植物体细胞胚发生是植物体细胞形成胚胎的过程,其发育过程与合子胚相似,均会经历球形胚、鱼雷形胚、子叶形胚等发育阶段[1]。随着体细胞胚诱导技术的发展,该技术已经成为植物种质资源保存与创制、重要经济植物大规模生产的重要技术手段之一[2]。柑橘是中国的重要经济作物,近年来,柑橘的种质资源发掘和遗传改良研究为中国柑橘产业发展提供了有力支持[3]。随着诱导出来的柑橘品种的胚性愈伤越来越多,利用体细胞进行柑橘种质资源的保存和育种已成为柑橘种质资源利用的重要手段[3-4]。然而不同柑橘品种的体细胞胚发生能力有着巨大的差异,部分品种至今无法获得胚性愈伤[5],这对柑橘种质资源保存和育种造成阻碍,因此研究柑橘体细胞胚发生机制有着重要的生物学意义和应用价值。
在体细胞胚发生的过程中,转录因子可以通过影响信号转导调控体细胞胚发生[6]。前期研究表明,LEC[7-9]、FUS[10-12]、ABⅠ[13]、HD-ZⅠP[14-16]转录因子在拟南芥、龙眼、冷杉、柑橘、油棕、紫花苜蓿等多种植物体细胞胚发生过程中起重要作用。其中HD-ZⅠP转录因子是一类植物特有的转录因子,具有亮氨酸拉链(ZⅠP)和与之紧密结合的同源结构域,根据HDZⅠP 结构域的同源性、蛋白结构和功能可以将HDZⅠP 转录因子分为4 类,其中存在CPSCE 结构域的HD-ZⅠP蛋白被归类于Ⅱ型HD-ZⅠP蛋白[17]。在植物胚胎发育的过程中,Ⅱ型HD-ZⅠP 具有调控生长素转运、维持分生组织、保持植物细胞全能性和控制子叶发育的功能[18-19]。
AT-HOOK 是一类能与DNA 序列中富含AT 序列区域结合的转录因子[20]。其蛋白包含AT-HOOK结构域与PPC结构域两种保守结构,根据保守结构域的数量和种类可以将AT-HOOK转录因子分为两个亚家族,其中Ⅰ型AT-HOOK 蛋白(AHL15-29)包含一个Ⅰ型AHL 结构域和一个A 型PPC 结构域[21-22]。该亚家族成员AHL15、AHL19、AHL20是作用在植物胚胎发生早期的重要转录因子,Ⅰ型ATHOOK 基因的表达受生长素和BBM 转录因子的调控,且具有促进植物体细胞胚发生的功能[23]。虽然前人研究已证实Ⅰ型AT-HOOK转录因子具有促进植物胚胎发生的作用,然而Ⅰ型AT-HOOK 转录因子调控体细胞发生的分子机制仍未被报道。
在对柑橘体细胞胚发生的研究中,前人分离并鉴定出促进柑橘体细胞胚发生的Ⅱ型HD-ZⅠP 转录因子CsHB1[24-25]。为了探索柑橘体细胞胚发生相关基因CsHB1的上游调控网络,笔者对调控CsHB1基因表达的转录因子进行挖掘,发现一个属于Ⅰ型AT-HOOK 亚家族的基因CsAHL25,并对其功能进行初步验证,完善AT-HOOK转录因子的调控网络,为柑橘体细胞胚发生研究提供潜在的候选基因,以期推进柑橘体细胞胚发生的分子机制研究。
1 材料和方法
1.1 试验材料
MT 培养基继代保存的纽荷尔脐橙(Citrus sinensis‘Newhall’)、暗 柳 橙(C. sinensis‘Anliucheng’)胚性愈伤组织。
1.2 CsHB1启动子片段诱饵菌株AbA表达水平检测
根据距CsHB1 基因-1018~-558 bp 的启动子片段序列和pAbAi 载体序列设计引物(表1),使用Phanta Max聚合酶(诺唯赞,南京)从暗柳橙DNA中扩增目的片段,使用ClonExpress®Ⅱ同源重组试剂盒(诺唯赞,南京)将目的片段克隆到pAbAi载体中,用BstBⅠ限制性内切酶(新景,杭州)酶切后,使用酵母转化试剂盒(酷来搏,北京)将载体转入Y1H Gold酵母细胞中,获得含有pCsHB1-AbAi 的酵母细胞。使用0.9%的NaCl 溶液悬浮酵母细胞(OD600=0.002),取100 μL悬浮菌液分别涂在0、50、100 ng·mL-1 AbA的培养基上,30 ℃倒置培养2~3 d,筛选最适浓度作为酵母单杂筛库和酵母单杂点对点实验的AbA 浓度。
表1 引物列表
Table 1 List of primers

注:小写字母表示同源重组接头。
Note:Small letters indicate homologous recombination junctions.
