吸果夜蛾是一类世界性的重要果树害虫,种类繁多,中国约有60种,全世界有100种以上。吸果夜蛾趋化性强,以成虫刺吸水果进行危害,1头成虫可以刺吸多个果实,危害范围包括柑橘、桃、李、苹果、荔枝和猕猴桃等多种经济水果,中国以南方丘陵山区果园受害最为严重。吸果夜蛾根据口器特点和危害习性可以分为嗜好果类、嗜坏果类和兼食类,其中嗜好果类是主要防控对象,包括鸟嘴壶夜蛾Oraesia excavata(Butler)、嘴壶夜蛾Oraesia emiarginata(Fabricius)和艳叶夜蛾Eudocima salaminia(Cramer)等。嗜好果类吸果夜蛾危害严重时可使果园减产达2/3 甚至绝收,造成严重经济损失,是水果产业重点防控害虫之一[1-4]。
1 吸果夜蛾生物生态学特性
1.1 危害习性
吸果夜蛾主要以成虫刺吸水果进行危害,幼虫寄主通常是各类杂草,不危害水果,如嘴壶夜蛾和鸟嘴壶夜蛾幼虫寄主为防己科杂草,这是与其他鳞翅目害虫的主要区别之一[5]。成虫趋化性强,对芳香和甜味敏感,羽化后需要补充营养,会优先吸食薄皮多汁、香味浓重的水果,也会和其他夜蛾一样吸食花蜜或其他营养物。危害时期受水果成熟度和环境温度的影响,吸果夜蛾在温度16 ℃以上时较为活跃,13 ℃时数量开始下降,10 ℃及以下几乎不出没,以老熟幼虫或蛹进行越冬,越冬场所通常在背风向阳的杂草丛内,田间世代重叠。
吸果夜蛾成虫白天通常潜伏在山地的杂草和灌木丛中,傍晚开始陆续飞入果园,在晴朗、闷热及无风的晚上数量最多,21:00—22:00达到危害高峰。Fay等[6]研究指出,晚上飞入果园的吸果夜蛾70.8%是雄蛾,雄蛾多数在19:00—24:00 到达果园,雌蛾则在24:00—5:00。凌晨4:00左右,吸果夜蛾陆续飞回潜伏场所,且山地或近山地果园更易受吸果夜蛾危害[7]。
