草莓(Fragaria×ananassa Duch.)是一种广泛栽培的丰产水果,生长周期短,经济效益高。然而,草莓在生产的每个阶段都极易遭受病虫害侵染,导致产量及品质下降,严重制约现代草莓产业的发展[1-3]。由病原菌链格孢菌(Alternaria alternata)引起的草莓黑斑病是一种严重影响草莓生产和经济价值的重要病害,该病害主要危害草莓浆果、叶片、茎等部位,发病症状表现为在草莓果实表面产生黑色病斑,且上有黑灰色霉层,或叶片表面产生灰褐色不规则病斑,并常带黄色晕圈[4-5]。目前在美国[6]、韩国[7]、意大利[8]、伊朗[9]和中国[10]等地均有报道。利用化学药剂是防治该病害最常用的方法,但易产生农药残留,造成环境污染、危害人体健康等问题。与化学防治比较,生物防治具有无污染、无残留、绿色持效以及降低抗药风险等优势[11]。然而现有研究表明,草莓黑斑病已被众多学者高度重视,但目前可用于防治该病害的生物农药仅有外源褪黑素一种[12],有关草莓黑斑病生物防治研究领域尚处起步阶段。因此,利用并开发植物内生菌进行草莓黑斑病的生物防治是现代草莓生产亟待解决的问题。
镰刀属真菌可侵染多种不同类型的植物,导致植物病害[13],但近年来研究发现,有些内生镰刀菌也能对宿主起到有益作用,达到抗病促生的效果,例如,内生砖红镰刀菌(Fusarium lateritium)能提高马铃薯对晚疫病的耐受性[14],且对烟草青枯病有抑制效果,起到增强烟草抗病性的作用[15]。但砖红镰刀菌对草莓黑斑病的防治研究目前尚未见报道。因此,为了明确内生砖红镰刀菌对草莓黑斑病的抑制作用,进而达到开发利用植物内生菌防治草莓黑斑病的目的,笔者在本研究中从内生砖红镰刀菌对草莓黑斑病的抑制活性进行分析,测定了该菌株对草莓黑斑病的防治效果以及菌株上清液对其细胞膜通透性的影响,为草莓黑斑病的生物防治奠定基础。
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料
供试草莓品种为红颜。供试菌株:草莓黑斑病菌(A.alternata)菌株XGB-1,从中国农业科学院郑州果树研究所新乡试验基地采集草莓病果,经组织分离、纯化和鉴定后获得菌株,4 ℃下保存备用。砖红镰刀菌(F.lateritium)菌株Pa2是从苹果枝条上分离获得,保存在中国微生物菌种保藏管理委员会普通微生物中心,保藏编号为CGMCC No.40605。
供试培养基及试剂:马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂培养基(potato dextrose agar,PDA),马铃薯葡萄糖培养基(potato dextrose broth,PDB);咪鲜胺(有效成分450 g·L-1,深圳诺普信农化股份有限公司),乙酸乙酯分析纯(上海吉至生化科技有限公司),甲醇分析纯(西陇科学股份有限公司)。
仪器:JJ-CJ-1FD 超净工作台(苏州市金净净化设备科技有限公司)、MJX-260 HS 智能霉菌培养箱(宁波扬辉仪器有限公司)、VHX-1000E超景深三维立体显微镜(基恩士)、TCS SP5 激光共聚焦显微镜(德国LEICA公司)。
1.2 菌株Pa2拮抗活性的测定
采用平板对峙法[16]测定内生真菌砖红镰刀菌菌株Pa2对草莓黑斑病菌的抑制效果。将培养好的草莓黑斑病菌用灭菌打孔器(直径0.5 cm)打成菌饼,由菌落边缘挑起菌饼接于PDA平板中央,四周各放一块同样大小的Pa2 菌饼,每处理3 皿,3 次重复。以仅接种草莓黑斑病菌的处理为对照,28 ℃黑暗培养9 d,用十字交叉法测量菌落生长直径,计算抑制率。抑制率/%=([对照组菌落直径-处理组菌落直径)(/对照组菌落直径-0.5)]×100。同时,在超景深三维立体显微镜下观察不同处理草莓黑斑病菌丝的形态特征,并拍照。
1.3 菌株Pa2上清液抑菌活性的测定
将菌株Pa2培养3 d后,用0.5 cm打孔器在其边缘打孔,取5 个菌饼置于100 mL 的PDB 培养基中,于28 ℃、180 r·min-1摇床中培养7 d,得到孢子悬浮液,经4000 r·min-1 离心20 min 后,依次用孔径为0.45 μm 和0.22 μm 的滤膜过滤,得到无菌上清液。将上清液与PDA 培养基按体积比配制成终浓度为5%、10%的上清液培养基,对照为不含上清液的PDA平板,在平板中央接种直径为0.5 cm的草莓黑斑病菌菌饼,28 ℃黑暗培养9 d,用十字交叉法测量菌落直径,计算不同浓度处理的抑制率,每处理3皿,3次重复。
1.4 菌株Pa2 上清液对草莓黑斑病菌孢子萌发的影响
参照Li等[17]、程海洋等[18]的方法,将草莓黑斑病菌于PDA 平板培养20 d 后,用移液枪吸取5 mL 无菌水至平板上,刮取平板菌落置于无菌离心管中,摇晃混匀,然后用4层无菌擦镜纸过滤,并用血球计数板计数,制成浓度为1×106 CFU·mL-1的孢子悬浮液。将孢子悬浮液与Pa2上清液按体积比配制成终浓度为5%、10%的混合液,在疏水玻璃载玻片上分别滴入20 μL的分生孢子悬浮液,置于培养皿中(直径200 mm),28 ℃保湿培养,分别在4、8、16、32 h时在显微镜下观察孢子萌发情况,以无菌水为对照,每处理设置3个载玻片,3次重复,使用TCS SP5激光共聚焦显微镜拍照,并计算不同浓度处理的孢子萌发率。萌发率/%=(萌发孢子数/检查孢子总数)×100。
