贡柑是广东省本地农家种。史料记载,在广东省四会市从唐代就有贡柑种植,距今1100 多年[1]。目前,在广东德庆、仁化及广西钟山等地,贡柑是主栽品种,总面积约2.67万hm2,是当地果农主要收入来源。
贡柑果实近球形,果皮橙黄,果肉淡橙色,较易剥皮。11 月上中旬进入果实转色期,此时果肉清甜,完熟后蜜味浓。受近年柑橘市场逐渐饱和的影响,多数本地主栽品种如砂糖橘、红江橙等均在12月中旬开始集中上市,柑橘售价出现下滑。贡柑因转色期(市场称为“青果”)可上市,较其他中熟柑橘品种价格稍高。但“青果”随着贡柑成熟期的变化,品质极不一致,影响市场对贡柑的消费信心,打压后续上市成熟且优质贡柑的效益。现有基于芽变选种的柑橘品种多集中于无核性状,如华柑四号[2]等。同样,贡柑品种,如华蜜无核贡柑[3]、无籽贡柑[4]等也多集中于无核或少核性状,未见成熟期较贡柑提前的品种。因此,选育出早熟贡柑品种显得尤为重要,是解决“青果”上市品质不一的有效手段,也是避免上市期过于集中的有效途径。
1 选育过程
2016年开始,广东省农业科学院果树研究所与韶关学院、韶关市农业科技推广中心、仁化县农业农村发展服务中心在韶关市联合开展贡柑优异单株筛选。2017年9月在韶关市仁化县下营村果园内发现一单株(编号G20170922)的果实较贡柑早转色,即取其枝条与对照贡柑枝条同时嫁接于酸橘砧上。2018年4月将贡柑及单株G20170922种植于发现单株的同一果园内,2020年开始结果,同时按照《植物新品种特异性、一致性和稳定性测试指南柑橘》(NY/T 2435—2013)开展田间测试。经过连续3 a(年)生物学特性观察记录,单株G20170922 果实膨果期早、较贡柑早熟特性稳定,定名仁选早柑,2023年获得农业农村部颁发的植物新品种权证书(CNA20201005931)(图1)。
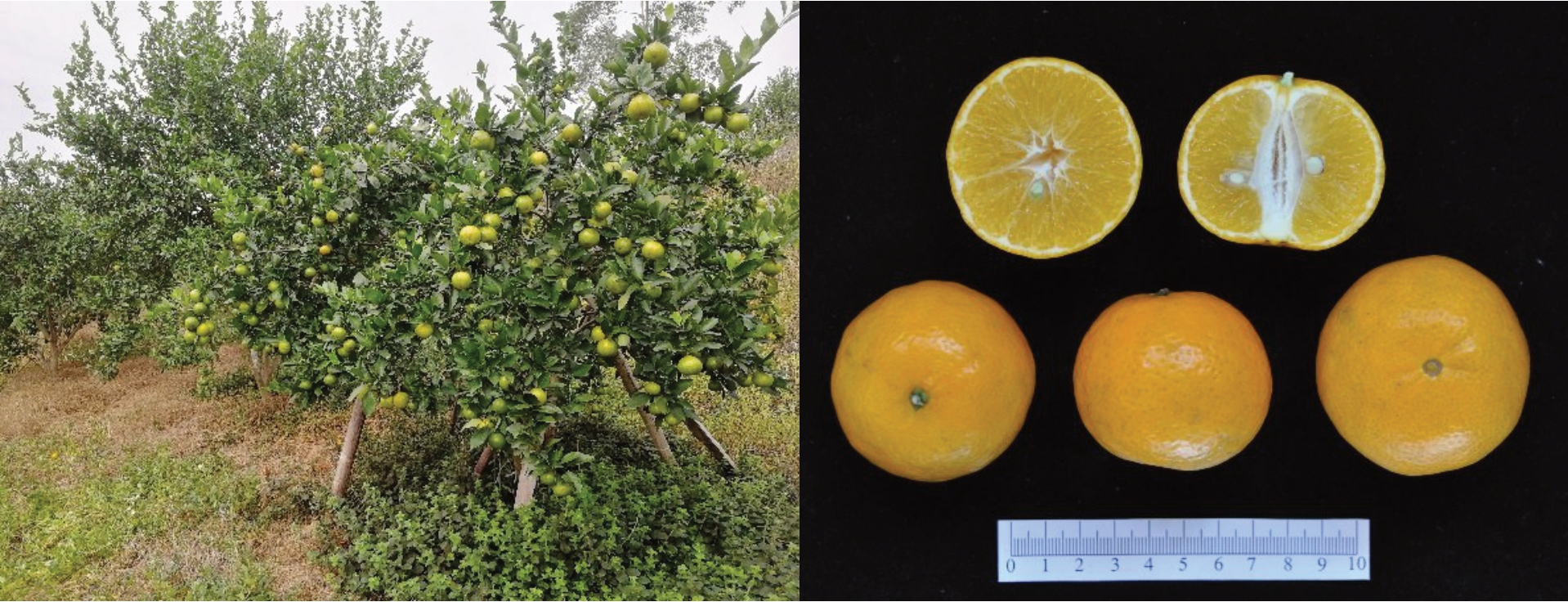

图1 早熟柑橘新品种仁选早柑
Fig.1 A new early-ripening citrus cultivar Renxuanzaogan
2 主要性状
2.1 植物学特征
