桃蛀螟(Conogethes punctiferalis)属于鳞翅目(Lepidoptera)草螟科(Crambidae)多斑野螟属(Conogethes)。在中国北方1年发生2~4代、长江流域3~5 代。幼虫蛀入果实内取食危害,蛀道内虫粪积满,蛀孔外流出胶状液体与排泄出来的褐色粪便混黏,污染桃果表面,具有转果危害的特征,造成果品不堪食用,失去经济价值[1-2]。
果园中桃蛀螟的防治主要采取“预防为主,综合防治”的策略,多种防治方法相结合进行综合防治[3-4]。昆虫性信息素及灯诱技术都在果园中广泛应用。其中灯光诱杀是农业害虫田间监测和防治的重要措施之一,主要包括黑光灯、频振式杀虫灯和高压汞灯、LED 灯等[5]。LED 灯具有操作简便、成本低、绿色安全等优点,但LED 灯专一性差,诱杀效率和专一性有待提高[6-7]。目前性信息素的使用主要分为虫情监测、诱捕诱杀、迷向防治三方面[8]。性信息素因具有绿色、安全、灵敏度高、对环境友好等优点在害虫综合治理中发挥着重要作用[9-10]。
笔者选取不同波长的光,筛选出对桃蛀螟成虫引诱效果较好的波长,提高LED 诱集桃蛀螟效果。将LED灯与性信息素相结合,能够有效提高诱杀效率和专一性,降低成本。目前关于LED诱虫灯和性信息素联用的研究较少,马广源等[11]和林清彩等[12]的研究表明,诱虫灯和性信息素联用对二点委夜蛾和斜纹夜蛾的诱捕具有协同增效的作用。为了探究桃蛀螟性信息素诱芯和LED灯联用效果,通过田间调查分析不同波长光与性信息素联用对桃蛀螟的诱捕效果,以期为提升果园中桃蛀螟的诱捕效率提供理论依据。
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料
试验地点位于河南省新乡市原阳县桥北镇桃园,果园面积7 hm2,株行距2 m×5 m,桃树品种主要为中油蟠9号、中桃9号,树龄11 a(年),试验果园商业化管理。
供试诱芯为桃蛀螟性信息素诱芯;诱捕器为三角形诱捕器,三角形诱捕器长26 cm×宽20 cm×高11 cm,内置同等长宽粘虫板,均购自中捷四方生物科技股份有限公司。
LED 灯3 W,选取可见光范围内颜色不同的波长,分别为紫光430 nm、蓝光453 nm、青光492 nm、绿光533 nm、黄绿光568 nm、黄光591 nm、红光620 nm,购自西安尼克劳斯灯饰有限公司;LED灯开启后使用多功能光谱分析仪0HSP 35OP 感光的探头验证LED灯波长,多功能光谱分析仪购自杭州虹谱光色科技有限公司。
供试的桃蛀螟虫源来自河南农业大学,然后在中国农业科学院郑州果树研究所采用水果玉米饲养。饲养条件为温度(26±1)℃、相对湿度(65±5)%、光周期L//D=14 h//10 h。
昆虫趋光行为测定装置参考唐良德等[13]设计制作。外观为正八角体,主体分为两个部分,中间为中空小八角体的活动栖息室,边缘为8个选择小室,活动栖息室与8个选择小室中间设隔断板。不同小室连接不同波长的LED 灯装置,底部和侧壁由黑色KT 板(黑色塑料泡沫板)构成,顶部为PET 膜(透明塑料膜)(图1)。
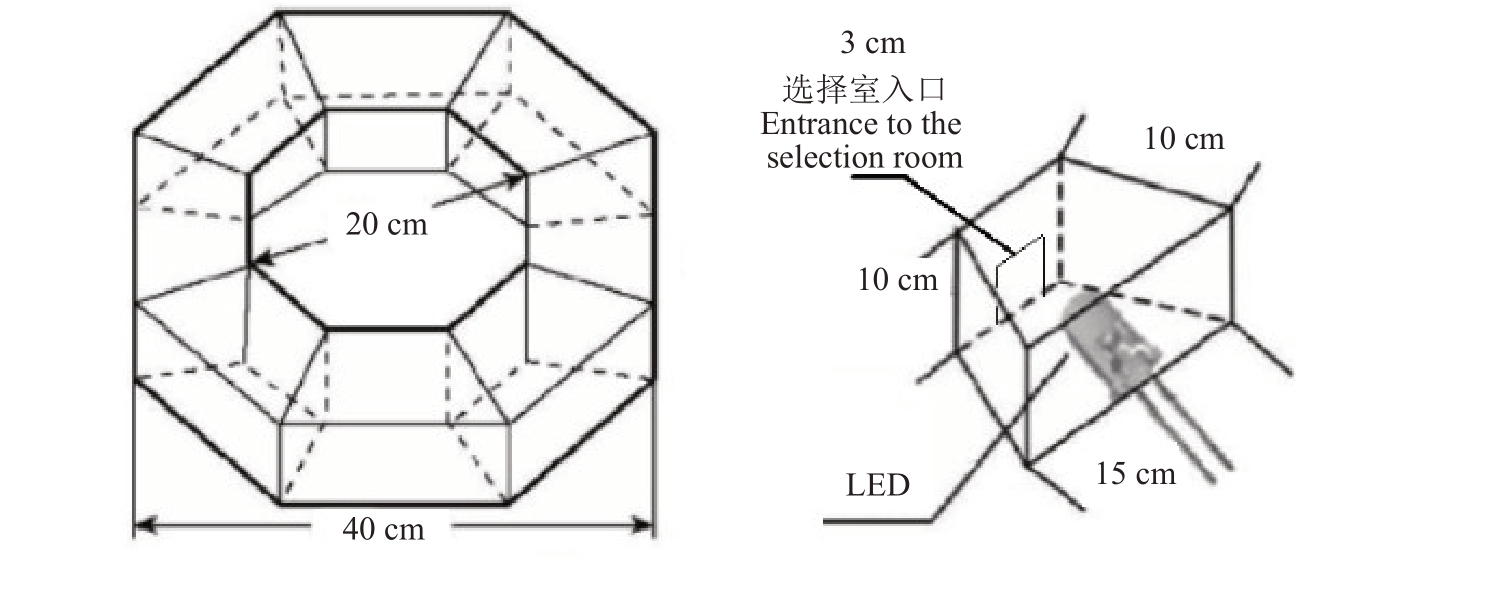
图1 趋光行为测定装置
Fig.1 Phototaxis as a measuring device
左侧为趋光性测定装置整体图,右侧为选择室局部图。
The left side shows the overall diagram of the phototaxis measurement device,while the right side shows a partial diagram of the selection chamber.