吸果夜蛾成虫通常利用针状口器刺吸成熟或将要成熟的果实,果实被害处可以看到明显的针眼大小吸孔,挑开吸孔可以看到果皮内具有明显的孔穴,内呈海绵状,用手挤压有绵软感。一段时间后,吸孔周围受到感染开始腐烂变褐,最终导致果实脱落。1头成虫夜间可以刺吸多个果实,当果实成熟期与羽化高峰期接近时,可使果园大面积落果,造成严重经济损失[6-10]。
1.2 主要种类
强喙夜蛾亚科(Ophiderinae)和裳夜蛾亚科(Catocalinae)占吸果夜蛾大多数,是其主要种类(表1)。与一般仅吸食花蜜的夜蛾相比,二者喙的构造更为发达和复杂,且与取食有关的肌肉数目和功能也有所不同。吸果夜蛾的喙缘主要有2 种类型,一类为全缘具钩,端缘有朝上的弯钩,有强几丁质化的附属物,另一类为喙缘有可直立的倒刺[8-9]。但口器发达并不意味着该种夜蛾就是吸果夜蛾,黄地老虎Agrotis segetum(Denis et Schiffermüller)与吸果夜蛾口器相似,但未见其刺吸水果的报道[8]。
表1 (续) Table 1 (Continued)
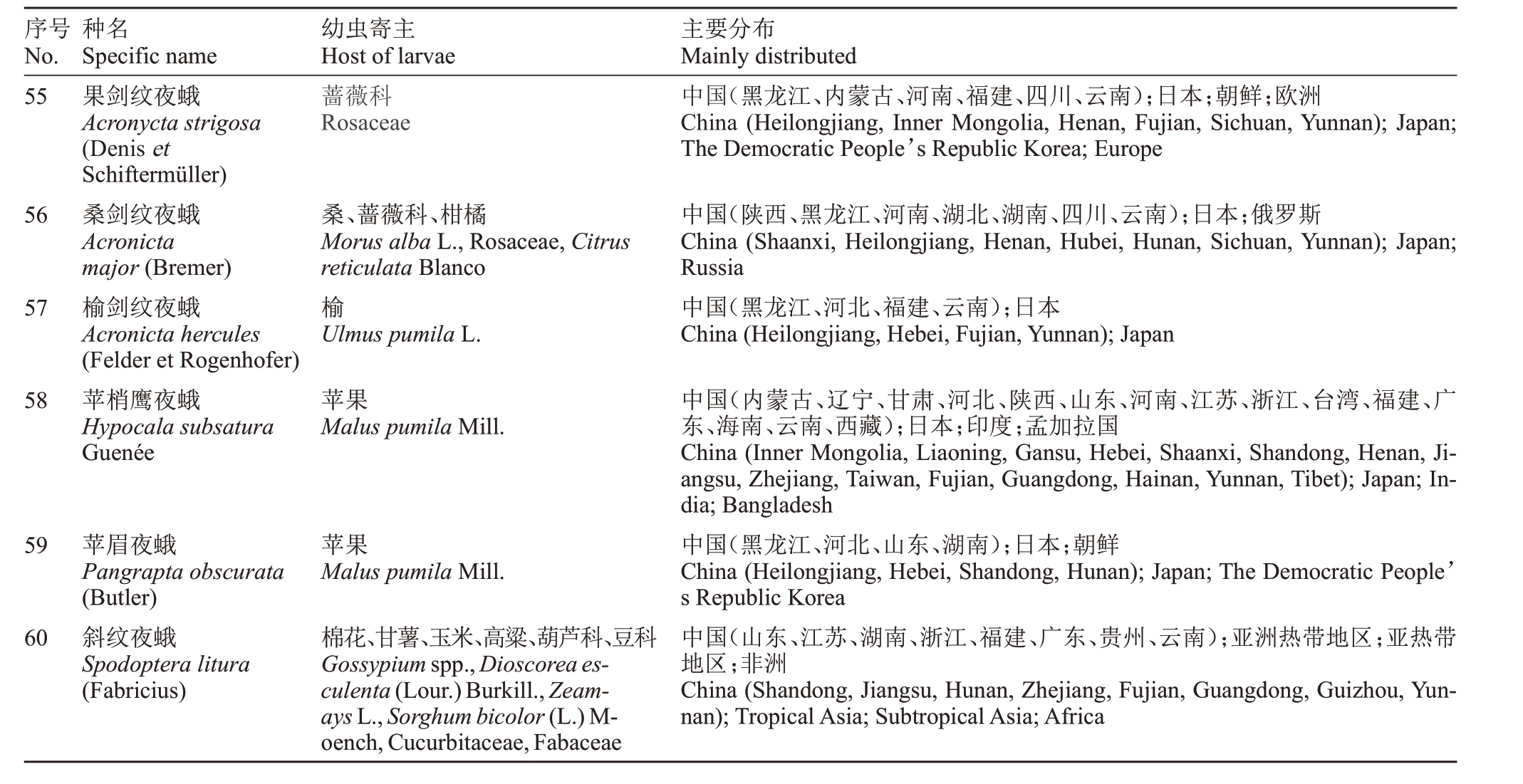
注:序号1~10 为嗜好果类,11~60 为嗜坏果类,*表示该种在部分文献中被分为兼食类。
Note:Numbers 1-10 are primary piercers and 11-60 are secondary piercers,*indicates that this type is classified as facutative piercers in some literature.
