油桃(Prunus persica var. nectarines)是蔷薇科桃属的重要变种[1-2],其果实外观亮丽、商品价值高、食用方便且富含多种营养成分[3]、能带来可观的经济收益,优势十分明显。然而,当前油桃品种仍存在风味偏淡、成熟期遇雨易裂果、果肉质地较软、货架期短等问题,为油桃品种选育工作带来了巨大挑战[4]。
油桃原产于中国。自20世纪70年代以来,中国引进了一些欧美油桃栽培品种(如ER2等[5]),但这些品种大多是与国内消费者口味偏好不相符的甜酸型品种。为此,国内育种专家利用引进品种与本土栽培品种进行杂交育种,成功培育出多个栽培适应性好、综合性状优良的油桃品种,包括早熟品种中油桃4号[6]、中油桃5号[7],中熟品种中油20号[8],以及晚熟品种中油桃8号[9]。这些品种的推广显著改变了早期油桃果实偏酸、果个小、易裂果的市场印象,获得了消费者的广泛认可[10]。
目前,油桃在中国桃产业中的占比逐年提升,种植面积已占桃总面积的20%以上[11]。然而,早熟耐贮运油桃品种的选育仍相对滞后。针对这一问题,笔者团队重点开展耐贮运、货架期长的油桃新品种选育工作,尤其注重选育果面干净、无毛、外观亮丽、果个大且品质优良的油桃品种,以进一步满足市场需求。
中国农业科学院郑州果树研究所选育的中油19号油桃品种,具有早熟、果肉硬质、黄肉等显著特点。其果实圆形,果面着色鲜艳,耐贮藏且不易裂果,同时表现出良好的自花结实能力和丰产性。中油19号于2024年通过中华人民共和国农业农村部非主要农作物品种登记(GPD桃(2024)410043)。区域试验结果表明,中油19号在河南省新乡市、山东省蒙阴县、安徽省砀山县、陕西省西安市等地均表现出较好的栽培适应性。
1 选育过程
油桃品种的改良、培育工作于1999年开始。选用北1-9作为母本、早熟白肉油桃中油桃5号作为父本进行杂交育种,成功选育出编号为99-43-58的优良单株。观察结果显示:该单株果实成熟期集中于6月中下旬,果肉白色且肉质极硬,单果质量约210 g,但存在果面着色不好的现象。为进一步改良99-43-58单株的性状,笔者研究团队于2005年配置了新的杂交组合,以早熟、硬质、白肉且着色优良的中油桃14号为母本,99-43-58为父本,在母本花蕾期进行人工去雄和定向授粉,田间管理采用标准化栽培技术。
中油桃14号×99-43-58组合在当年获得45个杂交果种子,6月15日完成果实采收工作。通过对杂交果实进行胚挽救和低温处理,最终培育出16株杂种实生苗。翌年4月中旬,当杂种实生苗高度约1 m、粗度0.6 cm以上时,定植到桃育种圃,株距为1.5 m,行距为3.0 m。整形方式为主干形,田间管理同常规栽培管理。
该杂交组合中编号为05-1-139的单株,于2009年开花结果。花型为蔷薇型,花粉活力高。果实于6月上中旬成熟,果实圆形,果皮色泽鲜艳,品质优异,耐贮运,极丰产。在2009年—2011年连续3年进行观测,其主要经济性状表现稳定。2011年,通过接穗高接方法进行复选;2013年,待各高接株系表型一致时,随即开展多点区域试验。该品种于2024年通过中华人民共和国农业农村部非主要农作物品种登记,登记号:GPD桃(2024)410043,正式定名为中油19号(图1~图2)。
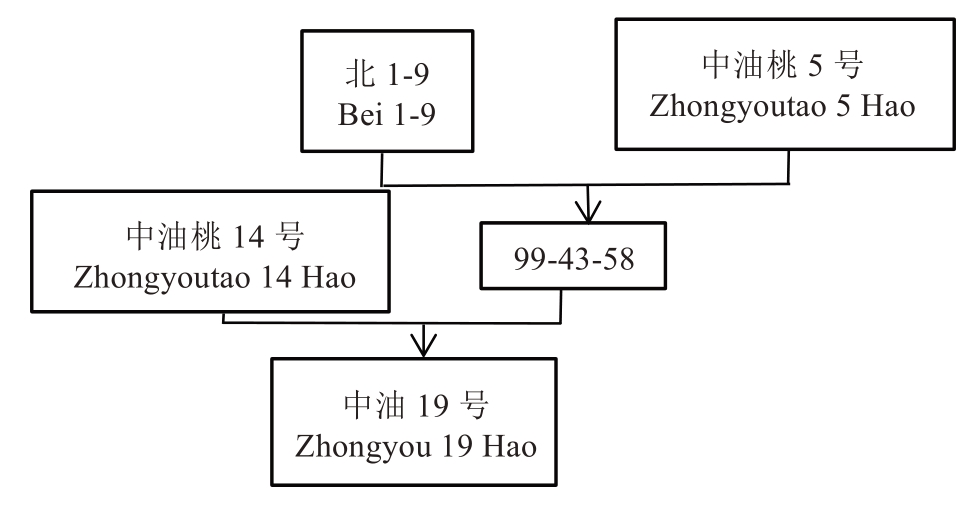
图1 油桃新品种中油19号系谱
Fig. 1 Pedigree of new oil peach cultivar Zhongyou 19 Hao
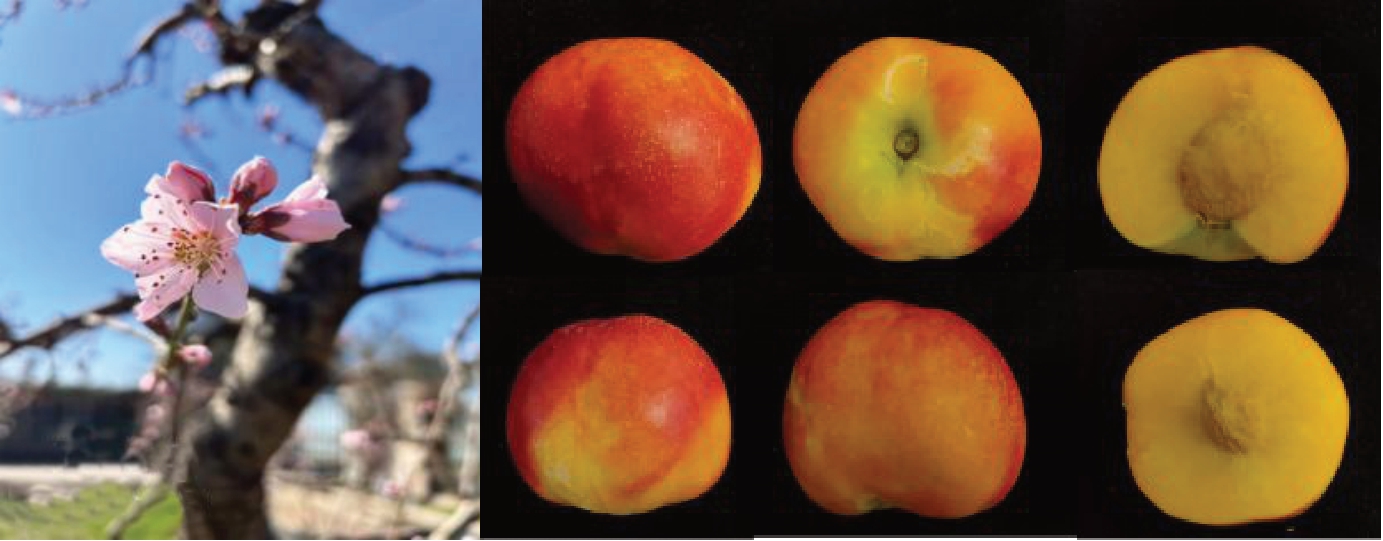