1.2 方法
1.2.1 室内筛选桃蛀螟的敏感波长 试验在暗室中进行,室温为25~30 ℃。试验前随机将7 种不同波长的LED 光源(430 nm、453 nm、492 nm、533 nm、568 nm、591 nm、620 nm)分别置于7 个不同的选择室中,第8 个选择室为暗室,LED 灯连接电源(接线于选择室侧壁)。试验选择桃蛀螟雌雄成虫各30头以上,试验前提前暗处理1 h,3次重复,每次重复随机更换LED 灯位置,试验昆虫放入后每次间隔10 min 记录1 次桃蛀螟趋向各选择室数量,共记录30 min,趋光率/%=趋光选择室虫数/试虫数×100。试验前用乙醇擦拭箱内,自然晾干,以消除气味影响。
1.2.2 新乡桃园桃蛀螟周年动态调查 共放置3个三角形诱捕器,桃园中放置诱捕装置,共15个处理,其中单性诱1个,单灯诱7个,灯诱性诱联用7个,均设3次重复(表1)。
表1 不同装置的不同处理
Table 1 Different treatments for different devices

?
各诱捕器间隔20 m×20 m,采用等距离分布原则在桃园中随机均匀分布,保证各诱捕器间互不影响。灯高大于1.5 m,24 h 持续照射。每7 d 记录1次诱捕器上桃蛀螟的数量,并更换电池及集虫袋,每30 d更换性信息素诱芯。
1.3 数据分析
采用WPS 办公软件进行数据收集与整理以及图表绘制,采用SPSS 24分析工具进行单因素ANOVA分析,判断不同处理之间的差异显著性。
2 结果与分析
2.1 室内趋光装置中桃蛀螟的趋光偏好性
桃蛀螟雌性成虫和雄性成虫对7个波长LED灯的总趋光率不存在显著差异(图2)。趋光率分别为66.10%和69.31%。
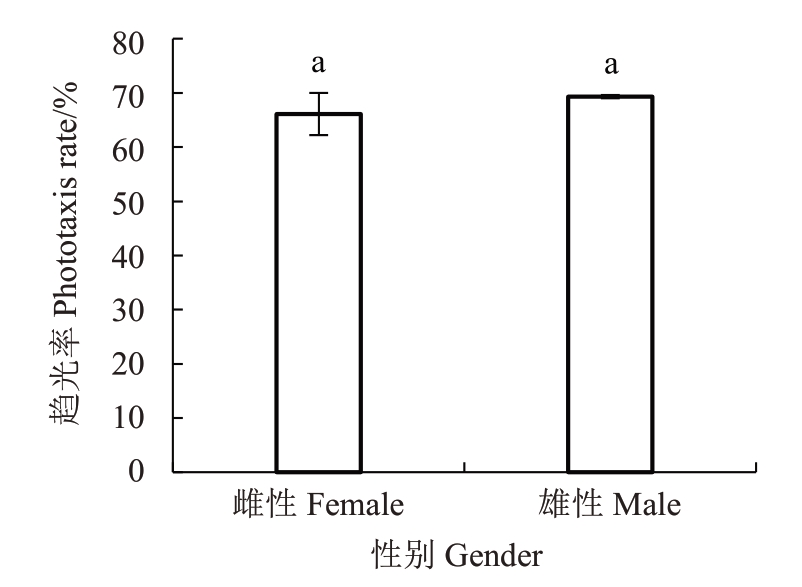
图2 桃蛀螟雌雄趋光率比较
Fig.2 Phototaxis rate of male and female C.punctiferalis
不同小写字母表示在0.05 水平差异显著。下同。
Different small letters indicate significant difference at 0.05 level.The same below.
