红树莓(Rubus idaeus L.)为蔷薇科(Rosaceae)悬钩子属(Rubus L.)多年生落叶果树,为小浆果灌木。果实颜色鲜艳,味道酸甜,营养价值高,富含人体所需的多种营养元素[1-3],被称为 “天然绿色食品” 、 “维生素宝库” ,具有食品、医药等多领域的开发潜力和利用价值[4-6]。
我国有200多个红树莓品种[7],野生种质资源非常丰富,但多处于未经深度研究与开发利用的状态[8]。虽然国内市场上红树莓品种繁多但产地各异,而不同产地的红树莓品质存在较大差距。目前国内对于红树莓的果实品质相关研究也多集中于相同产地间[9-10],李鹏举[11]对绥化地区引种的26个树莓品种果实品质经综合分析后发现,北京32和红玉的平均单果质量最大,澳洲红维生素C含量、欧洲红花青素含量较高。陈天乐[12]对北京基地栽植的24 个树莓品种果实的感官品质、营养成分、香气成分等相关指标进行调查和测定,结果表明,R24和R33的综合性状较好,果实大小、营养成分含量突出,为育种亲本选择提供了依据。有研究对东北地区24 个红树莓品种的综合品质进行评价,利用主成分分析法筛选出8 个重要的加工属性指标,并初步筛选出糖酸比适宜、适合鲜食或直接加工成果汁或其他产品的品种[13]。目前对于不同产地间红树莓营养品质的差异却鲜见报道。野生红树莓具有很高价值,尤其我国本土野生红树莓,不仅在糖分含量、口感气味及抵御病虫害方面有着优异表现,还具有可溶性固形物含量较高、丰产性和抗逆性较强等突出特点[14]。近年来红树莓的综合利用逐渐成为研究热点,国内分布的野生红树莓也因具有较强的抗性且营养成分突出[15],受到了更多研究者的关注。
河北省山区的红树莓资源丰富,挖掘出适应河北省的野生红树莓资源,对种质资源高效利用、功能食品开发和乡村振兴等具有重要意义。因此笔者依托河北省丰富的红树莓野生资源,进行果实特性的调查和测定,比较省内不同区域野生红树莓的果实品质差异,对果实品质进行综合评价,对合理开发利用红树莓野生资源、推进不同用途红树莓良种选择和定向育种具有重要作用。
1 材料和方法
1.1 研究区概况
河北省野生红树莓多沿燕山及太行山山区分布,燕山和太行山都处于暖温带大陆性季风气候区。燕山、太行山年均温6~10 ℃,年降水量534~700 mm。河北省不同地区都具有较多的野生红树莓资源,依照河北省野生红树莓种质资源分布状况[16],将调查地主要划分为4大区域,分别是冀东区(秦皇岛市)、冀北区(承德市)、冀西北区(张家口市)以及冀西太行山区(保定市),共包含13个样地。采集区具体信息如表1所示。
表1 河北省野生红树莓分布区域样地地理位置
Table 1 Geographical location of sample plots of wild red raspberry distribution area in Hebei province

区域Region冀西北区Northwest Hebei冀西北区Northwest Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀东区Eastem Hebei冀东区Eastem Hebei冀西太行山区West Hebei Taihang Mountains冀西太行山区West Hebei Taihang Mountains冀西太行山区West Hebei Taihang Mountains样地Sample area张家口市下花园鸡鸣乡芦苇沟村Luweigou village,Jiming town,Xiahuayuan district,Zhangjiakou city张家口市赤城大海陀自然保护区Dahaituo Nature Reserve,Chicheng county,Zhangjiakou city承德市宽城县汤道河镇季杖子村Jizhangzi village,Tangdaohe town,Kuancheng county,Chengde city承德市承德县六沟镇化营村Huaying village,Liugou town,Chengde county,Chengde city承德市兴隆县兴隆镇王平石村Wangpingshi village,Xinglong town,Xinglong county,Chengde city承德市滦平县金沟屯镇大杨树沟村Dayangshugou village,Jingoutun town,Luanping county,Chengde city承德市隆化县茅荆坝乡千松甸村Qiansongdian village,Maojingba town,Longhua county,Chengde city承德市围场县马鞍山乡嵩松沟村Songsonggou village,Ma′anshan town,Weichang county,Chengde city秦皇岛市昌黎县两山乡长峪山村Changyushan village,Liangshan town,Changli county,Qinhuangdao city秦皇岛市抚宁县新寨镇小河峪村Xiaoheyu village,Xinzhai town,Funing county,Qinhuangdao city保定市易县千佛山森林公园Qianfoshan Forest Park,Yi county,Baoding city纬度Latitude/°N 40°30′25.82″经度Longitude/°E 115°24′04.84″海拔Altitude/m 1217 40°36′23.20″115°44′17.11″1259 40°32′29.00″118°55′03.00″586 41°20′46.00″118°19′04.00″605 40°21′07.00″117°34′14.00″678 41°01′23.41″117°12′55.32″941 41°31′46.00″118°17′40.00″1349 41°55′23.00″116°50′18.00″1642 39°46′54.00″119°09′55.00″116 40°01′41.00″119°22′30.00″218 39°29′34.00″115°24′28.00″250保定市涞水赵各庄镇平峪村Pingyu village,Zhaogezhuang town,Laishui county,Baoding city 39°39′32.00″115°19′13.00″357保定市阜平县龙泉关镇骆驼湾村Luotuowan village,Longquanguan town,Fuping county,Baoding city 38°52′46.00″113°49′30.00″1767
1.2 试验材料
