猕猴桃隶属猕猴桃科(Actinidiaceae)猕猴桃属(Actinidia Lindl.),有54个种和21个变种,共约75个分类群,目前栽培种主要为中华猕猴桃(A.chinensis Planch.var. chinensis)和美味猕猴桃(A.chinensis Planch.var.deliciosa)[1]。金怡猕猴桃是湖北省农业科学院果树茶叶研究所进行猕猴桃野生资源考察时,将在湖北省房县采集的野生中华猕猴桃经播种得到的实生后代选育而成[2]。金怡猕猴桃是优质的早熟中华猕猴桃新品种,于2011年获得农业部植物新品种保护授权,其果肉呈金黄色或黄绿色,品质细腻多汁,成熟果实可溶性固形物含量为17.0%~20%,可溶性总糖含量可达12.1%,可滴定酸含量可达1.28%,维生素C含量可达1322 mg·kg-1,品质极佳[2]。
猕猴桃是雌雄异株植物,若雌雄株配比不合理,将导致受精不良,从而使果实种子数量少、果实内源激素不足,最终果实偏小或形成扁果[3]。前人对猕猴桃花粉活力、散粉规律以及花粉保存条件等开展了较多的工作。研究表明,采粉期在花蕾期时花粉活力较高[4],花朵花粉量最大[5]。用恒温箱干燥法制取、离体萌发法测定的猕猴桃花粉活力最高[6-7]。在密闭环境下,温度越低贮藏效果越好,-20 ℃贮藏30 d 花粉活力还保持在较高水平,可以短期贮藏[8]。筛选出花粉量大、花粉活性高的优良雄株,可以提高授粉效率,节约生产成本,并且提高果实品质,在生产上有一定意义。目前已报道的猕猴桃雄株品种并不多,截至2023 年1 月已授权的猕猴桃植物新品种权共114项,其中雄株品种4个(磨山雄1号、磨山雄2 号、磨山雄3 号、磨山雄5 号),占比约3.51%[9]。另外,近期首个软枣猕猴桃雄株新品种金猕枣雄1 号也已授权[10]。新西兰作为猕猴桃主要出口国,选育出了许多猕猴桃优良品种,这些品种也都有相应的适配雄株。如六倍体美味猕猴桃雄株品种马吐阿(Matua)、陶木里(Tomuri)、Chieftain 等为绿肉猕猴桃品种海沃德(Hayward)的授粉品种,Bruce是为黄肉品种Hort16A 的专用授粉品种,现在主推的新一代黄肉品种Gold3(G3)的授粉树多用四倍体中华猕猴桃雄株M91[11-13]。笔者在本研究中以120 株金怡猕猴桃实生后代雄株资源为试验材料,统计其花药数(平均每朵花包含的花药数量)、花粉量(平均每粒花药包含的花粉数量)、花粉萌发率(每个样本平均萌发率)等性状,并进行性状分析、变异分析、离群值分析、分布规律分析和主成分分析,以期解析金怡猕猴桃实生后代雄株株系变异的丰富性,筛选性状优良雄株,为猕猴桃育种提供资源。
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料
材料为120株4年生金怡猕猴桃实生后代,定植于湖北省赤壁市神山兴农科技有限公司半岛猕猴桃基地育种园。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 样品采集方法 对金怡后代群体中的雄株,每天早上10:00 左右采集铃铛花期花蕾10 枚,小心用镊子分别将每个花苞的花药剥下平铺于称量纸上,拍照统计花药数。每朵花中随机选取10个花药(共100个)放入15 mL离心管中,于25 ℃恒温烘箱烘干48 h,用于测量花粉量。将剩余花药混合后收集在铺有称量纸的培养皿中,置于25 ℃恒温烘箱烘干24 h,将花粉收集到10 mL 离心管中保存于-20 ℃冰箱,用于后续花粉萌发试验。
1.2.2 花药数统计 对金怡后代群体中的雄株每株10 枚花朵的花药数进行统计。用镊子小心剥取铃铛花花药分散于称量纸上,拍照后用Adobe Photoshop软件的计数功能进行统计,然后计算花药数的平均值。
1.2.3 单花药花粉量的测定 用血球计数板法对花粉量进行测定。称取5 g 偏磷酸钠粉末定容至100 mL,置于振荡器中振荡2 h以上形成悬浊液,取出后静置0.5 h,再用移液枪吸取5 mL 上层悬浊液至收集有100 个花药的离心管中,用涡旋振荡仪震荡,使花粉粒均匀分散开。用移液枪吸取10 μL 离心管内的液体滴到血球计数板的中间计数区域中心,用盖玻片压平,避免出现气泡。每个样本3次重复,每个重复记5 个中方格。最后在显微镜下选取合适位置拍照计数,按照“记上不记下,记左不记右”的规则计数。5 mL 悬浊液包含的花粉粒数计算公式为:X(/16×1/4000)×5×103 mm3·mL-1=1.25×105×X(X为血球计数板中格包含的平均花粉粒数)。
1.2.4 花粉萌发率的测定 采用离体培养基萌发法检测花粉萌发率,固体培养基的配方为:10%蔗糖+1%琼脂+0.1%硼酸。使用1 mL 的移液枪将培养基点涂在双凹载玻片凹面处,冷却。待培养基凝固后,将花粉从冰箱取出,用毛笔蘸取少许花粉后均匀洒在培养基平面上,将载玻片置于垫有湿滤纸的培养皿中,放入恒温26 ℃培养箱培养3.5~4.0 h,再用显微镜观察花粉萌发情况,随机选择10个20×视野拍照进行萌发率统计。