LED灯开启10、20、30 min后桃蛀螟对7个波长总趋光率有显著差异(图3)。趋光率分别为76.86%、65.67%和60.58%。10 min时桃蛀螟趋光率最高,显著高于20 min和30 min,且随着开灯时间的延长,桃蛀螟趋光率有所下降。
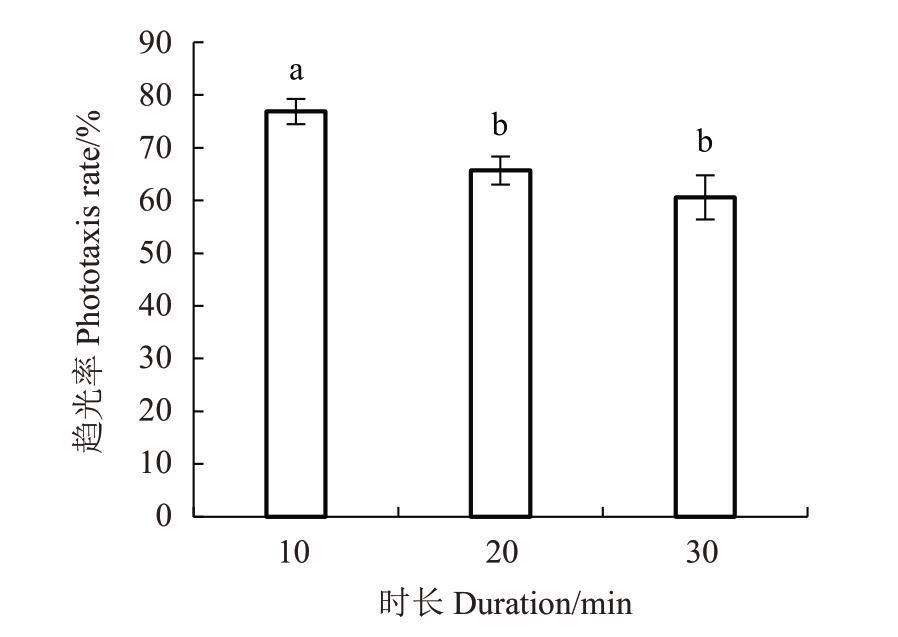
图3 不同时长桃蛀螟趋光率比较
Fig.3 Comparison of phototaxis rate of C.punctiferalis at different times
桃蛀螟对不同波长LED灯趋光率有显著差异(图4)。桃蛀螟对紫光430 nm 的趋性最高,为23.86%。对青光492 nm、绿光533 nm、黄绿光568 nm、黄光591 nm和红光620 nm趋性显著低于430 nm紫光,趋光率分别为13.76%、11.3%、14.28%、9.16%和10.05%。
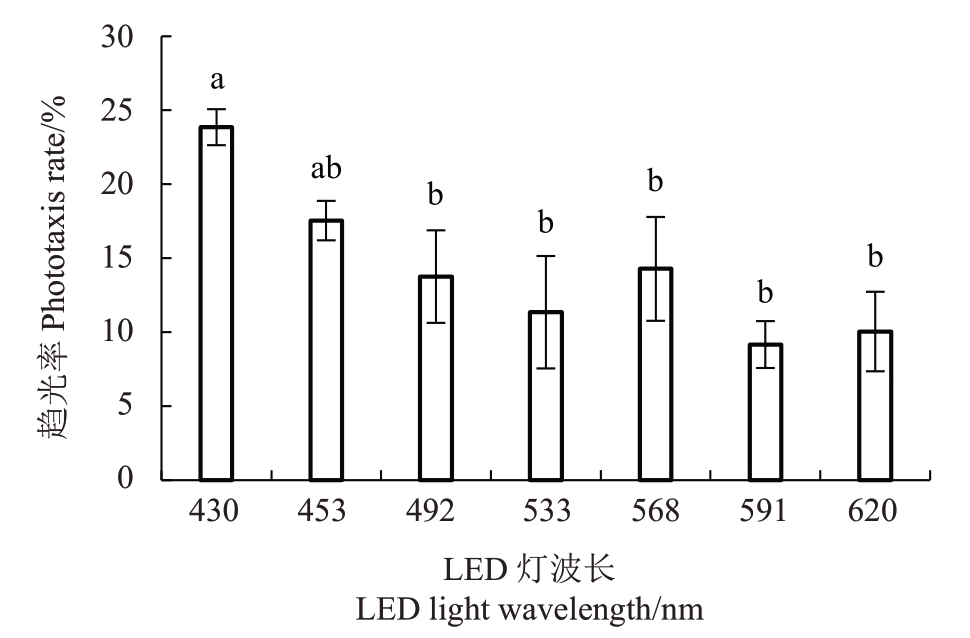
图4 不同波长LED 灯桃蛀螟趋光率比较
Fig.4 Comparison of phototaxis rate of C.punctiferalis with different wavelengths of LED light
2.2 2024年新乡桥北桃园桃蛀螟发生动态调查