55 56 57 58 59 60果剑纹夜蛾Acronycta strigosa(Denis et Schiftermüller)桑剑纹夜蛾Acronicta major(Bremer)榆剑纹夜蛾Acronicta hercules(Felder et Rogenhofer)苹梢鹰夜蛾Hypocala subsatura Guenée苹眉夜蛾Pangrapta obscurata(Butler)斜纹夜蛾Spodoptera litura(Fabricius)蔷薇科Rosaceae桑、蔷薇科、柑橘Morus alba L.,Rosaceae,Citrus reticulata Blanco榆Ulmus pumila L.苹果Malus pumila Mill.苹果Malus pumila Mill.棉花、甘薯、玉米、高粱、葫芦科、豆科Gossypium spp.,Dioscorea esculenta(Lour.)Burkill.,Zeamays L.,Sorghum bicolor(L.)Moench,Cucurbitaceae,Fabaceae中国(黑龙江、内蒙古、河南、福建、四川、云南);日本;朝鲜;欧洲China (Heilongjiang, Inner Mongolia, Henan, Fujian, Sichuan, Yunnan); Japan;The Democratic People’s Republic Korea;Europe中国(陕西、黑龙江、河南、湖北、湖南、四川、云南);日本;俄罗斯China (Shaanxi, Heilongjiang, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Sichuan, Yunnan); Japan;Russia中国(黑龙江、河北、福建、云南);日本China(Heilongjiang,Hebei,Fujian,Yunnan);Japan中国(内蒙古、辽宁、甘肃、河北、陕西、山东、河南、江苏、浙江、台湾、福建、广东、海南、云南、西藏);日本;印度;孟加拉国China (Inner Mongolia, Liaoning, Gansu, Hebei, Shaanxi, Shandong, Henan, Jiangsu,Zhejiang,Taiwan,Fujian,Guangdong,Hainan,Yunnan,Tibet);Japan;India;Bangladesh中国(黑龙江、河北、山东、湖南);日本;朝鲜China(Heilongjiang,Hebei,Shandong,Hunan);Japan;The Democratic People s Republic Korea中国(山东、江苏、湖南、浙江、福建、广东、贵州、云南);亚洲热带地区;亚热带地区;非洲China (Shandong, Jiangsu, Hunan, Zhejiang, Fujian, Guangdong, Guizhou,Yunnan);Tropical Asia;Subtropical Asia;Africa序号No.种名Specific name幼虫寄主Host of larvae主要分布Mainly distributed’
表1 吸果夜蛾主要种类[8-16]
Table 1 Main species of fruit-piercing moths

序号No.种名Specific name幼虫寄主Host of larvae主要分布Mainly distributed 123456789嘴壶夜蛾Oraesi aemiarginata(Fabricius)鸟嘴壶夜蛾Oraesia excavata(Butler)壶夜蛾Calyptra thalictri(Borkhausen)翎壶夜蛾Calyptra gruesa(Draudt)平嘴壶夜蛾Calyptra lata(Butler)防己科Menispermaceae防己科Menispermaceae防己科、唐松草Menispermaceae,Sibiricum Linnaeus防己科Menispermaceae中国(福建、山东、浙江、江苏、台湾、广东、海南、广西、云南);日本;朝鲜;印度China (Fujian, Shandong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Taiwan, Guangdong, Hainan,Guangxi,Yunnan);Japan;The Democratic People’s Republic Korea;India中国(山东、浙江、湖南、江苏、广西、台湾、福建、广东、云南);朝鲜;日本China (Shandong, Zhejiang, Hunan, Jiangsu, Guangxi, Taiwan, Fujian, Guangdong,Yunnan);The Democratic People’s Republic Korea;Japan中国(辽宁、黑龙江、福建、新疆、山东、河南、云南、浙江、四川);日本;朝鲜;欧洲China (Liaoning, Heilongjiang, Fujian, Xinjiang, Shandong, Henan, Yunnan,Zhejiang,Sichuan);Japan;The Democratic People’s Republic Korea;Europe中国(浙江、湖北、陕西、湖南);日本China(Zhejiang,Hubei,Shaanxi,Hunan);Japan防己科、紫堇、唐松草Menispermaceae,Corydalisedulis