当前,随着生活节奏的加快,鲜切果因健康、方便、100%可食的特性越来越被消费者接受[1],对鲜切果品质的要求也越来越高,而鲜切果产品的开发与果肉组织褐变抗性直接相关[2]。枇杷[Eriobotrya japonica(Thunb.)Lindl.]是蔷薇科苹果亚科枇杷属植物,风味甜酸适口,营养丰富,有“早春第一果”的美誉,深受消费者青睐。探索枇杷果肉褐变快速高效的鉴定评价方法,有利于高效筛选耐褐变种质资源,为优异资源的创新利用奠定基础。
近年来,随着交叉学科的兴起,许多基于计算机视觉快速识别农作物病虫害及果实品质分级的方法被挖掘[3-5],深度学习在植物病害识别和病虫害范围评估等植保领域成为研究热点[6-9],如柑橘[10]、苹果[11]、荔枝[12]等植物叶病害检测分割已有了系统研究。在颜色性状上,计算机视觉的图像处理技术亦有广泛运用[13],刘佳浩等[14]利用机器视觉的边缘检测及HSI 颜色模型对苹果品质进行准确分级;高燕萍等[15]利用MATLAB 图像分割技术实现了甘薯耐褐变种质资源的快速鉴定。目前对枇杷种质资源的鉴定评价主要集中在外观(果形、色泽等)、风味(可溶性固形物、可溶性糖、可滴定酸、维生素C含量等)等品质性状[16]。对果肉色泽及色泽变化的研究则多基于肉眼观察判定或利用色差仪测定[17]。预试验观察发现,枇杷种质资源间的果肉褐变抗性有明显差异,且存在不均匀褐变现象,但果肉的褐变抗性尚未开展系统鉴定研究。笔者在本研究中拟应用MATLAB 图像二值分割算法分析枇杷果肉切面颜色值的差异变化,计算果肉褐变指数及褐变面积,根据果肉褐变特性和抗褐变能力对枇杷资源进行分级排序,探索适用于枇杷耐褐变种质资源快速鉴定评价的方法,为准确、批量识别枇杷种质资源颜色表型提供研究新思路。
1 材料和方法
1.1 试验材料
观测的10份枇杷资源(表1)均取自国家枇杷种质资源圃(福州)。在果实成熟期,每份资源统一由有经验的科技人员挑选出大小、色泽和成熟度一致的果实,用不锈钢刀纵切二等分,一半果肉去除种子后放入光源固定的简易柔光摄影灯箱内,拍照记录鲜切0、10、30、60 min时色泽表型(相机参数:光圈值F=5.6,感光度ISO=1000,快门速度640,拍摄背景为灰色,相片保存格式为.jpg),另一半果肉用于色差仪法(D65 光源10°视场)测定0、60 min 切面Lab 及RGB 值。观测环境的温度保持在25 ℃。单果为一个处理,3次重复。
表1 供试的10 份枇杷资源
Table 1 Ten loquat resources for testing