1.2.5 数据处理及分析 利用Adobe Photoshop 软件计数功能进行统计,用Excel进行数据整理和变异分析,将用Excel 整理后的数据导入IBM SPSS Statistics 26 软件,选择图形功能中的箱图进行离群值分析,选择分析功能中的描述统计进行正态分布分析。在主成分分析之前,参考刘科鹏等[14]的方法采用隶属函数法对数据进行Z-score标准化,然后利用IBM SPSS Statistics 26 进行主成分分析和可视化处理,再将主成分分析的结果使用Excel计算综合评价得分。综合评价得分(Dn)的计算公式为:Dn=Xa×X1+Xb×X2+Xc×X3(Xa、Xb、Xc分别为标准化处理后的3个指标的特征向量值,X1、X2、X3分别为标准化处理后的3个指标的测量值)。
2 结果与分析
2.1 雄花性状分析
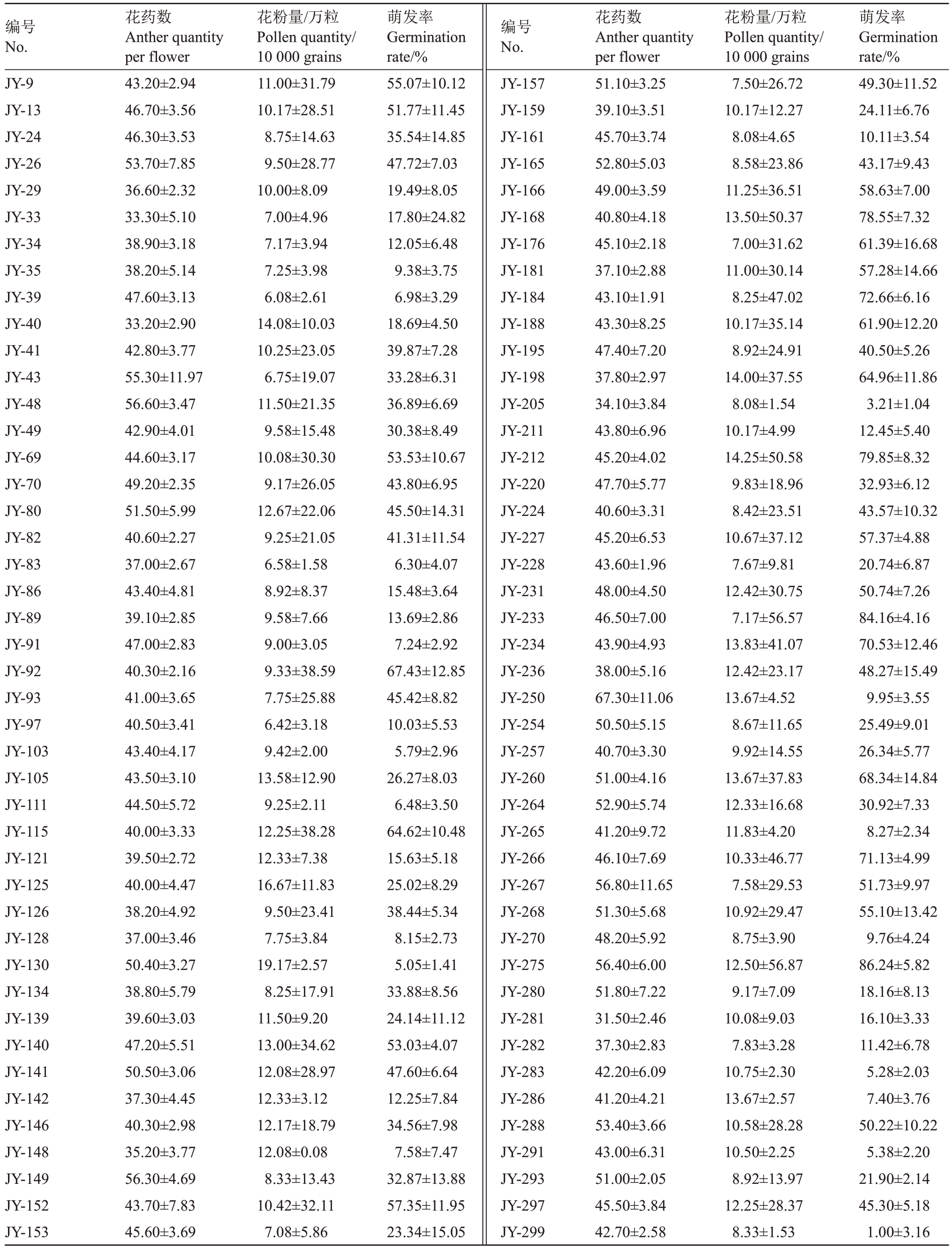
为探究120 株金怡猕猴桃实生后代雄株花性状,对花药数、花粉量、花粉萌发率进行了统计分析(表1)。分析结果表明花药数、花粉量、萌发率平均值分别为45.60 个±8.30 个、10.30 万±2.33 万粒、34.66%±22.24%(表1)。
表1 120 株金怡实生后代雄株花性状统计
Table 1 Flower traits of 120 male seedlings of Jinyi
注:数据为平均值±标准差。
Note:The data are presented as the mean±standard deviation.
编号No.花药数Anther quantity per flower花粉量/万粒Pollen quantity/10 000 grains萌发率Germination rate/%编号No.花药数Anther quantity per flower花粉量/万粒Pollen quantity/10 000 grains萌发率Germination rate/%JY-9 JY-13 JY-24 JY-26 JY-29 JY-33 JY-34 JY-35 JY-39 JY-40 JY-41 JY-43 JY-48 JY-49 JY-69 JY-70 JY-80 JY-82 JY-83 JY-86 JY-89 JY-91 JY-92 JY-93 JY-97 JY-103 JY-105 JY-111 JY-115 JY-121 JY-125 JY-126 JY-128 JY-130 JY-134 JY-139 JY-140 JY-141 JY-142 JY-146 JY-148 JY-149 JY-152 JY-153 43.20±2.94 46.70±3.56 46.30±3.53 53.70±7.85 36.60±2.32 33.30±5.10 38.90±3.18 38.20±5.14 47.60±3.13 33.20±2.90 42.80±3.77 55.30±11.97 56.60±3.47 42.90±4.01 44.60±3.17 49.20±2.35 51.50±5.99 40.60±2.27 37.00±2.67 43.40±4.81 39.10±2.85 47.00±2.83 40.30±2.16 41.00±3.65 40.50±3.41 43.40±4.17 43.50±3.10 44.50±5.72 40.00±3.33 39.50±2.72 40.00±4.47 38.20±4.92 37.00±3.46 50.40±3.27 38.80±5.79 39.60±3.03 47.20±5.51 50.50±3.06 37.30±4.45 40.30±2.98 35.20±3.77 56.30±4.69 43.70±7.83 45.60±3.69 11.00±31.79 10.17±28.51 8.75±14.63 9.50±28.77 10.00±8.09 7.00±4.96 7.17±3.94 7.25±3.98 6.08±2.61 14.08±10.03 10.25±23.05 6.75±19.07 11.50±21.35 9.58±15.48 10.08±30.30 9.17±26.05 12.67±22.06 9.25±21.05 6.58±1.58 8.92±8.37 9.58±7.66 9.00±3.05 9.33±38.59 7.75±25.88 6.42±3.18 9.42±2.00 13.58±12.90 9.25±2.11 12.25±38.28 12.33±7.38 16.67±11.83 9.50±23.41 7.75±3.84 19.17±2.57 8.25±17.91 11.50±9.20 13.00±34.62 12.08±28.97 12.33±3.12 12.17±18.79 12.08±0.08 8.33±13.43 10.42±32.11 7.08±5.86 55.07±10.12 51.77±11.45 35.54±14.85 47.72±7.03 19.49±8.05 17.80±24.82 12.05±6.48 9.38±3.75 