莱阳茌梨又名慈梨,原产于山东莱阳五龙河畔,栽培历史悠久,是中国名特优水果、中国国家地理标志产品。梨果实萼片脱落或宿存是衡量梨果外观品质的指标之一,并影响果实内在品质。莱阳茌梨幼果期萼端突出,需在谢花后约10 d,在人工疏果的同时进行掐花萼处理。研究认为,掐花萼可以刺激莱阳茌梨果实生长并使其果肉石细胞数量减少,增加果实可食用部分比例,提高果实可溶性固形物含量,降低果实酸度,改善其食用品质[1-2],但掐花萼增加了人工成本。
新茌梨为莱阳茌梨实生选育的新品种,具有自然脱萼的特性。现将其选育过程、生物学特性等予以介绍,并与莱阳茌梨进行比较。
1 选育过程
2009年,在烟台市牟平区观水镇生金泊村偶然发现一棵莱阳茌梨实生树,已结果多年(图1)。2011年,采集接穗高接于6年生中梨1号上进行性状观察,高接树于2012年结果。2012年,进一步嫁接到杜梨上进行苗木扩繁,并于2013年建园。2014年,进行品种验收,命名为新茌。2016年,新植园结果。此后连续3年对新植园与高接树结果性状进行比较,果实主要性状如平均单果质量、自然脱萼率、可溶性固形物含量等表现稳定。2020年,申请植物新品种权,2023年9月获批植物新品种权,品种权号为CNA20201003780。
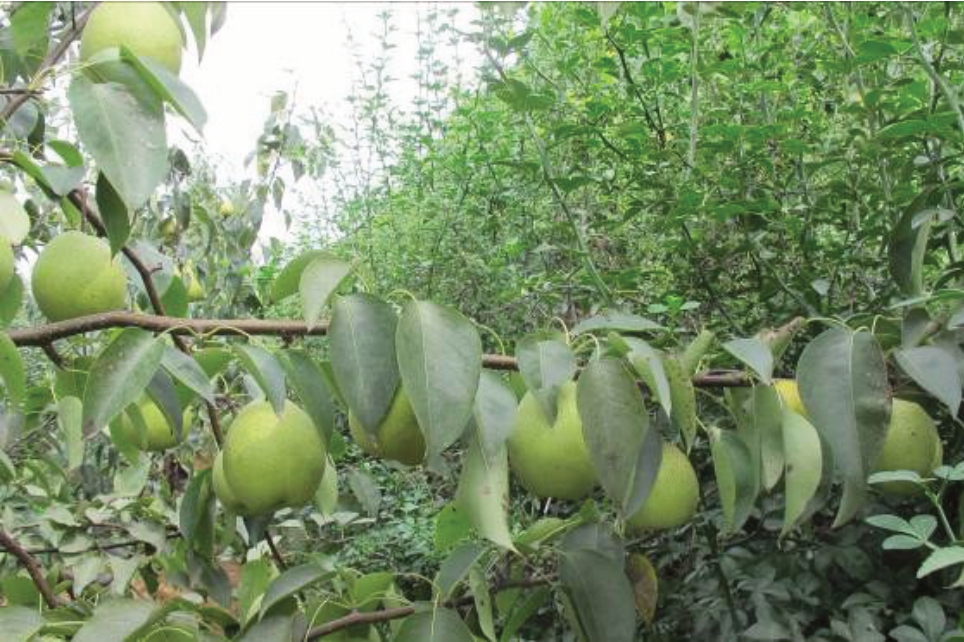

图1 自然脱萼型梨新品种新茌
Fig. 1 A new natural calyx shedding pear Xinchi
2 主要性状
根据曹玉芬等[3]编著的《梨种质资源描述规范和数据标准》,以及研究人员对梨果实性状的评价标准[4-5],对新茌梨的植物学特征、果实经济性状、生长结果习性、物候期等进行了调查。
2.1 植物学特征
枝干黑褐色,表面光滑。1年生枝橙褐色,平均枝长37.7 cm,枝粗0.49 cm,节间长3.46 cm,皮光洁,皮孔大,白色,长圆形,小而稀,无针刺。叶芽尖,离生。幼叶褐红色,叶片卵圆形,大而长,叶长17.09 cm,叶宽9.67 cm,叶柄长3.42 cm,叶柄粗0.13 cm,老叶绿色,叶缘锐锯齿、具刺芒,叶端急尖,叶基圆形。花的形态特征与莱阳茌梨相同[6]。每花序为3~6朵花,花蕾浅粉色,花瓣5枚,圆形,邻生,花柱基部无茸毛,柱头高于花药,花药淡紫红色(图2)。