1.5 菌株Pa2萃取物对草莓黑斑病菌的抑制作用
利用1.3中的方法制备菌株Pa2上清液,将旋转蒸发浓缩至原体积的1/10,使用上述浓缩液体积2倍的乙酸乙酯萃取,2 次重复,合并萃取液,旋转蒸发浓缩至浸膏,使用甲醇将其溶解,使粗提物质量浓度为20 mg·mL-1。在PDA 平板中央接种草莓黑斑病菌菌饼(直径0.5 cm),四周放置直径0.6 cm的牛津杯,向牛津杯中滴加50 μL 萃取物溶液,每处理3 个皿,3次重复,以加入50 μL等浓度甲醇处理为对照。
1.6 菌株Pa2 上清液对草莓黑斑病菌细胞内容物的影响
参照Li 等[19]的方法并进行调整,通过测定细胞OD260、OD280检测草莓黑斑病菌孢子细胞膜通透性的变化,利用1.4中的方法制备浓度为1×106 CFU·mL-1的孢子悬浮液,吸取1 mL 孢子悬浮液置于PDB中,28 ℃、180 r·min-1培养3 d 后,3000 r·min-1离心5 min,吸除上清液,使用无菌水清洗2遍后,分别置于20 mL含5%与10%Pa2上清液的无菌水中,对照组不含上清液,在0、12、24、36 h取样,测定各处理的OD260、OD280值。
1.7 菌株Pa2 上清液对草莓黑斑病菌细胞质膜的影响
挑取草莓黑斑病菌菌丝置于PDB 培养基中,28 ℃、180 r·min-1摇床中培养1 d,挑取少量菌丝置于菌株Pa2 上清液中,对照组置于PDB 培养基中,在28 ℃培养箱放置12 h,取少量菌丝,经体积分数为0.5 μL·mL-1的SYTOX绿菁死细胞核酸染料染色5 min后,用无菌水重复清洗2~3次,洗去表面染料,挑取菌丝制成玻片,在激光共聚焦显微镜下观察并拍照。
利用1.4 中的方法,使用菌株Pa2 上清液,制备浓度为1×106 CFU·mL-1的孢子悬浮液,对照组使用PDB培养基制备相同浓度孢子悬浮液,在28 ℃培养箱放置12 h,3000 r·min-1离心5 min,吸除上清液,加入1 mL体积分数为1 μL·mL-1的SYTOX绿菁死细胞核酸染料,颠倒混匀,染色5 min后,3000 r·min-1离心5 min,吸除上清液,重复清洗2~3 次,洗去表面染料,最后加入1 mL无菌水颠倒混匀,吸取20 μL制成玻片,在激光共聚焦显微镜下观察并拍照。
1.8 菌株Pa2对草莓黑斑病的防治作用
参照杨丽萍等[20]和袁洪波等[21]的方法,测定菌株Pa2对草莓黑斑病的防治效果。选用新鲜、健康草莓果实和叶片,用无菌水清洗、晾干。喷施菌株Pa2孢子悬浮液至整体湿润,放入通风柜晾干后,进行接种试验。无菌水处理作为阴性对照、咪鲜胺处理作为阳性对照。果实接种:用针刺法造成微伤口,用微量加样器接入草莓黑斑病孢子悬浮液(1×106 CFU·mL-1)10 μL,将其置于培养盒中保湿培养,每个处理包括5个草莓,3次重复,于25 ℃光照培养箱中培养5 d,测量病斑长度。叶片接种:取草莓黑斑病菌菌饼(直径为0.5 cm),正面朝下贴于叶片上,每处理接种10个病斑,3次重复,于25 ℃光照培养箱中保湿培养,7 d后测量病斑直径,计算发病率并统计防治效果。发病率/%=发病接种点数/总接种点数×100。防治效果/%=无病症的接种点数/总接种点数×100。
1.9 数据统计与分析
试验数据采用Microsoft Excel 软件进行整理,用SPSS 24.0 软件进行统计分析,采用Duncan 法以及Tukey检验进行数据分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 菌株Pa2对草莓黑斑病菌生长的影响
平板对峙试验结果显示,菌株Pa2 能显著抑制草莓黑斑病菌的生长,并导致其菌丝出现结节、末端膨大等畸形现象,甚至导致其菌丝膜破裂,原生质体泄露(图1-A、B)。统计结果显示,当对照组的草莓黑斑病菌菌落直径达到7.58 cm时,经Pa2处理后的菌落直径仅有1.85 cm,进一步统计的结果显示菌株Pa2 对草莓黑斑病菌生长的抑制率达80.96%(图1-C)。以上结果表明,菌株Pa2 能显著影响草莓黑斑病菌菌落生长及菌丝形态。
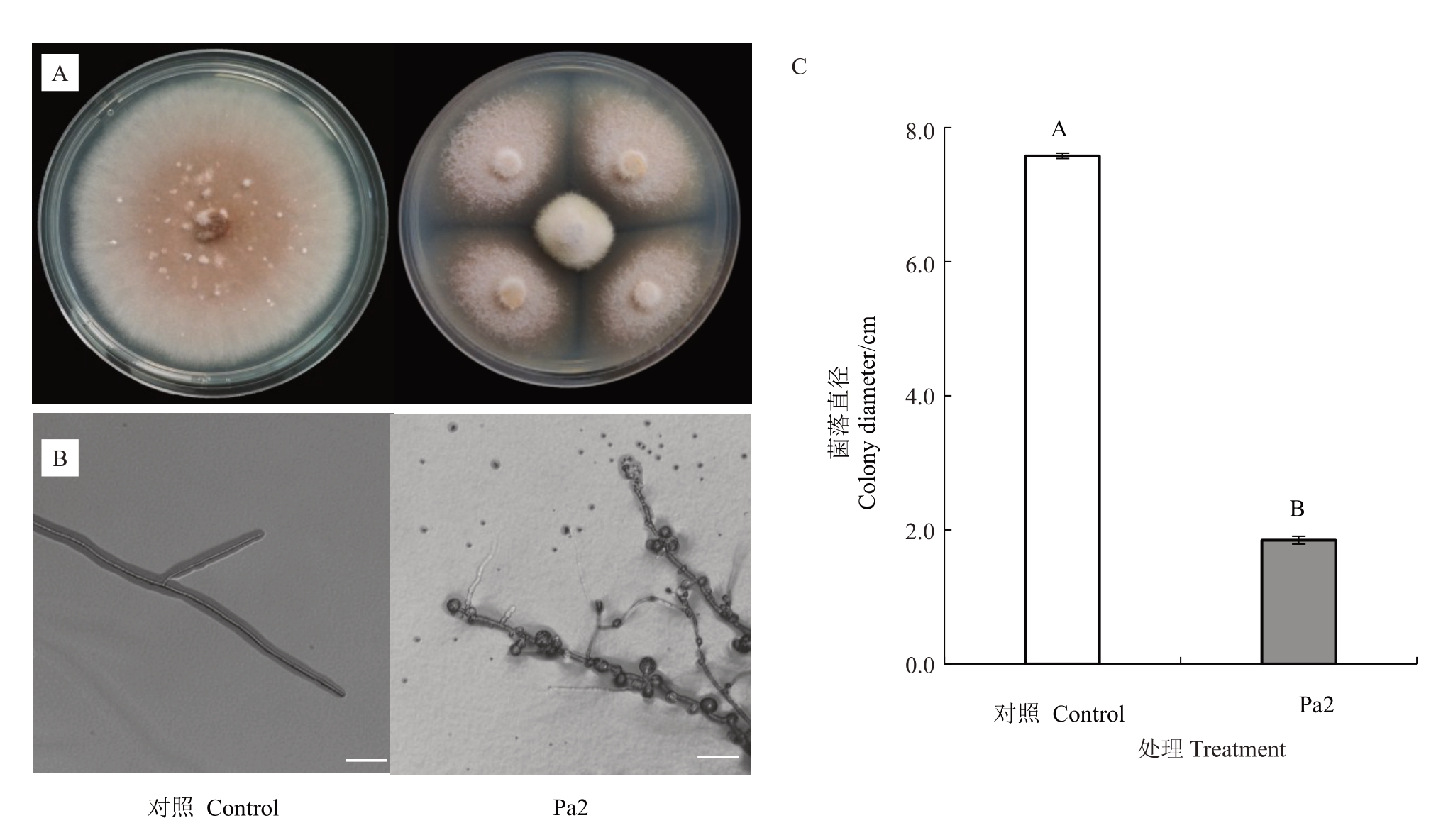
图1 菌株Pa2 对草莓黑斑病菌菌丝生长的抑制作用
Fig.1 Inhibitory effect of strain Pa2 on mycelial growth of A.alternata
A.菌株Pa2 对草莓黑斑病菌菌落的抑制作用;B.菌株Pa2 对草莓黑斑病菌菌丝的影响;C.菌落直径统计。标尺为50µm。不同大写字母代表差异极显著(Tukey’s tests,p<0.01)。下同。
A.Inhibition of strain Pa2 on colony of A.alternata;B.Effect of strain Pa2 on mycelium morphology of A.alternata;C.Statistical analysis of colony diameter.Scale bar is 50µm.Different capital letters indicate extremely significant difference(p<0.01)based on Tukey’s tests.The same below.