6.98±3.29 18.69±4.50 39.87±7.28 33.28±6.31 36.89±6.69 30.38±8.49 53.53±10.67 43.80±6.95 45.50±14.31 41.31±11.54 6.30±4.07 15.48±3.64 13.69±2.86 7.24±2.92 67.43±12.85 45.42±8.82 10.03±5.53 5.79±2.96 26.27±8.03 6.48±3.50 64.62±10.48 15.63±5.18 25.02±8.29 38.44±5.34 8.15±2.73 5.05±1.41 33.88±8.56 24.14±11.12 53.03±4.07 47.60±6.64 12.25±7.84 34.56±7.98 7.58±7.47 32.87±13.88 57.35±11.95 23.34±15.05 JY-157 JY-159 JY-161 JY-165 JY-166 JY-168 JY-176 JY-181 JY-184 JY-188 JY-195 JY-198 JY-205 JY-211 JY-212 JY-220 JY-224 JY-227 JY-228 JY-231 JY-233 JY-234 JY-236 JY-250 JY-254 JY-257 JY-260 JY-264 JY-265 JY-266 JY-267 JY-268 JY-270 JY-275 JY-280 JY-281 JY-282 JY-283 JY-286 JY-288 JY-291 JY-293 JY-297 JY-299 51.10±3.25 39.10±3.51 45.70±3.74 52.80±5.03 49.00±3.59 40.80±4.18 45.10±2.18 37.10±2.88 43.10±1.91 43.30±8.25 47.40±7.20 37.80±2.97 34.10±3.84 43.80±6.96 45.20±4.02 47.70±5.77 40.60±3.31 45.20±6.53 43.60±1.96 48.00±4.50 46.50±7.00 43.90±4.93 38.00±5.16 67.30±11.06 50.50±5.15 40.70±3.30 51.00±4.16 52.90±5.74 41.20±9.72 46.10±7.69 56.80±11.65 51.30±5.68 48.20±5.92 56.40±6.00 51.80±7.22 31.50±2.46 37.30±2.83 42.20±6.09 41.20±4.21 53.40±3.66 43.00±6.31 51.00±2.05 45.50±3.84 42.70±2.58 7.50±26.72 10.17±12.27 8.08±4.65 8.58±23.86 11.25±36.51 13.50±50.37 7.00±31.62 11.00±30.14 8.25±47.02 10.17±35.14 8.92±24.91 14.00±37.55 8.08±1.54 10.17±4.99 14.25±50.58 9.83±18.96 8.42±23.51 10.67±37.12 7.67±9.81 12.42±30.75 7.17±56.57 13.83±41.07 12.42±23.17 13.67±4.52 8.67±11.65 9.92±14.55 13.67±37.83 12.33±16.68 11.83±4.20 10.33±46.77 7.58±29.53 10.92±29.47 8.75±3.90 12.50±56.87 9.17±7.09 10.08±9.03 7.83±3.28 10.75±2.30 13.67±2.57 10.58±28.28 10.50±2.25 8.92±13.97 12.25±28.37 8.33±1.53 49.30±11.52 24.11±6.76 10.11±3.54 43.17±9.43 58.63±7.00 78.55±7.32 61.39±16.68 57.28±14.66 72.66±6.16 61.90±12.20 40.50±5.26 64.96±11.86 3.21±1.04 12.45±5.40 79.85±8.32 32.93±6.12 43.57±10.32 57.37±4.88 20.74±6.87 50.74±7.26 84.16±4.16 70.53±12.46 48.27±15.49 9.95±3.55 25.49±9.01 26.34±5.77 68.34±14.84 30.92±7.33 8.27±2.34 71.13±4.99 51.73±9.97 55.10±13.42 9.76±4.24 86.24±5.82 18.16±8.13 16.10±3.33 11.42±6.78 5.28±2.03 7.40±3.76 50.22±10.22 5.38±2.20 21.90±2.14 45.30±5.18 1.00±3.16