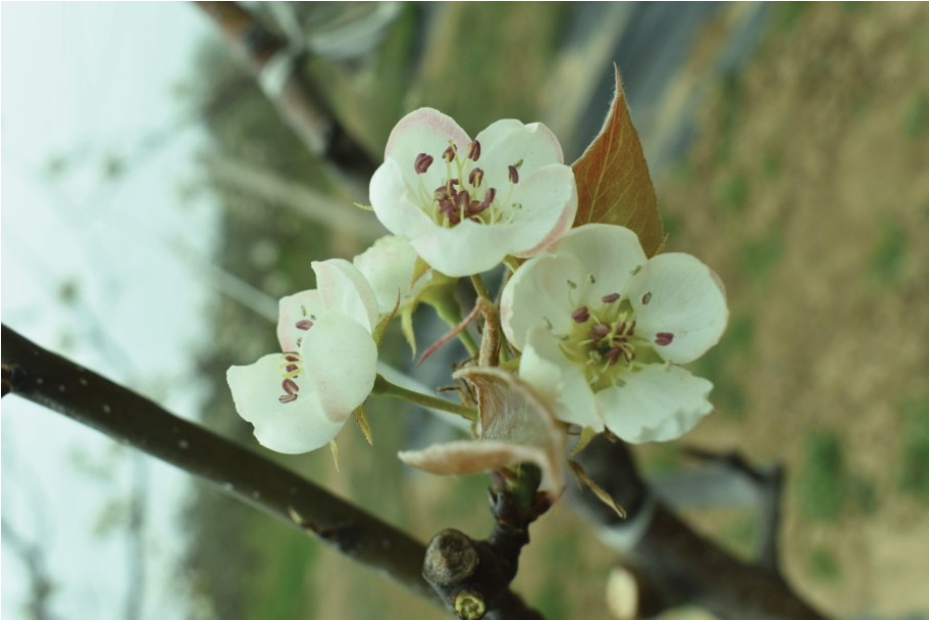

图2 新茌梨花序
Fig. 2 Flowers of Xinchi pear
2.2 果实经济性状
果实卵圆形,平均单果质量385.6 g,最大单果质量540.0 g,果实纵径11.16 cm,果实横径9.76 cm,果形指数1.14,高于人工剪萼莱阳茌梨。梗洼深,萼洼深,萼片自然脱落率达96%,远高于宿萼莱阳茌梨(9.5%)。果柄长4.5 cm,粗0.3 cm。果皮中厚,黄绿色,果点较大。果肉白色,肉质细脆,石细胞小而少,汁液丰富,果肉去皮硬度7.7 kg·cm-2。可溶性固形物含量13.7%,可食率74%,均与人工剪萼莱阳茌梨相当。新茌梨风味浓郁,品质上等。果实耐贮性与莱阳茌梨相同[7],冷库条件下可贮藏5~7个月(图3,表1)。
表1 新茌梨与莱阳茌梨果实性状比较Table 1 Comparison of the fruit traits between Xinchi pear and Laiyang Chili
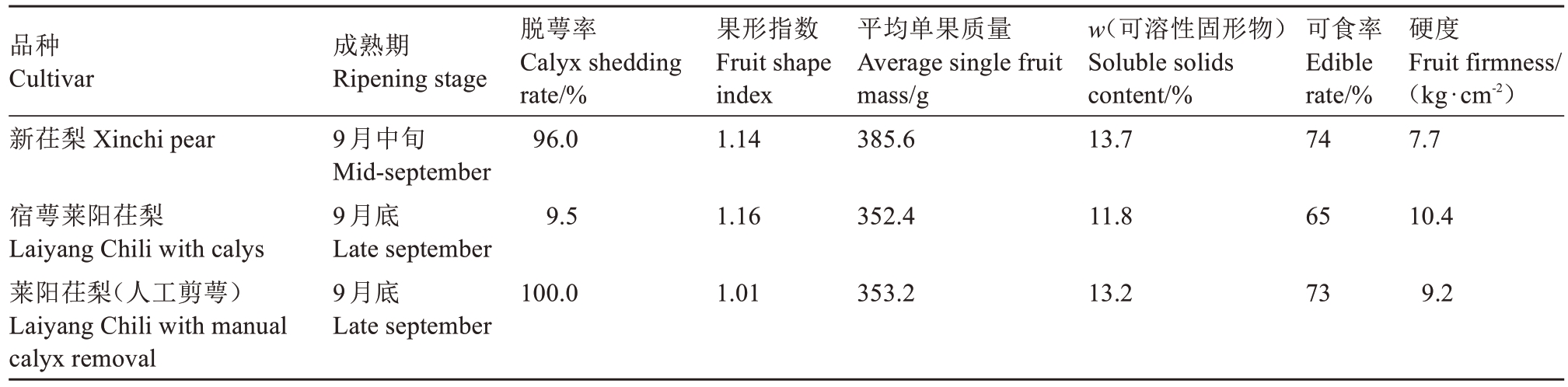
品种Cultivar新茌梨 Xinchi pear脱萼率Calyx shedding rate/%96.0果形指数Fruit shape index 1.14平均单果质量Average single fruit mass/g 385.6 w(可溶性固形物)Soluble solids content/%13.7可食率Edible rate/%74硬度Fruit firmness/(kg·cm-2)7.7宿萼莱阳茌梨Laiyang Chili with calys莱阳茌梨(人工剪萼)Laiyang Chili with manual calyx removal成熟期Ripening stage 9月中旬Mid-september 9月底Late september 9月底Late september 9.51.16352.411.86510.4 100.01.01353.213.2739.2