于2020—2021年每年6—8月,在河北省4个分区共13 个分布区域中,分别随机选取3~6 株生长健壮、长势一致、具有代表性的野生红树莓植株,选取成熟度一致、果实面完全均匀着色、无病虫害的果实进行采集,各样地随机取样100个果实,设3次重复,分装后放入车载冰箱-16 ℃保存。
1.3 测定指标与方法
1.3.1 外部形态指标测定 在采集地现场进行外部形态指标测定,主要包括:(1)果实大小及果形:随机选取大小均匀的果实10颗,用数显游标卡尺测量果实横径、果实纵径,重复测定3 次,精确到0.01 mm,计算果形指数(纵径/横径);(2)果实产量:随机选取新鲜采摘的不带花托的果实10个,置于电子天平上称取质量,重复测定3次,精确到0.01 g,计算平均去托单果质量。观测记录各植株的果实数量取均值,根据单果质量估算野生红树莓的单株产量。
1.3.2 内在营养成分测定 除可溶性固形物含量用仪器即时测定外,其他营养成分均是对前期采集并用车载冰箱保存带回的红树莓果实,进行-20 ℃低温冷冻,试验时进行破碎处理后测定。主要包括:(1)可溶性糖含量测定:蒽酮比色法[17];(2)可滴定酸含量测定:氢氧化钠滴定法[18];(3)可溶性固形物含量测定:手持折光仪测量,精确到0.01%,重复测定3~5 次取平均值[19];(4)可溶性蛋白含量测定:考马斯亮蓝染色法[20];(5)维生素C含量测定:2,6二氯靛酚滴定法[21];(6)氨基酸含量测定:茚三酮显色法[22];(7)黄酮含量测定:氯化铝显色法[23];(8)总酚含量测定:福林酚试剂比色法[24];(9)花青素含量测定:pH示差法[25]。
1.4 数据处理
使用Excel 进行统计分析,使用SPSS Statistics 24 软件对不同区域野生红树莓的果实品质指标进行差异显著性分析、相关性分析、主成分分析及聚类分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 野生红树莓果实特性
2.1.1 野生红树莓果实主要经济性状差异 13 个样地的野生红树莓果实如图1所示。由表2可知,各地区野生红树莓果实的纵径与横径分别在9.64~14.41 mm、9.48~16.30 mm 之间。其中兴隆、围场和隆化的红树莓果个显著大于其他地区,以兴隆地区的果个最大;宽城、承德县、滦平次之;而昌黎和阜平的果个最小,两地间果个差异不显著。综合对比发现,冀北区红树莓的果个显著大于其他地区,果形方面地区间差异不显著,除下花园、宽城、兴隆、承德县为圆形果外,其他地区均为圆锥形果。

图1 13 个样地野生红树莓果实
Fig.1 Fruits of wild red raspberries from 13 sample areas
A.下花园;B.赤城;C.宽城;D.承德县;E.兴隆;F.滦平;G.隆化;H.围场;Ⅰ.昌黎;J.抚宁;K.易县;L.涞水;M.阜平。
A. Xiahuayuan; B. Chicheng; C. Kuancheng; D. Chengde county; E. Xinglong; F. Luanping; G. Longhua; H.Weichang; Ⅰ. Changli; J. Funing; K.Yi county;L.Laishui;M.Fuping.
表2 各区域野生红树莓的果实性状比较
Table 2 Comparison of fruit characters of wild red raspberries in each region

注:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(p<0.05)。下同。
Note:Different small letters in the same column indicate significant difference at p<0.05.The same below.
区域Region县域County纵径Longitudinal diameter/mm横径Transverse diameter/mm果形Fruit shape单果质量Single fruit mass/g单株产量Yield per plant/g冀西北区Northwest Hebei冀西北区Northwest Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀东区Eastem Hebei冀东区Eastem Hebei冀西太行山区West Hebei Taihang Mountains冀西太行山区West Hebei Taihang Mountains冀西太行山区West Hebei Taihang Mountains下花园Xiahuayuan赤城Chicheng宽城Kuancheng承德县Chengde county兴隆Xinglong滦平Luanping隆化Longhua围场Weichang昌黎Changli抚宁Funing易县Yi county 11.52±0.33 c 12.94±0.34 d纵横比Ratio of longitudinal diameter to transverse 0.89 0.74±0.01 d最大单果质量Maximum fruit mass/g 1.41单株果数Number of fruits per plant 97±2.03 d 71.21±1.49 d 11.97±0.33 bc 12.36±0.30 de0.97 0.79±0.02 cd1.19 87±2.73 e 68.18±2.15 d 12.73±0.20 b 15.11±0.25 b 0.84 1.05±0.04 b1.38 151±1.76 c 254.91±3.65 b 11.68±0.34 c 14.16±0.26 bc0.82 0.86±0.03 c1.32 226±3.21 a 224.36±2.78 b 14.41±0.31 a 16.30±0.33 a 0.89 2.03±0.04 a2.68 168±2.31 b 306.70±3.57 a 11.74±0.27 c 14.40±0.26 bc0.82 0.85±0.03 c1.36 242±3.46 a 248.96±3.26 b 13.82±0.24 a 14.02±0.19 c 0.99 0.83±0.02 c1.36 164±2.64 b 138.62±2.14 c 14.11±0.33 a 14.14±0.32 c 1.00 0.84±0.02 c 1.42 172±2.46 b 144.48±2.45 c 9.64±0.18 d 9.78±0.12 g 0.96 0.34±0.01 e 0.48 