结果表明,在新乡桥北桃蛀螟成虫有4 个高峰期,第1 次成虫高峰期为越冬代羽化高峰期,在4 月下旬至5月下旬;第2次为6月中旬至7月中旬;第3次为8 月中旬;第4 次为9 月下旬,为全年发生最高峰(图5)。
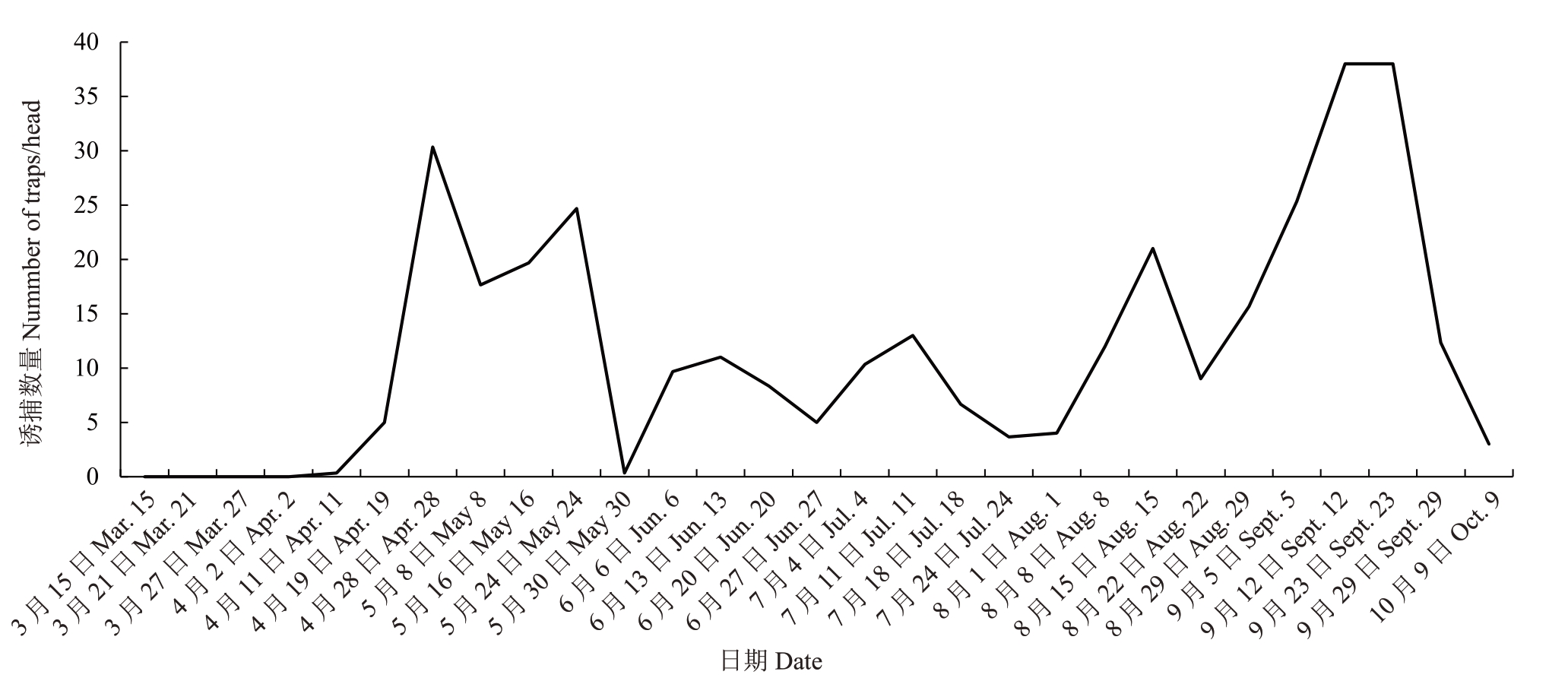
图5 新乡桥北桃园桃蛀螟发生动态(2024 年)
Fig.5 Occurrence dynamics of C.punctiferalis in Qiaobei,Xinxiang(In 2024)
2.3 不同波长LED 灯单灯诱装置对桃蛀螟田间诱捕效果
2024年5月30日至7月4日,7个不同波长LED灯单灯诱装置在桃园共诱集到昆虫为116 头,其中桃蛀螟10头,占比9%;益虫25头,占比22%;害虫91头,占比78%(表2)。
表2 单灯诱的诱虫数量
Table 2 The number of insects attracted by a single light

?
单灯诱桃园诱集到的昆虫涉及4目8科,以鳞翅目和鞘翅目为主,其中,分别诱捕鳞翅目夜蛾科、卷蛾科害虫49、12头;诱捕鞘翅目金龟科害虫15头;诱捕脉翅目草蛉科益虫14头(表3)。
表3 单灯诱诱虫种类与数量
Table 3 Single light lure insect species and quantity

?