树冠近圆形,树姿开张。春梢节间长度1.40 cm,部分具短刺,刺长0.10 cm。叶片阔披针形,波状缘,叶形指数2.07,基部楔形,尖端渐尖具缺刻,叶柄长0.85 cm,翼叶窄。花白色,花瓣5 枚,长1.32 cm,宽0.59 cm,花丝13~16条,部分联合,花药淡黄,花柱弓状,高于雄蕊。
2.2 物候期
在韶关,该品种3 月上旬春梢抽发,3 月上中旬开花,5 月上中旬第一次生理落果,5 月中下旬夏梢抽发,8月上中旬秋梢抽发,果实9月下旬至10月上旬转色,11月上中旬成熟。丰产稳产,5年生树产量18 750~37 500 kg·hm-2。
2.3 生长结果特性
果实近球形,平均单果质量78.07 g,果形指数0.84,果基圆形,果顶平,乳突不明显,果面有光泽,油胞平,果皮黄橙色,厚度0.15 cm,较易剥皮,果心半充实,囊瓣半月形,整齐,9~12瓣,囊壁薄,较易分离,汁胞紧实,纺锤形,果肉颜色均匀,橙色,脆嫩较化渣。可食率73.86%,果汁含量(w,后同)为48.89%,可溶性固形物含量为14.0%,总酸含量为0.52%,总糖含量为11.2%,维生素C 含量(ρ)为356 mg·L-1(表1)。单果种子数3~10 粒,种子楔形,子叶白色,多胚。
表1 果实性状与熟期性状差异
Table 1 Differences in fruit traits and fruit maturation period
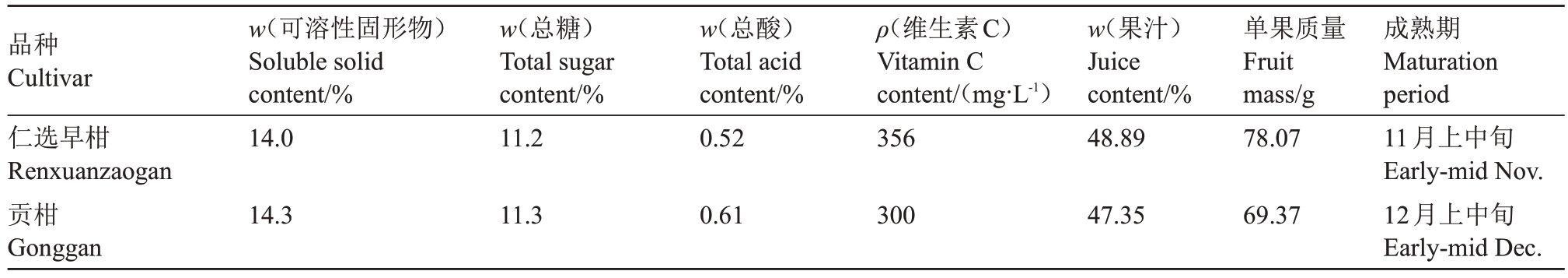
品种Cultivar仁选早柑Renxuanzaogan贡柑Gonggan w(可溶性固形物)Soluble solid content/%14.0 w(总糖)Total sugar content/%11.2 w(总酸)Total acid content/%0.52 ρ(维生素C)Vitamin C content/(mg·L-1)356 w(果汁)Juice content/%48.89单果质量Fruit mass/g 78.07 14.3 11.3 0.61 300 47.35 69.37成熟期Maturation period 11月上中旬Early-mid Nov.12月上中旬Early-mid Dec.