2.2 菌株Pa2上清液对草莓黑斑病菌的抑制作用
如图2所示,砖红镰刀菌菌株Pa2上清液对草莓黑斑病菌具有强烈的抑菌活性,且随着浓度的增大抑制效果增强。当对照组菌落直径为7.47 cm时,经5%、10% Pa2 上清液处理的菌落直径显著小于对照,分别为2.91 cm和2.30 cm(图2-B)。统计结果显示,5%、10% Pa2 上清液对草莓黑斑病菌的抑制率分别为65.39%和74.15%(图2-C)。
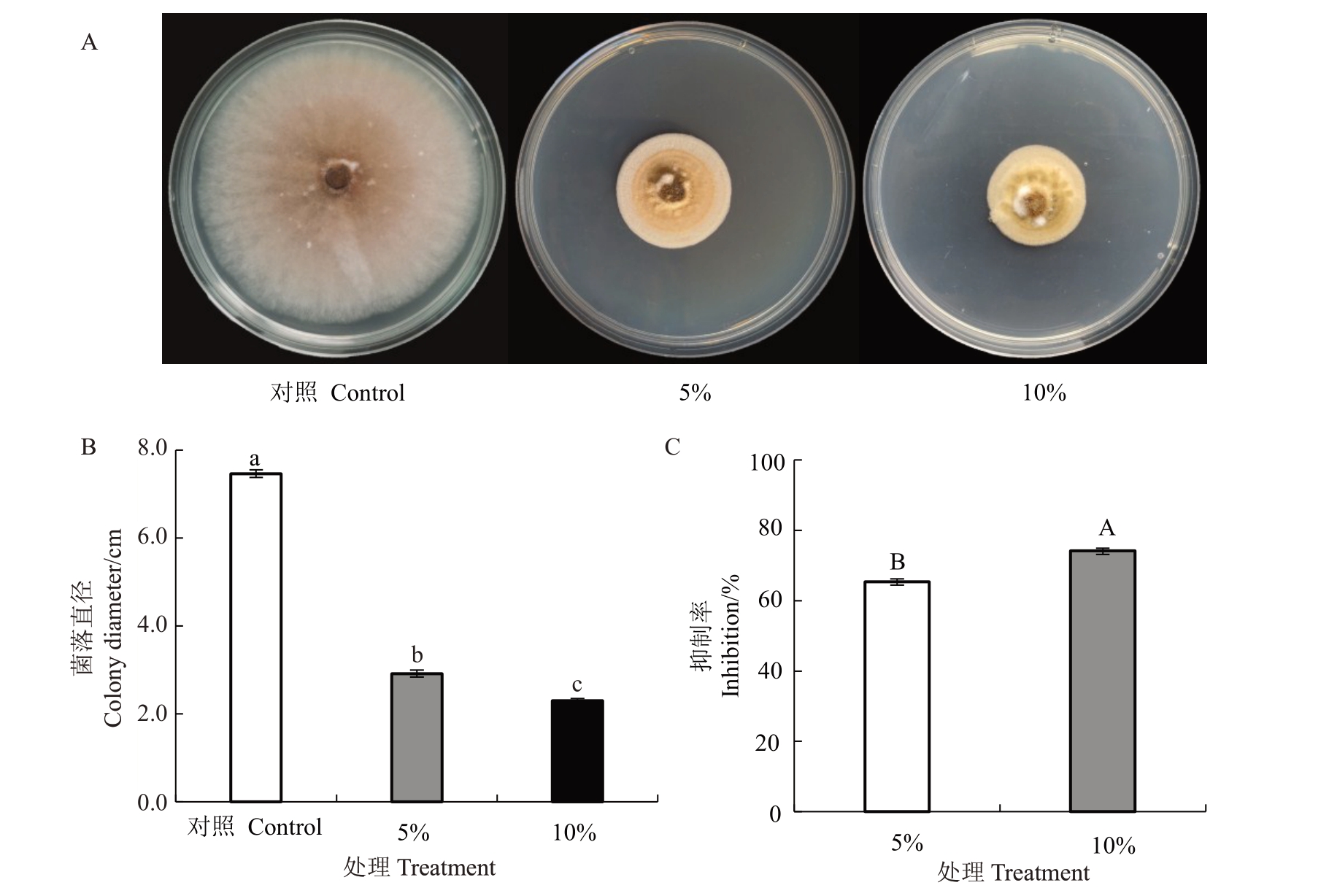
图2 菌株Pa2 上清液对草莓黑斑病菌的抑制作用
Fig.2 Suppressing effect of strain Pa2 supernatant on A.alternata
A.不同浓度的菌株Pa2 上清液对草莓黑斑病菌菌落生长的影响;B.不同处理草莓黑斑病菌菌落直径;C.菌株Pa2 上清液对草莓黑斑病菌的抑制率。不同小写字母表示差异显著(Duncan’s tests,p<0.05),下同。
A.Effect of strain Pa2 supernatant on colony growth of A. alternata;B.Colony diameter of A. alternata under different treatment;C.Inhibition rate of strain Pa2 supernatant on A.alternata.Different small letters denote statistical differences(p<0.05)based on Duncan’s tests,the same below.