不同波长LED灯单灯诱对桃蛀螟诱捕效果有显著差异(图6),整体诱捕数量较少。紫光430 nm 诱捕效果最好,每7 d平均诱捕数量为8头。
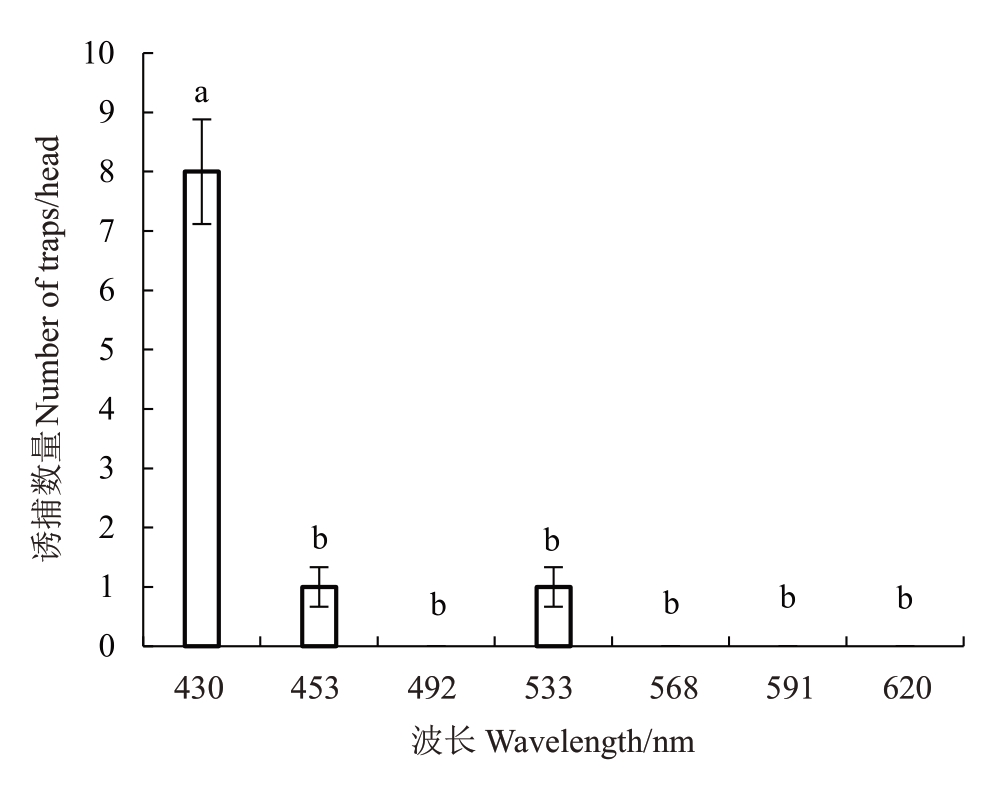
图6 不同波长LED 灯单灯诱装置诱捕桃蛀螟效果
Fig.6 Effects of using different wavelength LED lights as a single lamp lure device to trap C.punctiferalis
2.4 桃蛀螟性信息素与不同波长LED 灯联用装置对桃蛀螟田间诱捕效果
灯诱性诱联用在桃园诱集到昆虫总数为597头,诱捕数量为单灯诱诱捕数量的5倍,诱捕靶标昆虫效果较好。诱捕桃蛀螟304 头,占比51%;诱捕到益虫32 头,占比5%;诱捕害虫565 头,占比95%(表4)。灯诱性诱联用诱捕桃蛀螟的数量是单灯诱的30倍,所占比例增加了42%。灯诱性诱联用诱捕害虫的数量是单灯诱的9 倍,占比增加17%。灯诱性诱联用诱捕益虫占比相比单灯诱下降了17%。
表4 灯诱性诱联用的诱虫数量
Table 4 The number of insect attractants used in combination of lamp and sexual attractants

?
灯诱性诱联用在桃园诱集到的昆虫涉及4 目7科,以鳞翅目和鞘翅目为主,其中,分别诱捕鳞翅目卷蛾科、夜蛾科害虫147、87 头;诱捕鞘翅目金龟科害虫26头;诱捕脉翅目草蛉科益虫25头(表5)。灯诱性诱联用诱捕鳞翅目卷蛾科害虫占比相比单灯诱分别增加了14.3%;灯诱性诱联用诱捕草蛉科益虫占比相比单灯诱下降了7.5%。
表5 灯诱性诱联用的诱虫种类与数量
Table 5 The types and quantities of insect attractants used in combination with lamp and sexual attractants

?
灯诱性诱联用、单灯诱、单性诱三种诱捕方式对桃蛀螟诱捕效果差异显著(图7)。诱捕效果依次为灯诱性诱联用>单性诱>单灯诱。

图7 不同诱捕方式诱捕桃蛀螟效果
Fig.7 The effectiveness of different trapping methods in trapping Conogethes punctiferalis
L+S:灯诱性诱联用;L:单灯诱;S:单性诱。
L+S:Combination of lamp and sexual attraction;L:Single lamp lure;S:Single sex lure.