表1 (续) Table 1 (Continued)
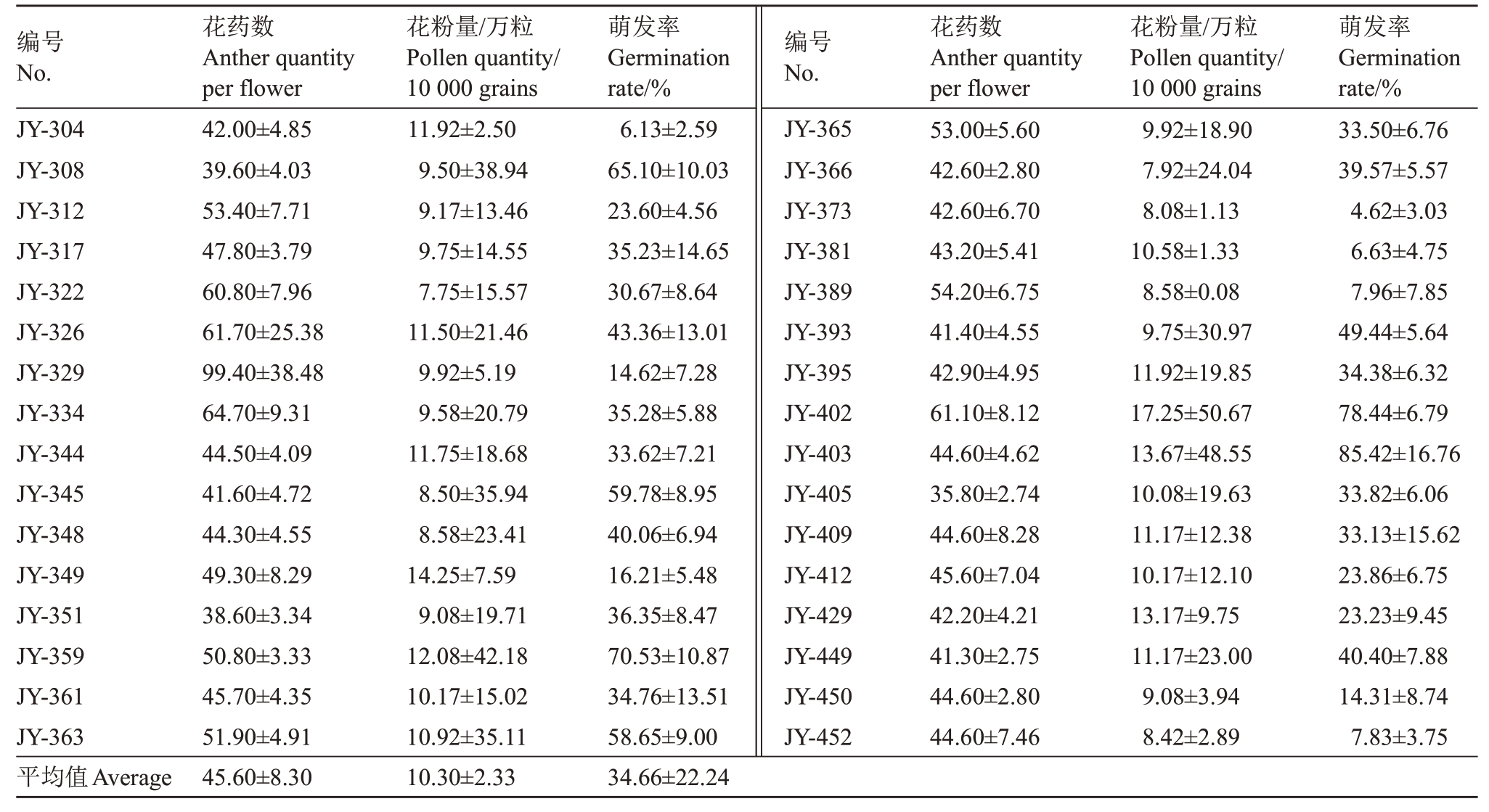
编号No.花药数Anther quantity per flower花粉量/万粒Pollen quantity/10 000 grains萌发率Germination rate/%编号No.花药数Anther quantity per flower花粉量/万粒Pollen quantity/10 000 grains萌发率Germination rate/%JY-304 JY-308 JY-312 JY-317 JY-322 JY-326 JY-329 JY-334 JY-344 JY-345 JY-348 JY-349 JY-351 JY-359 JY-361 JY-363 42.00±4.85 39.60±4.03 53.40±7.71 47.80±3.79 60.80±7.96 61.70±25.38 99.40±38.48 64.70±9.31 44.50±4.09 41.60±4.72 44.30±4.55 49.30±8.29 38.60±3.34 50.80±3.33 45.70±4.35 51.90±4.91 11.92±2.50 9.50±38.94 9.17±13.46 9.75±14.55 7.75±15.57 11.50±21.46 9.92±5.19 9.58±20.79 11.75±18.68 8.50±35.94 8.58±23.41 14.25±7.59 9.08±19.71 12.08±42.18 10.17±15.02 10.92±35.11 6.13±2.59 65.10±10.03 23.60±4.56 35.23±14.65 30.67±8.64 43.36±13.01 14.62±7.28 35.28±5.88 33.62±7.21 59.78±8.95 40.06±6.94 16.21±5.48 36.35±8.47 70.53±10.87 34.76±13.51 58.65±9.00 JY-365 JY-366 JY-373 JY-381 JY-389 JY-393 JY-395 JY-402 JY-403 JY-405 JY-409 JY-412 JY-429 JY-449 JY-450 JY-452 53.00±5.60 42.60±2.80 42.60±6.70 43.20±5.41 54.20±6.75 41.40±4.55 42.90±4.95 61.10±8.12 44.60±4.62 35.80±2.74 44.60±8.28 45.60±7.04 42.20±4.21 41.30±2.75 44.60±2.80 44.60±7.46 9.92±18.90 7.92±24.04 8.08±1.13 10.58±1.33 8.58±0.08 9.75±30.97 11.92±19.85 17.25±50.67 13.67±48.55 10.08±19.63 11.17±12.38 10.17±12.10 13.17±9.75 11.17±23.00 9.08±3.94 8.42±2.89 33.50±6.76 39.57±5.57 4.62±3.03 6.63±4.75 7.96±7.85 49.44±5.64 34.38±6.32 78.44±6.79 85.42±16.76 33.82±6.06 33.13±15.62 23.86±6.75 23.23±9.45 40.40±7.88 14.31±8.74 7.83±3.75平均值Average 45.60±8.30 10.30±2.33 34.66±22.24
2.2 雄花性状变异分析
2.2.1 雄花性状变异分析 如表2所示,花药数、花粉量、萌发率中位数分别为44.10、10.04、33.72,众数分别为44.60、10.17、70.53,分布区间分别为31.50~99.40、6.08~19.17、1.00~86.24。3个指标变异系数都在18%以上,花粉萌发率变异程度最大,高达64.17%(表2、图1),表明样本的花粉萌发率变异最丰富,花粉量和花药数变异较丰富。从极差值看,3个雄花性状的最大值均为最小值的数倍,其中萌发率的倍数最大,为86.24 倍,其次是花药数,为3.16倍,最小是花粉量,为3.15 倍(表2)。综上,金怡猕猴桃雄株3 个雄花性状均存在广泛变异,花粉萌发率变异最大。
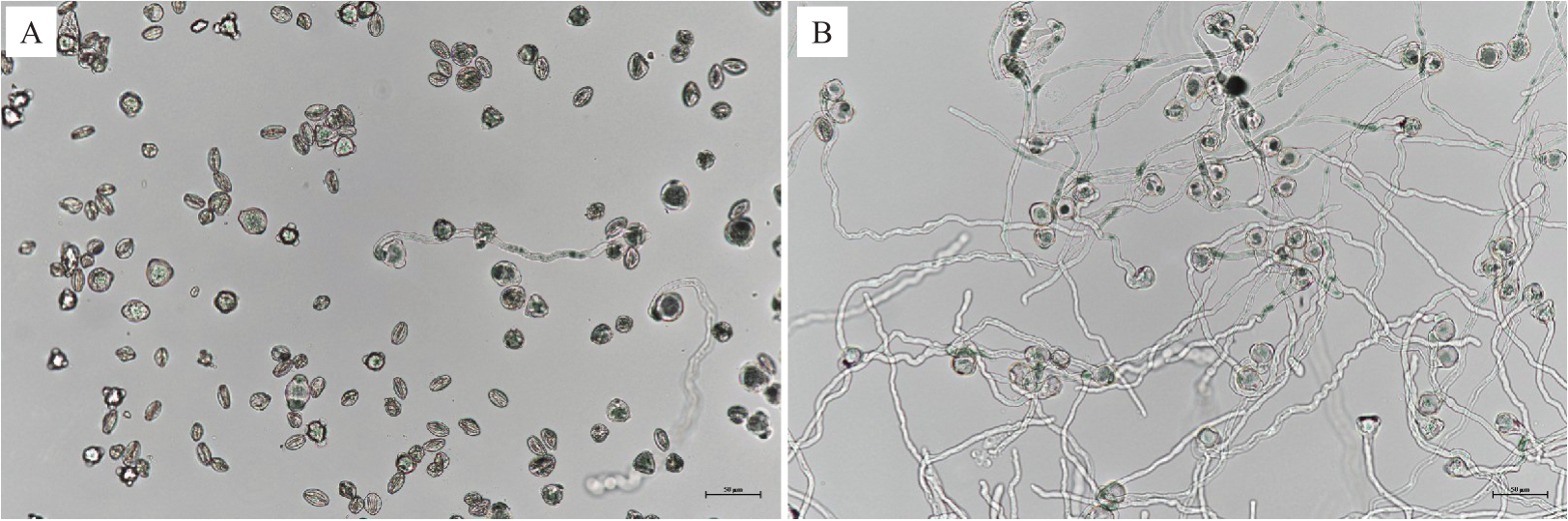
图1 不同单株花粉萌发情况对比
Fig.1 Pollen germination of different male seedlings
A.低萌发率雄株花粉萌发情况;B.高萌发率雄株花粉萌发情况。
A.Pollen germination of male seeding with low germination rate;B.Pollen germination of male seeding with high germination rate.