68±2.31 f 23.89±0.49 e 11.19±0.34 c 11.99±0.17 e 0.93 0.82±0.02 cd1.12 83±2.91 e 137.20±1.89 c 10.42±0.24 cd 10.86±0.32 f 0.96圆形Circular圆锥形Conicalness圆形Circular圆形Circular圆形Circular圆锥形Conicalness圆锥形Conicalness圆锥形Conicalness圆锥形Conicalness圆锥形Conicalness圆锥形Conicalness 0.75±0.01 d1.08 80±2.74 e 124.12±2.26 c涞水Laishui 10.36±0.32 cd 10.54±0.18 f 0.98圆锥形Conicalness 0.72±0.02 d1.06 80±2.41 e 76.36±2.46 d阜平Fuping 9.98±0.27 d 9.48±0.26 g 1.05圆锥形Conicalness 0.46±0.03 e0.68 72±1.78 f 36.21±0.83 e
野生红树莓果实产量有着明显区域性差异,各地区野生红树莓果实的单果质量及单株产量分别在0.34~2.03 g、23.89~306.70 g 之间,其中兴隆地区果实的单果质量及单株产量显著高于其他地区;宽城的单果质量及宽城、承德县和滦平的单株产量都次之;而昌黎和阜平果实的单果质量及单株产量最低,两地间差异不显著。综合比较发现,冀北区的单果质量及单株产量显著高于其他地区,其余各地均存在一定差异。
2.1.2 野生红树莓果实营养成分差异 由表3可知,各地区野生红树莓果实的可溶性蛋白与氨基酸含量(w,后同)分别在1.10~1.97 mg·g-1、9.84~12.96 mg·g-1之间,抚宁红树莓的可溶性蛋白含量、赤城红树莓的氨基酸含量显著高于其他地区;各地区野生红树莓果实的维生素C 与花青素含量有较大差异,分别在8.40~29.79 mg·100 g-1、203.02~599.19 mg·kg-1之间,赤城红树莓的维生素C 含量、抚宁和昌黎红树莓的花青素含量显著高于其他地区;各地区野生红树莓果实中黄酮与总酚含量无区域性分布规律,分别在2.32~6.69 mg·g-1、1.91~4.24 mg·g-1之间,宽城地区红树莓的黄酮含量、滦平地区红树莓的总酚含量显著高于其他地区。综合比较发现,冀西北区野生红树莓具有较高的维生素C 和氨基酸含量;冀北区各样地营养成分存在个体差异;冀西太行山区和冀东区野生红树莓大多营养成分无显著差异,且相较其他地区具有较高的可溶性蛋白和花青素含量。
表3 各区域野生红树莓果实的营养成分
Table 3 Nutritional composition of wild red raspberry fruits in each region

区域Region县域County冀西北区Northwest Hebei冀西北区Northwest Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀东区Eastem Hebei冀东区Eastem Hebei冀西太行山区West Hebei Taihang Mountains冀西太行山区West Hebei Taihang Mountains冀西太行山区West Hebei Taihang Mountains下花园Xiahuayuan赤城Chicheng宽城Kuancheng承德县Chengde county兴隆Xinglong滦平Luanping隆化Longhua围场Weichang昌黎Changli抚宁Funing易县Yi county w(可溶性蛋白)Soluble protein content/(mg·g-1)1.10±0.01 g w(氨基酸)Amino acids content/(mg·g-1)12.47±0.05 b w(维生素C)Vitamin C content/(mg·100 g-1)22.83±0.30 b w(黄酮)Flavonoids content/(mg·g-1)2.33±0.02 e w(总酚)Total phenols content/(mg·g-1)1.91±0.05 e w(花青素)Anthocyanins content(mg·kg-1)388.98±4.04 c 1.19±0.02 f 12.96±0.02 a 29.79±0.32 a 2.32±0.02 e 2.78±0.03 d 513.51±5.43 b 1.81±0.02 b 11.14±0.02 c 8.40±0.03 d 6.69±0.13 a 3.74±0.04 b 378.78±2.26 c 1.48±0.02 d 12.38±0.03 b 8.54±0.03 d 3.82±0.02 d 3.82±0.04 b 376.36±2.07 c 1.50±0.02 d 10.07±0.03 d 12.53±0.10 c 5.34±0.14 c 2.69±0.05 d 203.02±3.61 e 1.37±0.02 e 12.46±0.03 b 8.69±0.14 d 3.72±0.04 d 4.24±0.02 a 269.62±4.29 d 1.62±0.01 c 11.16±0.03 c 12.66±0.02 c 5.39±0.08 c 2.64±0.04 d 386.74±3.73 c 1.57±0.01 c 11.08±0.03 c 12.73±0.14 c 5.24±0.12 c 2.76±0.04 d 394.80±3.24 c 1.48±0.02 d 9.92±0.03 d 8.54±0.08 d 3.89±0.06 d 2.73±0.03 d 587.82±5.64 a 1.97±0.04 a 10.05±0.01 d 12.24±0.09 c 5.75±0.08 b 3.61±0.01 c 599.19±4.81 a 1.84±0.03 b 10.08±0.02 d 12.08±0.12 c 5.16±0.10 c 3.32±0.03 c 508.54±2.67 b涞水Laishui 1.78±0.02 b 9.84±0.02 d 11.82±0.28 c 5.64±0.12 b 2.84±0.03 d 496.65±3.21 b阜平Fuping 1.81±0.02 b 11.16±0.02 c 11.96±0.16 c 5.20±0.12 c 3.46±0.04 c 502.63±2.87 b