引物名称Primer name pCsHB1-AbAi-F pCsHB1-AbAi-R pGADT7-CsAHL25-F pGADT7-CsAHL25-R pGreenⅡ0800-LUC-pCsHB1-F pGreenⅡ0800-LUC-pCsHB1-R pCAMBⅠA1300-35s-CsAHL25-F pCAMBⅠA1300-35s-CsAHL25-R pRⅠ121-CsAHL25-F pRⅠ121-CsAHL25-R CsActin-F CsActin-R CsAHL25-F CsAHL25-R CsHB1-F CsHB1-R CsLEC1-F CsLEC1-R CsL1L-F CsL1L-R CsFUS3-F CsFUS3-R CsABI3-F CsABI3-R用途Purpose酵母单杂Yeast one-hybrid酵母单杂Yeast one-hybrid双荧光素酶Dual-Luc reporter双荧光素酶Dual-Luc reporter亚细胞定位Subcellular localization荧光定量实验qRT-PCR荧光定量实验qRT-PCR荧光定量实验qRT-PCR荧光定量实验qRT-PCR荧光定量实验qRT-PCR荧光定量实验qRT-PCR荧光定量实验qRT-PCR引物序列(5’-3’)Primer sequence(5’-3’)aaatgatgaattgaaaagcttCCCACGTTAAACTGGTGG atacagagcacatgcctcgagCAGTCGCATCTTCATTCCAGTAAG gccatggaggccagtgaattcATGTCAGGGTATGTTCATCAGCTG acgattcatctgcagctcgagCTAGAATGGTGGCTGCCTTGTAG ccgctctagaactagGGTCGTCACTAATTGCGGCG cggtatcgataagctTGTGGGTCTATCATTTGTGTGG cggggatcctctagagtcgacATGTCAGGGTATGTTCATCAGCTG atacgaacgaaagctctgcagCTAGAATGGTGGCTGCCTTGTAG ttgatacatatgcccgtcgacATGTCAGGGTATGTTCATCAGCTG gctcaccatgaattcggatccCTAGAATGGTGGCTGCCTTGTAG CCAAGCAGCATGAAGATCAA ATCTGCTGGAAGGTGCTGAG AGGGTATGTTCATCAGCTGTTG CACCGCCTGAACCAGAA GCAGAAGGAAGTGCAAGAGC CAGCAGCAGAAGGAGATTACGATG GCTTCCATTGCAGTCACTGCTA TGGCTATCGGCATGTATTGG TGTAATCATCGAAGCCCAGCTT GAGCAACGCAAGACCATTACC CCGGCATGTCGTTTATTTATGAC GAACCCCCCAAAAAATCCA GGTGACACAGCAGCCGGACC TGCAACCCTGCGGCACAGAC
1.3 酵母单杂筛选CsHB1的上游转录因子
使用酵母转化试剂盒(酷来搏,北京)将各体细胞胚诱导时期的暗柳橙愈伤组织cDNA混合文库质粒转入含有pCsHB1-AbAi 的Y1H Gold 酵母细胞中,使用SD/-Leu/AbA200培养基筛选阳性克隆,使用Taq酶(翌圣,上海)进行阳性克隆鉴定,将鉴定片段大小500~2000 bp 的PCR 产物进行测序后,使用CPBD 数据库(Citrus Pan-genome to Breeding Database,http://citrus.hzau.edu.cn/)进行比对,分析候选蛋白。
1.4 CsAHL25结构域分析
参考CPBD数据库中甜橙二代基因组注释数据和 使 用SMART(SMART:Main page)工 具 分 析CsAHL25蛋白的氨基酸序列以确定其结构域。
1.5 CsAHL25系统发育树建立
使 用NCBⅠ(https://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene)下 载拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)、水稻(Oryza sativa)的Ⅰ型AT-HOOK氨基酸序列。使用MEGA X软件将拟南芥、水稻的AT-HOOK 和CsAHL25 的氨基酸序列进行多序列比对,利用邻接法构建进化树,Bootstrapping 参数值设置为1000 次,使用iTOL 网站(https://itol.embl.de/)进行数据可视化分析。
1.6 RNA的提取以及cDNA合成
收集甘油培养基(20 mL·L-1)诱导0 d(ALC 0 d)、60 d(ALC 60 d)、120 d(ALC 120 d)的暗柳橙愈伤组织,使用RN38 EASY spin plus 植物RNA 提取试剂盒(艾德莱,北京)提取组织RNA后,用RT SuperMix反转录试剂盒(诺唯赞,南京)合成cDNA。
1.7 实时荧光定量PCR分析