2.4 抗逆性
连续3 a 区域试验表明,与对照品种贡柑一样,该品种易感黄龙病,对褐斑病敏感。在网棚设施内栽培时,其产量较贡柑稳定。
3 全基因组重测序及分子鉴定
3.1 全基因组重测序
提取贡柑、仁选早柑基因组DNA,送北京百迈客生物科技有限公司(Biomarker Technologies)采用Illumina测序平台进行高通量测序,测序深度为10X,以克里曼丁橘(与贡柑同为橘橙杂交种)为参照,与克里曼丁橘基因组比较,仁选早柑鉴定出2 874 326个SNPs,588 506 个InDels,贡柑则鉴定出2 726 005 个SNPs,579 333个InDels(表2)。仁选早柑与贡柑二者间差异SNPs、InDels 分别为881 840 个、172 838 个,分别占贡柑鉴定出SNPs、InDels 总数的32.35%、29.83%。可见,仁选早柑与对照贡柑基因组间差异大。
表2 贡柑、仁选早柑全基因组差异
Table 2 Genome differences between Gonggan and Renxuanzaogan
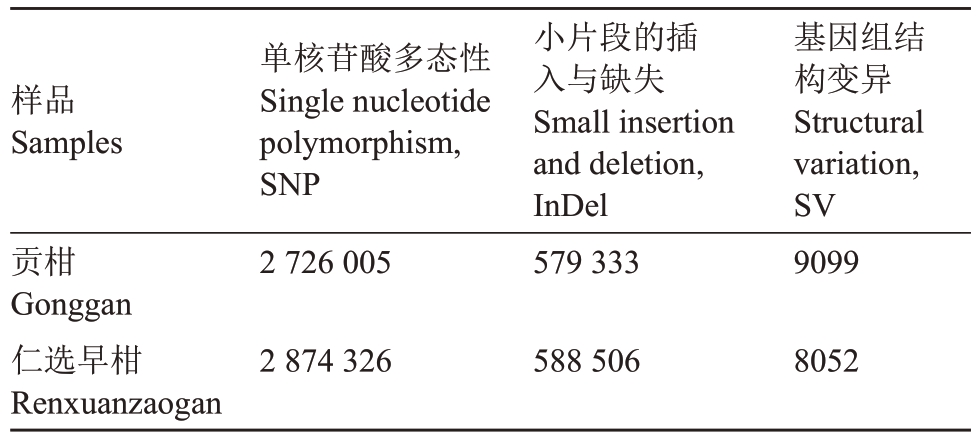
样品Samples贡柑Gonggan仁选早柑Renxuanzao SNPa In n Dd e d le let 2 726 005579 333 2 874 326588 506 gan单核苷酸多态性Single nucleotide polymorphism,小片段的插入与缺失Small insertion ion,基因组结构变异Structural variation,SV 9099 8052
3.2 仁选早柑与贡柑的SSR分子鉴定
提取仁选早柑与贡柑DNA,采用SSR方法并参照郭雁君等[5]的报道,引物为CMS30:F(5’-AA-CACCCCTTGGAGGGAG-3’),R(5’-GCTGTTCACACACACAACCC-3’)。如 图2 所 示,在200~300 bp 之间,仁选早柑与对照贡柑PCR产物电泳条带差异明显。
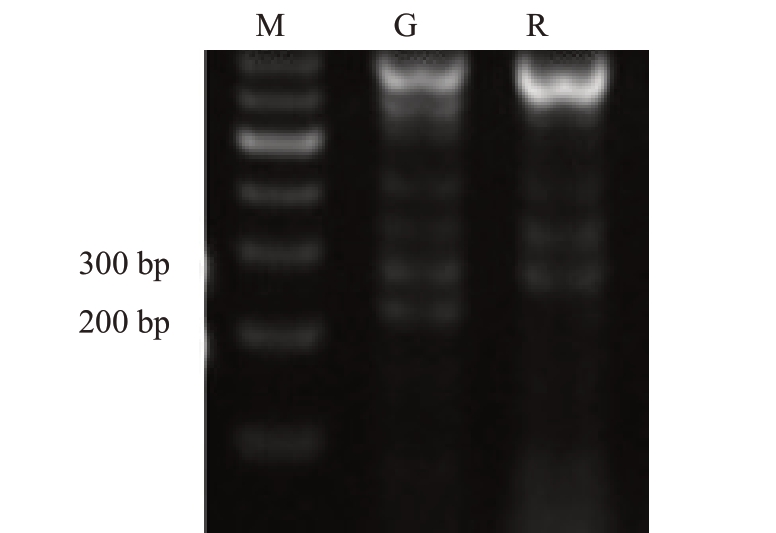
图2 仁选早柑与贡柑引物CMS30 PCR 扩增产物
Fig.2 Amplification of Renxuanzaogan and Gonggan by primer CMS30
M.DNA marker;G.贡柑;R.仁选早柑。
M.DNA marker;G.Gonggan;R.Renxuanzaogan.