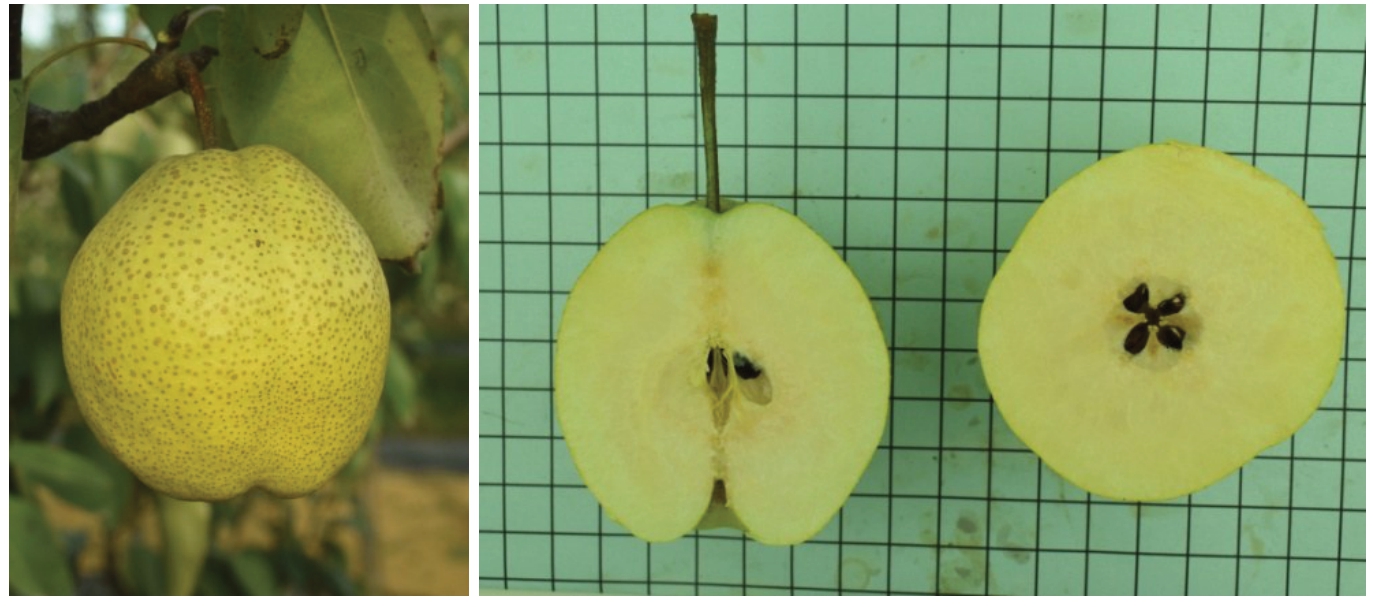

图3 新茌梨果实
Fig. 3 Fruit of Xinchi pear
2.3 生长结果习性
新茌梨树势强健,树姿半开张。成枝力强,以短果枝结果为主,其中短果枝比率为88.5%,中果枝比率为8.4%,长果枝比率为3.1%。新茌梨栽植园区为壤砂土,水肥条件较好。栽植后第3年开花结果,第5年进入盛果期。5年生、6年生、7年生树每666.7 m2产量分别为3475 kg、3620 kg和3690 kg,连续结果能力强。
2.4 物候期
在烟台地区,新茌梨于3月下旬叶芽萌动,4月下旬展叶,6月下旬春梢停止生长,11月上旬进入落叶期。3月底花芽萌动,4月中旬进入盛花期,9月中旬果实成熟,比莱阳茌梨提早10~15 d(表2)。
表2 2017—2019年新茌梨物候期
Table 2 Phenological phases of Xinchi pear and Laiyang Chili (2017—2019)
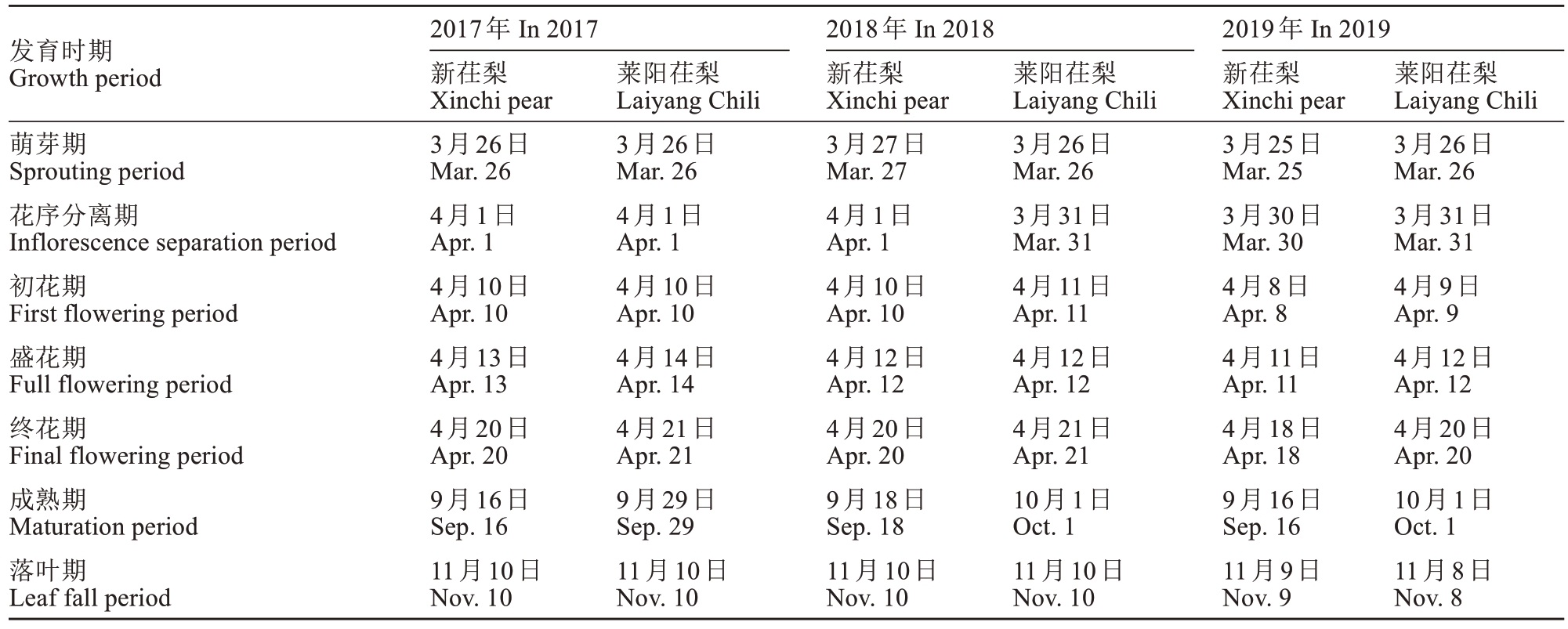
发育时期Growth period萌芽期Sprouting period花序分离期Inflorescence separation period初花期First flowering period盛花期Full flowering period终花期Final flowering period成熟期Maturation period落叶期Leaf fall period 2017年 In 2017新茌梨Xinchi pear 3月26日Mar. 26 4月1日Apr. 1 4月10日Apr. 10 4月13日Apr. 13 4月20日Apr. 20 9月16日Sep. 16 11月10日Nov. 10莱阳茌梨Laiyang Chili 3月26日Mar. 26 4月1日Apr. 1 4月10日Apr. 10 4月14日Apr. 14 4月21日Apr. 21 9月29日Sep. 