选取430 nm、453 nm、492 nm、533 nm、568 nm波长灯时不同诱捕方式对桃蛀螟诱捕效果依次为灯诱性诱联用>单性诱>单灯诱。430 nm、568 nm波长灯诱性诱联用与单性诱之间对桃蛀螟诱捕效果差异显著,单灯诱与单性诱之间对桃蛀螟诱捕效果差异不显著;453 nm、533 nm 波长灯诱性诱联用与单性诱之间对桃蛀螟诱捕效果差异不显著,灯诱性诱联用与单灯诱之间对桃蛀螟诱捕效果差异显著;492 nm波长灯诱性诱联用与单灯诱、单性诱之间对桃蛀螟诱捕效果差异显著。选取591 nm、620 nm波长灯时不同诱捕方式对桃蛀螟诱捕效果依次为单性诱>灯诱性诱联用>单灯诱。591 nm 波长灯诱性诱联用与单性诱之间对桃蛀螟诱捕效果差异显著,灯诱性诱联用与单灯诱之间对桃蛀螟诱捕效果差异不显著;620 nm 波长单灯诱与单性诱之间差异显著,灯诱性诱联用与单性诱之间对桃蛀螟诱捕效果差异不显著。
桃蛀螟性信息素与不同波长LED 灯联用装置对桃蛀螟诱捕效果有显著差异(图8)。桃蛀螟性信息素与不同波长LED 灯联用装置中,430 nm 与453 nm、492 nm、533 nm、568 nm、591 nm、620 nm波长灯之间对桃蛀螟诱捕效果差异显著,492 nm 与453 nm、533 nm 、568 nm 波长灯之间对桃蛀螟诱捕效果差异不显著,492 nm 与591 nm、620 nm 波长灯之间对桃蛀螟诱捕效果差异显著。430 nm 灯诱性诱联用时诱捕桃蛀螟数量最多,诱捕数量为104头;其次为492 nm,诱捕桃蛀螟数量为52头。
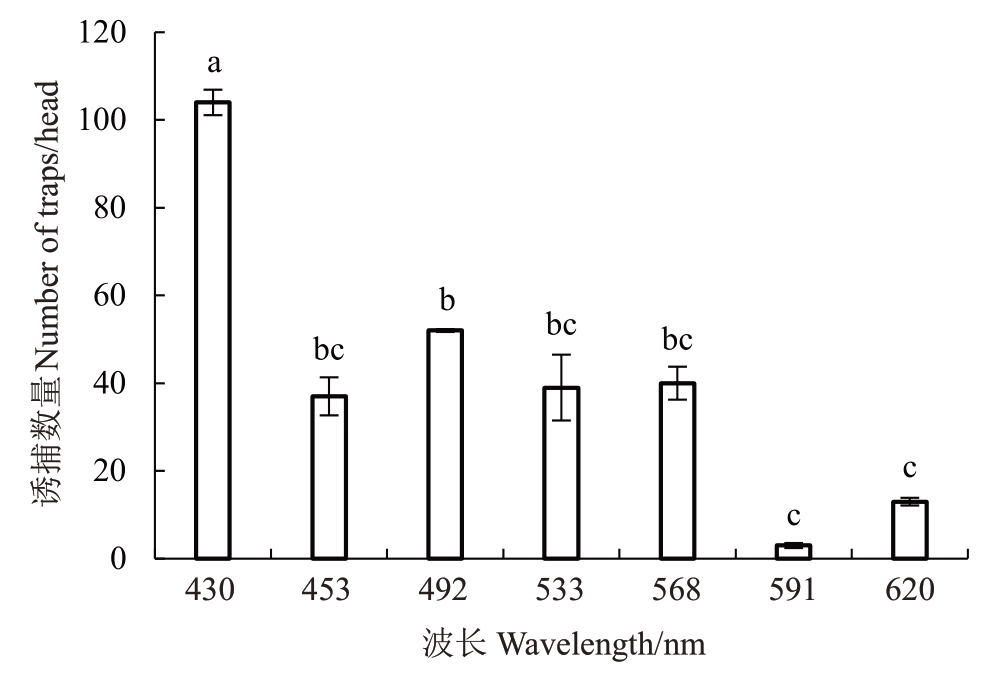
图8 桃蛀螟性信息素与不同波长LED 灯联用装置诱捕桃蛀螟效果
Fig.8 Effects of using a combination device of C.punctiferalis sex pheromones and different wavelength LED lights to trap Conogethes punctiferalis
3 讨 论
笔者在本研究中发现室内趋向性试验中桃蛀螟在趋光装置中放置10 min时趋光率最高,雌雄趋光率没有显著差异。桃蛀螟趋光反应率较高的波长为紫光430 nm。单灯诱及灯诱性诱联用装置中,430 nm 波长灯诱捕桃蛀螟效果最好,与室内桃蛀螟趋光偏好波长一致。蛾类诱捕器不同装置诱捕桃蛀螟数量从多到少依次为:性诱+灯诱>性诱>灯诱。7个不同波长LED灯单灯诱装置及灯诱性诱联用装置在桃园诱集到的桃蛀螟占比分别为9%、51%,灯诱性诱联用诱捕桃蛀螟占比相比单灯诱增加了42%,灯诱性诱联用对靶标昆虫桃蛀螟的诱捕效果更好。7个不同波长LED灯单灯诱装置及灯诱性诱联用装置在桃园诱集到的害虫占比分别为78%、95%,灯诱性诱联用诱捕害虫占比相比单灯诱增加了17%,灯诱性诱联用对桃园害虫诱捕效果更好。7个不同波长LED灯单灯诱装置及灯诱性诱联用装置在桃园诱集到的益虫占比分别为22%、5%,灯诱性诱联用诱捕害虫占比相比单灯诱下降了17%,灯诱性诱联用对桃园益虫的影响更小。灯诱性诱联用在桃园中引诱靶标昆虫桃蛀螟和其他害虫效果最好,且对果园益虫影响更小。
比较不同波长光对桃蛀螟的引诱效果,筛选引诱桃蛀螟专一性较强的波长,有效地提高了对桃蛀螟的诱捕效果。目前关于鳞翅目害虫敏感波长选择的研究较多,Pan等[14]研究发现,395 nm紫光LED 波长的诱捕器捕获的鳞翅目、半翅目、鞘翅目害虫总数高于所有其他物种,Sun 等[15]研究发现,梨小食心虫对绿色、紫色LED 灯较为敏感,郭虹等[16]研究发现,368 nm 杀虫灯对河北张家口常见鳞翅目害虫引诱效果最好,均与本试验结果吻合。笔者在本试验中筛选出紫光430 nm 诱捕果园鳞翅目害虫桃蛀螟效果较好,印证了前人的观点。
在实际生产中,性信息素技术和灯诱技术被广泛使用,但是两种技术组合进行复合型诱捕研究较少。研究发现,将桃蛀螟敏感波长与性信息素技术结合使用,可以提高对桃蛀螟的诱捕效率,对桃蛀螟的诱捕更具有针对性,降低诱集成本。在灯诱性诱联用技术研究中,马云波等[17]研究发现,诱虫灯与性诱剂相结合的诱捕效果与单用诱虫灯、单用性诱剂2 种方法比较成虫诱捕量大幅度提升,洪海林等[18]研究发现,灯诱与性诱组合防治时对茶尺蠖的防治效果较好,姜燕华等[19]研究发现,“杀虫灯+45 m 性诱捕器”组合诱捕茶尺蠖效果最佳,雷浩霖等[20]研究发现,杀虫灯与二化螟性诱剂联用对水稻二化螟具有较强的诱集作用,都验证了性信息素与诱虫灯联用装置可以大幅度提高对目标昆虫的诱捕量。
灯诱和桃蛀螟性信息素联用时诱捕数量增加,可能是因为单灯诱对桃蛀螟成虫具有引诱作用且辐射范围广,且单性诱对雄虫高度专一性较高,二者联用可同时吸引雌雄成虫并扩大诱捕范围;单性诱通过模拟性信息素吸引桃蛀螟雄虫交配,单灯诱则吸引桃蛀螟夜间活动、寻找栖息地或食物的成虫,灯诱性诱联用可覆盖桃蛀螟多种行为阶段,增加诱捕机会;此外,灯光先将桃蛀螟成虫吸引至一定范围,性诱芯再精准吸引雄虫,二者协同作用,显著增强对桃蛀螟成虫的吸引效果,从而提高诱捕数量。
