甜瓜(Cucumis melo L.)是全世界普遍栽培的一种葫芦科作物,具有较高的商品价值和经济价值[1]。甜瓜遗传基础狭窄,优异种质资源缺乏,传统育种技术周期长、效率低,导致优良品种更新慢,制约了我国甜瓜产业的可持续发展。双单倍体培养技术作为可以快速有效获取纯合种质的一种育种手段,已成为国内外甜瓜育种工作者研究的热点[2-4]。植物不定根的发生受多种内外因素的影响,内源植物激素是诱导不定根发生的主导因子[5-6]。王雪姣[7]的研究发现,吲哚乙酸(IAA)、赤霉素(GA3)、细胞分裂素(ZR)对不定根的形成有促进作用,脱落酸(ABA)则对不定根的形成有抑制作用,IAA/ABA比值的提高,有利于不定根的形成。多胺作为一类生长调控物质,可通过影响激素的代谢或信号传导调控不定根的发生与伸长[8-9]。Faivre-Rampant 等[10]对烟草的研究发现培养基中添加精胺(Spm)、亚精胺(Spd)、腐胺(Put)等多胺类物质对幼苗不定根形成有明显促进作用;相关氧化酶活性与植物不定根的发生和发展也有着密切的关系[11]。徐盼盼[12]对牡丹外植体组织培养研究,认为吲哚乙酸氧化酶(IAAO)能够氧化植物体内的IAA,从而影响不定根的形成,多酚氧化酶(PPO)、过氧化物酶(POD)可以催化酚类物质与IAA结合成一种“IAA-酚酸复合物”,加速不定根的产生。目前,国内外大多数学者对甜瓜双单倍体的研究多集中在培养体系建立方面,并取得了一定的研究进展[13-16],但有关诱导组培生根过程中内源激素、多胺类物质及相关氧化酶活性的变化未见报道。为此,笔者在本研究中主要通过探究甜瓜双单倍体芽生根培养过程内源激素、多胺类物质含量以及相关氧化酶活性的变化规律,以期阐明其对不定根诱导分化和伸长响应的生理机制,为调控甜瓜双单倍体组培苗快速生根提供参考。
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料
供试品种为锦绣脆玉,由河南省农业科学院园艺研究所选育的厚皮甜瓜杂交种;将其未受精子房离体培养获得的芽,经流式细胞仪鉴定为单倍体,利用秋水仙素进行加倍,再经流式细胞仪鉴定确认为双单倍体芽[17]。
1.2 试验设计
选取长势一致的双单倍体芽接入培养基(MS+IAA 0.1 mg·L-1+30 g·L-1 蔗糖+6 g·L-1 琼脂,pH=5.86)中,在温度(25±2)℃、光照度3 000~4 000 lx、光照时间16 h·d-1的条件下进行生根培养。每瓶接种8株,共接入120瓶。分别生长至0、7、14、21、28 d,取基部茎段(长度约0.5 cm)进行内源激素、多胺及相关酶活性的测定。试验采用随机区组设计,每个测定时段随机选6瓶,3次重复。
1.3 测定项目与方法
内源激素:吲哚乙酸、玉米素核苷(ZR)、赤霉素、脱落酸含量测定采用液相色谱法[18]。液相色谱条件:岛津LC-20AT,紫外检测器SPD-20A,柱温箱CTO-20AC,C18反相色谱柱(150 mm×4.6 mm,5 μm);流动相A:100%甲醇;B:0.1%乙酸水溶液;A∶B=55∶45;进样量20 μL,流速0.8 mL·min-1,柱温30 ℃,紫外波长254 nm。