29 11月10日Nov. 10 2018年 In 2018新茌梨Xinchi pear 3月27日Mar. 27 4月1日Apr. 1 4月10日Apr. 10 4月12日Apr. 12 4月20日Apr. 20 9月18日Sep. 18 11月10日Nov. 10莱阳茌梨Laiyang Chili 3月26日Mar. 26 3月31日Mar. 31 4月11日Apr. 11 4月12日Apr. 12 4月21日Apr. 21 10月1日Oct. 1 11月10日Nov. 10 2019年 In 2019新茌梨Xinchi pear 3月25日Mar. 25 3月30日Mar. 30 4月8日Apr. 8 4月11日Apr. 11 4月18日Apr. 18 9月16日Sep. 16 11月9日Nov. 9莱阳茌梨Laiyang Chili 3月26日Mar. 26 3月31日Mar. 31 4月9日Apr. 9 4月12日Apr. 12 4月20日Apr. 20 10月1日Oct. 1 11月8日Nov. 8
3 栽培技术要点
3.1 建园
新茌梨建园以选择土层深厚、排水良好、有机质含量≥1.5%、地下水位1 m以下的壤砂土为宜,土壤pH值范围为6.0~6.5,含盐量不超过0.3%。园地选择按NY/T 2628—2014中3.5执行。建园选用壮苗,株行距为(3~4) m×(4~5) m。
3.2 花果管理
新茌梨需要异花授粉,宜选择花期一致、亲和性好、花粉量大、果实具有一定经济价值的品种作授粉树,如翠玉、苏翠1号等。主栽品种与授粉品种栽植比例为4∶1~6∶1。
3.3 整形修剪
新茌梨可采用主干疏层形树形。主干高度为70~80 cm,具有明显的主干,主枝分层排列于主干上。第一层有3个主枝,第二层有2个主枝,第三层有1个主枝,全树共有6个主枝,相邻两层主枝不重叠。
3.4 肥水管理
施肥以有机肥为主,化肥为辅。成龄树需加强肥水管理,保持壮树稳产。有条件的果园可采用喷灌或滴灌技术,确保排水沟设施齐全,以便雨季及时排水。
3.5 病虫害防治