Maxim,Sibiricum Linnaeus艳叶夜蛾Eudocima salaminia(Cramer)枯叶夜蛾Eudocima tyrannus(Guenée)防己科Menispermaceae凡艳叶夜蛾Eudocima fullonica(Clerk)脱通木、木通Tetrapanax papyrifer(Hook.)K.Koch,Akebia quinata(Houtt.)Decne木通Akebia quinata(Houtt.)Decne防己科Menispermaceae中国(北京、河北、黑龙江、浙江、山东、陕西、云南、辽宁、福建);日本;朝鲜;俄罗斯China(Beijing,Hebei,Heilongjiang,Zhejiang,Shandong,Shaanxi,Yunnan,Liaoning,Fujian);Japan;The Democratic People’s Republic Korea;Russia中国(浙江、广东、广西、云南、福建、江西、台湾);印度;大洋洲;非洲China (Zhejiang, Guangdong, Guangxi,Yunnan, Fujian, Jiangxi,Taiwan); India;Oceania;Africa中国(辽宁、河北、山东、浙江、江苏、湖北、福建、台湾、海南、广西、四川、云南);日本;印度China (Liaoning, Hebei, Shandong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Hubei, Fujian, Taiwan,Hainan,Guangxi,Sichuan,Yunnan);Japan;India中国(黑龙江、山东、浙江、广东、广西、海南、四川、云南、江苏、湖南、福建、台湾);日本;朝鲜;非洲China (Heilongjiang, Shandong, Zhejiang, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Sichuan,Yunnan, Jiangsu, Hunan, Fujian,Taiwan); Japan;The Democratic People’s Republic Korea;Africa中国(福建、上海、浙江、江苏);斯里兰卡;缅甸;印度China(Fujian,Shanghai,Zhejiang,Jiangsu);Sri Lanka;Myanmar;India 10防己科Menispermaceae 11中国(黑龙江、北京、山东、江苏、浙江、湖北、湖南、福建);日本;朝鲜China (Heilongjiang, Beijing, Shandong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Hubei, Hunan, Fujian);Japan;The Democratic People’s Republic Korea中国(内蒙古、山东、河南、福建);欧洲;非洲China(Inner Mongolia,Shandong,Henan,Fujian);Europe;Africa 12肖金夜蛾Plusiodonta coelonota(Kollar)纯肖金夜蛾Plusiodonta casta(Butler)小桥夜蛾*Anomis flava(Fabricius)中桥夜蛾*Anomis mesogona(Walker)棉花、木槿、烟草Gossypium spp, Hibiscus syriacus Linn,Nicotiana tabacum L.红花悬钩子、芙蓉Rubusinopertus(Diels)Focke,Hibiscus mutabilis L.13超桥夜蛾*Anomis fulvida Guenée 14廉肖毛翅夜蛾*Thays juno(Dalman)棉花、木槿、芙蓉、大叶黄杨Gossypium spp, Hibiscus syriacus Linn,Hibiscus mutabilis L.,Buxus megistophylla Levl李、木槿、桦Prunus salicina Lindl,Hibiscus syriacus Linn,Betula L.15肖毛翅夜蛾*Thyas honesta Hübner中国(黑龙江、河北、山东、浙江、湖北、湖南、福建、海南、贵州、云南);日本;朝鲜;印度;斯里兰卡China(Heilongjiang,Hebei,Shandong,Zhejiang,Hubei,Hunan,Fujian,Hainan,Guizhou, Yunnan); Japan; The Democratic People’s Republic Korea; India; Sri Lanka中国(山东、浙江、福建、江西、广东、四川、云南);印度;印度尼西亚;斯里兰卡;缅甸;大洋洲;美洲China (Shandong, Zhejiang, Fujian, Jiangxi, Guangdong, Sichuan, Yunnan); India;Indonesia;Sri Lanka;Myanmar;Oceania;America中国(黑龙江、河北、辽宁、山东、河南、浙江、安徽、湖北、湖南、福建、海南、贵州、江西、四川、云南);印度;日本China (Heilongjiang, Hebei, Liaoning, Shandong, Henan, Zhejiang,Anhui, Hubei,Hunan,Fujian,Hainan,Guizhou,Jiangxi,Sichuan,Yunnan);India;Japan中国(广西、云南);印度;缅甸;斯里兰卡;新加坡;菲律宾China(Guangxi,Yunnan);India;Myanmar;Sri Lanka;Singapore;Philippines 16李、木槿、桦Prunus salicina Lindl,Hibiscus syriacus Linn,Betula L.