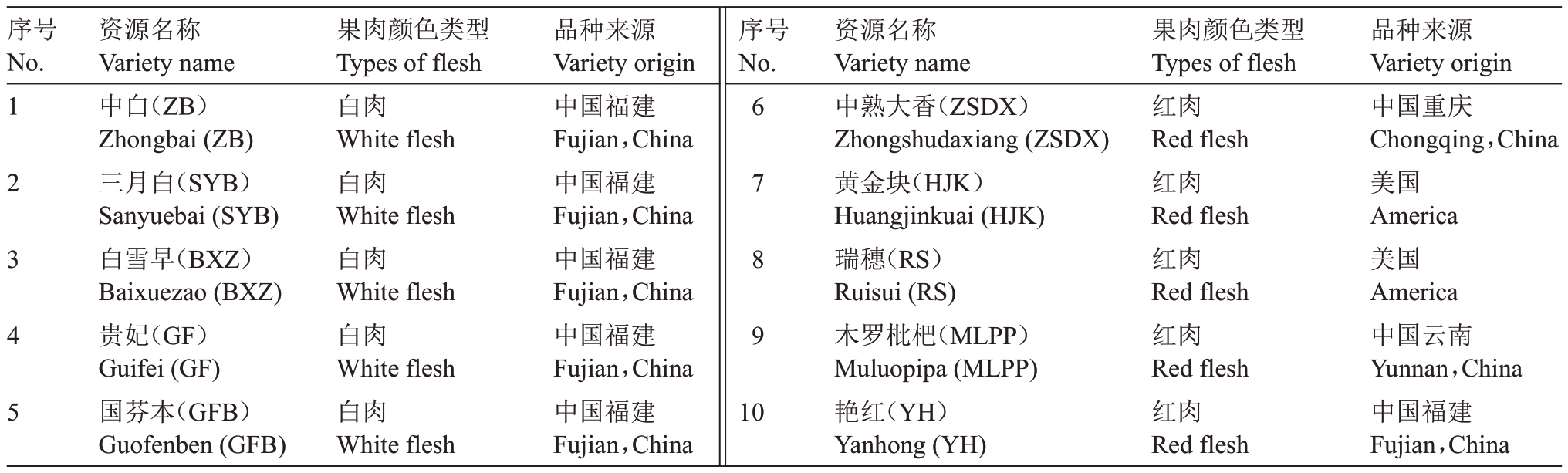
序号No.序号No.1 2 3 4 5资源名称Variety name中白(ZB)Zhongbai(ZB)三月白(SYB)Sanyuebai(SYB)白雪早(BXZ)Baixuezao(BXZ)贵妃(GF)Guifei(GF)国芬本(GFB)Guofenben(GFB)果肉颜色类型Types of flesh白肉White flesh白肉White flesh白肉White flesh白肉White flesh白肉White flesh品种来源Variety origin中国福建Fujian,China中国福建Fujian,China中国福建Fujian,China中国福建Fujian,China中国福建Fujian,China 6 7 8 9 10资源名称Variety name中熟大香(ZSDX)Zhongshudaxiang(ZSDX)黄金块(HJK)Huangjinkuai(HJK)瑞穗(RS)Ruisui(RS)木罗枇杷(MLPP)Muluopipa(MLPP)艳红(YH)Yanhong(YH)果肉颜色类型Types of flesh红肉Red flesh红肉Red flesh红肉Red flesh红肉Red flesh红肉Red flesh品种来源Variety origin中国重庆Chongqing,China美国America美国America中国云南Yunnan,China中国福建Fujian,China
1.2 枇杷果肉褐变的最适颜色空间筛选
参照包新月等[18]的方法,以白肉资源贵妃和红肉资源黄金块鲜切果肉为试验材料,使用MATLAB R2022a(软件来源于MathWorks公司)imread函数读取原始图片的RGB 通道,利用rgb2lab 和rgb2hsi 函数将原始图片(0、10、30、60 min时相机拍摄的图片)从RGB 空间转为Lab 空间和HSI 空间,以色差仪测试结果为对照,筛选适宜枇杷果肉色泽表型区分的最适颜色空间。
1.3 Lab值提取及褐变指数计算
1.3.1 图像分割 先使用MATLAB 软件rgb2gray函数将采集的原始图像(图1-A)转化为灰度图(图1-B)。以Sobel算子计算分割阈值,应用阈值得到分割后果肉切面的二值掩膜图像(图1-C),通过edge函数将原始图像的边缘和背景用二值图像的形式展现出来,达到边缘检测分割图像的目的[19]。二值掩膜显示图像中高对比度的线条,但这些线条没有很好地描绘出果肉切面对象的轮廓,与原始图像相比,梯度掩膜中对象周围的线条有间隙。利用imdilate函数对图像进行形态学膨胀得到果肉切面的轮廓,但内部仍有小孔(图1-D)。再用imfill 函数进行孔隙填充,得到完整的果肉切面图像(图1-E)。用imclearborder 函数删除边界连通对象(图1-F)。用imerode函数进行平滑处理,得到背景为0、目标区域为1的完整二值分割图像(图1-G)[20]。
