry fruits from the fruit and leaf dual-purpose mulberry cultivar Yuguo 1 and the control cultivar Hongguo 2
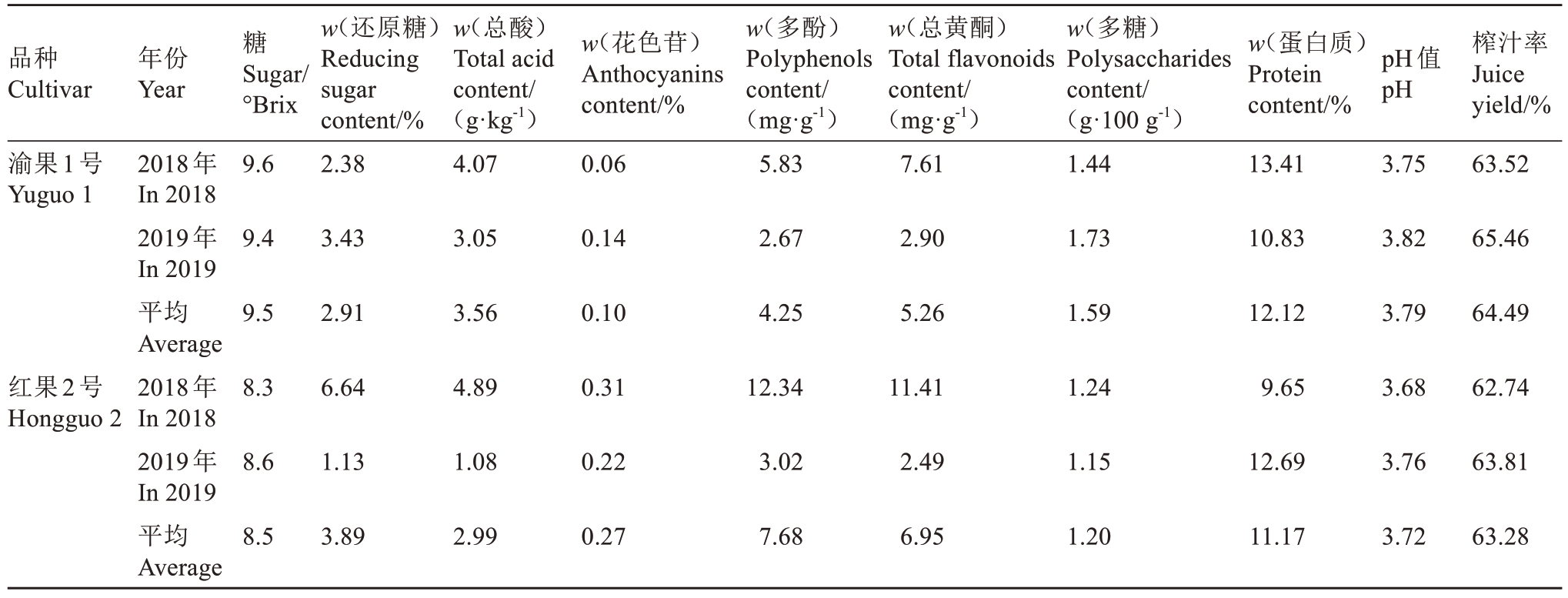
品种Cultivar年份Year糖pH值pH渝果1号Yuguo 1 Sugar/°Brix 9.6 w(还原糖)Reducing sugar content/%2.38 2018年In 2018 2019年In 2019平均Average 2018年In 2018 2019年In 2019平均Average w(总酸)Total acid content/(g·kg-1)4.07 w(花色苷)Anthocyanins content/%0.06 w(多酚)Polyphenols content/(mg·g-1)5.83 w(总黄酮)Total flavonoids content/(mg·g-1)7.61 w(多糖)Polysaccharides content/(g·100 g-1)1.44 w(蛋白质)Protein content/%13.413.75榨汁率Juice yield/%63.52 9.43.433.050.142.672.901.7310.833.8265.46 9.52.913.560.104.255.261.5912.123.7964.49红果2号Hongguo 2 8.36.644.890.3112.3411.411.249.653.6862.74 8.61.131.080.223.022.491.1512.693.7663.81 8.53.892.990.277.686.951.2011.173.7263.28
3 栽培技术要点
渝果1号是一个桑椹产量高、易于采收、观赏性强,且叶质优良、耐剪伐、发条力强的果叶兼用桑品种,适宜在长江、黄河及金沙江流域等地区栽植。
该品种适应性强,可在黏土、壤砂土或壤土上种植,土层厚度要求90~100 cm。栽植密度:每666.7 m2栽植200~250株,行株距2.00 m×1.33 m,或采用3.00 m×1.50 m×1.50 m宽窄行种植模式,每666.7 m2桑园枝条数控制在4000~5000条。杂交桑种或实生桑种在3—4月采用肥团育苗法培育砧木。12月下旬至翌年1月下旬采用冬季简易芽接法,4—6月采用嫩枝条双面削嫁接法进行幼苗嫁接。嫁接苗木成活后,及时去除砧芽,对未成活苗木进行补接。幼苗生长期需要防控蜗牛、桑尺蠖、桑毛虫、桑象虫等芽叶害虫,及时除草、施肥。春季不采叶,夏秋可以适当采叶养蚕。