2.3 菌株Pa2 上清液对草莓黑斑病菌孢子萌发率的影响
由图3可知,菌株Pa2上清液可显著抑制草莓黑斑病菌孢子的萌发,并且随着菌株Pa2 上清液浓度的增大,草莓黑斑病菌孢子的萌发率呈下降趋势。对照组草莓黑斑病菌的孢子随培养时间的延长,其萌发率急剧增长,在32 h 时萌发率为79.46%。然而,经5%、10%的Pa2上清液处理的草莓黑斑病菌孢子在32 h时的萌发率均低于50%,分别为46.99%和15.01%(图3-B)。
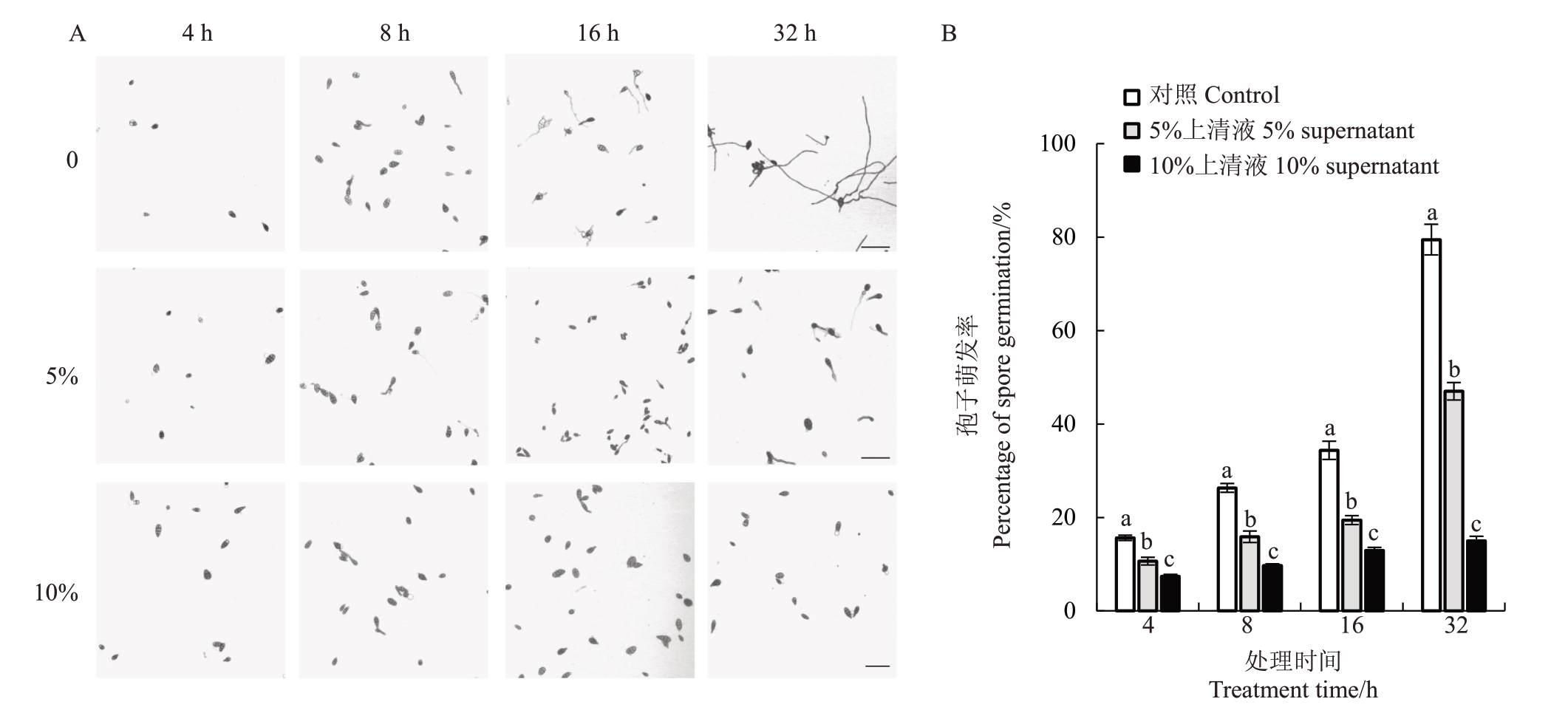
图3 不同浓度菌株Pa2 上清液对草莓黑斑病菌孢子萌发的影响
Fig.3 Effect of strain Pa2 supernatant at different concentrations on the spore germination of A.alternata
A.不同处理下草莓黑斑病菌孢子的萌发情况,标尺为50µm;B.不同处理对草莓黑斑病菌孢子萌发率的影响。
A.Germination of spores of A.alternata under different treatments,Scale bar is 50µm;B.Effect of different treatments on percentage of spore germination of A.alternata.
2.4 菌株Pa2萃取物对草莓黑斑病菌的抑菌活性
为进一步验证菌株Pa2的活性代谢产物对草莓黑斑病菌是否有抑制作用,利用乙酸乙酯对菌株Pa2 上清液进行萃取并测定其抑菌活性。结果表明,乙酸乙酯萃取物对草莓黑斑病菌具有强烈的抑菌作用(图4-A),当对照菌落直径为8.03 cm 时,处理菌落直径为3.20 cm(图4-B),其抑制率达到64.14%,说明菌株Pa2 的乙酸乙酯萃取物中含有草莓黑斑病菌抑菌活性物质。
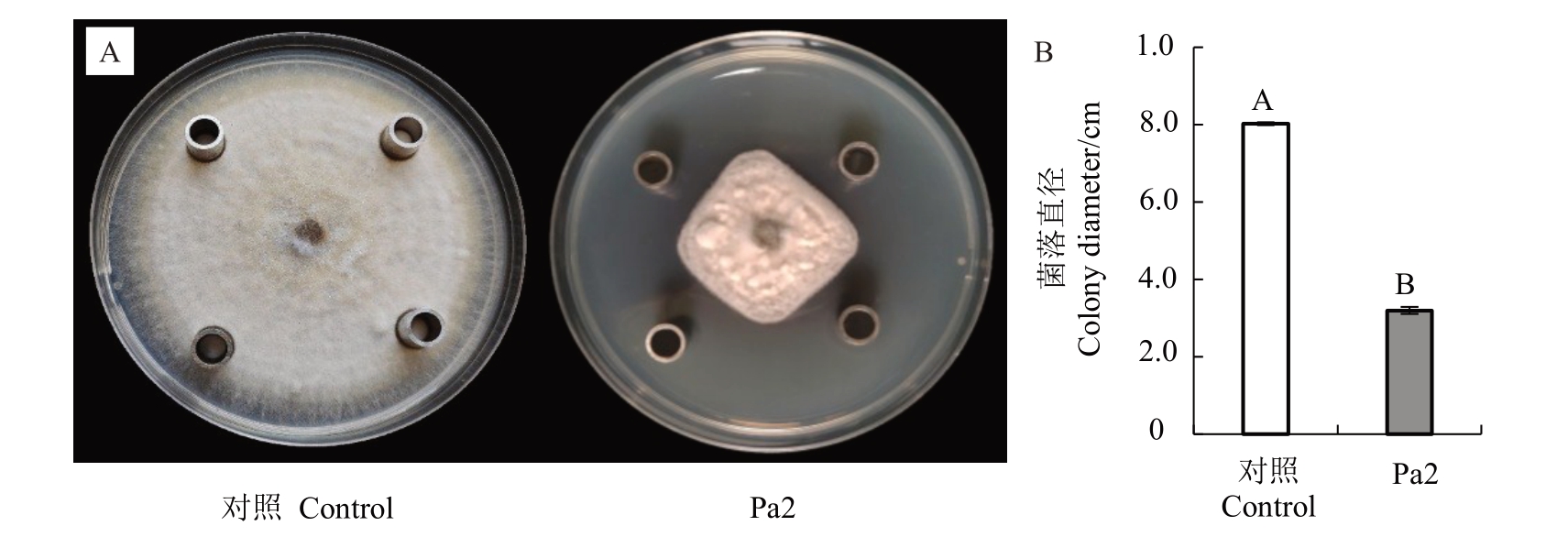
图4 菌株Pa2 萃取物对草莓黑斑病菌的拮抗活性检测
Fig.4 Antagonistic activity of strain Pa2 extracts on A.alternata
A.菌株Pa2 萃取物对草莓黑斑病菌的拮抗作用;B.菌落直径统计。
A.Antagonistic effect of strain Pa2 extracts on A.alternata;B.Statistical analysis of colony diameter.