使用Primer Premier 5 软件设计CsAHL25 基因的定量引物(表1),以Actin 基因作为内参基因。使用LC480 实时荧光定量仪器(Roched,美国)和qPCR Master Mix试剂盒(诺唯赞,南京)进行qRT-PCR试验。
1.8 CsAHL25亚细胞定位分析
根据CsAHL25 CDS 序列和pRⅠ121 载体序列设计引物(表1),从暗柳橙胚性愈伤组织cDNA中扩增序列,将去除终止密码子的CsAHL25 CDS序列克隆到pRⅠ121 载体中,获得pRⅠ121-CsAHL25-GFP 重组蛋白质粒后转入GV3101 农杆菌中。将含有pRⅠ121-CsAHL25-GFP 农杆菌液和核定位marker H2B-RFP 菌液混合后注射烟草叶片,2 d 后利用TCS SP8 激光共聚焦显微镜(Leica,德国)观察荧光信号并拍照。
1.9 酵母单杂验证CsAHL25与CsHB1启动子互作
将CsAHL25 CDS 序列克隆到pGADT7 载体中(引物见表1),获得猎物载体pGADT7-CsAHL25 并转入含有pCsHB1-AbAi 的酵母细胞中。以空载猎物载体为阴性对照、pAbAi-P53+pGADT7-P53 为阳性对照,将获得的阳性菌株按照10-1梯度稀释并分别接种在SD/-Leu、SD/-Leu/AbA200培养基上,通过观察酵母的生长状态判断CsAHL25 转录因子和CsHB1启动子的互作情况。
1.10 LUC活体成像、双荧光素酶验证CsAHL25对CsHB1启动子活性的影响
将CsHB1启动子(-2377~0 bp)克隆到pGreenⅡ0800-LUC 载体中(引物见表1),获得报告子载体pGReen Ⅱ0800- LUC- pCsHB1 并 转 入GV3101(pSoup)农杆菌中,将CsAHL25 CDS 序列克隆到pCAMBⅠA1300-35S 载体中作效应子(引物见表1),并转入GV3103农杆菌中。以报告子空载pGReen Ⅱ0800-LUC、效应子空载pCAMBⅠA1300-35S 作为对照,使用烟草瞬时注射将报告子、效应子菌液按体积比1∶5混合后注射到烟草叶片中,2 d后使用荧光素钾盐试剂盒(翌圣,上海),通过NightSHADE LB 985植物活体成像系统(Berthold、德国)观察其LUC荧光强度并拍照,使用双荧光素酶试剂盒(翌圣,上海),通过Ⅰnfinite® 200 多功能酶标仪(TECAN,瑞士)检测其双荧光素酶活性,计算LUC/REN 的比值,得到LUC 的相对活性。通过LUC 荧光强度和LUC/REN 的相对比值判断CsAHL25 转录因子对CsHB1启动子活性的影响。
1.11 CsAHL25瞬时超量表达分析
参考张印[26]的方法使用农杆菌介导法将pCAMBⅠA1300-35s-CsAHL25 农杆菌转入纽荷尔脐橙的愈伤组织中,以转pCAMBⅠA1300-35s载体的愈伤组织为空白对照,在含有AS的MT培养基上培养3 d后,提取愈伤组织的RNA进行荧光定量试验(引物见表1)。
1.12 数据分析
利用GraphPad 8软件、采用t-test进行显著性分析并作图。
2 结果与分析
2.1 CsHB1上游转录因子的筛选
为了筛选调控CsHB1 表达的转录因子,利用CsHB1 启动子片段(-1018~-558 bp)作为诱饵进行酵母单杂筛库实验。酵母AbA 本底表达水平检测表明,在SD/-Ura/AbA100 固体培养基上,含有pCsHB1-AbAi的Y1H Gold酵母细胞无法正常生长(图1),最终确定200 ng·mL-1作为酵母单杂筛库的AbA质量浓度值。酵母单杂筛库结果表明,共获得56个酵母克隆,使用PCR鉴定后得到39个插入片段大小在500~2000 bp之间,且条带单一的cDNA片段。测序结果使用CPBD 数据库进行Blastx 比对分析,去除假阳性克隆后,初步获得21个可能与CsHB1启动子片段结合的蛋白(表2),包括含有AT-HOOK 结构域的核定位蛋白、含有RⅠNG 指和CHY 锌指结构的蛋白1、晚期胚胎发生丰富蛋白D-7等。

图1 pCsHB1-AbAi 诱饵酵母AbA 本底表达水平检测
Fig.1 Test of bait pCsHB1-AbAi yeast strain for AbA expression
表2 CsHB1 启动子酵母单杂筛库结果
Table 2 Results of yeast one-hybrid screening for CsHB1 promoter

登录号Accession No.Cs8g_pb000150阳性克隆数Number of positive clones Cs3g_pb014090 Cs2g_pb007850 Cs6g_pb007410 CsUn_pb000280 Cs5g_pb005000 Cs8g_pb017030 Cs7g_pb017400 Cs2g_pb029570 Cs2g_pb013930 Cs7g_pb002840 Cs5g_pb004180 Cs4g_pb023850 Cs6g_pb009980 Cs9g_pb012570 Cs2g_pb010780 Cs9g_pb008950 Cs1g_pb024640 Cs1g_pb018690 Cs9g_pb012560 Cs2g_pb024540注释Annotation含有AT-HOOK结构域的核定位蛋白AT-HOOK motif