2.1.3 野生红树莓果实风味差异 果实内部可溶性糖和有机酸的含量,是影响水果风味最直观的因素。由表4可知,各地区野生红树莓的可溶性糖与可滴定酸含量存在显著差异,分别在51.24~84.69 mg·g-1、45.53~75.27 mg·g-1之间,宽城红树莓的可溶性糖含量、抚宁和易县红树莓的可滴定酸含量显著高于其他地区;各地区野生红树莓的糖酸比在0.72~1.48之间,兴隆的红树莓糖酸比最高,而昌黎最低;各地区野生红树莓的可溶性固形物含量与固酸比分别在9.53%~14.77%、1.45~2.67 之间,下花园红树莓的2个指标均高于其他地区。
表4 各区域野生红树莓的风味特征
Table 4 Flavor characteristics of wild red raspberry fruit in each region

区域Regional冀西北区Northwest Hebei冀西北区Northwest Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀东区Eastem Hebei冀东区Eastem Hebei冀西太行山区West Hebei Taihang Mountains冀西太行山区West Hebei Taihang Mountains冀西太行山区West Hebei Taihang Mountains县域County下花园Xiahuayuan赤城Chicheng宽城Kuancheng承德县Chengde county兴隆Xinglong滦平Luanping隆化Longhua围场Weichang昌黎Changli抚宁Funing易县Yi county w(可溶性糖)Soluble sugar content/(mg·g-1)75.35±0.29 b 69.10±0.13 c 84.69±0.23 a 66.47±0.18 d 67.30±0.26 d 66.98±0.14 d 69.45±0.34 c 69.54±0.21 c 51.24±0.16 f 59.07±0.37 e 60.23±0.28 e w(可滴定酸)Titratable acid content/(mg·g-1)55.33±0.02 d 53.83±0.03 e 62.30±0.03 c 72.17±0.02 b 45.53±0.02 g 71.30±0.03 b 52.86±0.02 e 50.70±0.03 f 71.23±0.02 b 75.27±0.02 a 74.64±0.02 a w(可溶性固形物)Soluble solids content/%14.77±0.20 a 11.23±0.15 b 11.07±0.12 bc 10.54±0.03 c 9.53±0.09 d 10.57±0.29 c 11.02±0.01 bc 10.97±0.03 bc 10.42±0.18 c 11.50±0.29 b 11.42±0.18 b糖酸比Sugar-acid ratio 1.36 1.28 1.36 0.92 1.48 0.94 1.31 1.37 0.72 0.78 0.81固酸比Solids-acid ratio 2.67 2.09 1.78 1.45 2.09 1.48 2.08 2.16 1.46 1.53 1.53涞水Laishui 62.54±0.18 e 72.46±0.02 b 11.18±0.22 b 0.86 1.54阜平Fuping 65.84±0.12 d 64.26±0.02 c 10.36±0.24 c 1.02 1.61
综合比较发现,冀西北区和冀北区的宽城、兴隆和围场有着较高的可溶性糖含量、固酸比和糖酸比,以及较低的可滴定酸含量,因此果实口味更甜、口感更加丰富;而冀东区的昌黎和抚宁、冀西太行山区的易县、涞水和阜平果实中可溶性糖含量较低,可滴定酸含量较高,果实口味偏酸。
2.2 野生红树莓果实品质综合评价
2.2.1 果实品质性状相关性分析 对野生红树莓果实性状、产量、营养成分及其风味共18 项指标进行相关性分析,由图2可知,共有19对指标相关性达到显著水平(p<0.05),28对指标相关性达到极显著水平(p<0.01)。在3 个果形指标中,果实的横径与纵径呈极显著正相关,而与纵横比呈显著负相关;在4个果实产量指标中,单果质量和最大单果质量都与果实纵径和横径呈极显著正相关,而单株产量也与果实纵径、横径、单果质量和单株果数呈极显著正相关,说明果个和果数都显著影响野生红树莓的产量;在6 个果实营养成分指标中,黄酮含量与可溶性蛋白含量呈极显著正相关,而与氨基酸含量呈极显著负相关,与维生素C 含量呈显著负相关。花青素含量与多种果形以及果实产量指标呈显著、极显著负相关,即果个越大、单株产量越多的野生红树莓果实含有的花青素含量越少;在5个果实风味指标中,固酸比与可溶性固形物含量呈显著正相关,与可滴定酸含量呈极显著负相关。而糖酸比不仅与可溶性糖含量和固酸比呈极显著正相关,与可滴定酸含量呈极显著负相关,还与果形指标纵径、横径呈极显著正相关,与果实产量指标中的单果质量和最大单果质量呈显著正相关,这说明影响果实风味的糖酸比和固酸比有协同一致的作用,且果形及单果质量越大的果实,其糖酸比越高,风味越好。

图2 野生红树莓果实品质性状相关性分析
Fig.2 Correlation analysis of fruit quality traits of wild red raspberry
2.2.2 果实品质性状主成分分析 对各地区野生红树莓有关果实品质的18项指标进行主成分分析,共提取出特征值>1 的4 个主成分。由表5 可知,4 个主成分方差贡献率由大到小依次为42.009%、26.101%、14.090%、6.330%,累积方差贡献率为88.530%,基本代表了果实指标中的18个性状,可作为评价指标。为了更好地解释成分,对其旋转后系数更接近1,使各成分贡献率在累积贡献率不变的情况下重新分配。
表5 野生红树莓果实品质的主成分特征值及方差贡献率
Table 5 Principal component eigenvalues and variance contribution of fruit quality of wild red raspberries from different areas
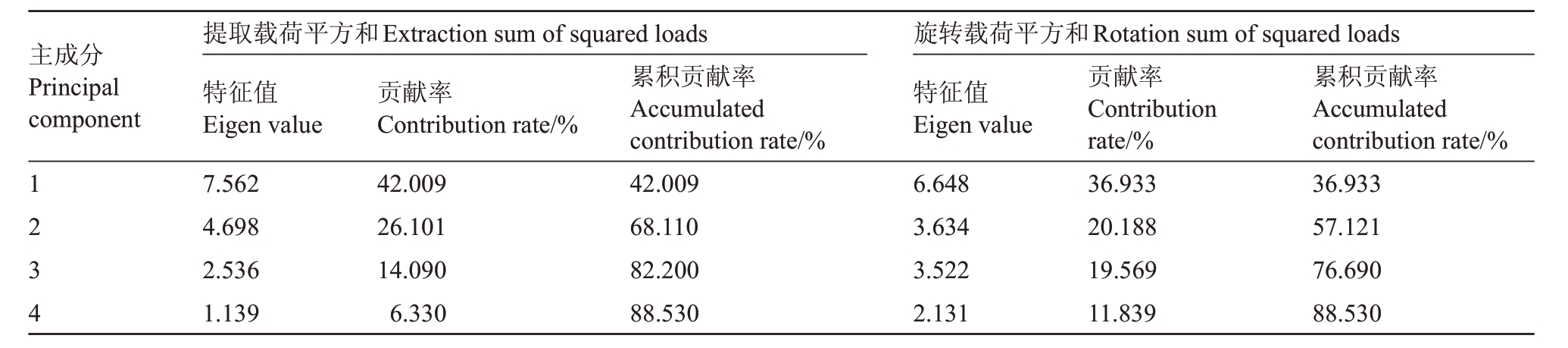
主成分Principal component 1234提取载荷平方和Extraction sum of squared loads特征值Eigen value 7.562 4.698 2.536 1.139贡献率Contribution rate/%42.009 26.101 14.090 6.330累积贡献率Accumulated contribution rate/%42.009 68.110 82.200 88.530旋转载荷平方和Rotation sum of squared loads特征值Eigen value 6.648 3.634 3.522 2.131贡献率Contribution rate/%36.933 20.188 19.569 11.839累积贡献率Accumulated contribution rate/%36.933 57.121 76.690 88.530