多胺类物质:精胺、亚精胺、腐胺含量测定采用液相色谱法[19]。液相色谱条件:伍丰LC-100,C18反相色谱柱(150 mm×4.6 mm,5 μm);流动相A:90%乙腈/10%(含0.1%乙酸的0.1 mol·L-1乙酸胺);B:10%乙腈/90%(含0.1%乙酸的0.1 mol·L-1乙酸胺);A∶B=60∶40;进样量20 μL,流速0.8 mL·min-1,柱温35 ℃,紫外波长254 nm。
相关酶活性:多酚氧化酶活性测定采用邻苯二酚法,吲哚乙酸氧化酶和过氧化物酶活性测定采用比色法,均参照李合生[20]的方法略有改动。
1.4 数据处理
试验数据用Microsoft Excel 2013 和SPSS 20.0软件进行处理分析,差异性比较采用Duncan’s新复极差法。
2 结果与分析
2.1 甜瓜双单倍体生根过程中不同时期的变化
从图1可以看出,接种后7 d时茎段基部细胞开始启动分化,愈伤组织开始出现,以后进入细胞分裂旺盛期,14 d时不定根根原基逐渐开始形成,21 d时外植体上形成肉眼可见的不定根,之后不定根数量和长度逐渐增加和伸长,28 d 以后须根数量和伸长量明显增加。
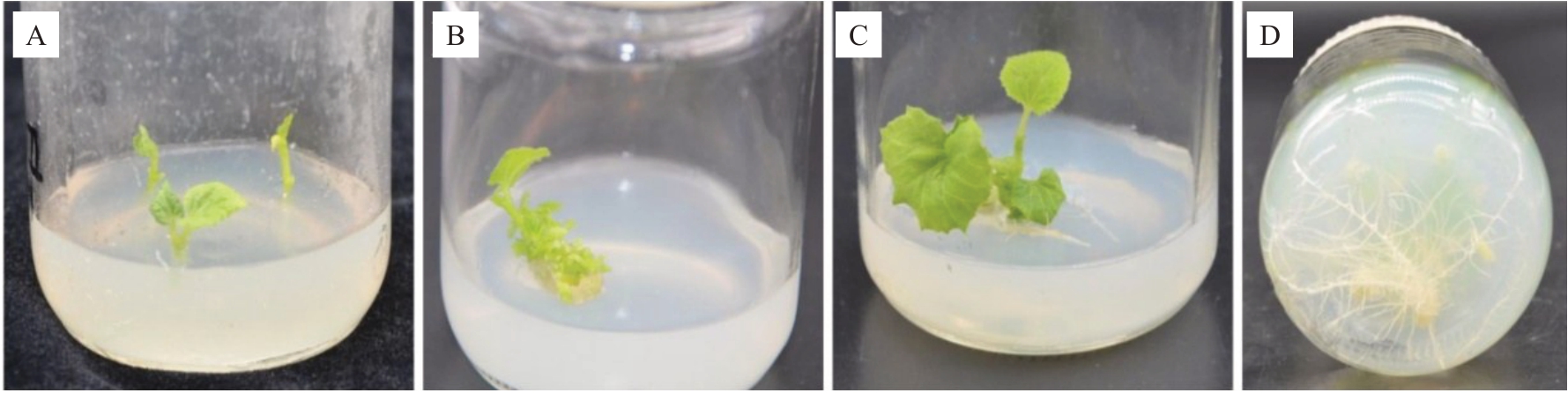
图1 甜瓜双单倍体芽生根状况
Fig.1 Rooting of muskmelon double haploid
A.接种后7 d;B.接种后14 d;C.接种后21 d;D.接种后28 d。
A.7 days after inoculation;B.14 days after inoculation;C.21 days after inoculation;D.28 days after inoculation.
2.2 甜瓜双单倍体生根过程中内源激素含量及比值的变化
甜瓜双单倍体生根过程中内源激素IAA、ABA含量(w,后同)均呈现下降-升高的趋势,GA3含量呈现升高-下降的趋势,ZR含量则呈现下降-升高-下降的趋势(图2)。其中,IAA含量在第7天时最低,0~7 d下降迅速,7~21 d 上升缓慢,21~28 d 上升迅速,在28 d达到最高值,为0.33 μg·g-1;ABA含量在0 d时最高,为0.35 μg·g-1,在第14天达到最低,0~14 d迅速下降,14~28 d缓慢上升;GA3含量在第7天达到最高值,为4.41 μg·g-1,0~7 d 上升迅速,7~21 d 下降速度较快,21~28 d下降平缓;ZR含量在0~7 d缓慢下降,7~21 d 迅速上升,21~28 d 又迅速下降,在21 d 时最高为3.11 μg·g-1。上述结果表明,甜瓜双单倍体组培苗生根与IAA、ABA、ZR、GA3 4 种内源激素密切相关,在幼苗发育后期,一定范围内的IAA、ABA含量升高及GA3、ZR含量降低有利于不定根诱导分化和生长发育。

图2 不同培养时间IAA、ABA、GA3和ZR 的含量
Fig.2 The contents of IAA,ABA,GA3 and ZR at different culture times
同一图中不同小写字母表示差异显著(p<0.05)。下同。
The small letters on the same figure represent the significant difference(p<0.05).The same below.