表2 120 株金怡实生后代雄株花性状分析
Table 2 Analysis of flower traits of 120 male seedlings of Jinyi
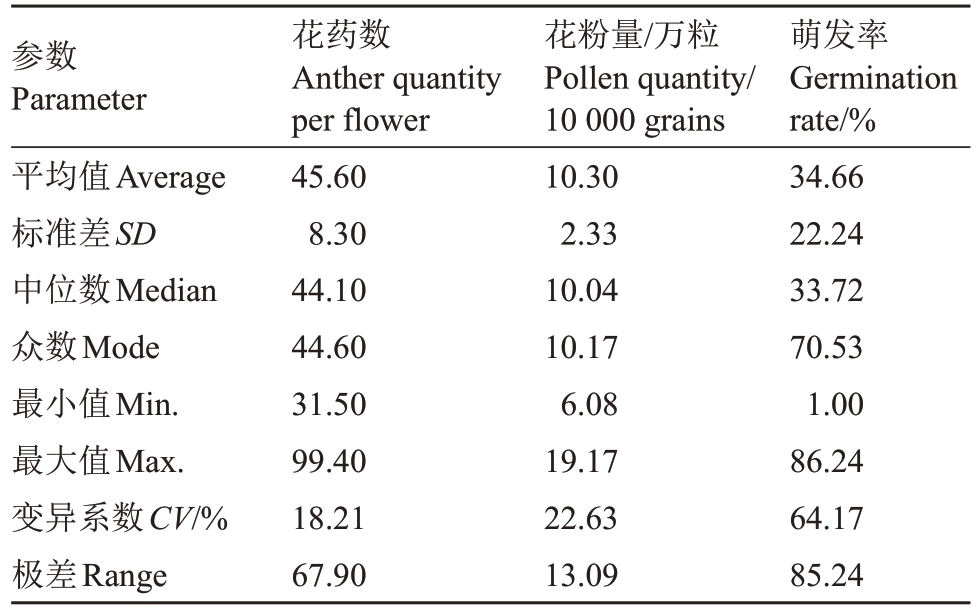
参数Parameter平均值Average标准差SD中位数Median众数Mode最小值Min.最大值Max.变异系数CV/%极差Range花药数Anther quantity per flower 45.60 8.30 44.10 44.60 31.50 99.40 18.21 67.90花粉量/万粒Pollen quantity/10 000 grains 10.30 2.33 10.04 10.17 6.08 19.17 22.63 13.09萌发率Germination rate/%34.66 22.24 33.72 70.53 1.00 86.24 64.17 85.24
2.2.2 离群值分析 为了探究120株金怡猕猴桃实生后代雄株花性状分离情况,进行了离群值筛选。结果表明,在平均花药数上,JY-334、JY-250 为温和高离群值,JY-329为极端高离群值;在花粉量上,JY-402、JY-130 为温和高离群值,萌发率无离群值(图2)。综上,在120 株金怡猕猴桃实生后代雄株雄花性状分析中,JY-334、JY-250、JY-402、JY-130、JY-329这5个样本均为高离群值。
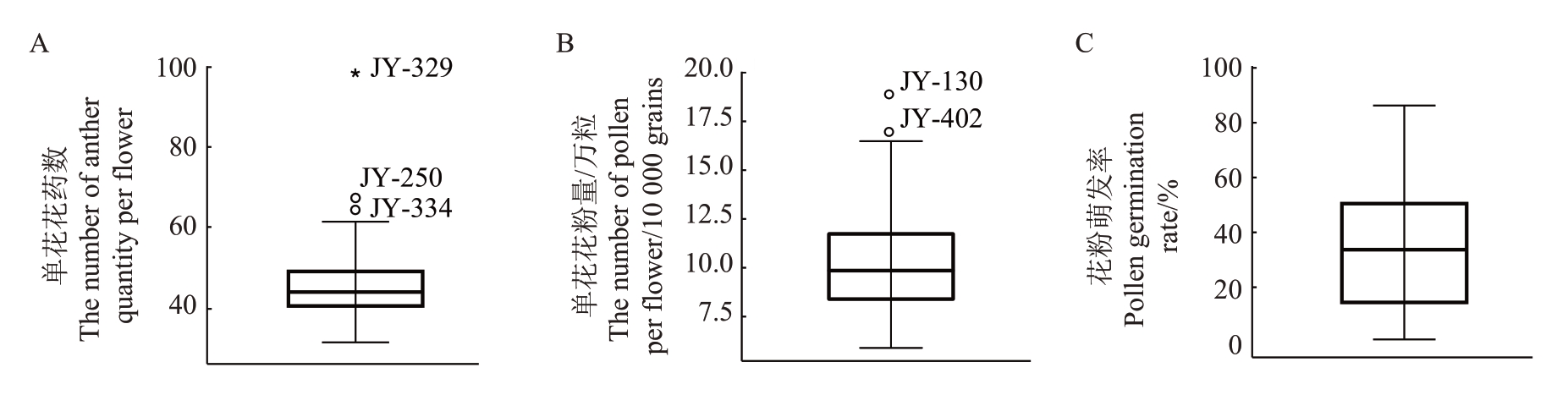
图2 120 株金怡实生后代雄株花性状离群值分析
Fig.2 Outlier value analysis of flower traits of 120 male seedlings of Jinyi
2.2.3 分布规律分析 为了探究数据的分布特点,对数据进行正态分布分析(去除离群值)。分析发现花药数中位数为43.80 粒,主要分布在36.00~54.00粒,占所有样本的82.50%;花粉量中位数为9.98 万粒,主要分布在7.00 万~13.00 万粒,占所有样本的80.83%;萌发率中位数为33.72%,主要分布在10.00%~60.00%,占所有样本的65.83%(表3,图3)。3 个雄花性状指标正态曲线偏度值Sk分别为0.514、0.406、0.417,峰度值Su分别为0.085、-0.280、-0.740(表3)。由频率分布图可看出,萌发率、花粉量和花药数在株系中的分布是连续的,在分布区间两边植株数量少,中间植株数量多,符合正态分布特点(图3)。
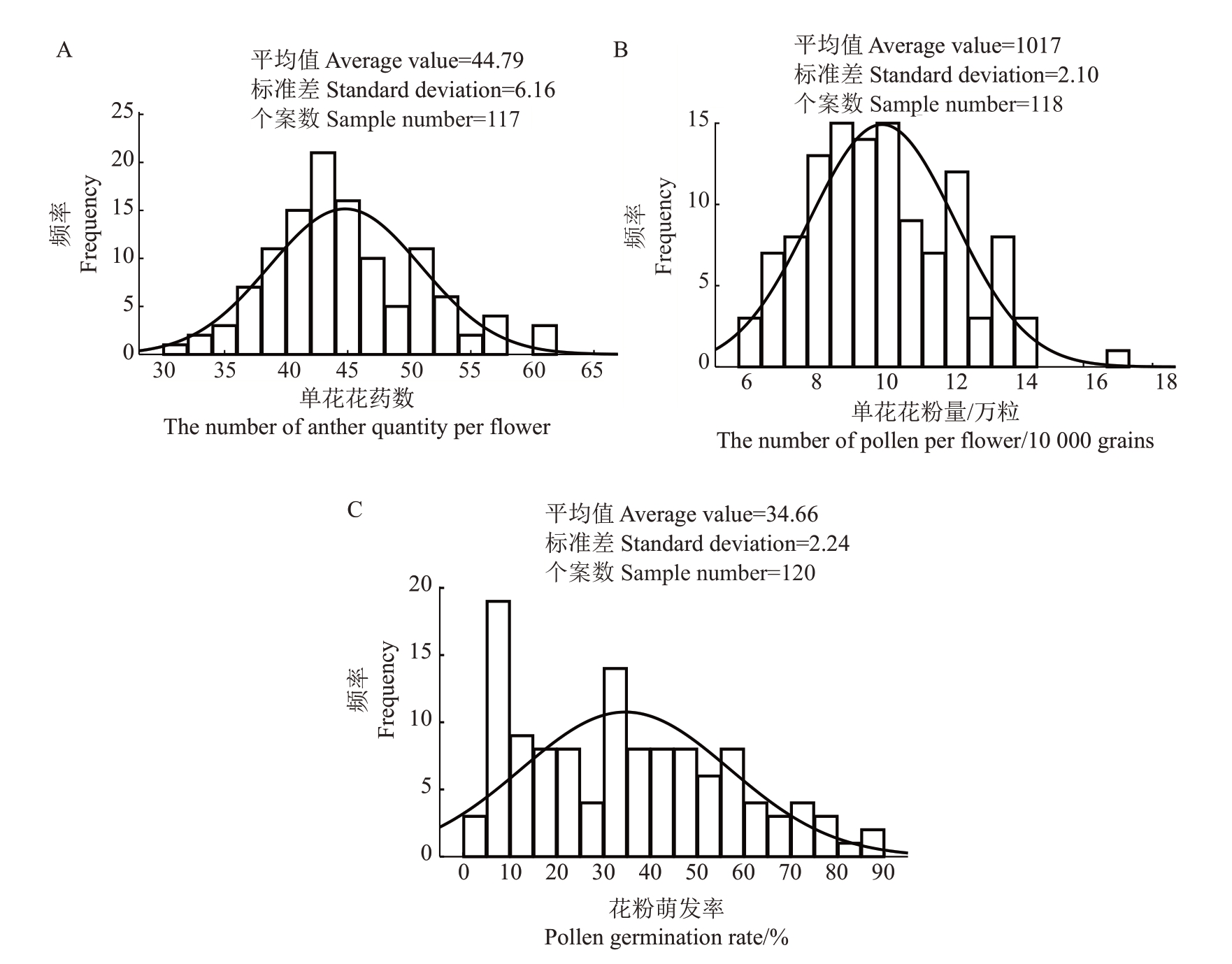
图3 120 株金怡实生后代雄株花性状频率分布
Fig.3 Frequency distribution of male flower traits in 120 male seedlings of Jinyi
表3 120 株金怡实生后代雄株花性状正态曲线偏度与峰度值
Table 3 The skewness and kurtosis values of the normal curve for male flower traits of 120 male seedlings of Jinyi
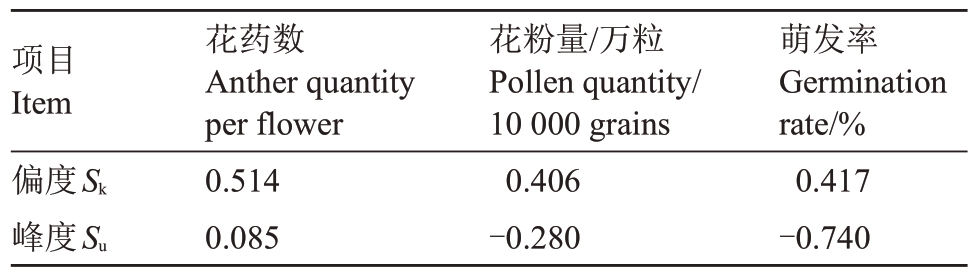
项目Item偏度Sk峰度Su花药数Anther quantity per flower 0.514 0.085花粉量/万粒Pollen quantity/10 000 grains 0.406-0.280萌发率Germination rate/%0.417-0.740
2.2.4 主成分分析 为了探究120个金怡实生后代雄株株系雄花性状主要贡献成分,进行主成分分析。萌发率、花粉量和花药数在3个主成分中的特征向量值、特征值、贡献率以及累计贡献率如表4。第一主成分的特征值1.30,贡献率为43.16%,萌发率和花粉量的特征向量值较高,分别为0.76和0.71。表明雄花性状主要由萌发率和花粉量决定(表4)。
表4 主成分分析
Table 4 Principal component analysis
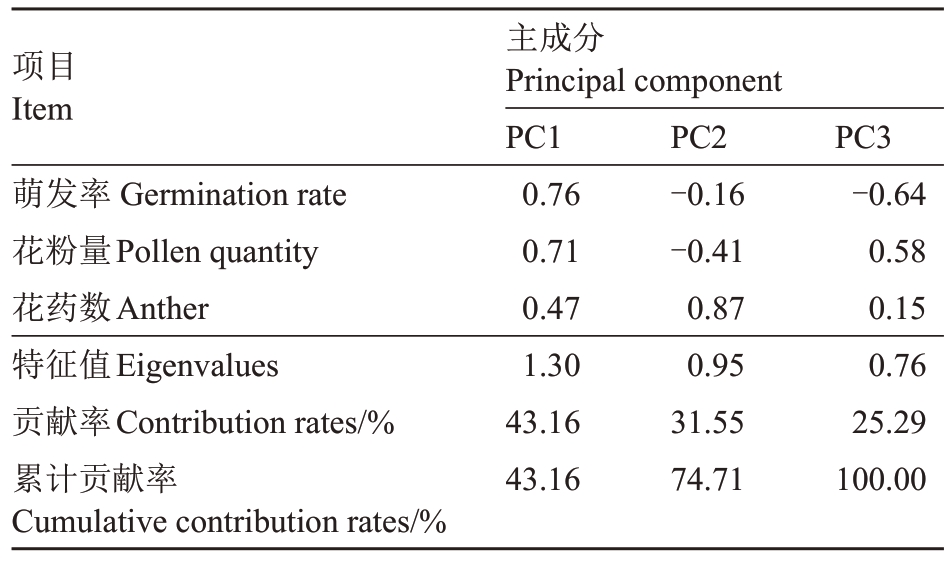
项目Item萌发率Germination rate花粉量Pollen quantity花药数Anther特征值Eigenvalues贡献率Contribution rates/%累计贡献率Cumulative contribution rates/%主成分Principal component PC1 0.76 0.71 0.47 1.30 43.16 43.16 PC2-0.16-0.41 0.87 0.95 31.55 74.71 PC3-0.64 0.58 0.15 0.76 25.29 100.00