2.5 菌株Pa2 上清液对草莓黑斑病菌细胞内容物的影响
为明确胞外核酸与蛋白质含量的变化情况,测定胞外溶液在260 nm与280 nm处的吸光度。从图5可以看出,经菌株Pa2上清液处理后,草莓黑斑病菌的孢子悬浮液在260 nm、280 nm处的吸光度值均呈上升趋势,表明菌株Pa2上清液对病原菌细胞膜具有破坏作用,能够引起草莓黑斑病菌细胞内核酸与蛋白质的泄露。在36 h时5%、10%上清液处理后的OD260值分别达到2.31 和2.68,OD280 值分别为2.20 和2.54。而对照组的OD260值和OD280值在整个试验过程中无显著变化。以上结果表明,菌株Pa2上清液能改变细胞膜的通透性,并且随着上清液浓度的增大,对细胞膜通透性的损伤程度也随之加大。
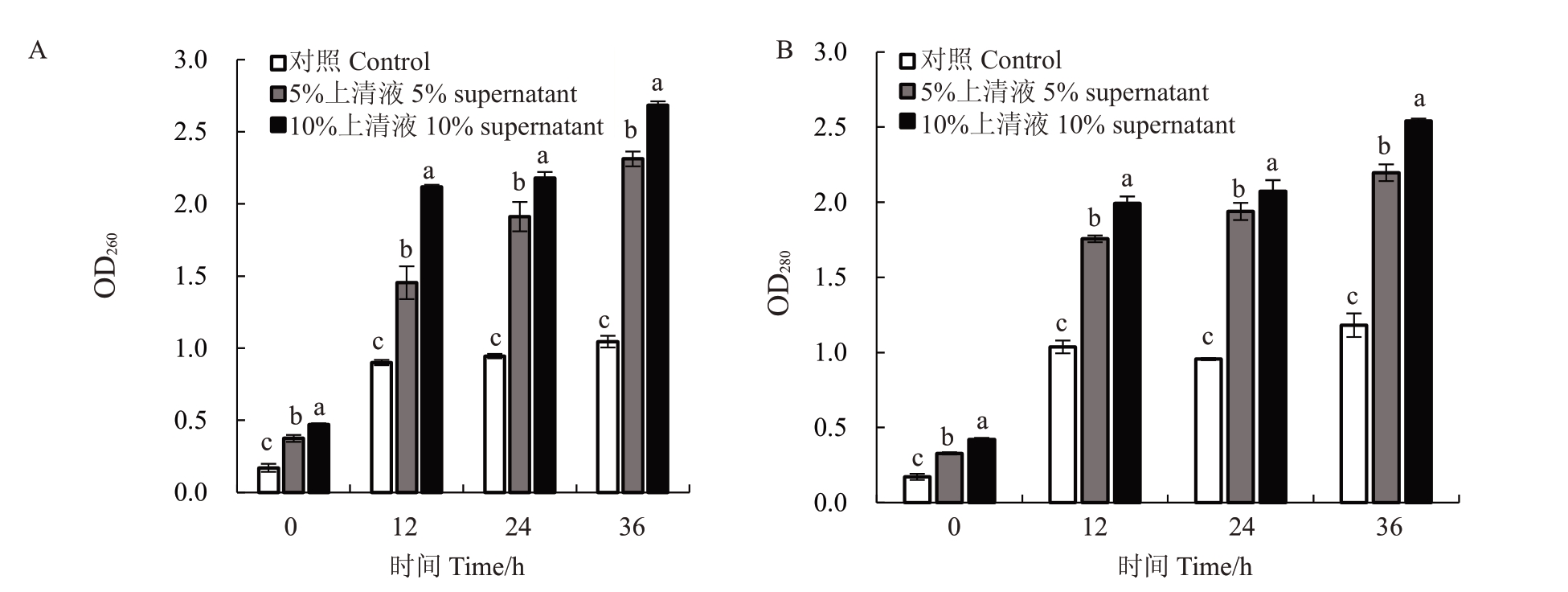
图5 不同浓度菌株Pa2 上清液对草莓黑斑病菌细胞内容物泄露的影响
Fig.5 Effect of strain Pa2 supernatant at different concentrations on cell content leakage of A.alternata
2.6 菌株Pa2上清液对草莓黑斑病菌菌丝细胞质膜的影响
SYTOX是一种绿色核酸染料,能够穿过受损细胞质膜而不能透过活细胞质膜。如图6所示,经SYTOX染色后,对照草莓黑斑病菌菌丝均未被染色,而经菌株Pa2上清液处理后的菌丝不仅在形态上发生变化,而且呈现出可见荧光,表明菌株Pa2上清液能够破坏草莓黑斑病菌菌丝的细胞膜,使染料透过其损伤的细胞膜。
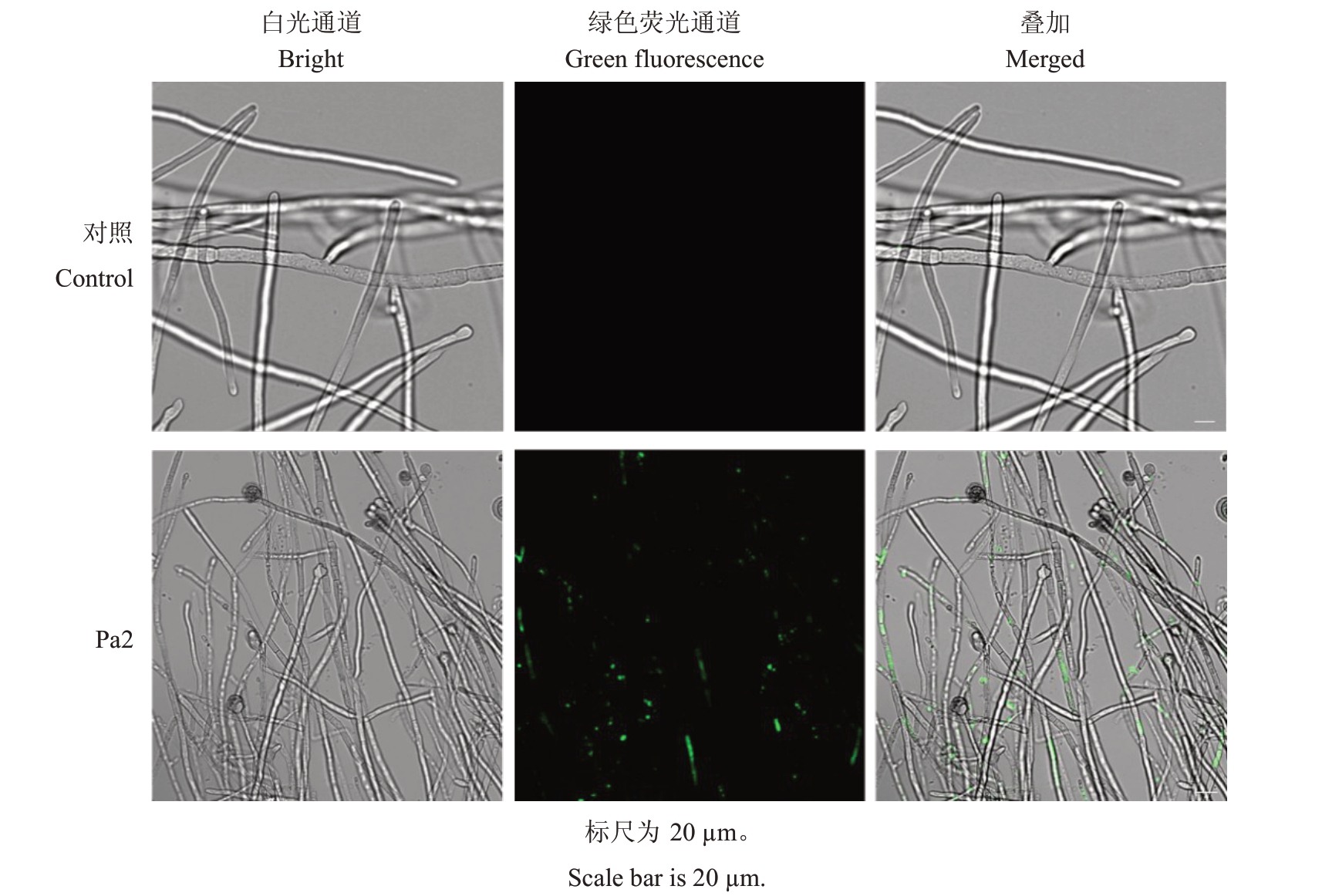
图6 菌株Pa2 上清液对草莓黑斑病菌菌丝细胞质膜的影响