IAA/ABA 值呈现逐渐增长趋势,其中0~7 d 增长缓慢,7~28 d增长迅速;IAA/ZR值呈现升高-下降-升高的变化趋势,0~21 d 变化较为平缓,21~28 d 升高迅速(图3)。表明IAA/ABA、IAA/ZR的值与甜瓜双单倍体生根有紧密关系,后期IAA/ABA 和IAA/ZR值的升高有利于不定根的发生。
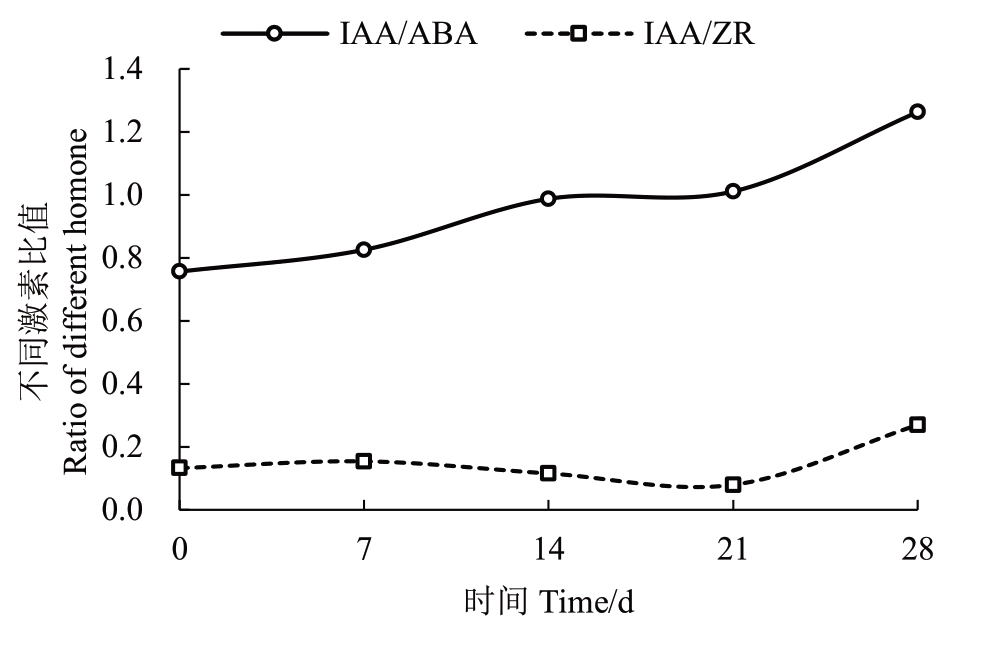
图3 不同培养时间IAA/ABA 和IAA/ZR 值
Fig.3 The values of IAA/ABA and IAA/ZR at different culture times
2.3 甜瓜双单倍体在生根过程中多胺类物质含量的变化
腐胺、精胺和亚精胺含量在诱导生根过程中均呈现升高-下降-升高的变化趋势(图4),0~14 d 和21~28 d 逐渐上升,14~21 d 逐渐下降,在14 d 时达到第一个峰值,分别为14.65 μg·g-1、4.90 μg·g-1、12.57 μg·g-1,且14~28 d均显著高于第0天,第28天分别比第0 天提高387.08%、796.55%、327.16%。Put 和Spm 含量0~7 d 变化较为平缓,7~28 d 变化幅度较大,Spd 含量则在0~7 d 变化幅度较大,7~28 d变化较为平缓。表明甜瓜双单倍体生根过程与多胺类物质Put、Spm 和Spd 含量有关,后期其含量的升高有利于不定根的形成。

图4 不同培养时间Spm、Spd 和Put 的含量
Fig.4 The contents ofSpm,Spd and Put at different culture times
2.4 甜瓜双单倍体在生根过程中相关酶活性的变化
甜瓜双单倍体在生根过程中,吲哚乙酸氧化酶、多酚氧化酶活性呈现升高-下降-升高的趋势,过氧化物酶活性呈现逐渐上升的趋势(图5)。其中,IAAO、PPO活性在0~7 d时上升较快,分别在第7天和第14 天时达到最大值,为201.55 μg·g-1·h-1、385.00 U·g-1,7~28 d时变化幅度相对较小,但其活性均显著高于第0 天;POD 活性在0~7 d 时上升较慢,7~28 d 时上升较快,在第28 天达到最大值,为1 105.54 U·g-1,除第0天和第7天差异不显著外,其他测定天数间差异均达显著水平。结果表明,甜瓜双单倍体在生根过程中可通过调控相关酶的活性来促进不定根的发生。
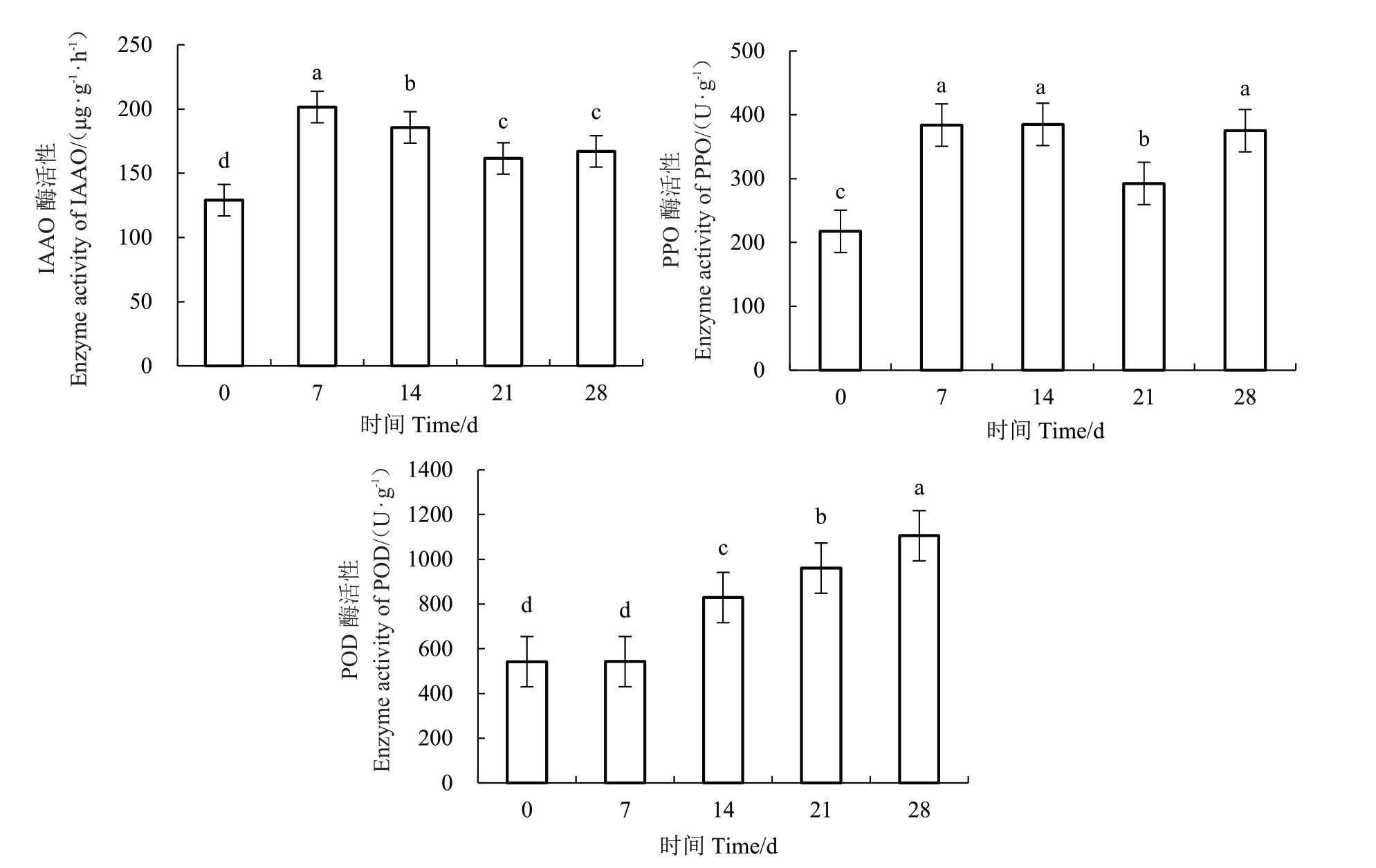
图5 不同培养时间IAAO、PPO 和POD 3 种酶活性
Fig.5 The IAAO,PPO and POD enzyme activities at different culture times
2.5 在诱导生根过程中多胺类物质、内源激素含量及关联酶活性的相关性分析