在先前的主成分分析中,提取1 个主成分,3 个性状特征向量值分别为0.76、0.71、0.47,标准化处理后为0.67、0.62、0.41,则第1个主成分综合评价得分由标准化后的特征向量和各雄株测量指标原始数值经过标准化后的数值计算得出。综合评价得分(Dn)的计算公式为:Dn=0.67 X1+0.62 X2+0.41 X3(X1、X2、X3分别为3个指标原始测量值标准化后的数值),第1个主成分综合评价得分前5个样本编号分别为JY-402、JY-275、JY-212、JY-403、JY-260(表5)。综上表明JY-402、JY-275、JY-212、JY-403、JY-260花性状综合表现最好。
表5 金怡实生后代优异雄株综合评价得分
Table 5 Comprehensive evaluation score of excellent male plant lines of Jinyi seedlings
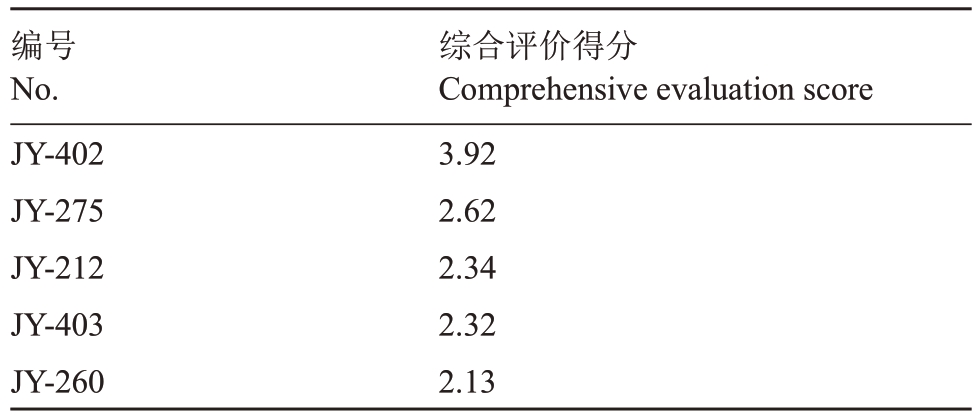
编号No.JY-402 JY-275 JY-212 JY-403 JY-260综合评价得分Comprehensive evaluation score 3.92 2.62 2.34 2.32 2.13
3 讨 论
本研究统计了金怡实生后代雄花花粉萌发率、花粉量、花药数和分布频率,并进行了特异值分析、相关性分析和主成分分析,探究金怡猕猴桃实生后代雄株株系花性状变异情况。在金怡实生后代雄株株系中花粉萌发率变异最大,花粉量、花药数变异相对较小,三者变异系数分别为64.17%、22.63%、18.21%;极差分别为85.24、13.09、67.9;最大值分别为86.24%、19.17 万粒、99.4 粒;最小值分别为1.00%、6.04 万粒、31.50 粒,表明金怡猕猴桃实生后代雄株有明显的性状分化。王斯妤等[15]对不同猕猴桃花粉量和萌发率进行差异分析,发现中华猕猴桃花粉量和萌发率变异较大。本研究结果与之一致。猕猴桃存在明显的花粉直感效应,不同花粉授粉后,后代果实性状差异明显[16-17],在生产上,选择树体健壮、花粉萌发率高、单花药花粉量多、单花花药数多的授粉雄株,有助于当代果实的品质性状改善[18-19]。金怡猕猴桃实生后代雄株花性状表现均较好,萌发率、花粉量、花药数的均值分别为34.66%、10.30 万粒、45.6粒;中位数分别为33.72%、10.04万粒、44.10粒。前人测定了不同品种猕猴桃平均单花药花粉量,如贵长猕猴桃雄株约1.52万粒[5]、毛花猕猴桃约0.70 万粒[20],以及其他测试的中华猕猴桃约0.14 万粒[15],本研究中,金怡猕猴桃单花药平均花粉量10.30 万粒,远远高于其他猕猴桃品种。有研究表明,花粉量与果实产量之间存在显著的相关性[21],因此金怡适合作为猕猴桃授粉雄株。前人在中华猕猴桃花粉萌发率的研究中发现,中华猕猴桃萌发率超过80%[15,22]。在实际生产过程中,作为授粉品种,花粉萌发率一般不低于30%[23],本研究金怡猕猴桃雄株萌发率平均值和中位数均超过30%,且变异丰富,有作为授粉品种的潜能。
经正态检验分析发现,萌发率、花粉量和花药数的数据分布两边少中间多、分布连续、符合正态分布特点。离群值分析发现,3 个性状极端变异材料数量大小为花药数>花粉量>萌发率,其中萌发率无极端变异情况,JY-402、JY-130、JY-329、JY-334、JY-250这5个样本均为高离群值,JY-329花药数为极高离群值。研究发现授粉是否充分决定了果实种子数量多少,而种子数量又与果实大小呈正相关[24],授粉充分也可提高坐果率,降低果实畸形率[25],而授粉效果又与花粉活性息息相关,有活性的花粉数量少,坐果率就低[26]。本试验主成分分析发现,第一主成分中萌发率特征向量值最大,贡献率为43.16%,表明萌发率在雄株评价中权重较大。单花中可萌发花粉量越高,坐果率和果实品质都可以大大提高。JY-402、JY-275、JY-212、JY-403、JY-260这5个雄株为主成分分析后综合评价得分前五的优系,可作为筛选金怡优良授粉雄株候选对象,其中JY-402综合性状最优,可重点关注。后续将对其花粉亲和力、授粉后坐果率、果实品质等方面进行研究,进而筛选出综合性状优良、可用于生产的雄株品种。
4 结 论
金怡猕猴桃雄株雄花性状变异丰富。JY-402、JY-275、JY-212、JY-403、JY-260可以作为进一步深入研究和筛选金怡优良授粉雄株的候选资源,JY-402综合性状最优,可重点关注。本试验为有效利用优良雄株资源提供了理论指导。