Fig.6 Effect of strain Pa2 supernatant on the mycelial membrane of A.alternata
2.7 菌株Pa2 上清液对草莓黑斑病菌孢子细胞质膜的影响
经菌株Pa2 上清液处理后,草莓黑斑病菌孢子均产生圆球状突起(图7),在形态上与对照有明显差异,且经SYTOX 染色后呈现清晰可见的荧光,表明菌株Pa2上清液能够破坏草莓黑斑病菌孢子的细胞质。

图7 菌株Pa2 上清液对草莓黑斑病菌孢子细胞质膜的影响
Fig.7 Effect of strain Pa2 supernatant on the spore membrane of A.alternata
2.8 菌株Pa2孢子悬浮液对草莓黑斑病的防治效果
为了明确菌株Pa2 对草莓黑斑病的防治效果,利用离体草莓果实和叶片进行防治试验。结果显示,与对照组相比,菌株Pa2 孢子悬浮液处理对草莓黑斑病具有良好的防治效果,可显著降低草莓黑斑病的病斑长度和发病率(图8,表1)。据统计分析,经Pa2 孢子悬浮液处理后的草莓叶片病斑长度仅为0.66 cm,且发病率显著低于对照,对照果实平均病斑长度为1.24 cm,而经Pa2 孢子悬浮液处理后的草莓果实病斑长度仅为0.16 cm,且发病率为26.67%,使用咪鲜胺处理后,叶片与果实均未出现病症(图8,表1)。上述结果表明,菌株Pa2 能够显著抑制草莓黑斑病菌在果实与叶片上的侵染能力,对草莓黑斑病具有较好的防治效果。
表1 菌株Pa2 对草莓黑斑病的防治效果
Table 1 Effectiveness of strain Pa2 on strawberry black spot
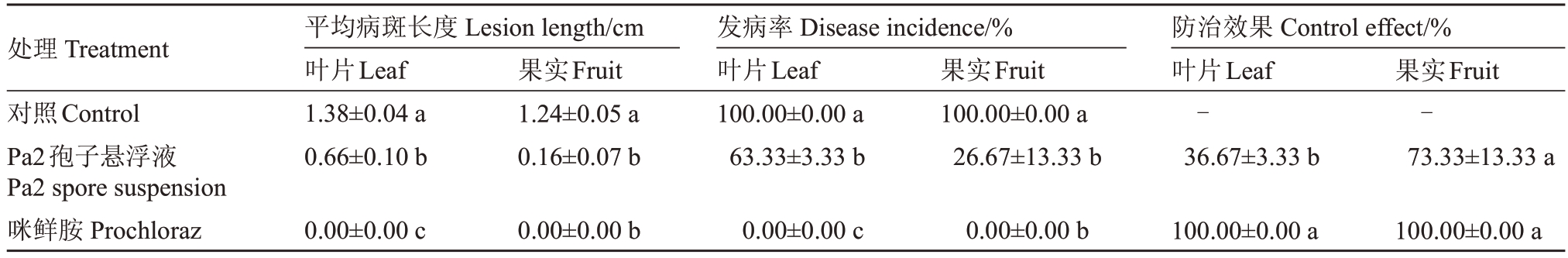
注:表中数据为平均值±标准误。
Note:Date are mean±standard error.

