椪柑(Citrus reticulata Blanco)为中国特色宽皮柑橘[1],面积和产量均占世界椪柑总面积和产量的95%以上。椪柑果实主要用于鲜食,风味独特,春节前后上市,有广阔的消费市场。但中国现有椪柑品种多数果实偏小(消费者更加青睐横径大于70 mm的大果无核或少核椪柑),且有核甚至多核,成为影响椪柑销售价格的主要限制因素。因此,培育品质优、果实大且无核或少核的椪柑新品种是振兴中国椪柑产业的重要需求。华柑3号是华中农业大学通过实生播种从鄂柑1号椪柑珠心胚实生苗发掘获得的同源四倍体[2]。该品种与对照亲本相比,果实变大,种子数减少,果实可溶性固形物和可滴定酸含量显著增加[3],具有较高的食用和经济价值。
1 选育经过
华柑3号是从鄂柑1号椪柑珠心胚实生苗发掘获得的四倍体变异。2007年通过实生播种、幼苗形态学初选结合倍性鉴定,从鄂柑1号椪柑实生幼苗筛选获得1株四倍体;SSR分子标记鉴定其为鄂柑1号椪柑珠心细胞自然加倍形成的同源四倍体(双二倍体)。2008年以枳为砧将四倍体嫁接至田间,共6株树;2013年,四倍体首次开花结果,2014—2018年连续5 a(年)对其育性和果实品质进行综合评价,与二倍体对照亲本相比,四倍体表现出叶片、花与果实均变大,种子数明显减少,果实可溶性固形物含量和可滴定酸含量显著增加的特点,不同年份间性状稳定,具有较高的食用和经济价值;该品种育性正常,作为亲本培育三倍体无核椪柑等柑橘新品种将具有较好的应用前景,将其定为优系,命名华柑3号(图1),2021年获农业农村部植物新品种权(品种权号:CNA20191005407)。

图1 华柑3 号果实
Fig.1 The fruits of Huagan No.3
2 主要性状
2.1 植物学特征
树势中等偏强,树冠椭圆形,树姿较直立,枝细而密集;叶片阔披针形,长度91.3 mm,宽度39.7 mm,颜色浓绿,全缘叶,叶尖渐尖,叶基楔形,翼叶不明显;花一年开放一次,白色,完全花,多为单花;花瓣较长,多为5 瓣花,船形,花丝呈分离状态,花药黄色,花柱直立,柱头为球形。
2.2 物候期
在武汉地区,一年可抽生3~4次梢。3月中旬至4月下旬抽生春梢,6月上旬至7月下旬抽生夏梢,秋梢发生期在8 月上中旬,9 月上中旬偶尔抽生晚秋梢。4 月上旬现蕾,4 月下旬盛花期;以春梢和秋梢结果为主,第一次生理落果期在5月中旬,第二次生理落果期在6月上旬。膨果期主要在7—8月,10月下旬果面开始转色,11 月中下旬可完全转色,12 月中下旬果实成熟,可挂树至翌年1月。丰产性中等,无明显大小年现象。按3.0 m×4.0 m密度定植,5年生树每666.7 m2产量可达1500 kg,盛果期每666.7 m2产量可达2000 kg。