由甜瓜双单倍体诱导生根过程中多胺类物质、内源激素含量与3种关联酶活性相关性分析(表1)可见,IAA/ABA 与Put、Spm、POD 呈显著或极显著正相关(r=0.93**、0.86*、0.96**);GA3与IAAO 酶活呈极显著正相关(r=0.97**);IAA 与IAA/ZR 呈显著正相关(r=0.86*)。Put与Spm、Spd和POD呈显著或极显著正相关(r=0.98**、0.85*、0.91*);Spm与Spd呈显著正相关(r=0.83*);IAAO 与PPO 呈显著正相关(r=0.91*)。表明IAA/ABA比值和Put含量对甜瓜双单倍体组培苗不定根诱导分化和生长有重要促进作用。
表1 不同生理生化指标相关性分析
Table 1 Correlation analysis of different physiological and biochemical parameters

注:**表示在0.01 水平显著相关,*表示在0.05 水平显著相关。
Note:**indicates significant correlation at 0.01 level,*indicates significant correlation at the 0.05 level.
指标Index ZR GA3 IAA ABA IAA/ABA IAA/ZR Put Spm Spd IAAO PPO POD POD 0.08-0.18 0.59-0.70 0.96**0.38 0.91*0.81 0.70 0.02 0.33 1.00 ZR 1.00 GA3-0.18 1.00 IAA-0.49-0.53 1.00 ABA-0.20-0.50 0.07 1.00 IAA/ABA-0.20-0.07 0.70-0.66 1.00 IAA/ZR-0.84*-0.10 0.86*0.02 0.61 1.00 Put-0.10 0.05 0.45-0.81 0.93**0.40 1.00 Spm-0.23 0.10 0.41-0.76 0.86*0.44 0.98**1.00 Spd-0.09 0.55 0.10-0.96**0.75 0.25 0.85*0.83*1.00 IAAO-0.28 0.97**-0.36-0.63 0.15 0.07 0.28 0.33 0.72 1.00 PPO-0.48 0.78 0.00-0.72 0.50 0.39 0.59 0.66 0.86*0.91*1.00
3 讨 论
不定根的形成在植物发育生物学中是一个重要的课题[21]。本研究表明,甜瓜双单倍体组培苗生根与IAA、ABA、ZR、GA34种内源激素以及IAA/ABA、IAA/ZR的比值密切相关。其中内源激素IAA、ABA含量变化呈现下降-升高的趋势,与闫帅等[22]对杜梨组培苗的研究结果一致;可能是根原基尚未形成时,IAAO 酶活性增强促使IAA 降解,后期不定根原基的诱导和局部生长素水平升高同时发生;在一定范围内ABA浓度升高可以促进不定根的发生,过高浓度ABA又会抑制不定根的发生,而贺丹等[23]对牡丹试管苗的研究则与本研究结果中ABA的变化相反,造成这种差异的原因可能与不同植物种类生根过程对ABA 的敏感程度以及所设置的环境条件不同有关。本试验结果中GA3含量呈现升高-下降的趋势,表明GA3的调节作用在根原基的形成后逐步显现,且后期GA3含量降低,在一定程度上促进了不定根的形成,与王金祥等[24]对绿豆插条生根的研究结果一致。