4 栽培技术要点
4.1 适栽区
该品种适宜在广东、广西年均温20 ℃以上的贡柑种植区域种植。建园应选择水源丰富的缓坡地,避免在低洼湿润的小盆地区域种植。为延缓柑橘黄龙病的传播,优选周边无九里香、柑橘等芸香科植物种植的区域建园,或设置适当的防风林或防风带。苗木繁育可使用枳、酸橘、香橙等作砧木。新建果园种植无病容器大苗可加速形成丰产树形,获得经济产量。
4.2 水肥管理
幼龄树施肥应勤施薄施,促成树冠。成年树在夏梢抽发期加强树体营养管理,避免落果。
4.3 病虫害防治
做好柑橘黄龙病防控,并在春、夏、秋梢抽发期做好传病虫媒介柑橘木虱、粉虱及蚜虫的防治。在新梢抽发期若遇雨季,尤其是气温处于20~28 ℃时,应注意加强柑橘褐斑病的防治。
[1]甘廉生,叶自行,马培恰,唐小浪,许建楷.广东的贡柑[J].中国南方果树,2008,37(5):5-6.GAN Liansheng,YE Zixing,MA Peiqia,TANG Xiaolang,XU Jiankai.Gonggan in Guangdong[J].South China Fruits,2008,37(5):5-6.
[2]吴巨勋,张雅菁,伊华林,谢宗周,邓秀新.无核柑橘新品种华柑4 号的选育[J].果树学报,2022,39(3):495-498.WU Juxun,ZHANG Yajing,YI Hualin,XIE Zongzhou,DENG Xiuxin.Breeding report of a new seedless ponkan cultivar Huagan No.4[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2022,39(3):495-498.
[3]秦永华,叶自行,胡桂兵,陈杰忠,徐超,李谷雨,林顺权.柑橘新品种‘华蜜无核贡柑’[J].园艺学报,2014,41(6):1267-1268.QIN Yonghua,YE Zixing,HU Guibing,CHEN Jiezhong,XU Chao,LI Guyu,LIN Shunquan.‘Huami Wuhe Gonggan’,A new Citrus cultivar[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2014,41(6):1267-1268.
[4]吴文,黄永敬,马培恰,唐小浪,易干军,王平.柑橘新品种‘无籽贡柑’的选育[J].果树学报,2013,30(5):898-899.WU Wen,HUANG Yongjing,MA Peiqia,TANG Xiaolang,YI Ganjun,WANG Ping.Selection of a seedless citrus cultivar‘Wuzi Gonggan’[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2013,30(5):898-899.
[5]郭雁君,曾继武,胡亚平,郭丽英,蒋惠,周希琴,吉前华.基于SSR 标记的肇庆地区柑橘品种分类地位研究[J].中国农学通报,2014,30(4):137-143.GUO Yanjun,ZENG Jiwu,HU Yaping,GUO Liying,JIANG Hui,ZHOU Xiqin,JI Qianhua.Classification of Zhaoqing local Citrus germplasm resources based on simple sequence repeat molecular marker analysis[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2014,30(4):137-143.