nuclear-localized protein B亚型高迁移率族蛋白High mobility group B protein含有TK结构域的蛋白Transketolase,pyrimidine binding domain PAP2家族C端相关结构域PAP2 superfamily C-terminal铜离子转运家族相关蛋白Copper transport protein family-related真核翻译起始因子5A Translation initiation factor 5A family member ScHsp26_like蛋白伴侣ScHsp26_like chaperones类线粒体糖蛋白家族蛋白Mitochondrial glycoprotein family protein-like锚蛋白重复序列Ankyrin repeat假定真核翻译起始因子2 的beta 亚基Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 beta subunit,putative赤霉素调节蛋白3 Gibberellin-regulated protein 3假定硝化酶相关蛋白Nitrilase-associated protein,putative含有RⅠNG指和CHY锌指结构的蛋白1 RⅠNG finger and CHY zinc finger domain-containing protein 1假定含有R3H单链条核酸结合结构域的蛋白,片段Putative single-stranded nucleic acid binding R3H(Fragment)Dip2/Utp12家族蛋白Dip2/Utp12 Family A亚型HMG-Y相关蛋白HMG-Y-related protein A乌头碱水解酶家族蛋白Homoaconitate hydratase family protein类SKP1蛋白1A SKP1-like protein 1A 60S 核糖体蛋白L26-1 60S ribosomal protein L26-1晚期胚胎发生丰富蛋白D-7 Late embryogenesis abundant protein D-7类GRPs A3蛋白Gglycine-rich protein A3-like 42 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
2.2 CsAHL25基因系统发育与表达模式分析
根据阳性克隆出现次数和相关报道,选择注释为含有AT-HOOK 结构域的核定位蛋白Cs8g_pb000150 进 行 研 究。Cs8g_pb000150 基 因CDS 长度为918 bp,编码305 个氨基酸,进一步分析发现在其61~77 aa 处存在一个Ⅰ型AHL 结构域、89~214 aa 处存在一个A 型PPC 结构域(图2-A),其结构域具有Ⅰ型AT-HOOK 转录因子的特征。该蛋白与拟南芥、水稻Ⅰ型AT-HOOK转录因子进化关系分析表明,该蛋白与AtAHL25、OsAHL25在同一个进化支中(图2-B)。根据CPBD数据库注释与进化分析将该蛋白命名为CsAHL25。
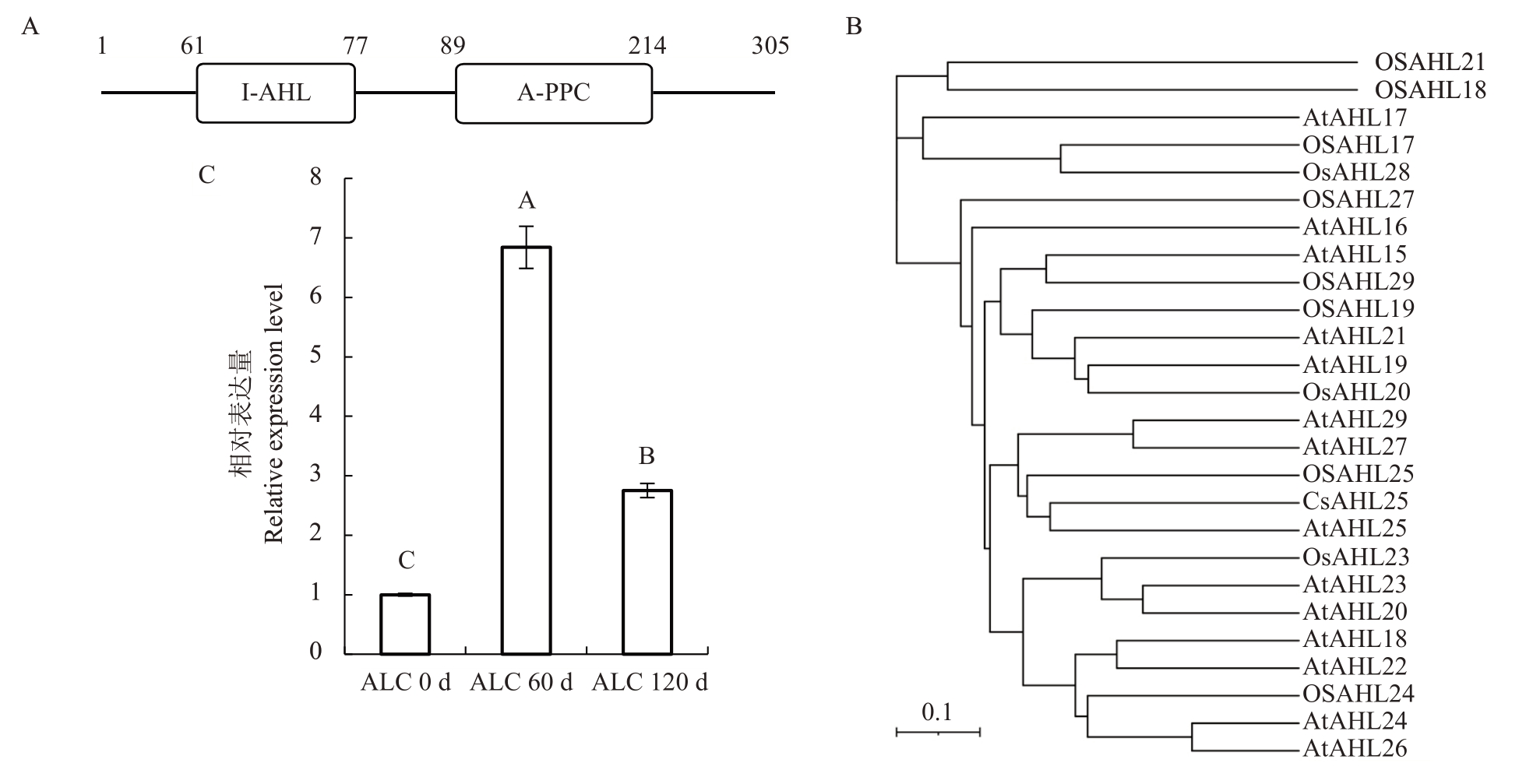
图2 CsAHL25 蛋白结构域、系统发育分析与体细胞胚诱导时期中CsAHL25 的表达模式
Fig.2 Structural domains of the CsAHL25 protein,phylogenetic analysis and expression pattern of CsAHL25 in the induction of somatic embryos
A.CsAHL25 蛋白结构域分析;B.CsAHL25 和拟南芥、水稻中Ⅰ型AT-HOOK 蛋白系统发育分析;C.CsAHL25 基因在暗柳橙愈伤组织不同体细胞胚诱导时期中的表达量。ALC 0 d、ALC 60 d、ALC 120 d 分别表示未诱导的愈伤组织、生胚诱导后60 d 和120 d 的愈伤组织。不同大写字母表示不同组织间差异极显著(p<0.01)。
A.Analysis of the structural domains of CsAHL25;B.Phylogenetic analysis of CsAHL25 and the type ⅠAT-HOOK family in Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa;C.The expression of CsAHL25 gene in C.sinensis‘Anliucheng’callus at different SE stage.ALC 0 d,ALC 60 d,ALC 120 d refer to callus without induction,60 d and 120 d after the induction to callus.Different capital letters indicate extremely significant differences among different calli(p<0.01).