图2 中油19号的花及果实
Fig. 2 The flowers and fruits of Zhongyou 19 Hao
2 主要特性
2.1 植物学特征
中油19号树体表现为强生长势,冠层呈半开张型结构,萌芽力与分枝能力均属中等水平。新生枝梢具有典型绿色表皮特征,向阳面可见红色色素沉积,节间平均长度达3.0 cm。叶片为椭圆披针形,叶片平均长度18.8 cm,平均宽度4.6 cm,叶片横截面呈水平状,叶片色泽呈黄绿至浅黄绿变化,叶基角接近直角,叶缘具钝圆锯齿。叶柄蜜腺肾形,有2~4个;花器官特征表现为:花型为蔷薇型;花瓣粉色、5枚,萼筒内壁橙黄色;花粉多,产量高。
2.2 果实经济性状
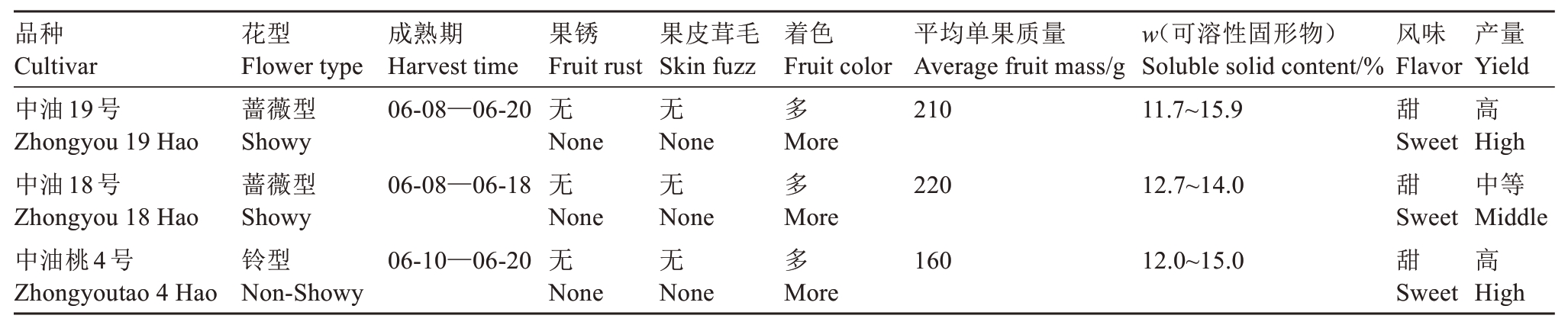
中油19号平均单果质量为210 g,最大为240 g。果实圆形,果顶圆平、无果尖。果实底部呈浅黄色,果面着色面积在80%以上,深红色,果实两半部对称;梗洼深度适中,果面无茸毛。果实品质方面:果肉黄色,肉质极硬。果实成熟期无皮下及近核花青苷显现,肉质细腻,纤维含量低,可溶性固形物含量(w)为11.7%~15.9%(表1)。果核卵圆形,褐色程度中等,表面具有核纹点及沟状,黏核,未出现裂核及裂果现象。
表1 中油19号与对照品种主要经济性状对比(2022年,原阳县)
Table 1 The main economical charavters of Zhongyou 19 Hao and the control cuitivars (2022,Yuanyang county)
?
2.3 生长结果习性
该品种营养生长势强,幼树阶段年抽梢频率为2~3次。其中,二次枝当年即具备结果能力。花芽分化起始位点在第2~4节位,复花芽占比68.9%(单花芽占比10.1%)。
幼树阶段以长果枝为主要结果枝条。盛果期后,树势趋于缓和,短、中、长果枝均实现稳定坐果,坐果率可达61.8%。结果枝以粗度0.5~0.8 cm的中果枝为主,并严格进行疏果。若栽培管理条件好,栽植第2年开始结果,第3年每666.7 m2产量可达1500 kg,第4年进入丰产阶段,每666.7 m2产量在2000 kg以上。
2.4 物候期(郑州地区)
中油19号芽体于2月底萌动,开花期在3月中下旬,花期持续7~10 d。果实成熟期在6月上中旬,果实发育时间约70 d。落叶期在11月中旬,年生育期约240 d。
3 栽培技术要点
3.1 建园
桃树不耐涝,建园时选择阳光充足、地势平坦、排水良好的土地,如壤砂土。桃树生长不喜过酸或过碱的土壤,土壤pH值在6.0~7.5之间最佳。种植方向选择南北行、东西向,地势低洼地块建议起垄栽培。株行距(1.5~2.0) m×4.0 m,根据地势、土壤肥力、整形方式适当调整。在砧木选择上,建议以山桃(北方地区)和毛桃(南方地区)为主。
3.2 整形修剪
一年生嫁接苗春季定植后,及时定干。定干高度在嫁接口以上40~50 cm处,选留饱满芽短截。萌芽后,当枝条伸长至50 cm左右时,根据树形选留生长强旺的新梢以培养主枝。采用Y字形整形,主枝上下间距约10 cm,夹角60°左右,并设立辅助支架。其余枝条为制造养分、供应树体快速生长,应保留10 cm左右进行中度短截。结果初期,夏季修剪尤为重要,其主要目的是抑制营养生长,促进生殖生长;盛果期,树冠已基本成型,应加强修剪力度,回缩结果枝,以更新结果枝组,改善树体内部通风透光条件;结果后期,为延缓树体衰老,可适当疏除徒长枝和多余分枝。
3.3 花果管理