通过最大方差法旋转后的矩阵表6可知,第1主成分综合了最大单果质量、纵径、单果质量、横径、糖酸比、可滴定酸含量、花青素含量、单株产量和固酸比的信息,PC1较大时,果实的果个、单株产量较大,且可滴定酸含量、花青素含量、糖酸比和固酸比较高;第2主成分综合了纵横比、总酚含量和单株果数的信息,PC2较大时,果实的纵横比、单株果数较大,且总酚含量较高;第3主成分综合了黄酮、可溶性蛋白、氨基酸和维生素C 含量的信息,PC3 较大时,果实中这4个成分的含量较高;第4主成分综合了可溶性糖和可溶性固形物含量的信息,PC4较大时,果实中这2个成分的含量较高。
表6 野生红树莓果实品质的主成分因子旋转载荷矩阵
Table 6 Rotated loading matrix of principal component factors for fruit quality of wild red raspberry

指标Ⅰndex最大单果质量Maximum fruit mass纵径Longitudinal diameter单果质量Single fruit mass横径Transverse diameter糖酸比Sugar-acid ratio可滴定酸含量Titratable acid content花青素含量Anthocyanins content单株产量Yield per plant固酸比Solids-acid ratio纵横比Ratio of longitudinal diameter to transverse diameter总酚含量Total phenols content单株果数Number of fruits per plant黄酮含量Flavonoids content可溶性蛋白含量Soluble protein content氨基酸含量Amino acids content维生素C含量Vitamin C content可溶性糖含量Soluble sugar content可溶性固形物含量Soluble solids content主成分1 PC1 0.942 0.914 0.904 0.851 0.806-0.794-0.768 0.698 0.532-0.245-0.238 0.521 0.163-0.234 0.045 0.065 0.465-0.233主成分2 PC2 0.117 0.035 0.123 0.437-0.201 0.415-0.404 0.662-0.467-0.816 0.814 0.752 0.037-0.002 0.371-0.492 0.224-0.234主成分3 PC3-0.041 0.034 0.108-0.060-0.162 0.240 0.154 0.202-0.430 0.205 0.350-0.113 0.983 0.944-0.734-0.662-0.015-0.400主成分4 PC4-0.040 0.190-0.151 0.195 0.493-0.248-0.112-0.046 0.530-0.086-0.126-0.011 0.017-0.080 0.441 0.307 0.823 0.660
各地区的野生红树莓主成分得分及果实品质排名如表7所示,兴隆、围场和隆化地区,滦平、承德县和宽城地区,宽城、抚宁和阜平地区,宽城、下花园和隆化地区分别在第1至第4主成分的得分较高,果实品质较好;果实品质最终综合评价得分(F)排名前三位的分别是宽城、兴隆和围场。比较发现冀北区的野生红树莓相较其他区域有着突出的果实品质。
表7 野生红树莓主成分得分及排名
Table 7 Principal component score and ranking of wild red raspberries from different regions

区域Region冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀北区Northern Hebei冀东区Eastem Hebei冀西太行山区West Hebei Taihang Mountains冀西太行山区West Hebei Taihang Mountains冀西北区Northwest Hebei冀西太行山区West Hebei Taihang Mountains冀西北区Northwest Hebei冀东区Eastem Hebei县域County宽城Kuancheng兴隆Xinglong围场Weichang隆化Longhua滦平Luanping承德县Chengde county抚宁Funing易县Yi county涞水Laishui下花园Xiahuayuan阜平Fuping赤城Chicheng昌黎Changli F1 0.394 2.613 0.829 0.702-0.062-0.163-0.754-0.721-0.615-0.049-0.938-0.030-1.207 F2 1.030-0.360-0.625-0.571 2.150 1.826-0.057-0.165-0.562-0.700-0.579-0.739-0.646 F3 1.453 0.179 0.305 0.370-0.798-0.621 1.016 0.586 0.715-1.741 0.636-1.784-0.317 F4 1.858-1.417 0.402 0.432-0.443-0.437-0.193-0.407-0.336 1.746 0.195 0.142-1.543 F 排序Ranking 0.969 0.858 0.324 0.302 0.229 0.153-0.129-0.263-0.271-0.331-0.357-0.556-0.927 123456789 10 11 12 13