图8 菌株Pa2 对草莓黑斑病发病程度的影响
Fig.8 Effect of strain Pa2 on the inhibition of strawberry black spot
3 讨论
由链格孢菌(A. alternata)或极细链格孢(A.tenuissima)引起的草莓黑斑病是草莓种植园中的一种常见病害,在世界范围内均有分布,严重影响草莓品质以及产量[22]。近年来,生物防治成为世界研究的前沿和热点,然而,有关草莓黑斑病生物防治的研究尚缺乏,仅有报道称外源褪黑素能有效抑制链格孢菌的菌丝生长,延缓草莓黑斑病的发病进程[12],但目前仍无可利用的草莓黑斑病生防菌。镰刀菌(Fusarium)作为植物病原菌,具有寄主种类多、侵染范围广的特点,能引起小麦赤霉病[23]、黄桃果实腐烂病[24]、金线兰茎腐病[25]以及番茄颈腐根腐病[26]等多种病害。但近年来的研究报道表明,内生砖红镰刀菌(F.lateritium)对马铃薯晚疫病[14]、烟草青枯病[15]、番茄枯萎病[27]等多种植物病原菌均具有较强抑制作用,郝芳敏等[28]研究也表明,一些菌株能对不同的病原菌表现出广谱拮抗活性。在本研究中,砖红镰刀菌菌株Pa2对草莓黑斑病病原菌抑制效果显著,引起菌丝畸形、破裂,原生质体泄露,具有开发成为生防菌的潜力。
抑制病原菌菌丝生长和孢子萌发是生防菌的潜在能力之一。本研究结果表明,砖红镰刀菌菌株Pa2 的无菌上清液对草莓黑斑病菌具有抑制作用,且10%的Pa2上清液对草莓黑斑病菌菌丝生长与孢子萌发的抑制率均高于70%,这可能与抑菌活性物质的分泌有关,未来将利用蛋白组学进一步分析筛选,确定抑菌物质。Wang等[29]研究也发现解淀粉芽孢杆菌(Bacillus amyloliquefaciens)的无菌上清液抑制链格孢、灰葡萄孢的菌丝生长和孢子萌发,并鉴定其抑菌物质为β-1,3-1,4-葡聚糖酶。
生防菌萃取物通常包含生防微生物产生的抑菌化合物,具有一定的抗菌活性。孙冰等[30]研究发现,抑菌物质的萃取物会破坏病原菌的菌丝形态、细胞膜结构及通透性,导致胞物质外泄,从而起到抑菌的效果。笔者在本试验中得出了相似的结果,即菌株Pa2的萃取物中含有能够抑制草莓黑斑病病菌生长的活性代谢产物,后续将利用色谱分离技术,对其代谢产物进行分离纯化。
许多抗菌物质通过作用于细胞膜来发挥其抑菌功能,当细胞膜受损时,细胞内部的核酸与蛋白质等物质会发生渗透现象,外部物质也可能进入胞内[31-32]。笔者在本研究中测定胞外溶液在260 nm与280 nm 处的吸光度值以反映胞外核酸与蛋白质含量的变化,并通过SYTOX 绿菁染色法进一步分析草莓黑斑病菌丝及孢子的细胞膜受损情况。结果表明,经菌株Pa2 上清液处理后草莓黑斑病病原菌细胞膜受到损坏,细胞内容物外泄,且链格孢菌(A.alternata)的孢子和菌丝细胞在Pa2 处理后显示出强荧光,与Xu等[33]对紫檀芪抑制荔枝霜霉病的研究结果一致,说明菌株Pa2 能够破坏生物膜从而对草莓黑斑病病菌起到抑制作用,这也可能是菌株Pa2 显著抑制草莓黑斑病在果实与叶片上侵染能力的主要原因之一。
4 结论
菌株Pa2对草莓黑斑病致病真菌链格孢菌具有显著的抑制活性,在10%的浓度下能有效抑制链格孢菌孢子萌发和菌丝生长,其孢子悬浮液能够显著抑制草莓黑斑病菌在果实与叶片上的侵染能力。
[1] DELBEKE S,CEUPPENS S,HESSEL C T,CASTRO I,JACXSENS L,DE ZUTTER L,UYTTENDAELE M.Microbial safety and sanitary quality of strawberry primary production in Belgium:Risk factors for Salmonella and Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli contamination[J].Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2015,81(7):2562-2570.
[2] HOU S F,LIU J J,XU T F,LI X F,LI X F,LI S,WANG H Q.Simultaneous detection of three crown rot pathogens in fieldgrown strawberry plants using a multiplex PCR assay[J].Crop Protection,2022,156:105957.
[3] 雷恒树,华战迎,范灵姣,王红清.北京地区草莓枯萎病病原的鉴定与防治[J].中国农业大学学报,2019,24(6):66-72.LEI Hengshu,HUA Zhanying,FAN Lingjiao,WANG Hongqing.Identification and prevention of strawberry wilt disease pathogen in Beijing[J].Journal of China Agricultural University,2019,24(6):66-72.
[4] 姜秋同,张爽,朱洪坤,赵丽娜.草莓病害的发生与防治措施[J].现代农村科技,2023(7):49-50.JIANG Qiutong,ZHANG Shuang,ZHU Hongkun,ZHAO Lina.Occurrence and control measures of strawberry disease[J].Xiandai Nongcun Keji,2023(7):49-50.
[5] NISHIKAWA J,NAKASHIMA C.Morphological and molecular characterization of the strawberry black leaf spot pathogen referred to as the strawberry pathotype of Alternaria alternata[J].Mycoscience,2019,60(1):1-9.
[6] HOWARD C M,ALBREGTS E E.A strawberry fruit rot caused by Alternaria tenuissima[J].Phytopathology,1973,63(7):938-939.
[7] CHO J T,MOON B J.The occurrence of strawberry black leaf spot caused by Alternaria alternata (Fr.) Keissler in Korea[J].Journal of Plant Protection,1980,19(4):221-227.
[8] WADA H,CAVANNI P,BUGIANI R,KODAMA M,OTANI H,KOHMOTOET K.Occurrence of the strawberry pathotype of Alternaria alternata in Italy[J].Plant Disease,1996,80(4):372-374.
[9] BAGHERABADI S,ZAFARI D,SOLEIMANI M J.First report of leaf spot of strawberry caused by Alternaria tenuissima in Iran[J].Journal of Plant Pathology &Microbiology,2015,6(3):258.
[10] KO Y,CHEN C Y,YAO K S,LIU C W,MARUTHASALAM S,LIN C H.First report of fruit rot of strawberry caused by an Alternaria sp.in Taiwan[J].Plant Disease,2008,92(8):1248.
[11] 尤佳琪,吴明德,李国庆.木霉在植物病害生物防治中的应用及作用机制[J].中国生物防治学报,2019,35(6):966-976.YOU Jiaqi,WU Mingde,LI Guoqing.Application and mechanism of Trichoderma in biological control of plant disease[J].Chinese Journal of Biological Control,2019,35(6):966-976.
[12] 孙子荀,倪照君,高志红,乔玉山,万春雁,古咸彬.外源褪黑素提高草莓黑斑病抗性的效果和作用机制初探[J].西北植物学报,2020,40(10):1679-1687.SUN Zixun,NI Zhaojun,GAO Zhihong,QIAO Yushan,WAN Chunyan,GU Xianbin.Effect and mechanism of exogenous melatonin on improvement of black rot disease resistance in strawberry[J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2020,40(10):1679-1687.
[13] DEAN R,VAN KAN J A L,PRETORIUS Z A,HAMMONDKOSACK K E,DI PIETRO A,SPANU P D,RUDD J J,DICKMAN M,KAHMANN R,ELLIS J,FOSTER G D.The Top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology[J].Molecular Plant Pathology,2012,13(4):414-430.
[14] 汪健康,肖青,查兴平,何张江,康冀川.对马铃薯具促生抗病作用的砖红镰刀菌及其遗传转化体系构建[J].菌物学报,2021,40(8):2008-2023.WANG Jiankang,XIAO Qing,ZHA Xingping,HE Zhangjiang,KANG Jichuan.Endophyte Fusarium lateritium showing potato growth promotion and disease resistance and the construction of its genetic transformation system[J].Mycosystema,2021,40(8):2008-2023.
[15] 查兴平,李永杰,汪健康,肖青,黄建明,何张江,康冀川.一株内生砖红镰刀菌促进烟草生长和增强青枯病抗性[J].菌物学报,2022,41(10):1658-1671.ZHA Xingping,LI Yongjie,WANG Jiankang,XIAO Qing,HUANG Jianming,HE Zhangjiang,KANG Jichuan.A strain of endophytic Fusarium lateritium promotes growth and resistance to bacterial wilt of tobacco[J].Mycosystema,2022,41(10):1658-1671.
[16] 梁艳琼,吴伟怀,习金根,李锐,郑金龙,谭施北,贺春萍,易克贤.生防菌JNC2 对柱花草炭疽病的生防效果及其机理作用[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2020,39(12):5567-5573.LIANG Yanqiong,WU Weihuai,XI Jingen,LI Rui,ZHENG Jinlong,TAN Shibei,HE Chunping,YI Kexian.Biocontrol effects and mechanism of antagonistic bacterial strain JNC2 against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides on Stylosanthes[J].Genomics and Applied Biology,2020,39(12):5567-5573.