新茌梨的主要病害有梨黑星病、锈病、轮纹病、黑斑病和炭疽病等,主要虫害有梨木虱、梨黄粉虫、梨二叉蚜、康氏粉蚧、绿盲蝽和梨小食心虫等。在防治中禁止使用剧毒、高毒、高残留的农药,提倡使用生物农药和低毒、低残留的农药。
4 应用前景
新茌梨为莱阳茌梨实生选育的新品种,平均单果质量大于莱阳茌梨,成熟期比莱阳茌梨提前10~15 d,果实品质与莱阳茌梨相当,最大特点是可自然脱萼,大大节约了人工剪萼的时间及劳动力成本,应用前景广阔。
[1] 刘成连,鞠志国,原永兵,张玉娜,蒋家慧. 掐花萼对莱阳茌梨品质的影响[J] . 莱阳农学院学报,1993,10(2):121-123.LIU Chenglian,JU Zhiguo,YUAN Yongbing,ZHANG Yuna,JIANG Jiahui. The effects of calyx nipping on quality of Laiyang Chili[J] . Journal of Laiyang Agricultural College,1993,10(2):121-123.
[2] 孙敏,代洪义,李培环,王然. 茌梨掐花技术的再探讨[J] . 烟台果树,1983(1):44.SUN Min,DAI Hongyi,LI Peihuan,WANG Ran. Revisiting flower thinning methods in Laiyang Chili cultivation[J] . Yantai Fruits,1983(1):44.
[3] 曹玉芬,刘凤之,胡红菊,张冰冰. 梨种质资源描述规范和数据标准[M] . 北京:中国农业出版社,2006.CAO Yufen,LIU Fengzhi,HU Hongju,ZHANG Bingbing. Descriptors and data standard for pear (Pyrus spp.)[M] . Beijing:China Agriculture Press,2006.