因此在实际生产中,本试验筛选出的桃蛀螟性信息素与430 nm 紫光LED 灯联用装置可以为果园鳞翅目害虫桃蛀螟的诱捕提供参考。
4 结 论
研究结果表明,桃蛀螟成虫对430 nm紫光趋性最高,桃蛀螟性信息素与430 nm紫光LED灯联用装置诱捕效果最好。桃蛀螟性信息素与430 nm 紫光LED 灯联用装置对田间桃蛀螟的诱捕具有增效作用,提高害虫的诱捕效果,并提升害虫监测精准度。
[1] 鹿金秋,王振营,何康来,刘勇.桃蛀螟研究的历史、现状与展望[J].植物保护,2010,36(2):31-38.LU Jinqiu,WANG Zhenying,HE Kanglai,LIU Yong. Research history,progresses and prospects in the yellow peach moth,Conogethes punctiferalis[J]. Plant Protection,2010,36(2):31-38.
[2] 张希涛,刘振兴,李红芳,王法杰,贾红梅.桃蛀螟发生规律及防治措施探讨[J].果农之友,2023(4):55-57.ZHANG Xitao,LIU Zhenxing,LI Hongfang,WANG Fajie,JIA Hongmei.Discussion on the occurrence pattern and control measures of Conogethes punctiferalis[J]. Fruit Growers’Friend,2023(4):55-57.
[3] 冯洪敏.板栗园桃蛀螟的发生规律及防治措施[J].果树实用技术与信息,2024(1):41-42.FENG Hongmin. The occurrence pattern and control measures of Conogethes punctiferalis in chestnut orchard[J]. Practical Techniques and Information for Fruit Trees,2024(1):41-42.
[4] 翟浩,王丹,马亚男,贾晓曼,张勇,李晓军.糖醋酒液对桃园和苹果园中桃蛀螟的诱捕效果分析[J].植物保护学报,2019,46(4):894-901.ZHAI Hao,WANG Dan,MA Yanan,JIA Xiaoman,ZHANG Yong,LI Xiaojun. Trapping effects of sugar-acetic acid-ethanol water solutions on yellow peach moth Conogethes punctiferalis in peach and apple orchards[J]. Journal of Plant Protection,2019,46(4):894-901.
[5] 桑文,黄求应,王小平,郭墅濠,雷朝亮.中国昆虫趋光性及灯光诱虫技术的发展、成就与展望[J].应用昆虫学报,2019,56(5):907-916.SANG Wen,HUANG Qiuying,WANG Xiaoping,GUO Shuhao,LEI Chaoliang. Progress in research on insect phototaxis and future prospects for pest light-trap technology in China[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology,2019,56(5):907-916.
[6] 吴霜,张谊模,郭萧,黄云峰,刘剑飞.不同波长LED 诱虫灯对菜地昆虫的诱集效果[J]. 应用昆虫学报,2021,58(1):172-180.WU Shuang,ZHANG Yimo,GUO Xiao,HUANG Yunfeng,LIU Jianfei. Effectiveness of different wavelength LED insect lamp traps in vegetable fields[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology,2021,58(1):172-180.
[7] 雷春媚,张俊杰,张天涛,周小毛,肖勇,李振宇.田间不同波长诱虫灯对草地贪夜蛾和亚洲玉米螟的诱集效果研究[J].应用昆虫学报,2023,60(4):1187-1194.LEI Chunmei,ZHANG Junjie,ZHANG Tiantao,ZHOU Xiaomao,XIAO Yong,LI Zhenyu.Relative effectiveness of different wavelength trap lamps for Spodoptera frugiperda and Ostrinia furnacalis[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology,2023,60(4):1187-1194.