[17] LI G J,CHEN Y,ZHANG Z Q,LI B Q,CHEN T,TIAN S P.2,3-Butanedione suppresses gray mold of postharvest fruit by activating the autophagy of Botrytis cinerea[J].Postharvest Biology and Technology,2022,193:112057.
[18] 程海洋,程亮,朱海霞,李娟,魏有海,郭青云.链格孢菌DTDYLC 菌株的除草活性及对作物的安全性[J].中国生物防治学报,2023,39(2):418-428.CHENG Haiyang,CHENG Liang,ZHU Haixia,LI Juan,WEI Youhai,GUO Qingyun.Herbicidal activity and safety to crops of Alternaria alternata DT-DYLC[J].Chinese Journal of Biological Control,2023,39(2):418-428.
[19] LI Y N,ZHANG S B,LV Y Y,ZHAI H C,CAI J P,HU Y S.Linalool,the main volatile constituent from Zanthoxylum schinifolium pericarp,prevents growth of Aspergillus flavus in postharvest grains[J].Food Control,2022,137:108967.
[20] 杨丽萍,金梦军,崔凌霄,李统华,安杰,魏立娟,畅涛,杨成德.甘肃省樱桃黑斑病病原菌的分离及鉴定[J].果树学报,2020,37(6):891-899.YANG Liping,JIN Mengjun,CUI Lingxiao,LI Tonghua,AN Jie,WEI Lijuan,CHANG Tao,YANG Chengde.Isolation and identification of the pathogen causing cherry black spot in Gansu Province[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2020,37(6):891-899.
[21] 袁洪波,王卓妮,袁梦佳,覃艮红,史冰柯,周厚成,侯珲,王丽,涂洪涛.贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1 对草莓褐色叶斑病菌的抑制活性及其促生作用[J].果树学报,2023,40(1):126-132.YUAN Hongbo,WANG Zhuoni,YUAN Mengjia,QIN Genhong,SHI Bingke,ZHOU Houcheng,HOU Hui,WANG Li,TU Hongtao.Antagonistic activity of Bacillus velezensis strain P2-1 against tan-brown leaf spot of strawberry and its growth-promoting effect[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2023,40(1):126-132.
[22] FU Y,ZHANG X F,LIU S J H,HU K L,WU X H.Characterization of Alternaria species associated with black spot of strawberry in Beijing municipality of China[J].Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology,2020,42(2):235-242.
[23] SCHERM B,BALMAS V,SPANU F,PANI G,DELOGU G,PASQUALI M,MIGHELI Q.Fusarium culmorum:Causal agent of foot and root rot and head blight on wheat[J].Molecular Plant Pathology,2013,14(4):323-341.
[24] ZHAO Z Y,LIU Y Y,YANG J H,YANG X L,WANG J H.First report of Fusarium lateritium causing fruit rot of yellow peach (Amygdalus persica) in China[J].New Disease Reports,2019,39(1):6.
[25] 叶炜,颜沛沛,王培育,罗维鸿,林敏水,沈绍榕,江金兰.金线兰茎腐病的病原菌鉴定与防治药剂的筛选[J].亚热带农业研究,2023,19(1):1-9.YE Wei,YAN Peipei,WANG Peiyu,LUO Weihong,LIN Minshui,SHEN Shaorong,JIANG Jinlan.Pathogen identification of Anoectochium roxborghil stem rot and screening of fungicides[J].Subtropical Agriculture Research,2023,19(1):1-9.
[26] 程琳,李珊珊,武玉芬,李艳青,张海娟,魏美甜.寿光设施番茄死棵病原真菌的分离及鉴定[J].中国瓜菜,2023,36(9):7-15.CHENG Lin,LI Shanshan,WU Yufen,LI Yanqing,ZHANG Haijuan,WEI Meitian.Isolation and identification of pathogenic fungi from dead tomato plants in Shouguang facilities[J].China Cucurbits and Vegetables,2023,36(9):7-15.
[27] 肖青,李永杰,汪健康,查兴平,黄建明,何张江,康冀川.内生砖红镰刀菌对番茄生长和抗病的影响[J].华中农业大学学报(自然科学版),2022,41(3):173-180.XIAO Qing,LI Yongjie,WANG Jiankang,ZHA Xingping,HUANG Jianming,HE Zhangjiang,KANG Jichuan.Effects of an endophytic Fusarium lateritium on growth and disease resistance of tomato[J].Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University(Natural Science Edition),2022,41(3):173-180.
[28] 郝芳敏,臧全宇,马二磊,丁伟红,王毓洪,黄芸萍.甜瓜多种真菌病害拮抗细菌NBmelon-1 的鉴定及其促生和生防效果[J].中国瓜菜,2021,34(7):14-19.HAO Fangmin,ZANG Quanyu,MA Erlei,DING Weihong,WANG Yuhong,HUANG Yunping.Identification,biocontrol and growth promoting effects of antagonistic bacteria NBmelon-1 of various fungal diseases in melon[J].China Cucurbits and Vegetables,2021,34(7):14-19.
[29] WANG R,LONG Z Y,LIANG X Y,GUO S L,NING N,YANG L N,WANG X,LU B H,GAO J.The role of a β-1,3-1,4-glucanase derived from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FS6 in the protection of ginseng against Botrytis cinerea and Alternaria panax[J].Biological Control,2021,164:104765.
[30] 孙冰,杨昌发,唐彩艳,张胜花,杨胡艳,葛永怡.橘绿木霉GF-11 的哌珀霉素鉴定及活性研究[J].农药,2023,62(6):411-415.SUN Bing,YANG Changfa,TANG Caiyan,ZHANG Shenghua,YANG Huyan,GE Yongyi.Identification and bioactivity detection of peptaibols from Trichoderma citrinoviride GF-11[J].Agrochemicals,2023,62(6):411-415.
[31] 夏飞,张处处,武子宁,曹时玲,邬培鸿.柠檬酸对食用菌腐败菌的抑制作用及其作用机制[J].陕西科技大学学报,2023,41(2):40-45.XIA Fei,ZHANG Chuchu,WU Zining,CAO Shiling,WU Peihong.Antibacterial effect and mechanism of citric acid on spoilage bacteria of edible mushroom[J].Journal of Shaanxi University of Science&Technology,2023,41(2):40-45.
[32] TAVEIRA G B,CARVALHO A O,RODRIGUES R,TRINDADE F G,DA CUNHA M,GOMES V M.Thionin-like peptide from Capsicum annuum fruits:Mechanism of action and synergism with fluconazole against Candida species[J].BMC Microbiology,2016,16:12.
[33] XU D D,DENG Y Z,XI P G,ZHU Z Q,KONG X Y,WAN L,SITU J J,LI M H,GAO L W,JIANG Z D.Biological activity of pterostilbene against Peronophythora litchii,the litchi downy blight pathogen[J].Postharvest Biology and Technology,2018,144:29-35.