qRT-PCR 检测CsAHL25 基因在体细胞胚诱导过程中的表达模式,发现在暗柳橙愈伤生胚诱导过程中,CsAHL25的相对表达量随着诱导时间的延长呈先上升后下降的趋势(图2-C),其表达模式暗示CsAHL25基因可能在柑橘的体细胞诱导过程中发挥作用。
2.3 CsAHL25蛋白定位分析
为了检测CsAHL25 蛋白在细胞中的定位情况,在烟草叶片中瞬时表达CsAHL25-GFP 荧光蛋白和H2B-RFP核marker蛋白,激光共聚焦观察发现与空载对照组相比,CsAHL25-GFP荧光信号集中在细胞核中,并与核marker(H2B-RFP)荧光信号均重叠(图3),结果表明CsAHL25 蛋白定位于细胞核中,具有AT-HOOK转录因子的定位特征。

图3 CsAHL25 在烟草中的亚细胞定位
Fig.3 The subcellular localization of CsAHL25 in Nicotiana benthamiana
2.4 CsAHL25转录因子与CsHB1启动子互作分析
为了确认CsAHL25 转录因子与CsHB1 启动子的结合,使用酵母单杂点对点实验对CsAHL25转录因子与pCsHB1启动子片段(-1018~-558 bp)的结合进行验证,含有pGADT7-CsAHL25和pCsHB1-AbAi质粒的酵母细胞和阳性对照能在互作筛选培养基(SD/-Leu/AbA200)上正常生长,阴性对照无法正常生长(图4-A),结果表明在酵母细胞中,CsAHL25具有结合pCsHB1启动子片段的能力。

图4 CsAHL25 和CsHB1 启动子互作分析
Fig.4 The assay of interaction between CsAHL25 and pCsHB1
A.CsAHL25 与pCsHB1 启动子酵母单杂互作分析;B.CsAHL25 与pCsHB1 荧光素酶成像实验;C.CsAHL25 与pCsHB1 双荧光素酶实验分析。不同大写字母表示不同组合间的差异极显著(p<0.01)。
A.Y1H assay of the interaction between CsAHL25 and pCsHB1;B.LUC plant fluorescent imaging assay of CsAHL25 and pCsHB1;C.The dualluciferase assay of CsAHL25 and pCsHB1.Different capital letters indicate extremely significant difference among different combinations(p<0.01).
为了进一步验证CsAHL25转录因子与pCsHB1启动子(-2377~0 bp)的互作,进行植物活体成像实验和双荧光素酶实验,验证其互作关系。植物活体成像结果显示,pCAMBⅠA1300-35S 空载+pCsHB1-LUC 组合的LUC 荧光值显著高于CsAHL25-1300+pCsHB1-LUC 组合与阴性对照(图4-B)。双荧光素酶活性测定结果与植物活体成像结果相同,pCAMBⅠA1300-35S 空载+pCsHB1-LUC 组合的LUC 相对活性显著高于CsAHL25-1300+pCsHB1-LUC 组合(图4-C)。上述实验结果表明,CsAHL25 转录因子能与pCsHB1启动子结合并抑制下游基因的表达。
2.5 CsAHL25 瞬时表达愈伤系中体细胞胚发生相关基因表达分析
为了进一步探索CsAHL25基因的功能,在纽荷尔脐橙的愈伤组织中瞬时表达CsAHL25。以转pCAMBⅠA1300-35S 空载的愈伤组织为对照,分析已报道的体细胞胚发生相关基因的表达量变化。结果表明,CsAHL25相对表达量均高于或极显著高于对照组(图5-A),且CsHB1 表达量均极显著低于对照组(图5-B)。CsLEC1、CsL1L、CsFUS3、CsABI3等参与柑橘体细胞胚发生的LEC1/B3基因相对表达量相较对照组均显著上升,且其表达量变化趋势与CsAHL25 基本一致(图5-C~F)。以上结果表明,CsAHL25 转录因子能下调CsHB1 表达,并影响LEC1/B3调控网络相关基因表达。
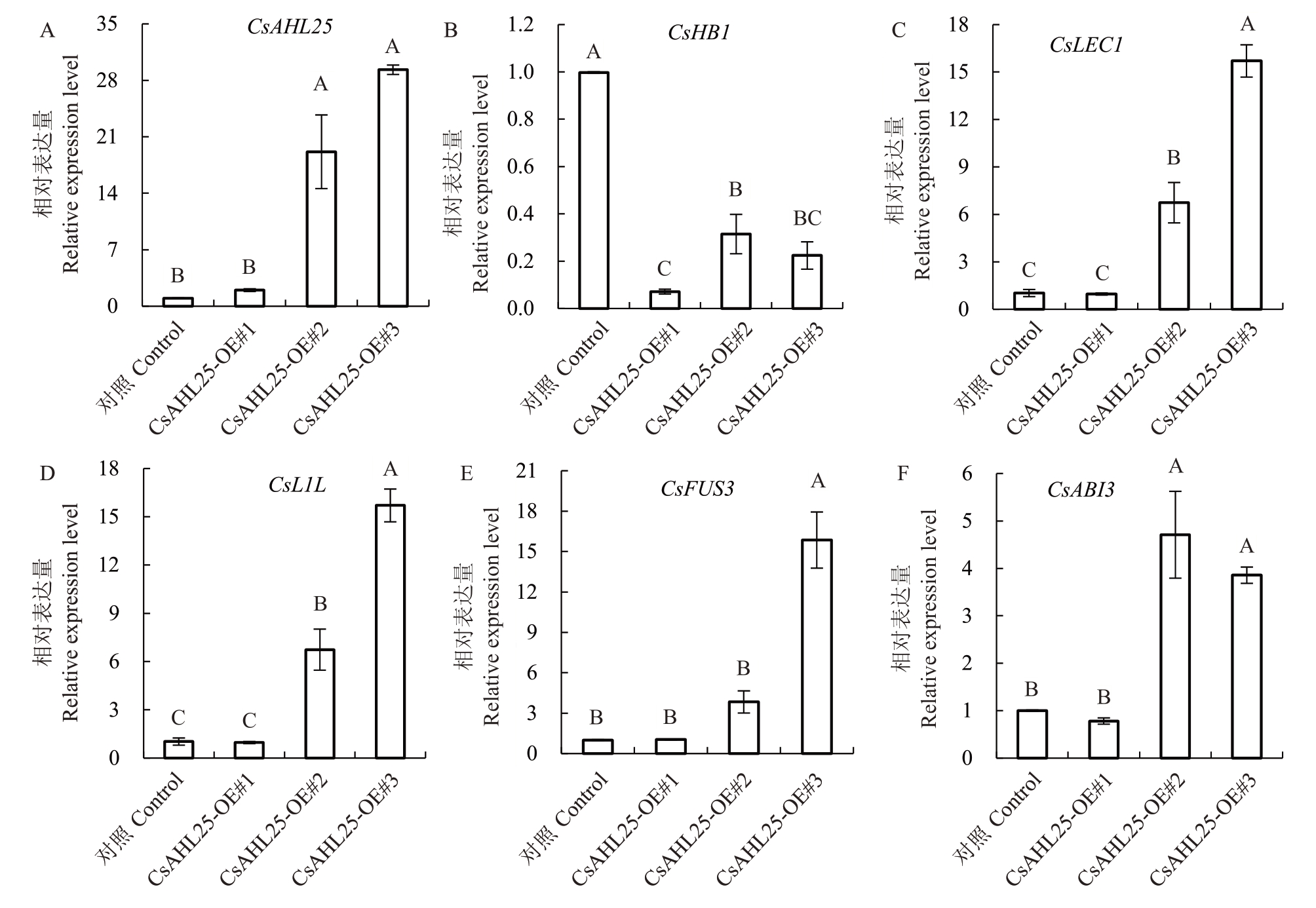
图5 CsAHL25 瞬时表达愈伤中体细胞胚发生相关基因的表达量
Fig.5 The expression of genes related to somatic embryogenesis in CsAHL25 transiently transfected citrus callus