2.2.3 聚类分析 依据野生红树莓果实品质的18项指标对13 个样地中分布的野生红树莓进行聚类分析。由图3可知,在欧式距离为7的情况下,可将各样地的野生红树莓分为3 类:第一类包括围场和隆化,此类野生红树莓果实品质相较其他地区,果个、糖酸比和固酸比相对较高,可用于营养成分含量均衡、果实风味相对较好的红树莓资源的筛选。第二类包括抚宁、易县、涞水、赤城、下花园、阜平和昌黎,此类野生红树莓果个、单果质量、单株果数以及单株产量较小,但部分营养元素含量较为突出,并且可以分为抚宁、易县和其他5 个地区2 个亚类,前者野生红树莓可溶性蛋白、花青素、可滴定酸含量较为突出,后者氨基酸、维生素C、可溶性固形物含量和固酸比较为突出,因此第二类可用于上述7 个成分指标含量较高的红树莓资源筛选。第三类包括滦平、承德、宽城和兴隆,此类的野生红树莓果个、单果质量、单株果数以及单株产量都较为突出,且同样可分为滦平、承德县和宽城、兴隆2 个亚类,前者的总酚含量较为突出,后者的黄酮、可溶性糖含量和糖酸比较为突出,因此第三类可用于果个、产量较大且上述4个成分指标含量较高的红树莓资源筛选。综合比较发现,冀北区的野生红树莓产量大、风味佳,适合鲜食生产,而其他3个区域的野生红树莓,果实有机物含量突出,适合加工生产。
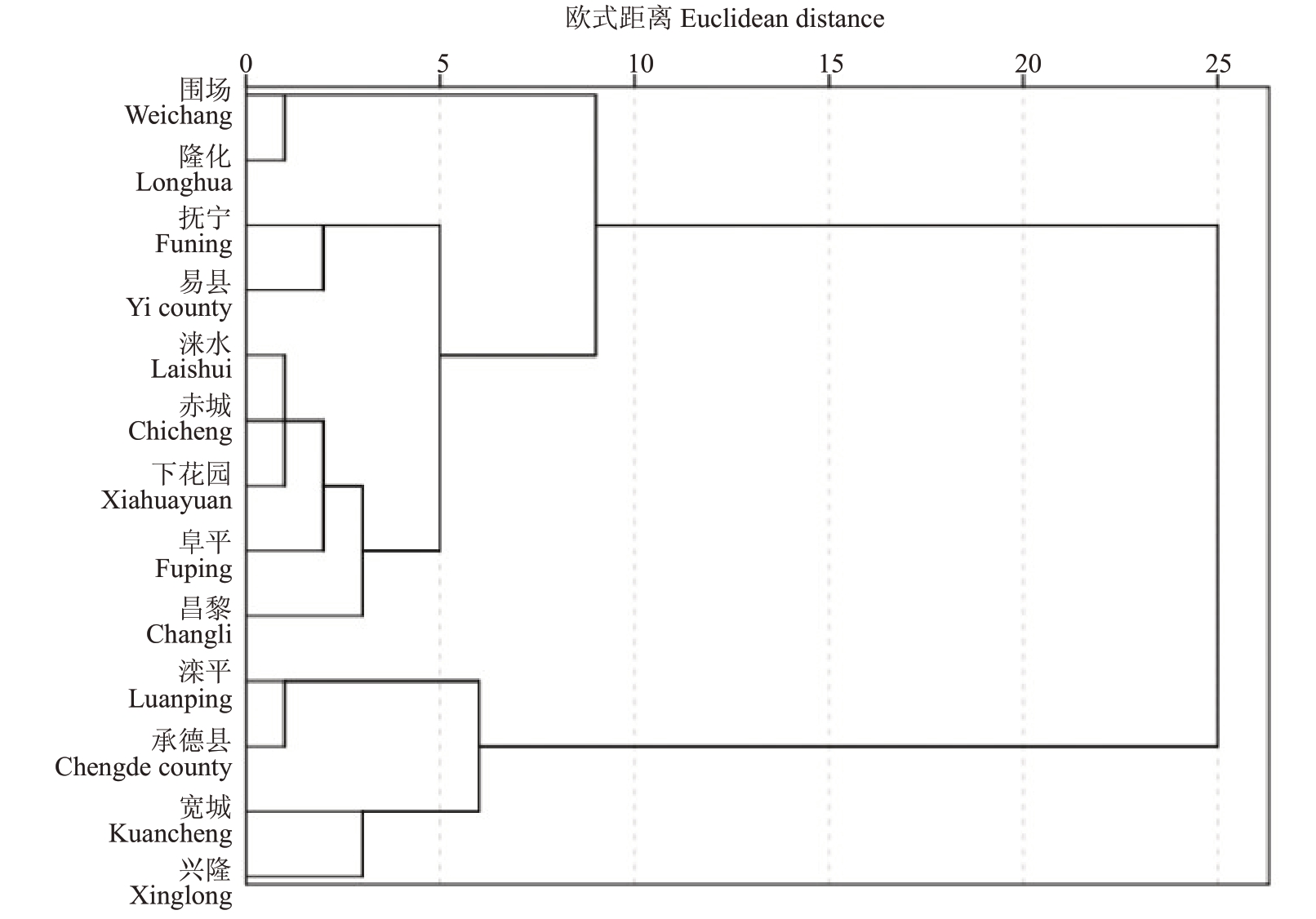
图3 各样地野生红树莓果实品质聚类分析
Fig.3 Cluster analysis of fruit quality of wild red raspberry in various areas
3 讨 论
3.1 野生红树莓的果实特性
野生红树莓果实的外部性状及产量通常受生长环境条件、基因等多个因素的影响[26-27],存在区域性差异。本研究结果表明,冀北区的红树莓果个显著大于其他区域,且该区单果质量更大,单株产量更高,这可能是由于该区所处地理位置及其气候、土壤等环境因素利于果实生长或受优良种质因素影响。其中兴隆地区的红树莓果个和单株产量显著高于其他地区,其单果质量(2.03 g)显著高于宋建新等[28]测定的Sunrise(1.62 g)、周双等[9]测定的DNS9(1.82 g)及陈乐天[12]测定的R22(1.606 5 g)、R10(1.857 g),有引种用于栽培生产的优势。
果实的维生素C、总酚和花青素等都是天然的抗氧化活性剂[29],可帮助人体增强免疫力,促进新陈代谢。根据研究结果可知,河北省不同区域的野生红树莓果实的营养品质存在显著差异。综合比较发现,冀西北区的野生红树莓具有较高的维生素C和氨基酸含量,其维生素C含量(22.83~29.79 mg·100 g-1)与张家口地区海尔特兹红树莓测定结果相近[30],但显著高于沈阳农业大学树莓种植基地采收的15 个树莓品种(6.86~10.60 mg·100 g-1)[28],是其中维生素C 含量最高品种Cuthbert 的2~3 倍;冀西太行山区和冀东区野生红树莓分别具有较高的可溶性蛋白和花青素含量,其中冀东区花青素含量(587.82~599.19 mg·kg-1)是北京基地栽植的R4、R6、R7 红树莓品种的2~3 倍[12],且各区域野生红树莓总酚含量(1.91~4.24 mg·g-1)显著高于北京基地栽植的14 个树莓品种(0.566~1.882 mg·g-1)[12],因此冀西北区、冀东区及冀西太行山区的红树莓果实富含天然抗氧化成分,具有较强的抗氧化活性,在延长食品加工保鲜期的同时,改善了口感,提高了营养价值[31]。分析冀西北区维生素C 含量较高的原因,可能是该区生长地光照充足,促进了植株的光合作用及生长发育。而冀东区花青素含量较高,则可能是由于该地区适宜的土壤条件和充足的降水促进了花青素积累,黄洁帆等[32]在研究中发现,该地区野生红树莓的适生土壤均为酸性土,加之雨水条件充足,有助于提高植物对铝、镁等合成花青素等关键矿质元素的吸收能力,Pott 等[33]在黑加仑果实品质的研究中也证明了降雨对果实中花青素的含量有积极影响。
综合比较各区域的果实风味发现,冀西北区和冀北部分地区的红树莓果实具有较高的糖分、糖酸比、固酸比及可溶性固形物含量,尤其冀西北区果实风味显著突出,原因可能是该区气候较为干旱,且山区地形起伏较大,导致昼夜温差变大,从而在一定程度上促进了果实中有机物的积累。王程宽等[34]对柑橘品质的研究同样表明,昼夜温差显著影响果实风味,较大的昼夜温差有助于果实糖分累积。
3.2 野生红树莓的果实品质综合评价
使用科学合理的评估方法挑选出品质优良的种质,对育种工作至关重要[35]。目前相关性分析、主成分分析及聚类分析被广泛应用在有关果实品质的数据分析和综合评价中[36-37]。笔者通过对各样地中有关野生红树莓果实性状、产量、营养成分及其风味共18项指标进行相关性分析,发现19对指标相关性达到显著水平,28 对指标相关性达到极显著水平,表明各项指标间既相互独立,又有一定关联性,相互影响。进而运用主成分分析,从18个果实品质指标中提取出4个主成分,包含所有品质指标88.530%的信息,可作为指标综合评价各样地的红树莓果实品质,并依据各指标得分综合评价不同样地的红树莓果实品质。
通过聚类分析,将13 个样地的野生红树莓果实分为3 类,在野生红树莓资源的开发利用中,果形大、产量且营养成分含量高的野生红树莓具有较高的价值,在优异种质选育中可以作为特异种质培养。
4 结 论
不同区域的野生红树莓果实特性及果实营养成分存在差异,冀北区的野生红树莓果个和产量显著大于其他区域;冀西北区的野生红树莓具有较高的维生素C 和氨基酸含量;冀西太行山区和冀东区野生红树莓具有较高的可溶性蛋白和花青素含量;而冀北区各样地红树莓营养成分存在个体差异。经主成分分析和聚类分析后,果实品质综合得分排名前三位的地区为宽城、兴隆和围场,结合河北省分区得出,冀北区的野生红树莓产量大、风味佳,有发展为鲜食生产的潜质,而冀西北区、冀西太行山区和冀东区的野生红树莓,果实有机物含量突出,适合不同需求的加工生产。
[1] VARA A L,PⅠNELA J,DⅠAS M Ⅰ,PETROVⅠĆ J,NOGUEⅠRA A,SOKOVⅠĆ M,FERREⅠRA ⅠC F R,BARROS L. Compositional features of the “Kweli” red raspberry and its antioxidant and antimicrobial activities[J].Foods,2020,9(11):1522.
[2] DE SOUZA V R,PEREⅠRA P A P,DA SⅠLVA T L T,DE OLⅠVEⅠRA LⅠMA L C,PⅠO R,QUEⅠROZ F. Determination of the bioactive compounds,antioxidant activity and chemical composition of Brazilian blackberry,red raspberry,strawberry,blueberry and sweet cherry fruits[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,156:362-368.