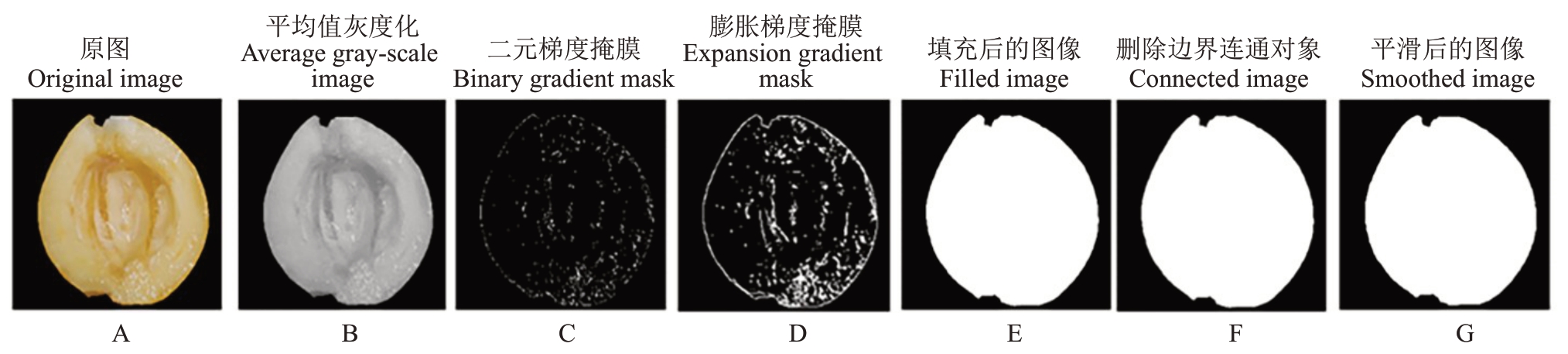
图1 图像二值化过程
Fig.1 Image binary segmentation process
1.3.2 褐变指数测算 MATLAB 算法使用边缘检测法对原始图像进行二值分割,形态学处理后白色区域数值为1,即目标果肉切面区域,黑色区域为背景,数值为0(图1-G),将数值为1的白色区域映射到原始图像中的Lab 通道,计算得出果肉切面Lab 均值。色差仪法则直接测定得到Lab值。根据色差公式计算枇杷果肉褐变指数(BI)。

1.3.3 欧氏距离褐变面积检测 以MATLAB ROI函数选择不规则的代表性枇杷果肉褐变区域,提取颜色特征值,利用欧氏距离完成对原始图像的褐变面积分割[21]。不同类型的枇杷果肉肉色差异显著,白肉资源分割阈值以贵妃60 min为例,红肉资源分割阈值以黄金块60 min 为例,设置不同程度的阈值,观测分割的相似度与一致性,确定最合适的阈值,计算出枇杷果肉褐变面积,即褐变部分占整个果肉切面的百分比。
枇杷果肉质地较软,鲜切后不同部位的褐变程度存在差异,在选择目标ROI区域时,尽量选择包含不同梯度褐变的区域,以便准确识别褐变区域(图2-A~B)。白肉类型果肉颜色与褐变色颜色值差异明显,用于分割的T值较大,在进行褐变面积分割时容易把握褐变区域和褐变阈值的选择,以不同阈值检测分割适宜性,其中70T、80T分割区域保守,部分褐变区域未能准确识别,而100T和110T却过度分割,因此在白肉资源中90T为相对合适的分割阈值(图2-C~G)。红肉资源果肉颜色橙红(黄),褐变色表现为果肉颜色的加深,用于分割的T值较小,在选取红肉类型的ROI区域时,尽量选择与果肉颜色差异最显著的区域(图2-H~I),根据图2-J~N 的分割适宜性检测,以25T作为红肉类型褐变占比计算的分割阈值。
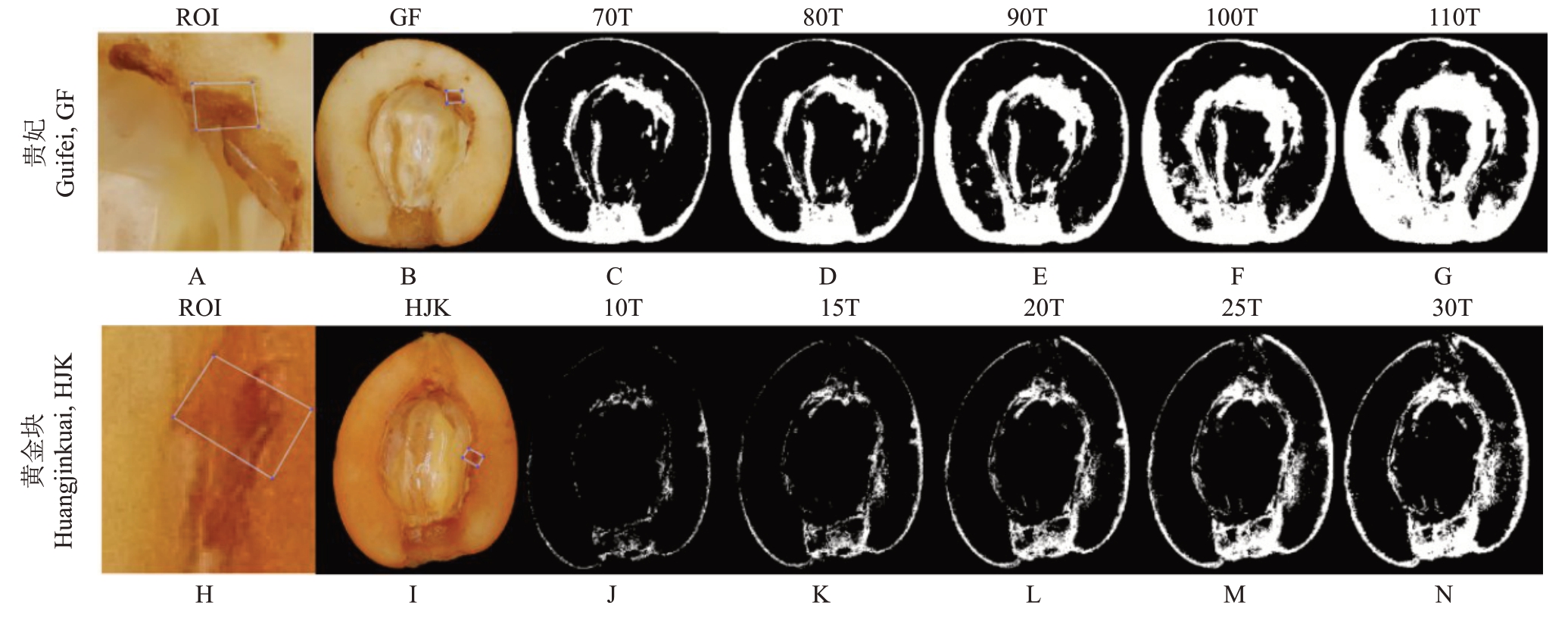
图2 贵妃(GF)、黄金块(HJK)60 min 不同阈值分割结果
Fig.2 Segmentation results of Guifei(GF)and Huangjinkuai(HJK)with different thresholds for 60 min