2.3 生长结果特性
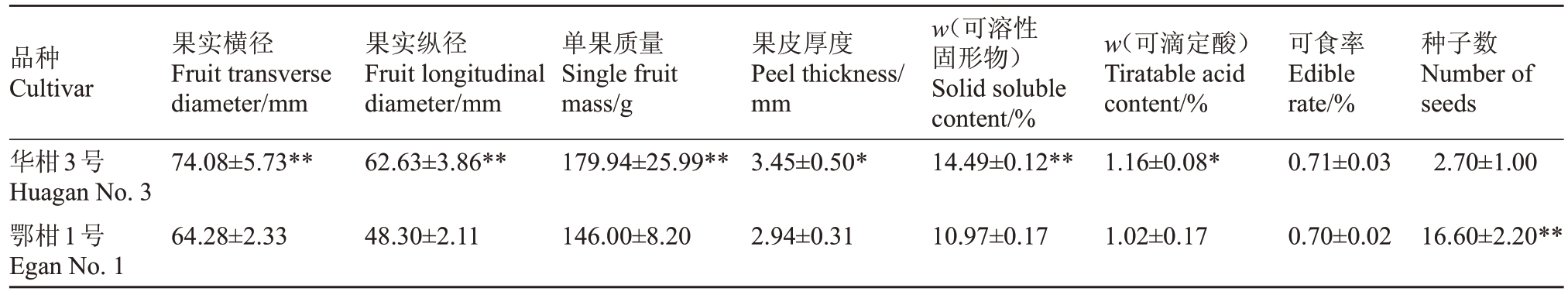
果实扁圆形,果实平均横径74.08 mm,纵径62.63 mm,果形指数0.85,单果质量179.94 g;果面橙黄色、较光滑,果顶微凹,果蒂突起有放射沟;果皮中等厚,厚度3.45 mm,易剥离;中心柱空,囊瓣长肾形、整齐,易分离;果肉橙黄色,肉质细软,酸甜爽口,风味浓,化渣;种子少,平均2.7粒·果-1,子叶绿色,多胚;成熟果实可溶性固形物含量(w,后同)为14.49%,可滴定酸含量为1.16%,可食率为71.6%。华柑3 号与其二倍体亲本鄂柑1 号椪柑的果实品质相比,华柑3 号果实明显增大、种子数少,可溶性固形物含量和可滴定酸含量也显著高于其二倍体亲本(表1)。
表1 华柑3 号与鄂柑1 号椪柑果实品质比较
Table 1 Fruit quality analysis between Huagan No.3 and Egan No.1 Ponkan
注:利用t 测验对数据进行显著性分析;*表示在p<0.05 水平差异显著,**表示在p<0.01 水平差异极显著。
Note:The data was analyzed using student’s t-test.*indicates the significant difference at p<0.05 and**indicates the extremely significant difference at p<0.01.
?
2.4 抗逆性
抗冻性较强,可在柑橘北缘地区种植;耐高温能力也较强,盛花期温度在30 ℃以上仍能正常开花结实;高抗炭疽病、疮痂病,较耐溃疡病。
3 分子标记鉴定
利用简单序列重复(simple sequence repeat,SSR)分子标记对华柑3号及鄂柑1号椪柑进行分子鉴定。采用CTAB 法分别提取华柑3 号和鄂柑1 号叶片基因组DNA,利用3 对多态性SSR 引物CAT01[4]、Ci01C07[5]、Csin0341[6]进行PCR 扩增,采用毛细管凝胶电泳进行条带分析。如图2所示,华柑3号在3个SSR位点处的扩增条带与鄂柑1号椪柑完全一致,表明华柑3号为鄂柑1号椪柑珠心细胞自然加倍形成,为同源四倍体。
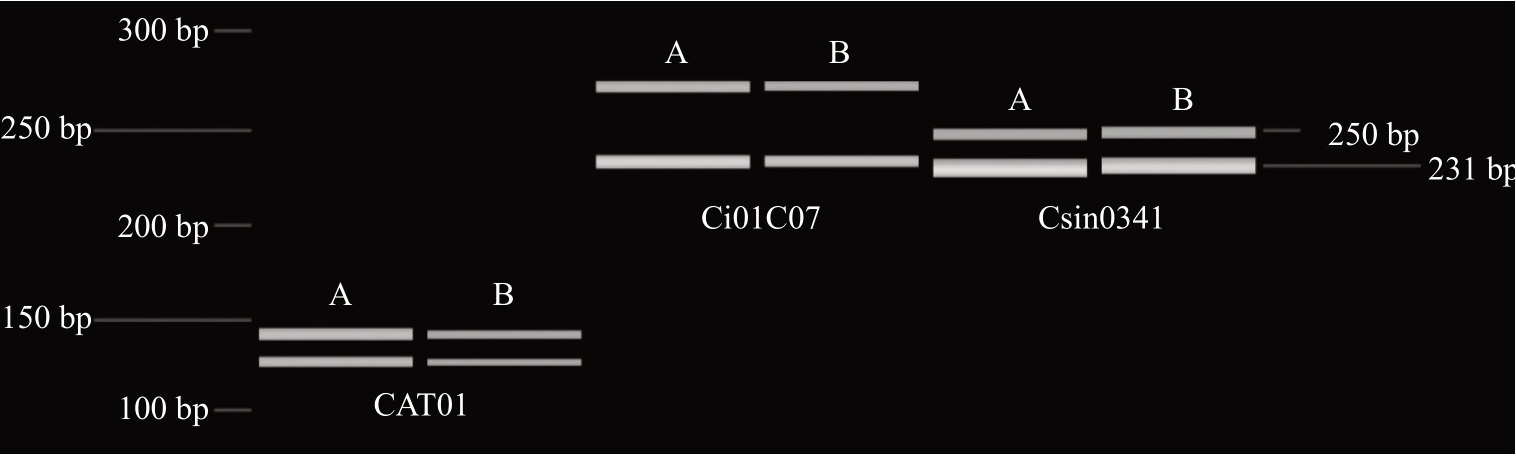
图2 利用毛细管电泳对华柑3 号进行SSR 指纹图谱分析
Fig.2 SSR fingerprint analysis of Huagan No.3 by capillary electrophoresis
A.鄂柑1 号椪柑;B.华柑3 号。
A.Egan No.1 Ponkan;B.Huagan No.3.