中油19号坐果率高,应根据坐果量及目标产量,及时进行疏花、疏果,保持树体的合理负载。疏果一般在花后2周和4~6周,疏果对象为小果、病虫果、畸形果、多余果、朝天果等。根据产量确定留果量,一般每隔10~15 cm留1个果。每666.7 m2产量控制在2000 kg左右。为促进花芽分化和果实发育,当新梢生长至5~10 cm时,应进行摘心或喷施多效唑等其他植物生长调节剂,控制枝条旺长。为促进果实膨大或防止裂果现象发生,可在开花前后喷施一定量的磷酸二氢钾溶液。
3.4 肥水管理
中油19号以秋施基肥为主,主要为长效有机肥。基肥施用时间在9月—10月,宜早不宜晚。进入盛果期后,在树体萌芽前根据树势、结果情况,追施适量的氮肥;硬核期追施适量的氮磷钾复合肥;果实膨大期为防止裂果、增加果核硬度,可追施适量的钾肥或钾氮复合肥。根据土壤墒情适时浇水,萌芽前浇水以保证树体萌芽和开花;硬核期宜浅浇水,满足树体对水分需求;采收前10 d不宜浇水;每年11月中下旬,树体落叶后应浇封冻水,以确保桃树安全越冬。
3.5 病虫害防控
中油19号成熟期早,果实于6月上中旬成熟,该阶段成熟的桃果实病虫害发生率较低。桃园清园、消毒的措施主要为:冬季彻底清除桃园内的病枝、病叶等;萌芽期全园消毒,可喷施5°Bé石硫合剂等杀菌剂。在树体生长期和果实发育期,主要的病虫害有红蜘蛛、桃蚜、细菌性穿孔病等。在田间管理过程中,根据病虫害发生规律及时做好病虫害防控工作。
4 应用前景
中油19号为早熟、黄肉油桃品种。该品种果实圆形,果面着色艳丽,耐贮运,不易裂果,产量高。在河南省新乡市、山东省蒙阴县、安徽省砀山县、陕西省西安市等地的区域试验结果表明,该品种在各桃主产区栽培适应性强,果实经济性状稳定,综合品质优良,具有良好的推广应用前景。
[1] 李丽娜. 油桃是不是转基因水果 [J] . 新农业,2019(10):41.LI Lina. Is nectarine a genetically modified fruit [J] . Modern Agriculture,2019(10):41.
[2] 杨科家,毛志远,徐春玉,郝瑞涛,陈志敏,孙浩,孙钦勇,刘立常. 油桃新品种玫瑰香的选育[J] . 中国果树,2023(10):103-104.YANG Kejia,MAO Zhiyuan,XU Chunyu,HAO Ruitao,CHEN Zhimin,SUN Hao,SUN Qinyong,LIU Lichang. Breeding of a new cultivar of nectarine Meiguixiang[J] . China Fruits,2023(10):103-104.
[3] BROWN A,GREEN B,WHITE C. Nutritional benefits and bioactive compounds of nectarines[J] . Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2021,93:103612.
[4] 宋惠安. 油桃有优劣 发展当谨慎[J] . 农村新技术,2005(5):52.SONG Huian. Nectarines have their advantages and disadvantages,and their development should be cautious[J] . New Rural Technology,2005(5):52.