1.4 数据处理
利用Excel 2013整理数据,利用SPSS 26.0进行统计学分析。隶属函数μ(Xij)=(Xij-Xmin)/(Xmax-Xmin),式中μ(Xij)表示第i个资源第j个指标的隶属函数值,Xij为指标测定值,Xmax、Xmin分别为所有参试资源中第j个指标测定值的最大值和最小值。
2 结果与分析
2.1 MATLAB图像识别枇杷果肉褐变的最适颜色空间
利用MATLAB 函数对表型差异较大的枇杷资源贵妃和黄金块进行不同颜色空间转换,以显示各分量下的枇杷果肉表型差异。在RGB空间中,两种色泽表型的R 通道值无显著差异;在HSI 空间中,H通道无显著区分;Lab颜色空间在3个通道同时显著区分色泽差异明显的果肉(图3)。
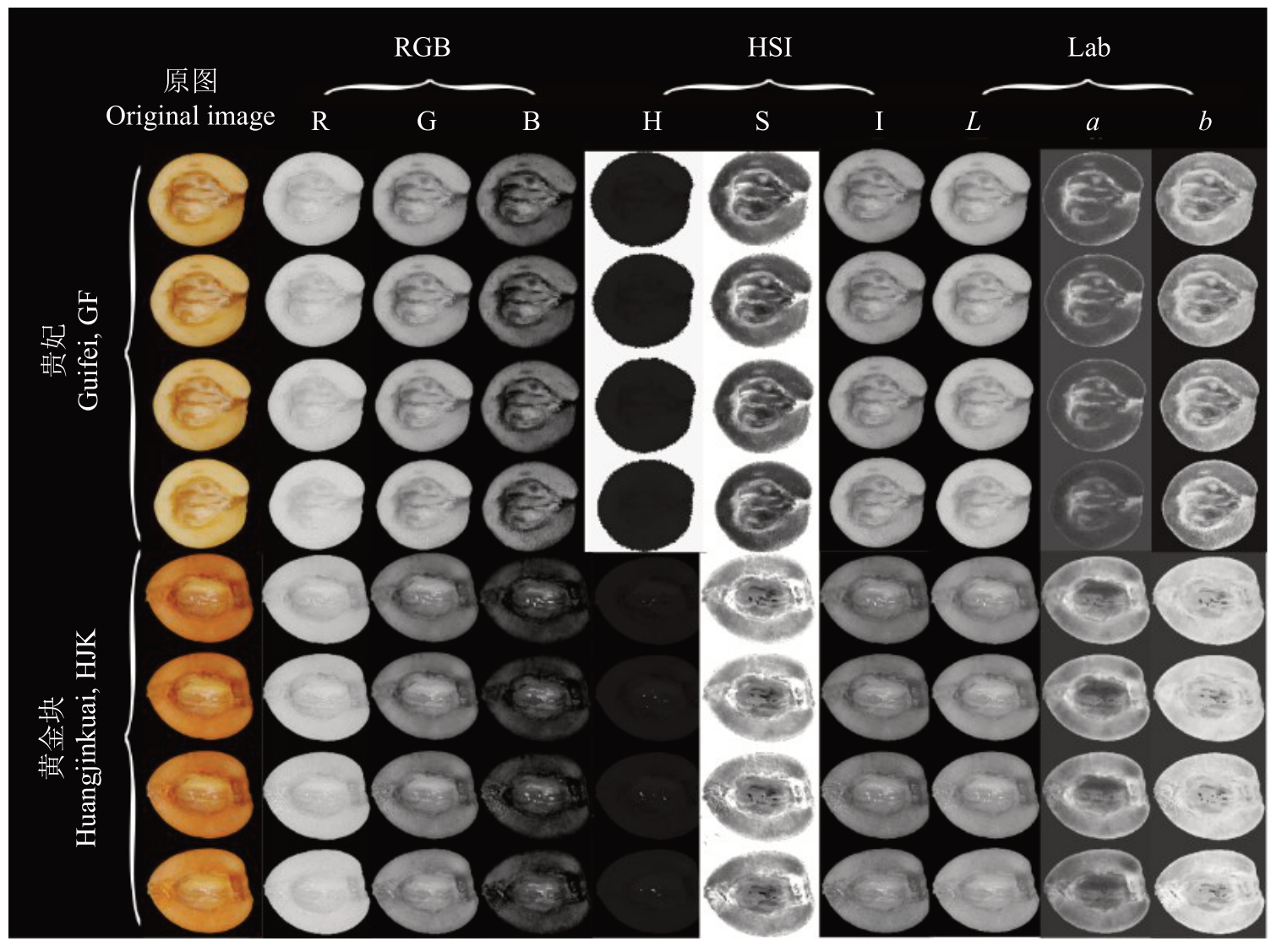
图3 两种类型枇杷果肉不同颜色空间灰度图
Fig.3 Two types of loquat fruit flesh with different color space grayscale images
将使用色差仪测定的RGB 值和Lab 值,与MATLAB 算法提取的RGB 值和Lab 值对比,结果(图4)显示,两份红肉、白肉资源鲜切后相同时间点Lab 颜色空间的L 值、a 值、b 值均有显著差异(图4-A~C);在RGB 空间中,色差仪和MATLAB 测定的两份资源的G值和B值均差异显著(图4-E~F),R值差异不显著(图4-D)。从两份资源鲜切后不同时间色差值变化比较来看,MATLAB 算法提取的Lab 值中0 min和60 min时的白肉资源贵妃和红肉资源黄金块的L 值、a 值均有显著差异,而RGB 颜色空间中仅白肉资源贵妃的R 值、G 值和B 值的果肉色泽变化达显著水平,红肉资源黄金块仅G 值差异显著,R 值和B 值均差异不显著。综上认为选用Lab颜色空间对枇杷资源进行颜色值提取及褐变鉴定更适合。
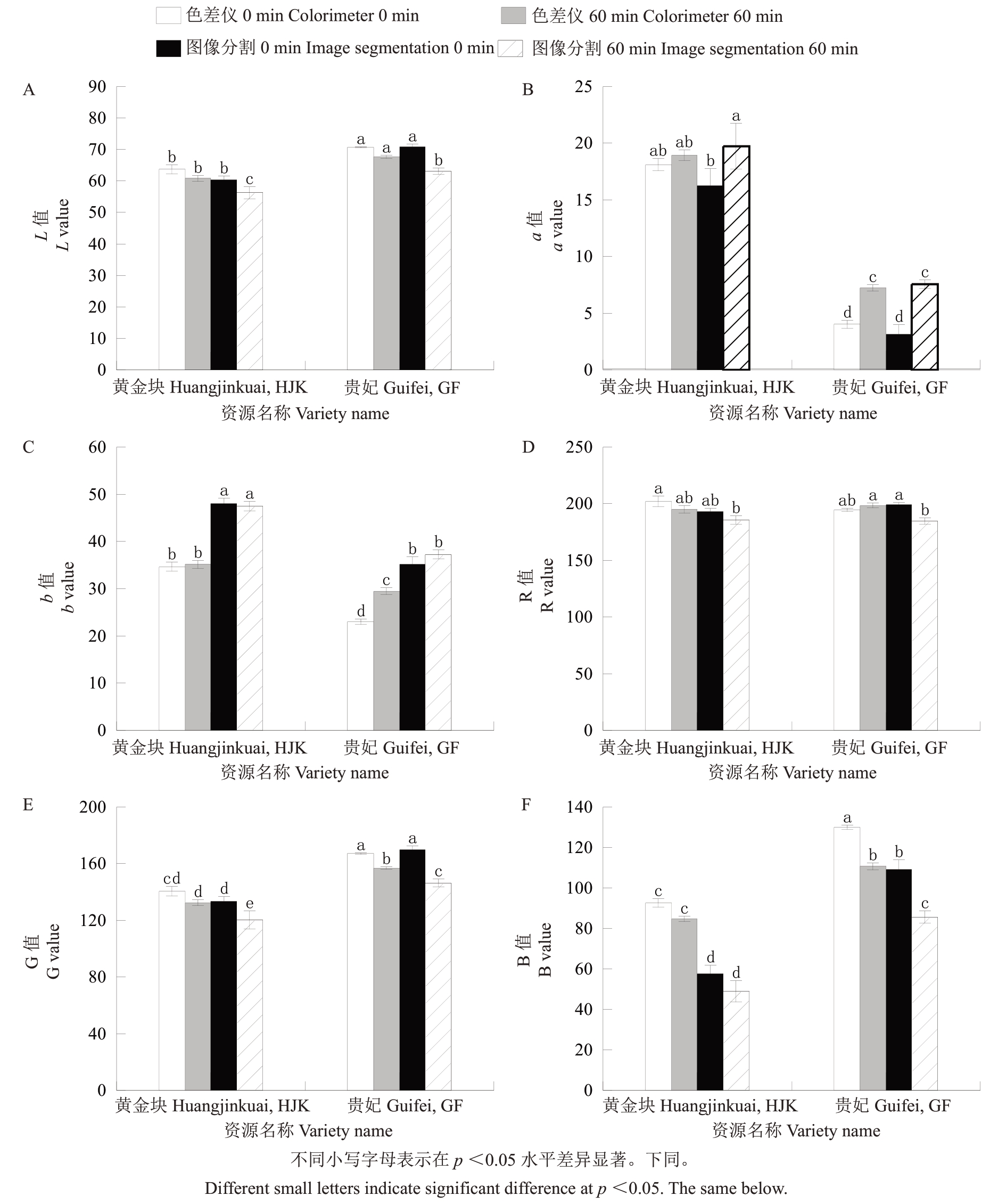
图4 MATLAB 算法与色差仪法提取果肉颜色Lab 与RGB 值差异Fig.4 MATLAB algorithm and colorimeter method to extract fruit flesh color Lab and RGB value differences
2.2 褐变过程Lab值及褐变指数的变化