不详Unknown 17三角夜蛾Chalciope mygdon(Cramer)中带三角夜蛾*Chalciope geometrica(Fabricius)中国(福建、台湾、江西、广东、海南、云南);印度(锡金);缅甸;新加坡;马来西亚China (Fujian, Taiwan, Jiangxi, Guangdong, Hainan, Yunnan); India (Sikkim);Myanmar;Singapore;Malaysia中国(浙江、湖北、台湾、广东、重庆、四川、贵州)China(Zhejiang,Hubei,Taiwan,Guangdong,Chongqing,Sichuan,Guizhou)18短带三角夜蛾*Trigonodes hyppasia(Cramer)石榴、柑橘、悬钩子、无患子Punica granatum L,Citrus reticulata Blanco, Rubus corchorifolius L.f.,Sapindus saponaria Linnaeus悬钩子、无患子Rubu scorchorifolius L.f.,Sapindus saponaria Linnaeus中国(湖北、江西、福建、台湾、广东、广西、四川)China(Hubei,Jiangxi,Fujian,Taiwan,Guangdong,Guangxi,Sichuan)
表1 (续) Table 1 (Continued)

序号No.种名Specific name幼虫寄主Host of larvae主要分布Mainly distributed 19青安钮夜蛾*Ophiusa tirhaca(Cramer)中国;印度;斯里兰卡;菲律宾;西亚;欧洲;非洲China;India;Sri Lanka;Philippines;Western Asia;Europe;Africa 20枯安钮夜蛾Ophiusa coronata(Fabricius)漆树、石榴、盐麸木Toxicodendron vernicifluum(Stokes)F.A.Barkl,Punica granatum L.,Rhus chinensis Mill.使君子Quisquali sindica L.21桃金娘科Myrtaceae中国(福建、海南、广东、广西、云南);印度(锡金);斯里兰卡;菲律宾;新加坡;大洋洲China (Fujian, Hainan, Guangdong, Guangxi,Yunnan); India (Sikkim); Sri Lanka;Philippines;Singapore;Oceania中国(广东、广西、海南);印度;越南;菲律宾;斯里兰卡China(Guangdong,Guangxi,Hainan);India;Vietnam;Philippines;Sri Lanka 22柑橘Citrus reticulata Blanco 23不详Unknown 24不详Unknown中国(浙江、山东、湖南、福建、台湾、广东、江西、云南、海南);印度;缅甸China (Zhejiang, Shandong, Hunan, Fujian, Taiwan, Guangdong, Jiangxi, Yunnan,Hainan);India;Myanmar中国(西藏、海南、广西、广东、云南);印度;新加坡;斯里兰卡;孟加拉国China(Tibet,Hainan,Guangxi,Guangdong,Yunnan);India;Singapore;Sri Lanka;Bangladesh中国(河南、湖北、浙江、四川)China(Henan,Hubei,Zhejiang,Sichuan)25李Prunus salicina Lindl.中国(浙江、湖南、四川);日本;印度;缅甸;斯里兰卡;印度尼西亚China(Zhejiang,Hunan,Sichuan);Japan;India;Myanmar;Sri Lanka;Indonesia 26蒙古栎Quercus mongolica Fisch.ex Ledeb中国(黑龙江、内蒙古、河南、云南、湖北);日本;俄罗斯China(Heilongjiang,Inner Mongolia,Henan,Yunnan,Hubei);Japan;Russia 27胡杨Populus euphratica Oliv中国(新疆、内蒙古);中亚地区China(Xinjiang,Inner Mongolia);Central Asia 28杨柳科Salicaceae 29不详Unknown中国(黑龙江、新疆、山东、河南、湖北);日本;朝鲜;欧洲China(Heilongjiang,Xinjiang,Shandong,Henan,Hubei);Japan;The Democratic People’s Republic Korea;Europe中国(河北、山东、江苏、江西、福建)China(Hebei,Shandong,Jiangsu,Jiangxi,Fujian)30蒙古栎Quercus mongolica Fisch.ex Ledeb中国(黑龙江、内蒙古、河南);日本;俄罗斯China(Heilongjiang,Inner Mongolia,Henan);Japan;Russia 31无患子Sapindus saponaria Linnaeus 32不详Unknown 33胡枝子Lespedeza bicolor Turcz.34合欢Albizia julibrissin Durazz.