玉米素核苷是天然细胞分裂素,在植物的生长过程中促进细胞分裂和扩大[25]。本研究中,ZR含量则呈现下降-升高-下降的变化趋势,可能与根原基形成前后及根伸长时细胞数量和分裂速度对ZR需求量存在差异有关,这在贺丹等[23]对牡丹试管苗生根的研究中得到了验证。本研究结果还表明,在诱导生根后期IAA/ABA和IAA/ZR比值增大更有利于甜瓜双单倍体不定根的发生和伸长,这与对菊花[9]、百合[26]组培生根的研究结果一致。激素作为植物的内源信号在生根过程中发挥着作用,内源激素之间可能会存在着一种协同或拮抗作用,但具体调控不定根的形成机制还有待进一步研究。
多胺代谢的特征之一是参与了植物的生物和非生物因素胁迫[27],其含量的变化可有效改变关联酶的活性以提高植物体的抗逆性,进而调控生命活动[28]。本研究结果表明,甜瓜双单倍体在生根过程中多胺类物质脯氨、精氨和亚精胺含量均呈现升高-下降-升高的变化趋势,后期其含量的升高有利于不定根的形成和伸长,与闫帅等[22]杜梨组培生根的研究结果一致。这可能是多胺类物质在根原基形成前和形成后主要参与对外界胁迫的抵御,根原基形成过程中则主要参与不定根根原基的诱导,但其具体原因还需进一步探讨。
植物的生根是一个复杂的生理活动过程,体内相关氧化酶如吲哚乙酸氧化酶、多酚氧化酶、过氧化物酶在这一过程中发挥重要作用[29]。在本研究中,IAAO、PPO 酶活性在愈伤组织诱导阶段逐渐上升,在不定根形成后呈现下降趋势,在伸长期又逐渐升高,与王瑞等[11]对油茶和贺丹等[23]对牡丹组培苗的研究结果基本一致,可能与2 种酶在生根过程中调控有关激素和多胺类物质的形成有关,这在2 种酶活性与相关激素和多胺类物质含量的相关性中也得到了证实;POD活性在生根过程中则呈现逐渐上升的趋势,可能与其调控IAA/ABA的比值有关。这充分揭示了甜瓜双单倍体不定根的发生和伸长与这3种氧化酶活性有密切关系。
4 结 论
甜瓜双单倍体组培苗生根与IAA、ABA、ZR、GA3以及多胺类物质Spm、Spd、Put 含量密切相关,一定范围内的IAA、ABA 含量升高及GA3、ZR 含量降低有利于不定根诱导分化和生长发育,IAA/ABA、IAA/ZR 比值升高有利于不定根的发生;后期组培苗体内Spm、Spd、Put含量的升高有利于不定根的形成;其中IAA/ABA 的比值及Put 含量在诱导生根过程中发挥着重要的调控作用,IAAO、PPO、POD酶活性与不定根的发生和伸长也有密切关系。
[1]张雪娇.甜瓜果实相关性状QTL 分析[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2013.ZHANG Xuejiao.The QTL analysis of traits related fruits in melon (Cucumis melo L.)[D].Harbin:Northeast Agricultural University,2013.