图像分割算法显示白肉资源的L值高于红肉资源,a 值和b 值则较低。在果肉褐变过程中,10 份种质资源的L 值均呈逐步下降趋势,0~10 min 变化最明显,30~60 min 白肉资源小幅度下降,红肉资源的L值趋于稳定(图5-A)。相反,随着时间的延长,a值呈上升趋势,30 min 后趋于稳定(图5-B)。值得注意的是,b 值在红肉和白肉类型中表现出不同的变化规律,白肉资源的b值逐步增大,红肉资源的b值却逐步降低(图5-C)。
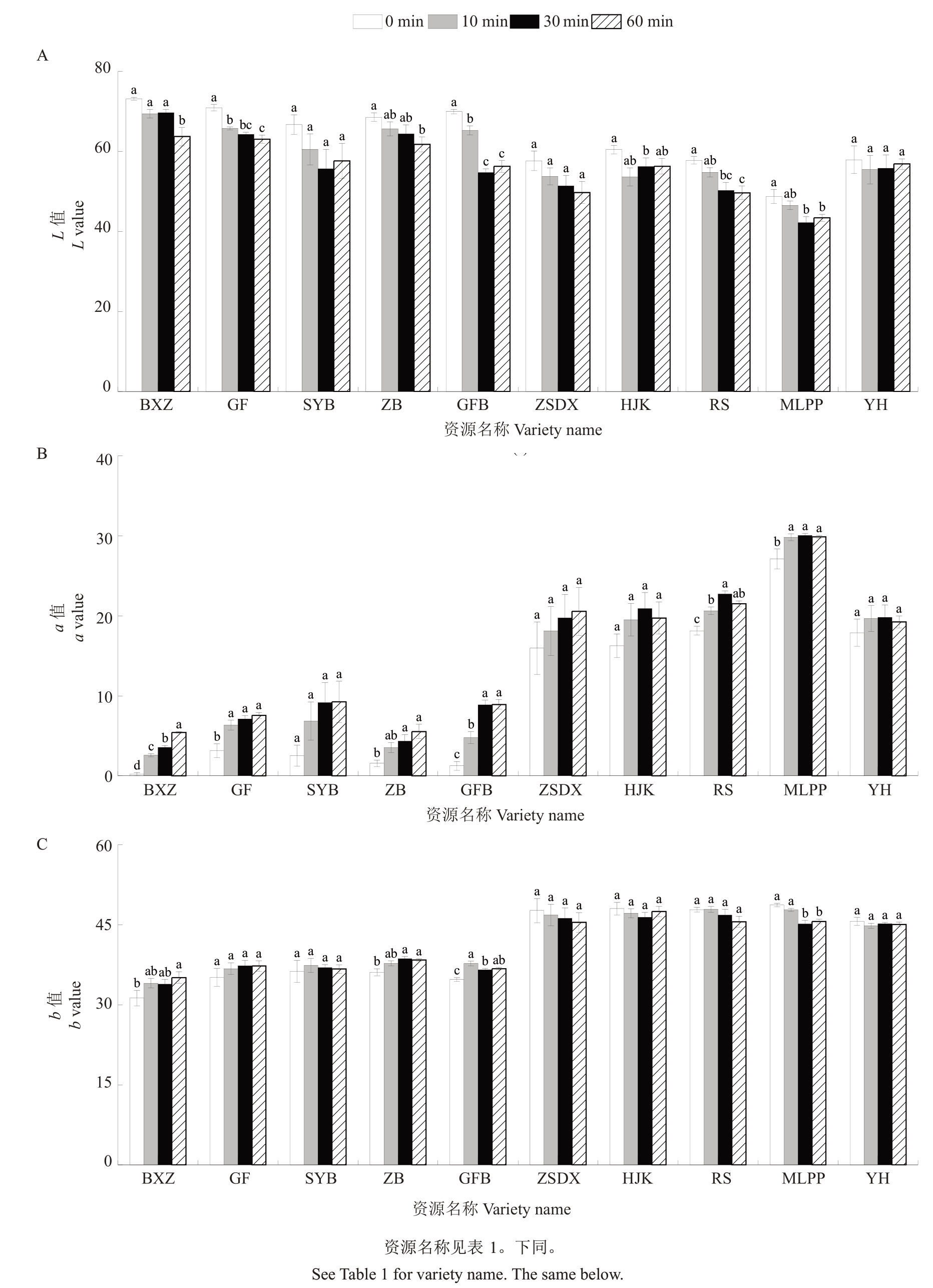
图5 10 份枇杷资源鲜切后不同时间Lab 值变化
Fig.5 Changes in Lab values at different times after fresh cutting of 10 loquat resources
利用色差公式根据Lab 值计算10 份资源在不同时间段的褐变指数(BI),如图6所示,白肉资源的褐变指数高于红肉资源,白雪早、贵妃、中白、中熟大香、黄金块、瑞穗、艳红随着时间延长,褐变指数增大,而三月白、国芬本、木罗枇杷则在鲜切30 min后达到褐变阈值,而后趋于稳定。
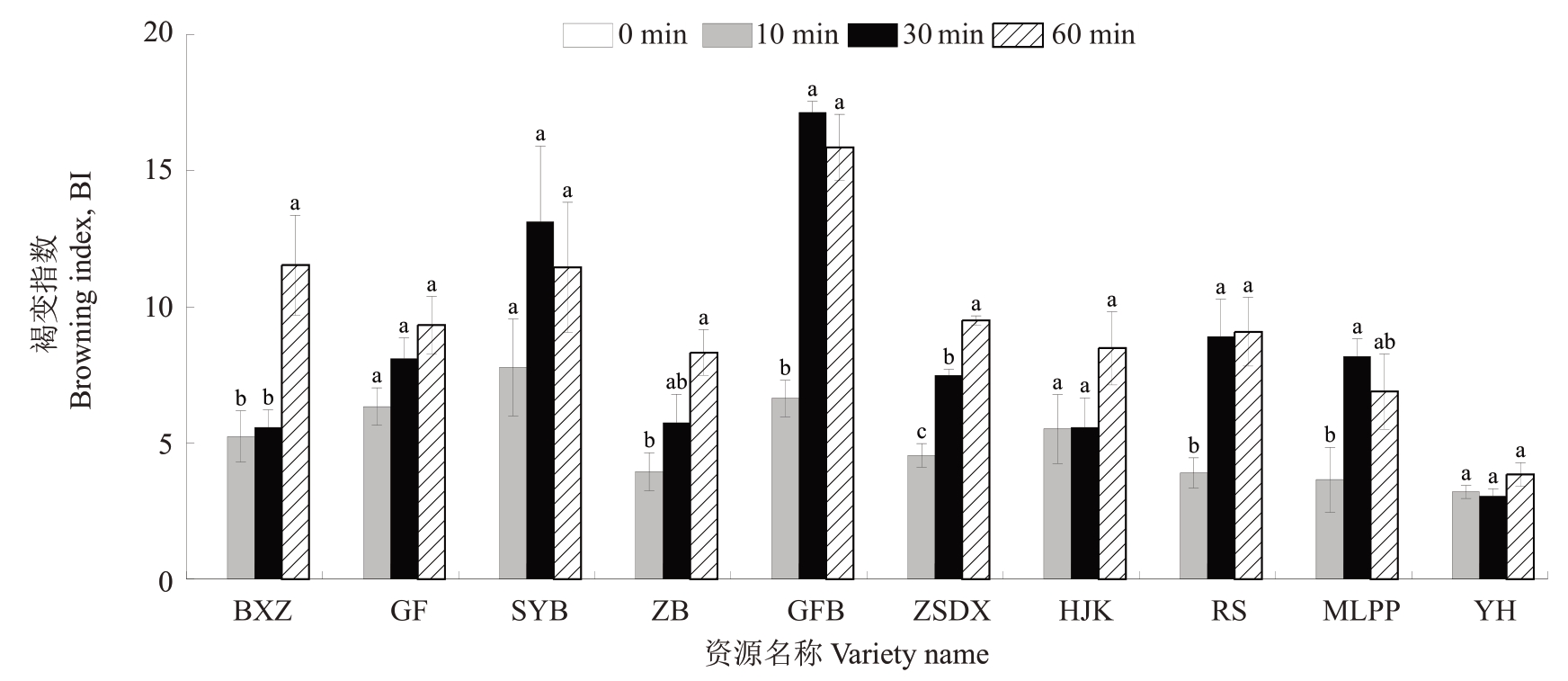
图6 10 份枇杷资源鲜切后不同时间褐变指数(BI)
Fig.6 Browning index(BI)of 10 loquat resources at different times after fresh cutting
2.3 10份资源不同时间褐变表型及褐变面积
按照果肉颜色的表型将10 份枇杷资源分为白肉和红肉两大类,由图7 可知,0~60 min,白肉资源褐变表型较红肉资源更明显,红肉资源表现出更强的抗褐变能力。鲜切0~10 min后,白肉类型的资源出现明显褐变症状,红肉资源无显著变化。30 min时,白肉资源达到了褐变阈值,与60 min 时的褐变表型无显著差异,而红肉资源才开始出现明显褐变。
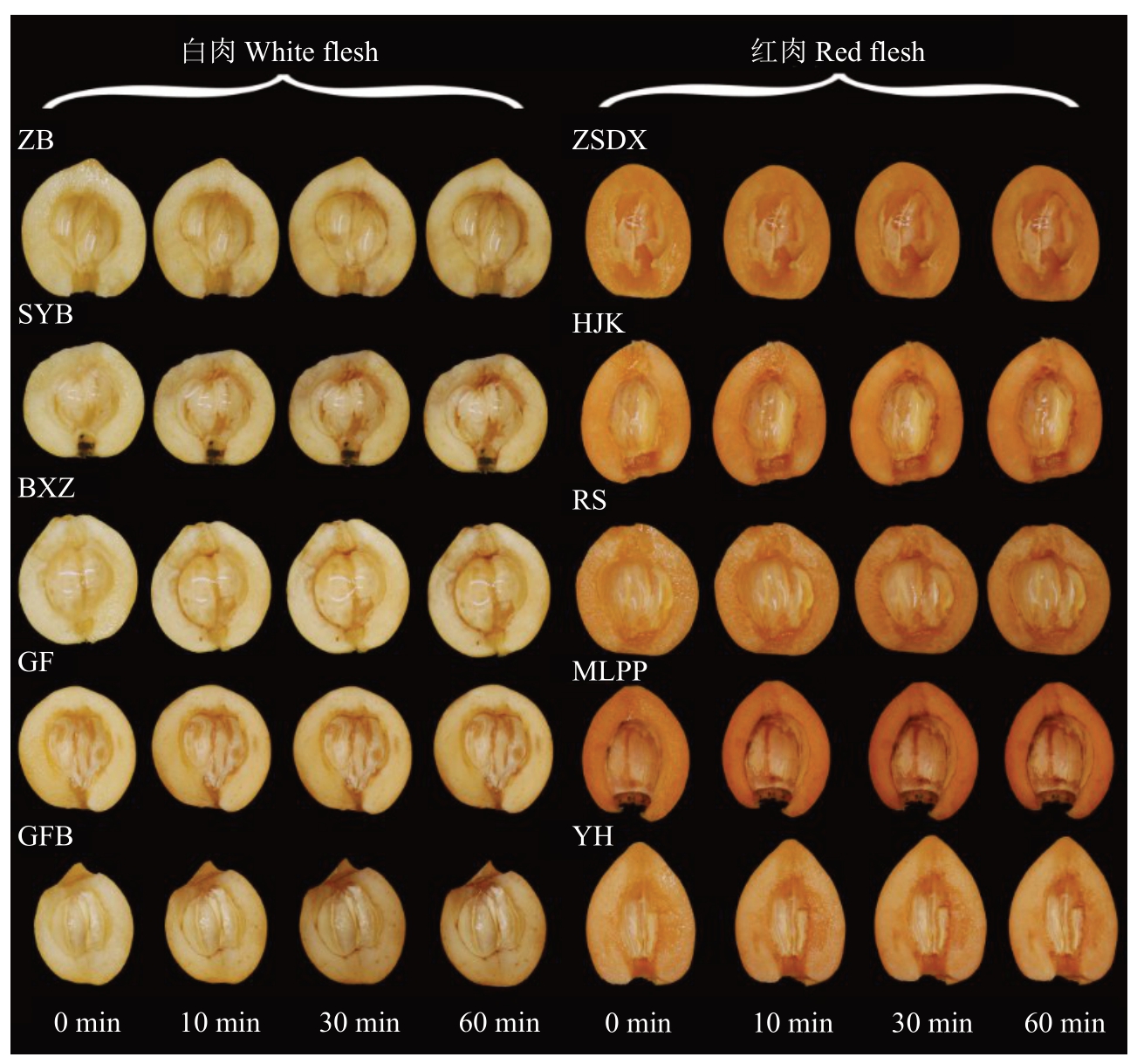
图7 10 份枇杷资源鲜切后不同时间褐变表型
Fig.7 Phenotypic changes in browning at different times after fresh cutting of 10 loquat resources
进一步用欧式距离算法计算10 份资源鲜切后不同时间节点的褐变面积。结果表明,国芬本的褐变进程最快,褐变面积最大,艳红的褐变进程最慢,且60 min时褐变面积最小(图8)。对白肉资源和红肉资源分组进行独立样本T 检验,发现不同时间节点白肉资源的褐变面积占比均显著高于红肉资源(表2),说明分割褐变面积可更精准地区分定位红肉和白肉类型的褐变表型差异。