4 栽培技术要点
4.1 适宜区域
适宜中国大多数柑橘主产区栽培,特别是椪柑主产区,土壤土层深厚、有机质含量高的土壤果实品质好。适宜生长的气候条件:年均温度16 ℃左右,绝对最低温度≥-5 ℃,但持续时间不能太长,年日照1100 h以上,≥10 ℃的年积温5500 ℃以上,无霜期不低于280 d;空气相对湿度<75%,年降水量在1000 mm以上。
4.2 定植
园地选择参照鄂柑1 号椪柑的要求,高标准建园,合理布局,综合配套,修筑必要的排灌和蓄水设施,实行山、水、田、林、路等综合治理。合理稀植,有利于对果园施行机械化和半机械化操作,定植密度建议3.0 m×4.0 m。
4.3 整形修剪和花果管理
可采用自然圆头形树形,主干高30~40 cm,主枝3~4 个,均匀分布,基角50°~60°。幼树期注意培养主枝,促使幼树多发新梢,迅速扩大树冠,疏除或削弱临近竞争枝。盛果期后,重点对着生在主侧枝上的枝组和辅养枝进行修剪,一般在冬季采果后至春季萌发前进行冬剪,主要疏剪枯枝、病虫害枝、衰弱枝、衰退的结果枝和结果母枝等,一般不进行小枝修剪。丰产性中等,大小年不明显,一般无需进行疏花疏果。
4.4 其他管理
华柑3号的土肥水管理和主要病虫害防治与鄂柑1号椪柑一致,无特殊要求。
5 综合评价
经连续多年对华柑3号果实性状和育种价值分析,其果实品质优良,果实大和少核性状稳定;其育性正常,可作为核心种源和倍性杂交亲本用于培育三倍体无核椪柑等新品种,具有较高的研究价值和育种应用潜力。
[1] 吴巨勋,张雅菁,伊华林,谢宗周,邓秀新.无核柑橘新品种华柑4 号的选育[J].果树学报,2022,39(3):495-498.WU Juxun,ZHANG Yajing,YI Hualin,XIE Zongzhou,DENG Xiuxin. Breeding report of a new seedless ponkan cultivar Huagan No.4[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2022,39(3):495-498.
[2] GUO W W,LIANG W J,XIE K D,XIA Q M,FU J,GUO D Y,XIE Z Z,WU X M,XU Q,YI H L,DENG X X.Exploitation of polyploids from 39 citrus seedling populations[J].Acta Horticulturae,2016(1135):11-16.
[3] TAN F Q,ZHANG M,XIE K D,FAN Y J,SONG X,WANG R,WU X M,ZHANG H Y,GUO W W. Polyploidy remodels fruit metabolism by modifying carbon source utilization and metabolic flux in Ponkan mandarin (Citrus reticulata Blanco)[J]. Plant Science,2019,289:110276.
[4] BARKLEY N A,ROOSE M L,KRUEGER R R,FEDERICI C T. Assessing genetic diversity and population structure in a citrus germplasm collection utilizing simple sequence repeat markers (SSRs)[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics,2006,112(8):1519-1531.
[5] FROELICHER Y,DAMBIER D,BASSENE J B,COSTANTINO G,LOTFY S,DIDOUT C,BEAUMONT V,BROTTIER P,RISTERUCCI A M,LURO F,OLLITRAULT P. Characterization of microsatellite markers in mandarin orange (Citrus reticulata Blanco)[J]. Molecular Ecology Resources,2008,8(1):119-122.
[6] XU Q,CHEN L L,RUAN X A,CHEN D J,ZHU A D,CHEN C L,BERTRAND D,JIAO W B,HAO B H,LYON M P,CHEN J J,GAO S,XING F,LAN H,CHANG J W,GE X H,LEI Y,HU Q,MIAO Y,WANG L,XIAO S X,BISWAS M K,ZENG W F,GUO F,CAO H B,YANG X M,XU X W,CHENG Y J,XU J,LIU J H,LUO O J,TANG Z H,GUO W W,KUANG H H,ZHANG H Y,ROOSE M L,NAGARAJAN N,DENG X X,RUAN Y J. The draft genome of sweet orange (Citrus sinensis)[J].Nature Genetics,2013,45:59-66.