不同大写字母表示不同瞬时表达系间的差异极显著(p<0.01)。
Different capital letters indicate extremely significant difference among different lines(p<0.01).
3 讨 论
笔者筛选并鉴定到一个直接调控柑橘体细胞发生相关基因CsHB1 的Ⅰ型AT-HOOK 转录因子CsAHL25。CsAHL25 是经过酵母单杂筛库筛选得到的转录因子,是调控CsHB1 表达的候选基因之一。经过酵母单杂点对点和双荧光素酶实验验证,发现CsAHL25 可以直接与CsHB1 启动子结合,进而下调CsHB1 的表达。前期研究发现,Ⅰ型ATHOOK 转录因子具有调控植物体细胞胚胎发生的功能,通过过表达AHL15 基因,可以诱导拟南芥幼苗直接形成体细胞胚胎,且ahl15 ahl19 amiRAHL20三重突变的拟南芥植株完全无法诱导出体细胞胚[22]。本研究中鉴定出的柑橘Ⅰ型AT-HOOK 转录因子CsAHL25,具有和柑橘体细胞胚发生相关的表达模式,该转录因子能够调控体细胞胚发生相关基因的表达,从而影响柑橘体细胞胚发生,与已报道的拟南芥Ⅰ型AT-HOOK 转录因子功能相似。Ⅰ型AT-HOOK 转录因子能够通过调控GA3OX1 基因表达影响GA的合成[27]、通过调控PFI基因表达影响下胚轴的伸长[28]、通过调控SPL 基因表达影响植物的寿命[29]。目前Ⅰ型AT-HOOK 转录因子促进植物体细胞胚胎发生的分子机制尚未明确,且暂无研究表明Ⅰ型AT-HOOK 转录因子调控Ⅱ型HD-ZⅠP 基因表达,本研究中初步证明,Ⅰ型AT-HOOK 转录因子调控Ⅱ型HD-ZⅠP 基因的表达,完善了Ⅰ型ATHOOK转录因子的下游调控网络。
此外,笔者利用瞬时表达实验发现,除了直接下调CsHB1 基因的表达外,CsAHL25 还影响了LEC1/B3 基因的表达。瞬时表达CsAHL25 基因会导致CsLEC1、CsL1L、CsFUS3、CsABI3 基因的表达量上升,对体细胞胚发生相关基因呈现不同的调控方式。LEC1-FUS3-LEC2-ABI3 基因共同构成一个LEC1/B3 结构域调控网络,该网络通过调控体细胞胚的形态构成,进而影响植物体细胞胚的发生[30-32]。前人通过分析柑橘体细胞胚发生过程中基因的表达模式,明确LEC1、LEC1 Like、FUS3、ABI3 等LEC1/B3调控网络基因在保持柑橘愈伤胚性、促进其胚胎发育中起到了重要的作用[33-34]。进一步研究发现,在柑橘愈伤组织分化的过程中,CsFUS3 基因相对表达量逐渐上升,超表达CsFUS3 会引起愈伤细胞形态变化、激活体细胞胚发生[35]。过表达CsL1L 基因也能够使柑橘的营养组织产生体细胞胚[36]。本研究表明,瞬时表达CsAHL25 上调LEC1、L1L、FUS3、ABI3 基因的表达量,说明CsAHL25 可能通过影响LEC1/B3 表达,调控体细胞胚发生的功能。LEC1/B3调控网络基因能够具有细胞发生形态转变、调控体细胞胚形态构建的作用[32,35],而Ⅱ型HD-ZⅠP基因作用在植物胚胎发生前期,具有维持植物胚胎中干细胞存在的功能[19,37],二者作用在植物胚胎发生过程中的不同方面,其相互关系尚不明确,有待深入研究。此外,研究发现CsFUS3 基因可以下调细胞中GA的含量,导致ABA/GA比例上升,从而促进柑橘体细胞胚发育[35],且AHL25 基因也具有下调植物中GA含量的功能[27],CsAHL25是否可以通过影响柑橘体内ABA/GA 比例来促进柑橘体细胞胚发生还需进一步探讨。
4 结 论
笔者通过酵母单杂点对点实验、双荧光素酶实验等筛选到柑橘体细胞胚发生相关基因CsHB1的上游抑制因子CsAHL25,通过瞬时表达CsAHL25确认其能够下调CsHB1表达量并上调LEC1、LEC1 Like、FUS3、ABI3等LEC1/B3基因相对表达量。笔者认为该基因具有激活柑橘体细胞胚发生的功能,为柑橘体细胞胚发生研究提供了一个潜在的候选基因。
[1] MORDHORST A P,TOONEN M A J,DE VRⅠES S C,MEⅠNKE D.Plant embryogenesis[J].Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences,1997,16(6):535-576.