[8] CUI G Z,ZHU J J. Pheromone-based pest management in China:Past,present,and future prospects[J]. Journal of Chemical Ecology,2016,42(7):557-570.
[9] 陈万斌,杨宸,黄晓丹,何康来,王振营.桃蛀螟性诱剂的筛选及其在黄淮海夏玉米区种群动态监测中的应用[J].植物保护,2022,48(1):211-219.CHEN Wanbin,YANG Chen,HUANG Xiaodan,HE Kanglai,WANG Zhenying. Screening of the sex pheromones formulation and application for population dynamics monitoring of Conogethes punctiferalis (Guenée) in Huang-Huai-Hai summer corn region in China[J].Plant Protection,2022,48(1):211-219.
[10] 任帅,郭素娟.桃蛀螟性信息素在板栗园中应用技术研究[J].环境昆虫学报,2015,37(1):96-101.REN Shuai,GUO Sujuan. Study on the applied technology of Conogethes punctiferalis'sex pheromone in Chestnut orchard[J].Journal of Environmental Entomology,2015,37(1):96-101.
[11] 马广源,党志红,李耀发,程志,潘文亮,高占林.性诱剂与诱虫灯结合使用对二点委夜蛾诱捕效果初探[J].中国植保导刊,2015,35(3):45-47.MA Guangyuan,DANG Zhihong,LI Yaofa,CHENG Zhi,PAN Wenliang,GAO Zhanlin. Preliminary study on the trapping effect of the combination of sex attractants and insect attractants on Athetis lepigone(Moschler)[J].China Plant Protection,2015,35(3):45-47.
[12] 林清彩,马罡,张薇,朱亮,马春森.诱虫灯与性诱剂联用对葡萄透翅蛾和斜纹夜蛾的诱杀效果[J].植物保护,2023,49(2):338-341.LIN Qingcai,MA Gang,ZHANG Wei,ZHU Liang,MA Chunsen. Combined effects of light and sex pheromone traps on Paranthrene regalis and Spodoptera litura[J]. Plant Protection,2023,49(2):338-341.
[13] 唐良德,韩云,吴建辉,李鹏,付步礼,邱海燕,刘奎.豆大蓟马室内对不同颜色及光波的趋性反应[J]. 植物保护,2015,41(6):169-172.TANG Liangde,HAN Yun,WU Jianhui,LI Peng,FU Buli,QIU Haiyan,LIU Kui. Preference of Megalurothrips usitatus(Thysanoptera:Thripidae) to different colors and light-waves in lab[J].Plant Protection,2015,41(6):169-172.
[14] PAN H S,LIANG G M,LU Y H. Response of different insect groups to various wavelengths of light under field conditions[J].Insects,2021,12(5):427.
[15] SUN Y X,TIAN A,ZHANG X B,ZHAO Z G,ZHANG Z W,MA R Y. Phototaxis of Grapholitha molesta (Lepidoptera:Olethreutidae)to different light sources[J].Journal of Economic Entomology,2014,107(5):1792-1799.
[16] 郭虹,韩献华,许志春.不同波长杀虫灯对鳞翅目害虫的诱杀效果[J].山西农业科学,2012,40(2):146-149.GUO Hong,HAN Xianhua,XU Zhichun. Effect comparison of different wavelengths insecticidal lamps in lepidopteran pests trapping[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences,2012,40(2):146-149.
[17] 马云波,高成龙.性诱与灯诱结合使用对沙棘木蠹蛾的诱捕效果试验[J].安徽农学通报,2017,23(8):76.MA Yunbo,GAO Chenglong. Experimental study on the trapping effect of the combination of sexual lure and light lure on Eogystia hippophaecolus (Hua,Chou,Fang et Chen)[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin,2017,23(8):76.
[18] 洪海林,洪迪甫,李伦,李罡,丁坤明,周玲玲,张敬锋,杨姣,程长松,陈国庆.灯诱与性诱及其组合对茶尺蠖的防治效果[J].湖北植保,2023(2):27-29.HONG Hailin,HONG Difu,LI Lun,LI Gang,DING Kunming,ZHOU Lingling,ZHANG Jingfeng,YANG Jiao,CHENG Changsong,CHEN Guoqing. The control effect of light lure,sexual lure and their combination on Ectropis obliqua[J]. Hubei Plant Protection,2023(2):27-29.
[19] 姜燕华,韩震,焦小波.性诱剂和杀虫灯处理对茶尺蠖的引诱效果[J].浙江农业科学,2021,62(12):2473-2474.JIANG Yanhua,HAN Zhen,JIAO Xiaobo . Effect of sexual attractants and pest killing lamp on Ectropis obliqua[J].Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences,2021,62(12):2473-2474.
[20] 雷浩霖,张宇瑶,刘伟,魏洪义.诱虫灯与性诱剂联用对二化螟和稻纵卷叶螟的诱杀效果[J]. 华中昆虫研究,2020,16:227-237.LEI Haolin,ZHANG Yuyao,LIU Wei,WEI Hongyi. Trapping efficiency of insect killing lamps combined with sex attractants on the striped stem borer and rice leaf folder in rice fields[J].Huazhong Insect Research,2020,16:227-237.