[1] 黄宏文.猕猴桃驯化改良百年启示及天然居群遗传渐渗的基因发掘[J].植物学报,2009,44(2):127-142.HUANG Hongwen.History of 100 years of domestication and improvement of kiwifruit and gene discovery from genetic introgressed populations in the wild[J].Chinese Bulletin of Botany,2009,44(2):127-142.
[2] 陈庆红,顾霞,张蕾,秦仲麒,盛敏.早熟猕猴桃新品种‘金怡’[J].果农之友,2013(2):7.CHEN Qinghong,GU Xia,ZHANG Lei,QIN Zhongqi,SHENG Min.A new early ripening kiwifruit variety Jinyi[J].Fruit Growers’Friend,2013(2):7.
[3] 张相文,赵菊琴,屈学农.海沃德猕猴桃果实变扁变小的原因及对策[J].山西果树,2007(3):30-31.ZHANG Xiangwen,ZHAO Juqin,QU Xuenong.Reasons and countermeasures of flattening and smallening of kiwifruit fruit in Hayward[J].Shanxi Fruits,2007(3):30-31.
[4] 陈永安,陈鑫,刘艳飞.采粉期及贮藏条件对猕猴桃花粉生活力的影响[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2012,40(8):157-160.CHEN Yongan,CHEN Xin,LIU Yanfei.Effects of different collecting pollen periods and storage conditions on pollen viability of kiwifruit[J].Journal of Northwest A& F University (Natural Science Edition),2012,40(8):157-160.
[5] 贺兴江,任晓晓,周文才,万炜,韦小平,王胤晨.贵长猕猴桃散粉规律及花粉活力研究[J].特种经济动植物,2021,24(3):10-12.HE Xingjiang,REN Xiaoxiao,ZHOU Wencai,WAN Wei,WEI Xiaoping,WANG Yinchen.Study on the law of dispersed powder and pollen vigor of kiwifruit[J].Special Economic Animals and Plants,2021,24(3):10-12.
[6] 杨红,余和明,李小艳,冯莹莹.猕猴桃花粉生活力测定方法及花药处理方法研究[J].北方园艺,2015(8):36-39.YANG Hong,YU Heming,LI Xiaoyan,FENG Yingying.Study on the method of measuring pollen viability and pretreatment of pollen[J].Northern Horticulture,2015(8):36-39.
[7] 姚春潮,龙周侠,刘旭峰,王西芳.不同干燥及贮藏方法对猕猴桃花粉活力的影响[J].北方园艺,2010(20):37-39.YAO Chunchao,LONG Zhouxia,LIU Xufeng,WANG Xifang.Effects of different dryness and storage methods on pollen viability in Actinidia deliciosa[J].Northern Horticulture,2010(20):37-39.
[8] 陈厚锡,杨技超,王胜艳,潘丽珊,罗充,李苇洁.影响猕猴桃花粉活力的因素探讨[J].中国果树,2021(9):59-62.CHEN Houxi,YANG Jichao,WANG Shengyan,PAN Lishan,LUO Chong,LI Weijie.Discussion on the factors of affecting the activity of kiwifruit pollen[J].China Fruits,2021(9):59-62.