[2]DONG Y Q,ZHAO W X,LI X H,LIU X C,GAO N N,HUANG J H,WANG W Y,XU X L,TANG Z H.Androgenesis,gynogenesis,and parthenogenesis haploids in cucurbit species[J].Plant Cell Reports,2016,35(10):1991-2019.
[3]李海伦,王琰,赵卫星,李晓慧,常高正,高宁宁,梁慎,康利允,徐小利.甜瓜未受精子房或胚珠离体培养研究进展[J].北方园艺,2019(10):134-140.LI Hailun,WANG Yan,ZHAO Weixing,LI Xiaohui,CHANG Gaozheng,GAO Ningning,LIANG Shen,KANG Liyun,XU Xiaoli.Advances in unfertilized ovary or ovule of melon in vitro culture[J].Northern Horticulture,2019(10):134-140.
[4]柯思佳,钱春桃,包卫红,倪维晨,李瑞霞.甜瓜离体雌核发育诱导单倍体研究进展[J].中国瓜菜,2018,31(9):1-5.KE Sijia,QIAN Chuntao,BAO Weihong,NI Weichen,LI Ruixia.Research progress of in vitro gynogenesis induction haploid in melon[J].China Cucurbits and Vegetables,2018,31(9):1-5.
[5]蒙海涛,韩清芳,贾志宽,李子芳,王莹.水培紫花苜蓿的茎段生根过程中内源激素含量变化[J].植物生理学通讯,2008,44(3):498-500.MENG Haitao,HAN Qingfang,JIA Zhikuan,LI Zifang,WANG Ying.Changes of the endogenous hormone contents in alfalfa stem segments during the rooting process under solution culture[J].Plant Physiology Communications,2008,44(3):498-500.
[6]马振华,赵忠,张晓鹏,张博勇,赵辉,詹晓红.四倍体刺槐扦插生根过程中氧化酶活性的变化[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2007,35(7):85-89.MA Zhenhua,ZHAO Zhong,ZHANG Xiaopeng,ZHANG Boyong,ZHAO Hui,ZHAN Xiaohong.Studied on the oxidation enzymes activities in the periods of making roots in the green branch of Robinia pseudoacacia[J].Journal of Northwest A&F University(Natural Science Edition),2007,35(7):85-89.