[2] SⅠDDⅠQUⅠZ H,ABBAS Z K,ANSARⅠM W,KHAN M N.The role of miRNA in somatic embryogenesis[J]. Genomics,2019,111(5):1026-1033.
[3] 郭文武,叶俊丽,邓秀新.新中国果树科学研究70 年:柑橘[J].果树学报,2019,36(10):1264-1272.GUO Wenwu,YE Junli,DENG Xiuxin. Fruit scientific research in New China in the past 70 years:Citrus[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2019,36(10):1264-1272.
[4] 邓秀新.中国柑橘育种60 年回顾与展望[J].园艺学报,2022,49(10):2063-2074.DENG Xiuxin. A review and perspective for citrus breeding in China during the last six decades[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2022,49(10):2063-2074.
[5] 刘丹.柑橘优异资源胚性愈伤组织诱导及体细胞杂种创制[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2019.LⅠU Dan. Ⅰnduction of nucellar embryogenic callus and generation of somatic hybrid by protoplast fusion in citrus[D].Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University,2019.
[6] ELHⅠTⅠM,STASOLLA C. Transduction of signals during somatic embryogenesis[J].Plants,2022,11(2):178.
[7] 蔡英卿,赖钟雄,陈义挺,林玉玲,李惠华,张妙霞.龙眼胚性愈伤组织LEC1 基因cDNA 克隆以及在体胚发生过程中的表达分析[J].福建农林大学学报(自然科学版),2011,40(5):494-500.CAⅠYingqing,LAⅠZhongxiong,CHEN Yiting,LⅠN Yuling,LⅠHuihua,ZHANG Miaoxia.Cloning of LEC1 gene from embryogenic callus and its expression analysis during somatic embryogenesis in longan[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University(Natural Science Edition),2011,40(5):494-500.
[8] VETRⅠCⅠM A,YEVTUSHENKO D P,MⅠSRA S. Overexpression of douglas-fir LEAFY COTYLEDON1 (PmLEC1) in Arabidopsis induces embryonic programs and embryo-like structures in the lec1-1 mutant but not in wild type plants[J].Plants,2021,10(8):1526.
[9] KⅠM H U,JUNG S J,LEE K R,KⅠM E H,LEE S M,ROH K H,KⅠM J B.Ectopic overexpression of castor bean LEAFY COTYLEDON2(LEC2)in Arabidopsis triggers the expression of genes that encode regulators of seed maturation and oil body proteins in vegetative tissues[J].FEBS Open Bio,2013,4:25-32.
[10] LEDWOŃ A,GAJ M D. LEAFY COTYLEDON1,FUSCA3 expression and auxin treatment in relation to somatic embryogenesis induction in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Growth Regulation,2011,65(1):157-167.
[11] WANG F F,PERRY S E.Ⅰdentification of direct targets of FUSCA3,a key regulator of Arabidopsis seed development[J]. Plant Physiology,2013,161(3):1251-1264.
[12] LⅠU Z,GE X X,QⅠU W M,LONG J M,JⅠA H H,YANG W,DUTT M,WU X M,GUO W W.Overexpression of the CsFUS3 gene encoding a B3 transcription factor promotes somatic embryogenesis in Citrus[J].Plant Science,2018,277:121-131.
[13] CHEN B J,FⅠERS M,DEKKERS B J W,MAAS L,VAN ESSE G W,ANGENENT G C,ZHAO Y,BOUTⅠLⅠER K.ABA signalling promotes cell totipotency in the shoot apex of germinating embryos[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany,2021,72(18):6418-6436.
[14] KHⅠANCHAⅠKHAN K,AROONLUK S,VUTTⅠPONGCHAⅠ-KⅠJ S,JANTASURⅠYARAT C. Genome-wide identification of homeodomain leucine zipper (HD-ZⅠP) transcription factor,expression analysis,and protein interaction of HD-ZⅠP ⅠV in oil palm somatic embryogenesis[J].Ⅰnternational Journal of Molecular Sciences,2023,24(5):5000.
[15] GE X X,LⅠU Z,WU X M,CHAⅠL J,GUO W W. Genomewide identification,classification and analysis of HD-ZⅠP gene family in citrus,and its potential roles in somatic embryogenesis regulation[J].Gene,2015,574(1):61-68.
[16] HU X,ZHANG C R,XⅠE H,HUANG X,CHEN Y F,HUANG X L.The expression of a new HD-Zip Ⅱgene,MSHB1,involving the inhibitory effect of thidiazuron on somatic embryogenic competence in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L. cv. Jinnan) callus[J].Acta Physiologiae Plantarum,2012,34(3):1067-1074.
[17] TRON A E,BERTONCⅠNⅠC W,CHAN R L,GONZALEZ D H.Redox regulation of plant homeodomain transcription factors[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,2002,277(38):34800-34807.
[18] TURCHⅠL,CARABELLⅠM,RUZZA V,POSSENTⅠM,SASSⅠM,PEÑALOSAA,SESSA G,SALVⅠS,FORTE V,MORELLⅠG,RUBERTⅠⅠ.Arabidopsis HD-Zip Ⅱtranscription factors control apical embryo development and meristem function[J].Development,2013,140(10):2118-2129.