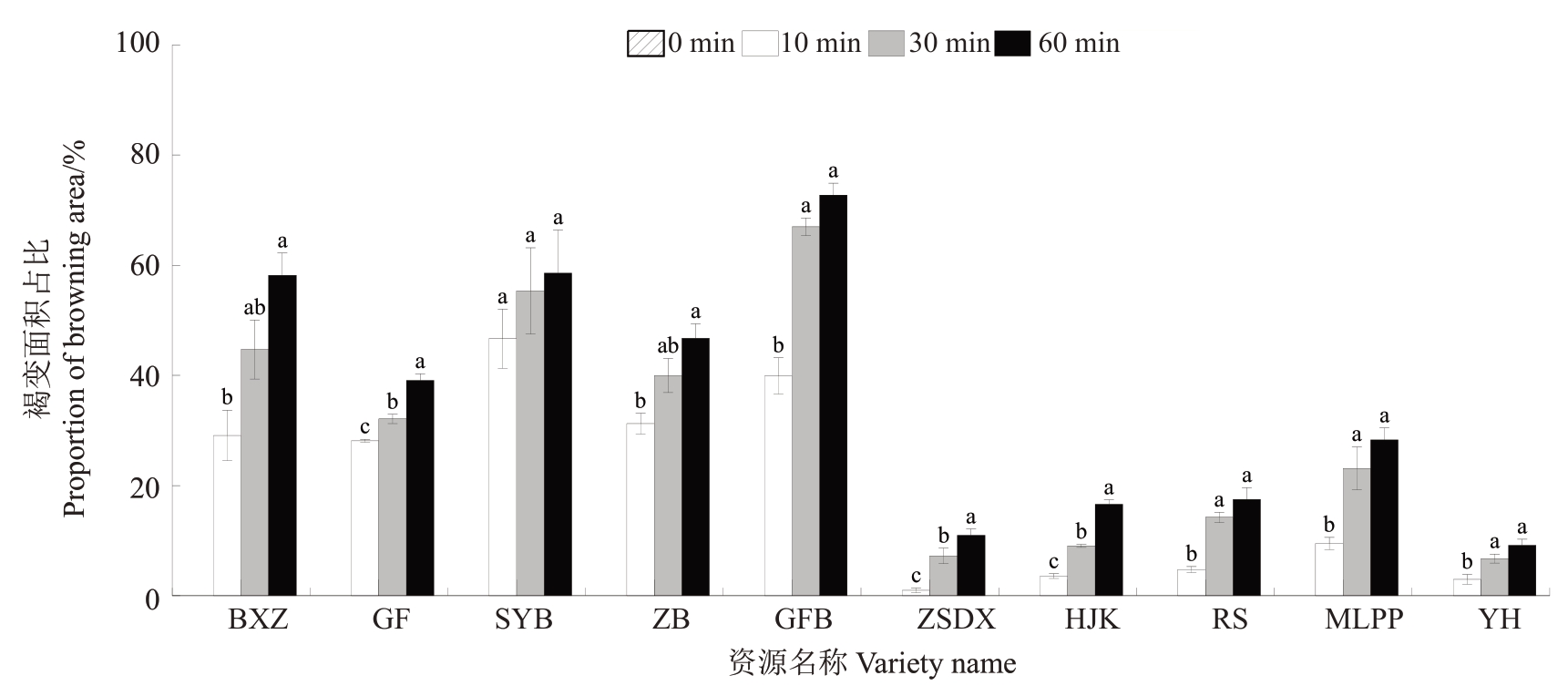
图8 10 份枇杷资源鲜切后不同时间褐变面积
Fig.8 Area of browning at different times after fresh cutting of 10 loquat resources
表2 红肉资源和白肉资源褐变面积差异检验
Table 2 Significance test of browning area difference between red flesh loquats and white flesh loquats
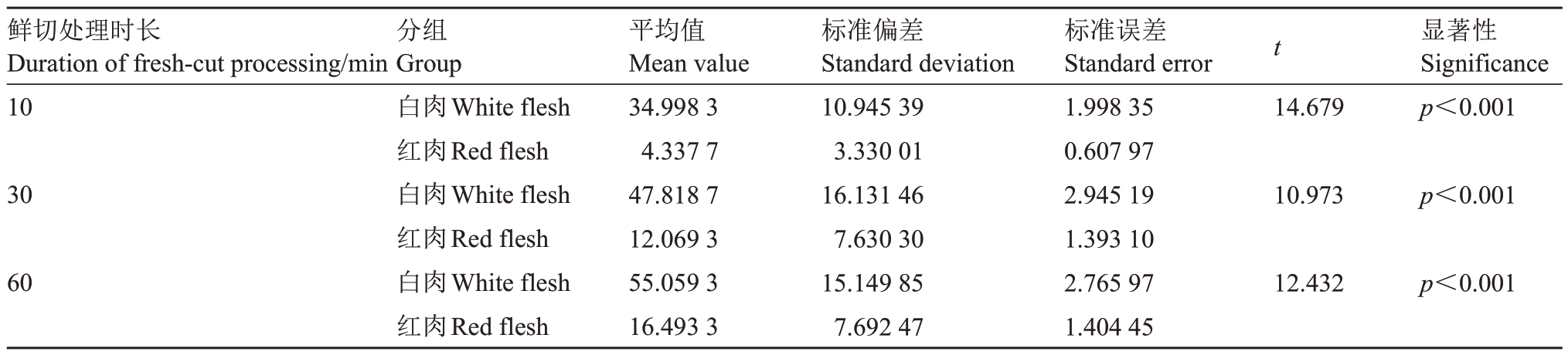
鲜切处理时长Duration of fresh-cut processing/min 10 t 显著性Significance p<0.001平均值Mean value 34.998 3 4.337 7 47.818 7 12.069 3 55.059 3 16.493 3 30标准偏差Standard deviation 10.945 39 3.330 01 16.131 46 7.630 30 15.149 85 7.692 47分组Group白肉White flesh红肉Red flesh白肉White flesh红肉Red flesh白肉White flesh红肉Red flesh标准误差Standard error 1.998 35 0.607 97 2.945 19 1.393 10 2.765 97 1.404 45 14.679 10.973 p<0.001 60 12.432 p<0.001
2.4 褐变过程隶属函数排名及耐褐变能力评价
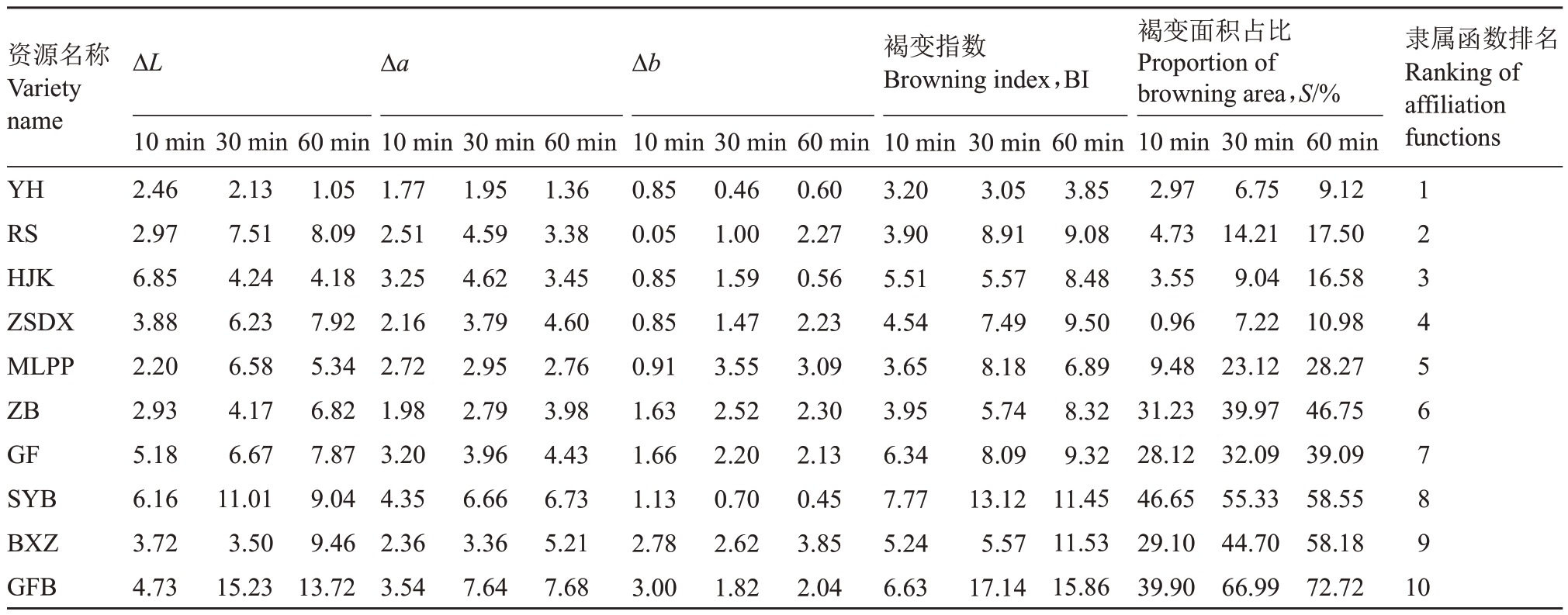
根据褐变过程Lab 值变化、不同时间褐变指数(BI)及褐变面积(S),应用主成分分析和隶属函数分析计算得出10 份资源的褐变隶属函数排名(表3)。根据隶属函数排名得到了最抗褐变的红肉资源艳红和白肉资源中白,而最易褐变的红肉类型为木罗枇杷,白肉类型国芬本最不抗褐变。
表3 10 份资源褐变过程隶属函数排名
Table 3 Ranking of the affiliation functions of the browning process of the 10 resources
注:资源名称见表1。
Note:See Table 1 for variety names.