中国(浙江、广东、广西、海南、四川、云南);印度;孟加拉国;缅甸;大洋洲;非洲China (Zhejiang, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Sichuan, Yunnan); India; Bangladesh;Myanmar;Oceania;Africa中国(陕西、浙江、湖南、福建、广西、四川)China(Shaanxi,Zhejiang,Hunan,Fujian,Guangxi,Sichuan)中国(辽宁、内蒙古、河北、陕西、山东、河南、浙江、福建、云南);日本;朝鲜China (Liaoning, Inner Mongolia, Hebei, Shaanxi, Shandong, Henan, Zhejiang,Fujian,Yunnan);Japan;The Democratic People’s Republic Korea中国China 35同安钮夜蛾Ophiusa disjungens(Walker)橘安钮夜蛾Ophiusa triphaenoides(Walker)直安钮夜蛾Ophiusa trapezium(Guenée)鸽光裳夜蛾Ephesia columbina(Leech)白光裳夜蛾Ephesia nivea(Butler)栎光裳夜蛾Ephesia dissimilis(Bremer)褛裳夜蛾Catocala remissa Staudinger柳裳夜蛾Catocala electa(Vieweg)晦刺裳夜蛾Mormonia abamita(Bremer et Grey)栎刺裳夜蛾Mormonia dula(Bremer)铃斑翅夜蛾Serrodes campana Guenée单析夜蛾Sypna simplex(Lecch)客来夜蛾Chrysorithrum amata(Bremer et Grey)旋目夜蛾Spciredonia retorta(Linnaeus)目夜蛾Erebus crepuscularis(Linnaeus)不详Unknown 36大红裙杂夜蛾Amphipyra monolitha Guenée不详Unknown 37苎麻夜蛾Arcte coerula(Guenée)亚麻、黄麻、豆科Linum usitatissimum L.,Corchorus capsularis L.,Fabaceae中国(福建、浙江、湖北、湖南、江西、云南、广东、海南、广西、四川);日本;印度;缅甸;斯里兰卡;新加坡China (Fujian, Zhejiang, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangxi, Yunnan, Guangdong, Hainan,Guangxi,Sichuan);Japan;India;Myanmar;Sri Lanka;Singapore中国(黑龙江、辽宁、河北、河南、湖北、江西、福建、广东、四川、云南);日本;印度;欧洲China (Heilongjiang, Liaoning, Hebei, Henan, Hubei, Jiangxi, Fujian, Guangdong,Sichuan,Yunnan);Japan;India;Europe中国(河北、山东、浙江、湖北、湖南、江西、福建、广东、海南、四川、云南);日本;印度(锡金);斯里兰卡China (Hebei, Shandong, Zhejiang, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangxi, Fujian, Guangdong,Hainan,Sichuan,Yunnan);Japan;India(Sikkim);Sri Lanka
表1 (续) Table 1 (Continued)

序号No.种名Specific name幼虫寄主Host of larvae主要分布Mainly distributed 38毛胫夜蛾*Mocis undata(Fabricius)鱼藤、刺槐、大豆、山马蝗属Derris trifoliata Lour,Robinia pseudoacacia L.,Glycine max(Linn.)Merr,Desmodium 39葛Pueraria lobata(Willd.)Ohwi 40奚毛胫夜蛾*Mocis ancilla(Warren)石榴巾夜蛾*Dysgonia stuposa(Fabricius)石榴、番石榴、月季Punica granatum L., Psidium guajava L.,Rosa chinensis Jacq 41玫瑰巾夜蛾*Dysgonia arctotaenia(Guenée)玫瑰、月季、石榴Rosa rugosa Thunb, Rosa chinensis Jacq,Punica granatum L.42霉巾夜蛾Dysgonia maturata(Walker)葡萄Vitis vinifera L.43不详Unknown中国(河北、河南、山东、江苏、浙江、湖南、福建、台湾、江西、广东、贵州、云南);日本;朝鲜;印度;斯里兰卡;缅甸;新加坡;菲律宾;印度尼西亚;非洲China (Hebei, Henan, Shandong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Hunan, Fujian, Taiwan, Jiangxi, Guangdong, Guizhou,Yunnan); Japan; The Democratic People’s Republic Korea;India;Sri Lanka;Myanmar;Singapore;Philippines;Indonesia;Africa中国(黑龙江、河北、山东、河南、浙江、湖南、福建);日本;朝鲜China(Heilongjiang,Hebei,Shandong,Henan,Zhejiang,Hunan,Fujian);Japan;The Democratic People’s Republic Korea中国(河北、山东、江苏、浙江、湖北、台湾、福建、江西、广东、海南、四川、云南);日本;朝鲜;印度;斯里兰卡;菲律宾;印度尼西亚China (Hebei, Shandong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Hubei, Taiwan, Fujian, Jiangxi,Guangdong,Hainan,Sichuan,Yunnan);Japan;The Democratic People’s Republic Korea;India;Sri Lanka;Philippines;Indonesia中国(河北、江苏、浙江、湖北、台湾、福建、江西、广东、广西、四川、贵州、云南);日本;朝鲜;印度;缅甸;斯里兰卡;孟加拉国;斐济China (Hebei, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Hubei, Taiwan, Fujian, Jiangxi, Guangdong,Guangxi, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan); Japan; The Democratic People’s Republic Korea;India;Myanmar;Sri Lanka;Bangladesh;Fiji中国(山东、河南、江苏、浙江、台湾、福建、江西、海南、四川、云南);日本;朝鲜;印度China(Shandong,Henan,Jiangsu,Zhejiang,Taiwan,Fujian,Jiangxi,Hainan,Sichuan,Yunnan);Japan;The Democratic People’s Republic Korea;India中国(浙江、福建、台湾、江西、湖南、云南);印度China(Zhejiang,Fujian,Taiwan,Jiangxi,Hunan,Yunnan);India 44余甘子Phyllanthus emblica L.45肾巾夜蛾*Dysgonia praetermissa(Warren)无肾巾夜蛾Dysgonia crameri Moore宽巾夜蛾*Dysgonia fulvotaenia(Guenée)不详Unknown 46叶下珠属Phyllanthus Linn.47野豌豆Vicia sepium L.中国(湖北、福建、广东、贵州、云南);泰国;印度;缅甸;阿富汗;斯里兰卡China (Hubei, Fujian, Guangdong, Guizhou, Yunnan); Thailand; India; Myanmar;Afghanistan;Sri Lanka中国(浙江、福建、台湾、广东、海南、云南);日本;印度;缅甸;新加坡;马来西亚;孟加拉国;斯里兰卡China (Zhejiang, Fujian, Taiwan, Guangdong, Hainan, Yunnan); Japan; India;Myanmar;Singapore;Malaysia;Bangladesh;Sri Lanka中国(江苏、广东、海南、云南);印度;缅甸;印度尼西亚;大洋洲China (Jiangsu, Guangdong, Hainan,Yunnan); India; Myanmar; Indonesia; Oceania中国(山东、江苏、湖北、湖南、福建、海南、广西、四川、云南)China(Shandong,Jiangsu,Hubei,Hunan,Fujian,Hainan,Guangxi,Sichuan,Yunnan)48盐麸木Rhus chinensis Mill.49隐巾夜蛾Dysgonia joviana(Guenée)胞短栉夜蛾Brevipecten consanguis Leech银斑砌石夜蛾Gabala argentata Butler间纹德夜蛾Lepidodelta intermedia Bremer不详Unknown 50杨柳科Salicaceae 51不详Unknown 52棘翅夜蛾Scoliopteryx libatrix(Linnaers)白斑陌夜蛾Trachea auriplena(Walker)变色夜蛾Hypopyra vespertilio(Fabricius)中国(浙江、湖南、江西、广东、海南、西藏);日本;朝鲜;印度;缅甸China(Zhejiang,Hunan,Jiangxi,Guangdong,Hainan,Tibet);Japan;The Democratic People’s Republic Korea;India;Myanmar中国(湖南、黑龙江、陕西、浙江、湖北、四川、云南);日本;朝鲜;印度;斯里兰卡;非洲China (Hunan, Heilongjiang, Shaanxi, Zhejiang, Hubei, Sichuan, Yunnan); Japan;The