[5] 吕义盛,李淑燕. 黄油桃ER2号引种成功[J] . 农业科技通讯,1990(11):18.LÜ Yisheng,LI Shuyan. Huangliantao ER2 successfully introduced[J] . Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology,1990(11):18.
[6] 王志强,刘淑娥,牛良,宗学普,宋银花. 油桃新品种‘中油桃4号’[J] . 园艺学报,2003,30(5):631.WANG Zhiqiang,LIU Shue,NIU Liang,ZONG Xuepu,SONG Yinhua. ‘Zhongyoutao 4’- A new early nectarine variety[J] . Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2003,30(5):631.
[7] 王志强,刘淑娥,牛良,宗学普,宋银花. 早熟油桃新品种‘中油桃5号’的选育[J] . 果树学报,2005,22(1):89-90.WANG Zhiqiang,LIU Shue,NIU Liang,ZONG Xuepu,SONG Yinhua. A new early-ripening nectarine cultivar ‘Zhongyoutao No. 5’[J] . Journal of Fruit Science,2005,22(1):89-90.
[8] 鲁振华,牛良,崔国朝,潘磊,曾文芳,王志强. 耐贮白肉油桃新品种‘中油20号’的选育[J] . 果树学报,2020,37(11):1766-1768.LU Zhenhua,NIU Liang,CUI Guochao,PAN Lei,ZENG Wenfang,WANG Zhiqiang. A new white flesh and stony-hard nectarine cultivar ‘Zhongyou 20’[J] . Journal of Fruit Science,2020,37(11):1766-1768.
[9] 牛良,刘淑娥,鲁振华,宋银花,宗学普,王志强. 晚熟油桃新品种‘中油桃8号’[J] . 园艺学报,2011,38(1):185-186.NIU Liang,LIU Shue,LU Zhenhua,SONG Yinhua,ZONG Xuepu,WANG Zhiqiang. A new late-ripening nectarine cultivar‘Zhongyoutao 8’[J] . Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2011,38(1):185-186.
[10] 王力荣. 我国桃产业现状与发展建议[J] . 中国果树,2021(10):1-5.WANG Lirong. Current situation and development suggestions of peach industry in China[J] . China Fruits,2021(10):1-5.
[11] 王田利. 我国油桃产业现状及高效栽培技术[J] . 中国果业信息,2014,31(10):21-24.WANG Tianli. The current situation and efficient cultivation techniques of China's peach industry[J] . China Fruit News,2014,31(10):21-24.