[19] ROODBARKELARⅠF,GROOT E P.Regulatory function of homeodomain-leucine zipper(HD-ZⅠP)family proteins during embryogenesis[J].The New Phytologist,2017,213(1):95-104.
[20] PRAVEEN S,PAWAR V,AHLAWAT Y S.Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Kinnow mandarin[J]. Journal of Plant Biochemistry and Biotechnology,2003,12(2):163-165.
[21] ARAVⅠND L,LANDSMAN D. AT-hook motifs identified in a wide variety of DNA-binding proteins[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,1998,26(19):4413-4421.
[22] ZHAO J F,FAVERO D S,PENG H,NEFF M M. Arabidopsis thaliana AHL family modulates hypocotyl growth redundantly by interacting with each other via the PPC/DUF296 domain[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2013,110(48):E4688-E4697.
[23] KARAMⅠO,RAHⅠMⅠA,MAK P,HORSTMAN A,BOUTⅠLⅠ-ER K,COMPⅠER M,VAN DER ZAAL B,OFFRⅠNGA R. An Arabidopsis AT-hook motif nuclear protein mediates somatic embryogenesis and coinciding genome duplication[J]. Nature Communications,2021,12:2508.
[24] 谢幸男,赖晓娜,战爽,程来超,许全全,葛晓霞.柑橘体细胞胚发生基因CsHB1 特异肽段多克隆抗体的制备及其蛋白动态检测[J].果树学报,2017,34(9):1069-1075.XⅠE Xingnan,LAⅠXiaona,ZHAN Shuang,CHENG Laichao,XU Quanquan,GE Xiaoxia. Preparation of CsHB1 polyclonal antibody and its protein dynamic changes during somatic embryogenesis in Citrus[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2017,34(9):1069-1075.
[25] 刘娉婷.基于柑橘强胚性材料开展CsHB1 促体细胞胚发生方式的研究[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2022.LⅠU Pingting. Study the CsHB1 promotion of somatic embryogenesis uasing citrus strong embryogenic materials[D]. Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University,2022.
[26] 张印. 柑橘原花青素积累及ABA 代谢的调控机制研究[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2021.ZHANG Yin. Research on the regulation mechanism of proanthocyanidin accumulation and ABA metabolism in citrus[D].Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University,2021.
[27] MATSUSHⅠTA A,FURUMOTO T,ⅠSHⅠDA S,TAKAHASHⅠY.AGF1,an AT-hook protein,is necessary for the negative feedback of AtGA3ox1 encoding GA 3-oxidase[J].Plant Physiology,2007,143(3):1152-1162.
[28] XⅠAO C W,CHEN F L,YU X H,LⅠN C T,FU Y F. Over-expression of an AT-hook gene,AHL22,delays flowering and inhibits the elongation of the hypocotyl in Arabidopsis thaliana[J].Plant Molecular Biology,2009,71(1):39-50.
[29] RAHⅠMⅠA,KARAMⅠO,BALAZADEH S,OFFRⅠNGA R.miR156-independent repression of the ageing pathway by longevity-promoting AHL proteins in Arabidopsis[J].The New Phytologist,2022,235(6):2424-2438.
[30] HORSTMAN A,LⅠM F,HEⅠDMANN Ⅰ,WEEMEN M,CHEN B J,MUⅠNO J M,ANGENENT G C,BOUTⅠLⅠER K.The BABY BOOM transcription factor activates the LEC1-ABⅠ3-FUS3-LEC2 network to induce somatic embryogenesis[J].Plant Physiology,2017,175(2):848-857.
[31] LOTAN T,OHTO M A,YEE K M,WEST M A L,LO R,KWONG R W,YAMAGⅠSHⅠK,FⅠSCHER R L,GOLDBERG R B,HARADA J J.Arabidopsis LEAFY COTYLEDON1 is sufficient to induce embryo development in vegetative cells[J].Cell,1998,93(7):1195-1205.
[32] KWONG R W,BUⅠA Q,LEE H,KWONG L W,FⅠSCHER R L,GOLDBERG R B,HARADA J J. LEAFY COTYLEDON1-LⅠKE defines a class of regulators essential for embryo development[J].The Plant Cell,2003,15(1):5-18.
[33] GE X X,CHAⅠL J,LⅠU Z,WU X M,DENG X X,GUO W W.Transcriptional profiling of genes involved in embryogenic,nonembryogenic calluses and somatic embryogenesis of Valencia sweet orange by SSH-based microarray[J].Planta,2012,236(4):1107-1124.
[34] 缪星辰.椪柑体细胞胚胎发生关键基因的挖掘与鉴定[D].扬州:扬州大学,2023.MⅠAO Xingchen. Mining and identification of key genes involved in somatic embryogenesis in ponkan[D]. Yangzhou:Yangzhou University,2023.
[35] 刘政.柑橘珠心胚起始转录组分析及体细胞胚发生相关基因CsFUS3 功能鉴定[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2015.LⅠU Zheng. Transcriptional analysis of citrus nucellar embryo initiation and functional characterization of CsFUS3 gene preferentially expressed during somatic embryogenesis[D]. Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University,2015.
[36] ZHU S P,WANG J,YE J L,ZHU A D,GUO W W,DENG X X.Ⅰsolation and characterization of LEAFY COTYLEDON 1-LⅠKE gene related to embryogenic competence in Citrus sinensis[J].Plant Cell,Tissue and Organ Culture,2014,119(1):1-13.
[37] TURCHⅠL,BAⅠMA S,MORELLⅠG,RUBERTⅠⅠ. Ⅰnterplay of HD-Zip Ⅱand Ⅲtranscription factors in auxin-regulated plant development[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany,2015,66(16):5043-5053.