[7]王雪娇.蓝莓组培苗扦插繁殖技术与生根机理的研究[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2016.WANG Xuejiao.Cutting propagation techinique and rooting mechanism of blueberries tissue culture[D].Harbin:Northeast Agricultural University,2016.
[8]MOHAN B S,HOSETTI B B.Phytotoxicity of cadmium on the physiological dynamics of Salvinia natans L.grown in macrophyte ponds[J].Journal of Environmental Biology,2006,27(4):701-704.
[9]徐东花,孙霞,孙宪芝,徐璐.亚精胺调控菊花不定根发生的生理机制[J].植物生理学报,2014,50(10):1546-1554.XU Donghua,SUN Xia,SUN Xianzhi,XU Lu.Physiological mechanism of spermidine regulation on formation of adventitious roots in Chrysanthemum[J].Plant Physiology Journal,2014,50(10):1546-1554.
[10]FAIVRE-RAMPANT O,KEVERS C,DOMMES J,GASPAR T.The recalcitrance to rooting of the micropropagated shoots of the rac tobacco mutant:implications of polyamines and of the polyamine metabolism[J].Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2000,38(6):441-448.
[11]王瑞,陈永忠,王湘南,彭邵锋,杨小胡,陈隆升,马力.油茶组培苗生根过程中生理生化指标的变化[J].经济林研究,2015,33(2):68-72.WANG Rui,CHEN Yongzhong,WANG Xiangnan,PENG Shaofeng,YANG Xiaohu,CHEN Longsheng,MA Li.Changes of physiological and biochemical indexes during tissue culture seedlings rooting in Camellia oleifera[J].Nonwood Forest Research,2015,33(2):68-72.
[12]徐盼盼.环境因子对牡丹试管苗生根的影响[D].郑州:河南农业大学,2011.XU Panpan.The effect of environmental factor on rooting culture of Paeonia suffruticosa in vitro[D].Zhengzhou:Henan Agricultural University,2011.
[13]牛明明.甜瓜离体雌核发育诱导单倍体研究[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2012.NIU Mingming.Study of gynogenesis in vitro to induce haploid plants in melon[D].Harbin:Northeast Agricultural University,2012.
[14]韩丽华.厚皮甜瓜未受精胚珠离体培养技术[D].保定:河北农业大学,2004.HAN Lihua. In vitro gynogenesis in melon (Cucumis melo L.)from unpollinated ovules[D].Baoding:Hebei Agricultural University,2004.
[15]高宁宁,李晓慧,康利允,常高正,梁慎,徐小利,李海伦,王慧颖,赵卫星.厚皮甜瓜未受精子房离体培养获得胚囊再生植株[J].果树学报,2020,37(7):1036-1045.GAO Ningning,LI Xiaohui,KANG Liyun,CHANG Gaozheng,LIANG Shen,XU Xiaoli,LI Hailun,WANG Huiying,ZHAO Weixing.Acquisition of plants regenerated from embryo sac of unfertilized ovary in muskmelon[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2020,37(7):1036-1045.
[16]贾媛媛,张永兵,刁卫平,陈劲枫,程志芳,张晓青.双单倍体甜瓜的获得及其初步定性研究[J].江苏农业科学,2008,36(1):116-118.JIA Yuanyuan,ZHANG Yongbing,DIAO Weiping,CHEN Jinfeng,CHENG Zhifang,ZHANG Xiaoqing.Obtainment of double haploid melon and its preliminary property study[J].Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2008,36(1):116-118.
[17]高宁宁,李晓慧,康利允,梁慎,常高正,李海伦,王慧颖,王琰,徐小利,赵卫星.单倍体甜瓜染色体加倍技术研究[J].中国瓜菜,2021,34(6):28-32.GAO Ningning,LI Xiaohui,KANG Liyun,LIANG Shen,CHANG Gaozheng,LI Hailun,WANG Huiying,WANG Yan,XU Xiaoli,ZHAO Weixing.Study on chromosome doubling technique of haploid muskmelon[J].China Cucurbits and Vegetables,2021,34(6):28-32.