[3] STOJANOV D,MⅠLOŠEVⅠĆ T,MAŠKOVⅠĆ P,MⅠLOŠEVⅠĆ N,GLⅠŠⅠĆ Ⅰ,PAUNOVⅠĆ G. Ⅰnfluence of organic,organo-mineral and mineral fertilisers on cane traits,productivity and berry quality of red raspberry (Rubus idaeus L.)[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2019,252:370-378.
[4] 张群英,文光琴,李永霞,聂飞,王瑶.优良树莓品种及当地野生树莓的引种比较研究[J].种子,2015,34(1):100-103.ZHANG Qunying,WEN Guangqin,LⅠ Yongxia,NⅠE Fei,WANG Yao. Comparative study on introduction between fine raspberry varieties and local wild raspberry[J]. Seed,2015,34(1):100-103.
[5] BOWEN-FORBES C S,ZHANG Y J,NAⅠR M G.Anthocyanin content,antioxidant,anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties of blackberry and raspberry fruits[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2010,23(6):554-560.
[6] KOWALSKA K,OLEJNⅠK A,ZⅠELⅠŃSKA-WASⅠELⅠCA J,OLKOWⅠCZ M. Raspberry (Rubus idaeus L.) fruit extract decreases oxidation markers,improves lipid metabolism and reduces adipose tissue inflammation in hypertrophied 3T3-L1 adipocytes[J].Journal of Functional Foods,2019,62:103568.
[7] WU L Y,YANG J,WANG C Y,LⅠN N,LⅠU Y P,DUAN A B,WANG T. Chemical compositions of raspberry leaves influenced by growth season,cultivar and leaf position[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2022,304:111349.
[8] 吴林,张强,王颖,李金英.中国树莓科学研究和产业发展的回顾与展望[J].吉林农业大学学报,2021,43(3):265-274.WU Lin,ZHANG Qiang,WANG Ying,LⅠJinying. Review and prospect of scientific research and industrial development of raspberry in China[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University,2021,43(3):265-274.
[9] 周双,孙兰英,杨光,焦奎宝,孙伟,段亚东,张鹍,宋鹏慧,李鹏举,张静华,王明洁.20 个品种树莓果实品质评价[J].食品研究与开发,2022,43(2):171-176.ZHOU Shuang,SUN Lanying,YANG Guang,JⅠAO Kuibao,SUN Wei,DUAN Yadong,ZHANG Kun,SONG Penghui,LⅠPengju,ZHANG Jinghua,WANG Mingjie. Evaluation of fruit quality of twenty varieties of raspberry[J]. Food Research and Development,2022,43(2):171-176.
[10] 王柏茗. 两个红树莓品种在天津地区引种及生长适应性研究[D].天津:天津农学院,2021.WANG Baiming. Study on the introduction and growth adaptability of two cultivars of raspberry in Tianjin[D].Tianjin:Tianjin Agricultural University,2021.
[11] 李鹏举.绥化地区引种树莓农艺学性状调查及评价[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2018:14-17.LⅠPengju. Ⅰnvestigation and evaluation of agronomic characters of introduced raspberry in Suihua area[D]. Harbin:Northeast Agricultural University,2018:14-17.
[12] 陈乐天.新引国外树莓品种农艺学性状调查及评价[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2020:17-21.CHEN Letian. Ⅰnvestigation and evaluation on agronomic traits of newly introduced foreign raspberry varieties[D]. Harbin:Northeast Agricultural University,2020:17-21.
[13] YU Y P,YANG G,SUN L Y,SONG X S,BAO Y H,LUO T,WANG J L.Comprehensive evaluation of 24 red raspberry varieties in Northeast China based on nutrition and taste[J]. Foods,2022,11(20):3232.
[14] 王小蓉,汤浩茹,邓群仙.中国树莓属植物多样性及品种选育研究进展[J].园艺学报,2006,33(1):190-196.WANG Xiaorong,TANG Haoru,DENG Qunxian.Advancement in research of genetic diversity of bramble (Rubus L.) and its breeding in China[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2006,33(1):190-196.
[15] 李晨,张秀玲,李凤凤,汲润,张文涛.五种小浆果抗氧化活性和相关营养物质的测定及主成分分析[J].食品与发酵工业,2022,48(14):226-234.LⅠChen,ZHANG Xiuling,LⅠFengfeng,JⅠRun,ZHANG Wentao. Determination of antioxidant activity,nutrients and quality evaluation using principal component analysis of five kinds of small berries[J]. Food and Fermentation Ⅰndustries,2022,48(14):226-234.
[16] 黄洁帆,顾玉红,张雪梅,牟洪香,刘炳响,谷佳旭.河北省野生红树莓种质资源分布及其植株表型性状对非生物生态因子的响应[J].河北林业科技,2023(1):1-8.HUANG Jiefan,GU Yuhong,ZHANG Xuemei,MU Hongxiang,LⅠU Bingxiang,GU Jiaxu.Distribution of wild Rubus idaeus resources and their plant phenotypic traits in response to abiotic ecological factors in Hebei Province[J]. The Journal of Hebei Forestry Science and Technology,2023(1):1-8.
[17] 李合生.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2000:195-197.LⅠHesheng. Principles and techniques of plant physiological biochemical experiment[M]. Beijing:Higher Education Press,2000:195-197.
[18] 张志良,瞿伟菁,李小方.植物生理学实验指导[M].4 版.北京:高等教育出版社,2009:262-264.ZHANG Zhiliang,QU Weijing,LⅠXiaofang.Experimental guidance on plant physiology[M]. 4th ed. Beijing:Higher Education Press,2009:262-264.
[19] 李艳婷,周铮,黄冬华,周超华,徐雷.翠冠梨果不同部位可溶性固形物及硬度测定比较研究[J]. 中国南方果树,2022,51(3):148-152.LⅠYanting,ZHOU Zheng,HUANG Donghua,ZHOU Chaohua,XU Lei. Comparative study on determination of soluble solids and hardness in different parts of Cuiguan pear[J]. South China Fruits,2022,51(3):148-152.
[20] 冷熹鸣,王迪海.陕北晋枣不同部位生长中可溶性糖及蛋白含量变化研究[J].西北林学院学报,2019,34(2):105-108.LENG Ximing,WANG Dihai.Changes of souble sugar and portein contents in different parts of Jin jujube in North Shaanxi[J].Journal of Northwest Forestry University,2019,34(2):105-108.