资源名称Variety name ΔL Δa Δb 隶属函数排名Ranking of affiliation functions YH RS HJK ZSDX MLPP ZB GF SYB BXZ GFB 10 min 2.46 2.97 6.85 3.88 2.20 2.93 5.18 6.16 3.72 4.73 30 min 2.13 7.51 4.24 6.23 6.58 4.17 6.67 11.01 3.50 15.23 60 min 1.05 8.09 4.18 7.92 5.34 6.82 7.87 9.04 9.46 13.72 10 min 1.77 2.51 3.25 2.16 2.72 1.98 3.20 4.35 2.36 3.54 30 min 1.95 4.59 4.62 3.79 2.95 2.79 3.96 6.66 3.36 7.64 60 min 1.36 3.38 3.45 4.60 2.76 3.98 4.43 6.73 5.21 7.68 10 min 0.85 0.05 0.85 0.85 0.91 1.63 1.66 1.13 2.78 3.00 30 min 0.46 1.00 1.59 1.47 3.55 2.52 2.20 0.70 2.62 1.82 60 min 0.60 2.27 0.56 2.23 3.09 2.30 2.13 0.45 3.85 2.04褐变指数Browning index,BI 10 min 3.20 3.90 5.51 4.54 3.65 3.95 6.34 7.77 5.24 6.63 30 min 3.05 8.91 5.57 7.49 8.18 5.74 8.09 13.12 5.57 17.14 60 min 3.85 9.08 8.48 9.50 6.89 8.32 9.32 11.45 11.53 15.86褐变面积占比Proportion of browning area,S/%10 min 2.97 4.73 3.55 0.96 9.48 31.23 28.12 46.65 29.10 39.90 30 min 6.75 14.21 9.04 7.22 23.12 39.97 32.09 55.33 44.70 66.99 60 min 9.12 17.50 16.58 10.98 28.27 46.75 39.09 58.55 58.18 72.72 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
3 讨 论
常用的表色系统包括RGB、Lab、HIS、HSV四种颜色空间,而在果蔬颜色性状表征时更多使用RGB和Lab两种颜色空间[22-23],其中Lab颜色空间是一种基于生理特征的颜色系统,以数字化的方法描述人的视觉感应,不受外源光照的影响[24],在果蔬褐变研究中被广泛使用[25]。在本研究中,枇杷果肉在褐变过程中呈现L 值下降而a、b 值上升的趋势,与马铃薯褐变Lab值变化特征相同[26]。此外,L值、a值和b值能够有效区分红肉和白肉两大类型[27]的果肉,也可用于枇杷种质资源肉色表型的鉴定分析。
果实颜色性状的评价分析常采用色差仪法[28-30],已有大量利用色差仪鉴定果蔬褐变表型的研究报道[17,23,26,31]。色差仪光源稳定,识别结果精确,适用于具体品种资源颜色性状的定性分析[32-33],但色差仪的测量口径较小,单个点的测量时间从1 s 到1.85 s不等[34-35]。笔者在本研究中发现,枇杷果肉褐变部位集中于靠近心皮及切口的部分,存在不同部位褐变程度不同的现象,且当枇杷果肉厚度较薄时,切面与色差仪口径贴合不当易产生偏差。MATLAB 图像识别算法精度高,精确到每个像素[19,36-37],能很好地弥补色差仪法仅测量局部而非整体褐变情况的不足;MATLAB 图像分割算法识别范围广、计算速度快,适用于大批量资源颜色动态变化过程的定量分析。枇杷果实成熟期较短,色差仪法在测定褐变Lab值时耗时较长,很难实现大批量样品的测定,而图像分割法仅需对鲜切后的果肉切面进行实时拍照用于后续Lab值提取,计算速度快,因此适用于大批量枇杷种质资源颜色性状鉴定。色差仪法和图像识别法在枇杷果肉颜色性状识别时适用场景不同。
提取果肉切面的Lab值[38]计算褐变指数能精确到每个像素进而量化果肉褐变情况,但如果样品成熟度、拍摄角度、光源等存在差异易导致计算结果出现偏差[30],因此为了提高计算结果的准确性,在挑选样品时需保证果实成熟度一致,并尽量选择更多样本或进行多次重复试验,拍摄设备也应尽量稳定,在获取原始图像过程中需严格控制一致的拍摄光源、角度及相机参数等[39]。欧式距离计算褐变面积不受光源等外界环境的限制,分割阈值及适宜性取决于观测者的肉眼判断[40],分割面积与肉眼观察到的褐变表型高度一致。但由于果肉褐变是一个缓慢发生的过程,褐变的不同程度呈现出不同的褐变色,在选择分割区域时要兼顾不同褐化程度的区域,阈值的选择至关重要[15]。在红肉类型中,较短时间内褐变色与果肉原始颜色的差异小,导致分割阈值更难把握,需要比白肉类型更长的鉴定间隔时间。在本研究中,图像识别仍受试验条件限制影响效率的提升,今后可进一步优化取样方法及拍摄条件,达到高精度快速鉴定枇杷果肉褐变性状的目的。
4 结 论
基于MATLAB 函数的图像识别算法可对枇杷果肉切面的L、a、b颜色值进行像素级提取并计算褐变指数、分割褐变面积,从不同维度描述果肉的褐变情况,二者结合能最大程度实现对枇杷资源果肉褐变抗性的综合鉴定评价。该方法亦适用于枇杷种质资源颜色性状评价。
[1] 石钰琢,杨松,黄栋,路超,张敏.鲜切果蔬物理保鲜技术研究进展[J].食品科技,2023,48(7):37-42.SHI Yuzhuo,YANG Song,HUANG Dong,LU Chao,ZHANG Min.Advances on physical preservation technology of fresh-cut fruits and vegetables[J].Food Science and Technology,2023,48(7):37-42.
[2] 李彩云,李洁,严守雷,王清章.果蔬酶促褐变机理的研究进展[J].食品科学,2021,42(9):283-292.LI Caiyun,LI Jie,YAN Shoulei,WANG Qingzhang.Progress in research on the mechanism of enzymatic browning in fruits and vegetables[J].Food Science,2021,42(9):283-292.
[3] BHARGAVA A,BANSAL A.Fruits and vegetables quality evaluation using computer vision:A review[J].Journal of King Saud University- Computer and Information Sciences,2021,33(3):243-257.
[4] 王明,张倩.我国基于深度学习的图像识别技术在农作物病虫害识别中的研究进展[J].中国蔬菜,2023(3):22-28.WANG Ming,ZHANG Qian.Research progress of image recognition technology based on depth learning in identification of pest and disease in crops in China[J]. China Vegetables,2023(3):22-28.
[5] 樊泽泽,柳倩,柴洁玮,杨晓峰,李海芳.基于颜色与果径特征的苹果树果实检测与分级[J]. 计算机工程与科学,2020,42(9):1599-1607.FAN Zeze,LIU Qian,CHAI Jiewei,YANG Xiaofeng,LI Haifang.Apple detection and grading based on color and fruit-diameter[J].Computer Engineering&Science,2020,42(9):1599-1607.
[6] LI L L,ZHANG S J,WANG B.Plant disease detection and classification by deep learning:A review[J]. IEEE Access,2021,9:56683-56698.
[7] FERENTINOS K P. Deep learning models for plant disease detection and diagnosis[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture,2018,145:311-318.
[8] ARNAL BARBEDO J G. Plant disease identification from individual lesions and spots using deep learning[J]. Biosystems Engineering,2019,180:96-107.
[9] YIN H,LI B,LIU Y D,ZHANG F,SU C T,OU-YANG A G.Detection of early bruises on loquat using hyperspectral imaging technology coupled with band ratio and improved Otsu method[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2022,283:121775.
[10] IQBAL Z,KHAN M A,SHARIF M,SHAH J H,UR REHMAN M H,JAVED K. An automated detection and classification of citrus plant diseases using image processing techniques:A review[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture,2018,153:12-32.
[11] JIANG P,CHEN Y H,LIU B,HE D J,LIANG C Q. Real-time detection of apple leaf diseases using deep learning approach based on improved convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Access,2019,7:59069-59080.
[12] 谢家兴,陈斌瀚,彭家骏,何培华,景庭威,孙道宗,高鹏,王卫星,郑代德,李君.基于改进ShuffleNet V2 的荔枝叶片病虫害图像识别[J].果树学报,2023,40(5):1024-1035.XIE Jiaxing,CHEN Binhan,PENG Jiajun,HE Peihua,JING Tingwei,SUN Daozong,GAO Peng,WANG Weixing,ZHENG Daide,LI Jun. Image recognition of leaf pests and diseases based on improved ShuffleNet V2 in litchi[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2023,40(5):1024-1035.
[13] WANG J,XIA D,WAN J Z,HOU X Y,SHEN G H,LI S S,CHEN H,CUI Q,ZHOU M,WANG J,REN R,HU W,LI J,ZHANG Z Q.Color grading of green Sichuan pepper(Zanthoxylum armatum DC.) dried fruit based on image processing and BP neural network algorithm[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2024,331:113171.
[14] 刘佳浩,高军伟,张炳星,王建冲.基于机器视觉的水果分级系统[J].食品与机械,2023,39(6):112-118.LIU Jiahao,GAO Junwei,ZHANG Bingxing,WANG Jianchong. Design of fruit grading system based on machine vision[J].Food&Machinery,2023,39(6):112-118.
[15] 高燕萍,何培文,吕尊富,崔鹏,徐锡明,庞林江,陆国权.基于图像分割的甘薯抗褐变种质资源的快速鉴定[J].中国农业大学学报,2023,28(7):46-56.GAO Yanping,HE Peiwen,LÜ Zunfu,CUI Peng,XU Ximing,PANG Linjiang,LU Guoquan. Rapid identification of browning resistant sweetpotato germplasm resources based on image segmentation[J].Journal of China Agricultural University,2023,28(7):46-56.
[16] 蒋际谋,姜帆,陈秀萍,胡文舜,邓朝军,郑少泉.枇杷主要品质评价指标研究[J].园艺学报,2013,40(12):2382-2390.JIANG Jimou,JIANG Fan,CHEN Xiuping,HU Wenshun,DENG Chaojun,ZHENG Shaoquan. Studies on several quality evaluation indices from loquat germplasm resources[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2013,40(12):2382-2390.