[18]郭敏敏,王清连,胡根海.利用高效液相色谱法分离和测定棉花组织培养过程中4 种内源激素[J].生物技术通讯,2009,20(2):213-216.GUO Minmin,WANG Qinglian,HU Genhai.Separation and determination of four plant hormones during somatic embryogenesis of Gossypium hirsutum L.with HPLC[J].Letters in Biotechnology,2009,20(2):213-216.
[19]刘俊,吉晓佳,刘友良.检测植物组织中多胺含量的高效液相色谱法[J].植物生理学通讯,2002,38(6):596-598.LIU Jun,JI Xiaojia,LIU Youliang.High performance liquid chromatography method for measuring polyamine content in plant tissue[J].Plant Physiology Communications,2002,38(6):596-598.
[20]李合生.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2000.LI Hesheng.Principles and techniques of plant physiological biochemical experiment[M].Beijing:Higher Education Press,2000.
[21]赵艳,高晓余,查友贵,王静,王斌,肖春,叶敏.植物生长调节剂与不定根的形成[J].湖北农业科学,2011,50(1):12-16.ZHAO Yan,GAO Xiaoyu,ZHA Yougui,WANG Jing,WANG Bin,XIAO Chun,YE Min.Plant growth regulators and adventitious root formation[J].Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2011,50(1):12-16.
[22]闫帅,张少瑜,徐锴,袁继存,李晓光,周江涛,程存刚,赵德英.杜梨组培生根过程中多胺、内源激素及相关氧化酶活性的变化[J].果树学报,2019,36(3):318-326.YAN Shuai,ZHANG Shaoyu,XU Kai,YUAN Jicun,LI Xiaoguang,ZHOU Jiangtao,CHENG Cungang,ZHAO Deying.Dynamic changes in polyamines,endogenous hormones and oxidase activities during rooting of in vitro plantlets of Pyrus betulifolia Bunge[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2019,36(3):318-326.
[23]贺丹,王政,何松林.牡丹试管苗生根过程解剖结构观察及相关激素与酶变化的研究[J].园艺学报,2011,38(4):770-776.HE Dan,WANG Zheng,HE Songlin.Adventitious root generating process and hormone and enzyme changes in vitro Paeonia suffruticosa[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2011,38(4):770-776.
[24]王金祥,潘瑞炽.绿豆插条生根过程中内源激素含量变化[J].植物生理学通讯,2004,40(6):696-698.WANG Jinxiang,PAN Ruichi.Changes in endogenous hormone contents of mung bean during adventitious root formation of cuttings[J].Plant Physiology Communications,2004,40(6):696-698.
[25]潘瑞炽.植物生理学[M].7 版.北京:高等教育出版社,2013.PAN Ruichi.Plantphysiology[M].7th ed.Beijing:Higher Education Press,2013.
[26]孙亮,王有国,贾文杰,王立,王齐.外源H2O2对百合小鳞茎生根发芽和内源激素含量的影响[J].中国农学通报,2017,33(16):65-70.SUN Liang,WANG Youguo,JIA Wenjie,WANG Li,WANG Qi.Effects of exogenous H2O2 on rooting and germination and endogenous hormone contents of lily bulb[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2017,33(16):65-70.
[27]李亚栋,何近刚.植物多胺代谢与胁迫响应研究进展[J].华北农学报,2012,27(S1):240-245.LI Yadong,HE Jingang.Advance in metabolism and response to stress of polyamines in plant[J].Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica,2012,27(S1):240-245.
[28]杜红阳,刘骨挺,杨青华,刘怀攀.小麦胚中不同形态多胺含量的变化及其与耐旱性的关系[J].作物学报,2016,42(8):1224-1232.DU Hongyang,LIU Guting,YANG Qinghua,LIU Huaipan.Dynamics in contents of different types of polyamine in wheat embryos and its relationship with resistance to drought stress[J].Acta Agronomica Sinica,2016,42(8):1224-1232.
[29]陈启文,周月琴,韩艳娜,李叶云,江昌俊.茶树扦插生根过程中3 种氧化酶活性及多酚含量变化研究[J].安徽农业大学学报,2013,40(6):908-911.CHEN Qiwen,ZHOU Yueqin,HAN Yanna,LI Yeyun,JIANG Changjun.Changes of three oxidase activities and polyphenol content in tea cuttings in the process of rooting[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural University,2013,40(6):908-911.