[21] 杨诗谣,李美英,宋正蕊.不同蔬菜水果中维生素C(VC)含量检测分析[J].中国检验检测,2020,28(2):38-39.YANG Shiyao,LⅠMeiying,SONG Zhengrui. Detection and analysis of vitamin C in different vegetables and fruits[J]. ChinaⅠnspection Body&Laboratory,2020,28(2):38-39.
[22] 杨宇,崔璨,张喜春,郭仰东.不同番茄品种果实中氨基酸含量分析[J].湖北农业科学,2022,61(24):136-139.YANG Yu,CUⅠCan,ZHANG Xichun,GUO Yangdong.Analysis of amino acid content in fruits of different tomato varieties[J].Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2022,61(24):136-139.
[23] 丛龙娇,史锐,吴鹏,刘苗苗,刘斯文,黄晓彤.不同产地黑果腺肋花楸果实中总多酚、总黄酮含量测定[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2021,23(1):31-34.CONG Longjiao,SHⅠRui,WU Peng,LⅠU Miaomiao,LⅠU Siwen,HUANG Xiaotong. Determination of total polyphenols and total flavonoids in fruits of Heiguoxianleihuaqiu (Aronia melanocarpa) from different habitats[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2021,23(1):31-34.
[24] 刘艺,王圳伊,张晶,鲁宝君.蓝莓果实色度值与化学成分含量的相关性研究[J].中国食品添加剂,2019,30(12):189-194.LⅠU Yi,WANG Zhenyi,ZHANG Jing,LU Baojun. Correlation analysis of blueberry active ingredient content and its chroma value based on chroma analysis principle[J]. China Food Additives,2019,30(12):189-194.
[25] 王一涵,吴镝,张铭津,张帆,王薇.黑果腺肋花楸花青素提取工艺研究[J].植物学研究,2021,10(1):56-62.WANG Yihan,WU Di,ZHANG Mingjin,ZHANG Fan,WANG Wei. Study on the extraction technology of anthocyanin from sorbus melanocarpa[J].Botanical Research,2021,10(1):56-62.
[26] 陈曼曼.南高丛蓝莓果实发育细胞学规律及相关基因的分离与表达分析[D].金华:浙江师范大学,2019:25-26.CHEN Manman.Comparative analysis of anatomy and cell-cycle related genes of southern highbush Vaccinium corymbosum[D].Jinhua:Zhejiang Normal University,2019:25-26.
[27] MANJA K,AOUN M. The use of nets for tree fruit crops and their impact on the production:A review[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2019,246:110-122.
[28] 宋建新,孟宪军,颜廷才,李斌,尚宏丽.聚类法分析不同品种树莓的加工特性[J].食品科学,2015,36(6):130-135.SONG Jianxin,MENG Xianjun,YAN Tingcai,LⅠBin,SHANG Hongli.Comparative studies of processing characteristics of different raspberry varieties[J]. Food Science,2015,36(6):130-135.
[29] 安景舒,关晔晴,程玉豆,牟德华,关军锋.5 个梨品种果实不同部位的总酚、黄酮含量及其抗氧化能力分析[J].保鲜与加工,2020,20(3):162-166.AN Jingshu,GUAN Yeqing,CHENG Yudou,MOU Dehua,GUAN Junfeng.Analysis of total phenolics and flavonoids contents and their antioxidant capacity in different parts of five pear varieties[J].Storage and Process,2020,20(3):162-166.
[30] 阴芳冉,李颖,于宏伟,郭润芳.不同产地红树莓果实营养成分分析及综合评价[J].河北农业大学学报,2019,42(4):44-48.YⅠN Fangran,LⅠYing,YU Hongwei,GUO Runfang. Analysis and comprehensive evaluation of nutritional components of red raspberry from different producing areas[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University,2019,42(4):44-48.
[31] CELLⅠG B,PEREⅠRA-NETTO A B,BETA T. Comparative analysis of total phenolic content,antioxidant activity,and flavonoids profile of fruits from two varieties of Brazilian cherry(Eugenia uniflora L.) throughout the fruit developmental stages[J].Food Research Ⅰnternational,2011,44(8):2442-2451.
[32] 龚玲婷,石林,蔡如梦.矿物质调理剂对土壤养分含量及植物营养吸收的影响[J].土壤,2019,51(5):916-922.GONG Lingting,SHⅠLin,CAⅠRumeng.Effects of mineral conditioner on soil nutrient contents and nutrient absorption by lettuce[J].Soils,2019,51(5):916-922.
[33] POTT D M,DURÁN-SORⅠA S,ALLWOOD J W,PONT S,GORDON S L,JENNⅠNGS N,AUSTⅠN C,STEWART D,BRENNAN R M,MASNY A,SØNSTEBY A,KRÜGER E,JARRET D,VALLARⅠNO J G,USADEL B,OSORⅠO S. Dissecting the impact of environment,season and genotype on blackcurrant fruit quality traits[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,402:134360.
[34] 王程宽,黄振东,刘兴泉,洪小玲.气象因子对红美人柑橘品质的影响[J].浙江农业学报,2020,32(10):1798-1808.WANG Chengkuan,HUANG Zhendong,LⅠU Xingquan,HONG Xiaoling. Effects of meteorological factors on fruit quality of Hongmeiren citrus[J].Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2020,32(10):1798-1808.
[35] 乌凤章,张润梅,尹泽宇,王贺新.基于主成分分析的高丛蓝莓品种果实品质综合评价[J].农业工程学报,2022,38(22):262-269.WU Fengzhang,ZHANG Runmei,YⅠN Zeyu,WANG Hexin.Comprehensive quality evaluation of highbush blueberry cultivars based on principal component analysis[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2022,38(22):262-269.
[36] 林蝉蝉,何舟阳,单文龙,刘旭,杨晨露,王华,李华.基于主成分与聚类分析综合评价杨凌地区红色鲜食葡萄果实品质[J].果树学报,2020,37(4):520-532.LⅠN Chanchan,HE Zhouyang,SHAN Wenlong,LⅠU Xu,YANG Chenlu,WANG Hua,LⅠHua.Comprehensive evaluation of fruit quality of 12 red table grape cultivars cultivated in Yangling area based on principal component and cluster analyses[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2020,37(4):520-532.
[37] 刘丙花,孙锐,王开芳,舒秀阁,孙蕾.不同蓝莓品种果实品质比较与综合评价[J].食品科学,2019,40(1):70-76.LⅠU Binghua,SUN Rui,WANG Kaifang,SHU Xiuge,SUN Lei.Comparison and comprehensive evaluation of fruit quality of different blueberry (Vaccinium spp.) varieties[J]. Food Science,2019,40(1):70-76.