[17] 范净,陈启亮,杨晓平,张靖国,田瑞,胡红菊.色差仪在砂梨果肉褐变分析上的应用[J].农业与技术,2017,37(18):38.FAN Jing,CHEN Qiliang,YANG Xiaoping,ZHANG Jingguo,TIAN Rui,HU Hongju.Application of colorimeter to the analysis of flesh browning of sand-pear[J].Agriculture and Technology,2017,37(18):38.
[18] 包新月,俞磊.计算机数字图像处理常用颜色空间及转换[J].电子技术与软件工程,2021(7):122-123.BAO Xinyue,YU Lei. Computer digital image processing common color space and conversion[J]. Electronic Technology &Software Engineering,2021(7):122-123.
[19] 迪娜·加尔肯.基于MATLAB 的图像分割算法研究及实现[J].科学技术创新,2021(26):84-86.Dina·Jiaerken. Research and implementation of image segmentation algorithm based on MATLAB[J]. Scientific and Technological Innovation,2021(26):84-86.
[20] 郑磊. 基于MATLAB 软件的数字图像处理[J]. 信息记录材料,2024,25(1):59-62.ZHENG Lei. Digital image processing based on MATLAB software[J].Information Recording Materials,2024,25(1):59-62.
[21] LEI L,YANG Q L,YANG L,SHEN T,WANG R X,FU C B.Deep learning implementation of image segmentation in agricultural applications:A comprehensive review[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review,2024,57(6):149.
[22] 任凯丽,孔维萍,唐桃霞,程鸿.基于Lab 表色系统的甜瓜果实颜色多样性分析[J].园艺学报,2022,49(9):2017-2022.REN Kaili,KONG Weiping,TANG Taoxia,CHENG Hong. Diversity analysis of melon fruit color based on the Lab system[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2022,49(9):2017-2022.
[23] 路绪强,袁明,何楠,赵胜杰,朱红菊,刘文革.利用色差仪快速检测西瓜番茄红素含量[J].中国瓜菜,2021,34(4):41-45.LU Xuqiang,YUAN Ming,HE Nan,ZHAO Shengjie,ZHU Hongju,LIU Wenge. Rapid determination of watermelon lycopene content by using chromatic meter[J]. China Cucurbits and Vegetables,2021,34(4):41-45.
[24] 吴庆岗,张卫国,李灿林,吴青娥,朱付保. 自然环境下基于Lab 空间的成熟苹果图像分割[J].江苏农业科学,2017,45(9):177-179.WU Qinggang,ZHANG Weiguo,LI Canlin,WU Qing’e,ZHU Fubao.Lab color space-based image segmentation of ripe apples in natural environments[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2017,45(9):177-179.
[25] 苏艳丽,高晓铭,杨健,王龙,王苏珂,张向展,薛华柏.梨果实发育过程中褐变度、酚类物质及相关酶的变化研究[J].园艺学报,2022,49(11):2304-2312.SU Yanli,GAO Xiaoming,YANG Jian,WANG Long,WANG Suke,ZHANG Xiangzhan,XUE Huabai. Dynamic changes of browning degree,phenolics contents and related enzyme activities during pear fruit development[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2022,49(11):2304-2312.
[26] 罗有中,刘全亮,李珍妮,罗磊,姚晏红,王娟,满正行.基于CIELab 及RGB 颜色空间的马铃薯块茎酶促褐变程度评价[J].农业技术与装备,2023(11):102-109.LUO Youzhong,LIU Quanliang,LI Zhenni,LUO Lei,YAO Yanhong,WANG Juan,MAN Zhengxing. Evaluation of enzymatic browning degree of potato tubers based on CIE-Lab and RGB color space[J]. Agricultural Technology & Equipment,2023(11):102-109.
[27] 孙淑霞,谢红江,李靖,涂美艳,陈栋,江国良.枇杷果肉色泽深浅性状的分子标记鉴定[J]. 西南农业学报,2012,25(6):2227-2230.SUN Shuxia,XIE Hongjiang,LI Jing,TU Meiyan,CHEN Dong,JIANG Guoliang. Molecular identification of fragments associated with fruit flesh color in loquat[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2012,25(6):2227-2230.
[28] YAN Y F,PICO J,GERBRANDT E M,DOSSETT M,CASTELLARIN S D.Comprehensive anthocyanin and flavonol profiling and fruit surface color of 20 blueberry genotypes during postharvest storage[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2023,199:112274.
[29] 杨兆甜,李方巍,王震昊,张馨月,曹家蕊,张燕.食品颜色评价及在食品工业中的应用[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(24):417-423.YANG Zhaotian,LI Fangwei,WANG Zhenhao,ZHANG Xinyue,CAO Jiarui,ZHANG Yan. Food color evaluation and application in food industry[J].Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(24):417-423.
[30] 黄娟,李新建.基于色差仪法的库尔勒香梨果实颜色分级标准[J].北方园艺,2018(17):38-44.HUANG Juan,LI Xinjian.The Korla fragrant pear color grading based on colorimeter[J].Northern Horticulture,2018(17):38-44.
[31] 赵萍,王莉,蒲育林,王雅,林樱姬,亓文静,杨明峰.不同品种马铃薯在不同生长期褐变的规律研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2010,31(11):101-104.ZHAO Ping,WANG Li,PU Yulin,WANG Ya,LIN Yingji,QI Wenjing,YANG Mingfeng.Study on the law of different varieties of potato’s browning in different growing period[J].Science and Technology of Food Industry,2010,31(11):101-104.
[32] 郭守鹏,黄昌见,卢绪鹏,杜岩,张文,齐增敏.色差仪在茄子果色评价中的应用[J].中国果菜,2022,42(11):61-65.GUO Shoupeng,HUANG Changjian,LU Xupeng,DU Yan,ZHANG Wen,QI Zengmin.Application of color difference meter in the evaluation of eggplant color[J]. China Fruit &Vegetable,2022,42(11):61-65.
[33] 代祥,梅菊芬,杨亦扬,王玉花.基于色差仪的茶树叶色量化研究[J].南京农业大学学报,2024,47(2):232-241.DAI Xiang,MEI Jufen,YANG Yiyang,WANG Yuhua.A quantitative study of leaf colors of tea plants based on the colorimeter[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University,2024,47(2):232-241.
[34] 温波,颜昌翔. 便携式分光测色仪光学设计[J]. 应用光学,2011,32(1):18-22.WEN Bo,YAN Changxiang. Optical design of portable spectrophotometer for colorimetry[J]. Journal of Applied Optics,2011,32(1):18-22.
[35] 朱纪忠,陈若雷,许士明. 分光测色仪的研制与性能分析[J].光学仪器,2003,25(5):31-34.ZHU Jizhong,CHEN Ruolei,XU Shiming.Researching and analyzing property of spectral color-meter[J].Optical Instruments,2003,25(5):31-34.
[36] 郭宏杰,马睿,王佳,赵威,马德新.基于卷积神经网络的苹果叶部病害图像识别研究[J].中国农机化学报,2024,45(5):239-245.GUO Hongjie,MA Rui,WANG Jia,ZHAO Wei,MA Dexin.Research on apple leaf disease image recognition based on convolutional neural network[J].Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization,2024,45(5):239-245.
[37] KUMAR D,KUKREJA V. Image segmentation,classification,and recognition methods for wheat diseases:Two decades’systematic literature review[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture,2024,221:109005.
[38] 任龙龙,冯涛,翟传龙,宋月鹏.基于MATLAB 图像处理的苹果大小、颜色、圆形度及缺陷度特征融合分级研究[J].数字技术与应用,2021,39(7):90-95.REN Longlong,FENG Tao,ZHAI Chuanlong,SONG Yuepeng.Research on feature fusion grading of apple size,color,roundness and defect based on MATLAB image processing[J]. Digital Technology&Application,2021,39(7):90-95.
[39] XIAO F,WANG H B,LI Y X,CAO Y,LV X M,XU G F. Object detection and recognition techniques based on digital image processing and traditional machine learning for fruit and vegetable harvesting robots:An overview and review[J]. Agronomy,2023,13(3):639.
[40] 李娜,安楠,张立杰,姜海勇,陈广毅,施宇.自然环境下苹果点云多维度特征分割方法研究[J].河北农业大学学报,2024,47(3):105-112.LI Na,AN Nan,ZHANG Lijie,JIANG Haiyong,CHEN Guangyi,SHI Yu. Research on apple point cloud segmentation techniques in natural environments[J].Journal of Hebei Agricultural University,2024,47(3):105-112.