[9] 高磊,张蕾,罗轩,白福玺,汪志,叶丽霞,陈庆红.猕猴桃雄株选育与利用研究进展[J].中国果树,2023(12):8-12.GAO Lei,ZHANG Lei,LUO Xuan,BAI Fuxi,WANG Zhi,YE Lixia,CHEN Qinghong.Research progress on breeding and utilization of male kiwifruit[J].China Fruits,2023(12):8-12.
[10] 罗轩,陈庆红,张蕾,高磊,白福玺,汪志,叶丽霞,彭珏.软枣猕猴桃雄性新品种‘金猕枣雄1 号’[J].园艺学报,2023,50(增刊2):19-20.LUO Xuan,CHEN Qinghong,ZHANG Lei,GAO Lei,BAI Fuxi,WANG Zhi,YE Lixia,PENG Jue.A new pollenizer cultivar of Actinidia arguta‘Jinmizao Xiong 1’[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2023,50(Suppl.2):19-20.
[11] SEAL A G,DUNN J K,JIA Y L.Pollen parent effects on fruit attributes of diploid Actinidia chinensis‘Hort16A’kiwifruit[J].New Zealand Journal of Crop and Horticultural Science,Taylor&Francis,2013,41(4):219-229.
[12] RIBEIRO H,MARIZ-PONTE N,PEREIRA S,GUEDES A,ABREU I,MOURA L,SANTOS C.Can photoselective nets’influence pollen traits?A case study in‘Matua’and‘Tomuri’kiwifruit cultivars[J].Plants,2024,13(12):1691.
[13] TWIDLE A M,BARKER D,SEAL A G,FEDRIZZI B,SUCKLING D M.Identification of floral volatiles and pollinator responses in kiwifruit cultivars,Actinidia chinensis var.chinensis[J].Journal of Chemical Ecology,2018,44(4):406-415.
[14] 刘科鹏,黄春辉,冷建华,陈葵,严玉平,辜青青,徐小彪.‘金魁’猕猴桃果实品质的主成分分析与综合评价[J].果树学报,2012,29(5):867-871.LIU Kepeng,HUANG Chunhui,LENG Jianhua,CHEN Kui,YAN Yuping,GU Qingqing,XU Xiaobiao.Principal component analysis and comprehensive evaluation of the fruit quality of‘Jinkui’kiwifruit[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2012,29(5):867-871.
[15] 王斯妤,钟敏,廖光联,陈璐,徐小彪.不同猕猴桃雄株花粉量及花粉活力差异研究[J].江西农业大学学报,2017,39(3):460-467.WANG Siyu,ZHONG Min,LIAO Guanglian,CHEN Lu,XU Xiaobiao.Comparison of pollen quantity and pollen viability of 41 male plants in Actinidia[J].Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis,2017,39(3):460-467.
[16] 杨技超,韩振诚,何茂梅,罗充,李良良,李苇洁.‘红阳’猕猴桃花粉直感效应研究[J].中国果树,2021(6):7-12.YANG Jichao,HAN Zhencheng,HE Maomei,LUO Chong,LI Liangliang,LI Weijie.Effect of pollen xenia on‘Hongyang’kiwifruit[J].China Fruits,2021(6):7-12.
[17] 赵凤军,闫春蕾,黄国辉.3 个软枣猕猴桃品种花粉直感效应研究[J].中国果树,2022(8):35-38.ZHAO Fengjun,YAN Chunlei,HUANG Guohui.Study on the pollen xenia of three Actinidia arguta varieties[J].China Fruits,2022(8):35-38.
[18] 张文慧,张百忍,李学宏,钟云鹏,李夏,郑敏,潘晓红.猕猴桃雄花特性与授粉果实性状相关性研究[J].农业资源与环境学报,2020,37(3):413-418.ZHANG Wenhui,ZHANG Bairen,LI Xuehong,ZHONG Yunpeng,LI Xia,ZHENG Min,PAN Xiaohong.Effects of the correlation between the characteristics of male flowers and pollinated fruit of kiwifruit[J].Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment,2020,37(3):413-418.
[19] 王丽华,郑晓琴,庄启国,李明章.红阳猕猴桃优良雄株选择初报[J].资源开发与市场,2013,29(8):792-793.WANG Lihua,ZHENG Xiaoqin,ZHUANG Qiguo,LI Mingzhang.Preliminary report of Hongyang’s excellent male plants choose[J].Resource Development & Market,2013,29(8):792-793.
[20] 钟敏,廖光联,李章云,邹梁峰,黄清,陈璐,黄春辉,陶俊杰,朱博,徐小彪.野生毛花猕猴桃雄花花器性状及SSR 遗传多样性研究[J].果树学报,2018,35(6):658-667.ZHONG Min,LIAO Guanglian,LI Zhangyun,ZOU Liangfeng,HUANG Qing,CHEN Lu,HUANG Chunhui,TAO Junjie,ZHU Bo,XU Xiaobiao.Genetic diversity of wild male kiwifruit(Actinidia eriantha Benth.) germplasms based on SSR and morphological markers[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2018,35(6):658-667.
[21] 单琨,刘布春,李茂松,武永峰.基于花粉量的作物产量预测模型研究进展[J].中国农业气象,2010,31(2):282-287.SHAN Kun,LIU Buchun,LI Maosong,WU Yongfeng.Research progress of pollen variable models for forecasting crop yield[J].Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology,2010,31(2):282-287.
[22] 何文娟.猕猴桃优良雄性单株观察测评与选择[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2019.HE Wenjuan.Observation,evaluation and selection of superior male single strains of kiwifruit[D].Yangling:Northwest A & F University,2019.
[23] 沈根华,王晓庆,骆军,张绍铃,钱培华,金凤雷.大棚栽培对梨花粉量及花粉生活力的影响[J].上海农业学报,2008,24(3):54-57.SHEN Genhua,WANG Xiaoqing,LUO Jun,ZHANG Shaoling,QIAN Peihua,JIN Fenglei.Effects of greenhouse culture on pear pollen quantity per anther and pollen viability[J].Acta Agriculturae Shanghai,2008,24(3):54-57.
[24] 董慧.猕猴桃精量控制授粉技术研究[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2014.DONG Hui.Research on precision control pollination of kiwifruit[D].Yangling:Northwest A&F University,2014.
[25] 秦红艳,张宝香,艾军,范书田,杨义明,王振兴,宋惠芳.2 个软枣猕猴桃品种的花粉育性研究[J].西北植物学报,2017,37(5):909-914.QIN Hongyan,ZHANG Baoxiang,AI Jun,FAN Shutian,YANG Yiming,WANG Zhenxing,SONG Huifang.Studies on pollen fertility of hardy kiwifruit (Actinidia arguta Planch.) two cultivars[J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2017,37(5):909-914.
[26] 钱超越.富平楸子杂交坐果率低的主要原因初步分析[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2017.QIAN Chaoyue.Preliminary analysis on the main reasons of low hybrid fruit setting rate of artificial pollination for Fupingqiuzi(Malus prunifolia)[D].Yangling:Northwest A&F University,2017.