该品种宜采用中干拳式树形培养。栽植第1年在35~40 cm高度处春伐定主干,保留3~4个芽,培养一级支干,冬季(12月至翌年1月)剪梢保条;第2年5月中下旬桑椹采摘后,在55~60 cm高度处夏伐,每根枝条保留2~3个芽,培养二级支干;第3年采果后,在70 cm高度处剪伐,每根枝条保留2~3个芽,培养三级支干。此后每年冬季剪梢保条,桑椹采摘后在枝条基部夏伐,按每666.7 m2桑园4000~5000根枝条的模式拳式培养。
该品种的施肥管理按有效氮磷钾质量比50∶25∶40的配合施肥,每666.7 m2桑园全年施肥总量为有机肥1700 kg、氮肥20 kg、磷肥45 kg、钾肥17 kg。夏秋季施肥以促进桑树营养生长为主,重施有机肥和速效肥;冬春季则以促进合理的果叶比为主,提高桑椹品质,即适当增施磷、钾肥。除此之外,还需及时除草,并保持桑园排灌畅通,减少桑椹菌核病与椹瘿蚊的危害,提高桑椹品质。
该品种为果叶兼用品种,应结合桑椹采摘和养蚕用叶情况制定病虫害综合防控方案,可采用农业、物理和化学防控手段。化学防控须严格按国家绿色水果(蔬菜)种植用药标准选择化学农药,在桑椹采摘前1个月禁用化学农药。需特别注意桑椹菌核病和椹瘿蚊的防控。
桑椹菌核病的防控,一是加强农业防控,即在菌核病原分生孢子形成前(2月上中旬)用地膜覆盖土面,该措施还可同时兼治椹瘿蚊和抑制桑园杂草生长。二是做好菌核病果收集与处理。在桑园发现菌核病病果后,应及时人工摘除,并挖50~70 cm土坑拌入新鲜石灰深埋。三是结合桑园冬耕,在冬季对桑园土壤进行20~30 cm的深翻。四是合理进行化学防控,在桑椹初花期、盛花期、末花期,用70%甲基硫菌灵1000~1500倍液和50%腐霉利1000~1500倍液交替喷施桑雌花,以桑花滴水为度,在桑椹采摘前1个月停止喷药。对椹瘿蚊的防控措施包括:一是结合菌核病防控和桑园除草,用地膜覆盖土面,减少椹瘿蚊成虫出土;二是在桑园内按照每666.7 m2悬挂30张黄色粘虫板,杀灭椹瘿蚊成虫;三是适当采用化学防控手段,根据虫情在椹瘿蚊幼虫孵化盛期,用5%吡虫啉乳油1500倍液对果桑植株的青椹喷雾1~2次,可兼治桑蓟马、桑瘿蚊、桑尺蠖等害虫,但务必在采果前1个月停止喷药。
[1] 于洁,韩智宏,郭俊英,高俊兰,孙明娜,杨璐,丁天龙,邓永进. 果桑新品种桑梓1号的选育[J] . 果树学报,2021,38(10):1824-1827.YU Jie,HAN Zhihong,GUO Junying,GAO Junlan,SUN Mingna,YANG Lu,DING Tianlong,DENG Yongjin. Breeding report on a new fruit mulberry cultivar Sangzi 1[J] . Journal of Fruit Science,2021,38(10):1824-1827.