[4] 张莹,曹玉芬,田路明,董星光,齐丹,霍宏亮,徐家玉,刘超,王立东. 梨种质资源果实若干数量性状评价指标研究[J] . 果树学报,2023,40(6):1053-1063.ZHANG Ying,CAO Yufen,TIAN Luming,DONG Xingguang,QI Dan,HUO Hongliang,XU Jiayu,LIU Chao,WANG Lidong.Evaluating standards of some fruit quantitative traits of pear genetic resources[J] . Journal of Fruit Science,2023,40(6):1053-1063.
[5] 殷晨,田路明,曹玉芬,董星光,张莹,霍宏亮,齐丹,徐家玉,刘超.梨果实糖酸研究进展[J] . 果树学报,2023,40(12):2610-2623.YIN Chen,TIAN Luming,CAO Yufen,DONG Xingguang,ZHANG Ying,HUO Hongliang,QI Dan,XU Jiayu,LIU Chao.Research progress in sugar and acid in pear fruit[J] . Journal of Fruit Science,2023,40(12):2610-2623.
[6] 牟红梅,于强,李庆余,王义菊,姜福东,李元军. “莱阳茌梨”在梨育种上的应用[J] . 安徽农业科学,2018,46(4):37-38.MOU Hongmei,YU Qiang,LI Qingyu,WANG Yiju,JIANG Fudong,LI Yuanjun. The application of Laiyang Chili in breeding[J] . Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2018,46(4):37-38.
[7] 姜礼正,王同兴. 莱阳茌梨栽培状况与管理[J] . 落叶果树,1986,18(2):18-20.JIANG Lizheng,WANG Tongxing. Cultivation status and management of Laiyang Chili[J] . Deciduous Fruits,1986,18(2):18-20.