[2] 凌楸桐,卢红伶,胡文君,蒋陈凯,沈国新,陈琳. 果桑新品种之葚1号的选育[J] . 浙江农业科学,2023,64(7):1699-1702.LING Qiutong,LU Hongling,HU Wenjun,JIANG Chenkai,SHEN Guoxin,CHEN Lin. Breeding report on a new mulberry cultivar Zhishen 1[J] . Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences,2023,64(7):1699-1702.
[3] 赵珮,黄传书,唐小平,何佳洋,雷霆,刘艳,吴均. 桑椹品质评价的主要指标及模型研究[J] . 蚕业科学,2020,46(3):295-305.ZHAO Pei,HUANG Chuanshu,TANG Xiaoping,HE Jiayang,LEI Ting,LIU Yan,WU Jun. Study on main indicators and model to evaluate mulberry fruit quality[J] . Science of Sericulture,2020,46(3):295-305.
[4] 李巨秀,王柏玉. 福林-酚比色法测定桑椹中总多酚[J] . 食品科学,2009,30(18):292-295.LI Juxiu,WANG Baiyu. Folin-ciocalteu colorimetric determination of total polyphenols in mulberry fruits[J] . Food Science,2009,30(18):292-295.
[5] 黄金枝,朱敏婕,俞燕芳,邓真华,杜贤明. 桑椹成熟过程中酚类物质及总黄酮含量的动态变化[J] . 蚕桑茶叶通讯,2017(5):1-3.HUANG Jinzhi,ZHU Minjie,YU Yanfang,DENG Zhenhua,DU Xianming. Dynamic changes of phenolic substances and total flavonoids during the maturation of mulberry fruit[J] . Newsletter of Sericulture and Tea,2017(5):1-3.
[6] 赵玉生,姚二民,赵俊芳. 超高压处理对猕猴桃汁品质的影响[J] . 食品科学,2008,29(1):60-63.ZHAO Yusheng,YAO Ermin,ZHAO Junfang. Effects of UHP treatment on kiwi juice quality[J] . Food Science,2008,29(1):60-63.
[7] 梁彬,孙婵婵,张民. 澄清型葡萄汁工艺研究[J] . 食品研究与开发,2018,39(23):75-81.LIANG Bin,SUN Chanchan,ZHANG Min. Research on technology of clarified grape juice[J] . Food Research and Development,2018,39(23):75-81.
[8] 中华人民共和国农业部. 水果及制品可溶性糖的测定-3,5-二硝基水杨酸比色法:NY/T 2742—2015[S] . 北京:中国农业出版社,2015.Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. Determination of soluble sugar in fruits and derived products-3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid colorimetry:NY/T 2742—2015[S] . Beijing:China Agriculture Press,2015.
[9] 国家卫生健康委员会,国家市场监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中总酸的测定:GB 12456—2021[S] . 北京:中国标准出版社,2021.National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China,State Administration for Market Regulation. Determination of total acid in food:GB 12456—2021[S] . Beijing:Standards Press of China,2021.
[10] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 出口植物源食品中粗多糖的测定 苯酚-硫酸法:SN/T 4260—2015[S] . 北京:中国标准出版社,2016.General Administration of Quality Supervision,Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Determination of crude polysaccharides in plant source foods for export-Pheholsulfuric acid colorimetry:SN/T 4260—2015[S] . Beijing:Standards Press of China,2016.
[11] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会,国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中蛋白质的测定:GB 5009.5—2016[S] . 北京:中国标准出版社,2017.National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, China Food and Drug Administration.National food safety standard determination of protein in food:GB 5009.5—2016[S] . Beijing:Standards Press of China,2017.