Democratic People’s Republic Korea;India;Sri Lanka;Africa中国(黑龙江、辽宁、陕西、河南、云南);日本;朝鲜;欧洲China(Heilongjiang,Liaoning,Shaanxi,Henan,Yunnan);Japan;The Democratic People’s Republic Korea;Europe中国(湖北、湖南、浙江、江西、福建、四川、云南);日本;印度;斯里兰卡China(Hubei,Hunan,Zhejiang,Jiangxi,Fujian,Sichuan,Yunnan);Japan;India;Sri Lanka中国(山东、江苏、浙江、福建、江西、广东、海南、云南);日本;印度;缅甸;印度尼西亚China (Shandong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Fujian, Jiangxi, Guangdong, Hainan, Yunnan);Japan;India;Myanmar;Indonesia 53 54桃剑纹夜蛾Acronicta intermedia Warren梨剑纹夜蛾Acronycta rumicis(Linnaeus)合欢、紫藤、柑橘、楹树Albizia julibrissin Durazz., Wisteria sinensis (Sims) Sweet, Citrus reticulata Blanco,Albizia chinensis(Osbeck)Merr.蔷薇科、榆、柑橘Rosaceae, Ulmus pumila L., Citrus reticulata Blanco蔷薇科、杨柳科Rosaceae,Salicaceae中国(内蒙古、河北、福建、四川、浙江);日本;朝鲜China(Inner Mongolia,Hebei,Fujian,Sichuan,Zhejiang);Japan;The Democratic People’s Republic Korea中国(新疆、江苏、浙江、湖北、湖南、福建、四川、贵州、云南、安徽、上海、河北);欧洲China (Xinjiang, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Hubei, Hunan, Fujian, Sichuan, Guizhou,Yunnan,Anhui,Shanghai,Hebei);Europe
吸果夜蛾根据危害习性和口器特点分为嗜好果类、嗜坏果类和兼食类,嗜好果类口器较硬、前端尖锐、角质化、有附属物,能刺破完好果皮,甚至扎穿套袋果实,通常危害好果,对生产威胁极大,是重点防控对象,主要种类有鸟嘴壶夜蛾、嘴壶夜蛾、艳叶夜蛾等;嗜坏果类口器较软、前端钝圆、膜质化、无特殊构造,通常吸食烂果或在嗜好果类造成的伤口上继续危害,一般不作为防治目标,主要种类有苎麻夜蛾Arctecoerula(Guenée)、变色夜蛾Hypopyra vespertilio(Fabricius)等;兼食类吸果夜蛾口器坚硬程度介于另外2类之间,通常在嗜好果类已危害但未腐烂的水果吸孔处取食,也可以吸食成熟薄皮的好果,但对好果的嗜食性不严格。兼食类吸果夜蛾的取食习性除口器构造外,还和危害果实种类、果皮厚薄、果实成熟度等相关,如青安钮夜蛾Ophiusa tirhaca(Cramer)会危害成熟且皮薄的桃果实,需要重视其危害情况,但在龙眼上仅吸食烂果,一般不作为防控目标。不同学者对兼食类具体种类的划分存在差异,值得进一步研究。因此,吸果夜蛾通常被分为一次危害种(直接危害)和二次危害种(间接危害)2类;但无论何种分类法,嗜好果类的具体划分基本一致,且通常是危害的优势种,是果园的重点防控对象[2,4,7,9-11]。
1.3 发生规律
吸果夜蛾不同种类的发生代数、发生时期和发生规律不尽相同。受降雨量、水果种类及果园周围寄主植物质量和数量的影响,同一地区不同果园中吸果夜蛾的种类组成也会有差异。通常优势种为嘴壶夜蛾、鸟嘴壶夜蛾和艳叶夜蛾等嗜好果类,在实际防控过程中要明确田间主要优势种及其发生规律,做到“对症下药”。通常情况下,吸果夜蛾危害高峰期接近当地果实成熟期[5]。
吸果夜蛾在中国各地果园均有发生,其中南方丘陵山区果园受害最为严重。Fay等[6]研究指出,潮湿的沿海地区吸果夜蛾数量可达干旱地区的2 倍。大多数吸果夜蛾1年发生4代,第一代成虫通常出现在4—5月,南方部分地区可提前至3月,危害的高峰期根据水果种类的不同可从6月下旬一直持续到11月中旬,11月下旬以后随着温度的下降和果实的采摘,吸果夜蛾开始进入越冬期[17-20]。王希等[17]调查了江西省兴国、宁都、大余3县柑橘园吸果夜蛾发生情况,发现吸果夜蛾从5月中旬至11月中旬均有发生,危害高峰期为9 月中旬至10 月下旬,主要优势种为鸟嘴壶夜蛾,1 年可发生4~5 代,果实被害率最高可达30%。苏燕钿等[18]调查广东省潮州市饶平县柑橘园吸果夜蛾发生情况,发现吸果夜蛾从1 月下旬至11月下旬均有发生,有2次危害高峰期,分别是1月下旬至3月下旬、9月上旬至11月下旬,主要优势种为嘴壶夜蛾,其次为鸟嘴壶夜蛾。姜英等[19]调查了江西省赣榆县黑莓吸果夜蛾的发生情况,发现主要优势种为中桥夜蛾,其成虫可以刺吸黑莓的果实,幼虫可以危害黑莓的叶、梢部,1年发生3代,发生时期为6月中旬至10月下旬,成虫具有迁飞性,发生重时新梢被害率为90%~100%。王华弟等[20]调查了浙东南山区杨梅吸果夜蛾的发生情况,主要优势种为嘴壶夜蛾和枯叶夜蛾,嘴壶夜蛾1年发生4代,发生时期为5 月下旬至6 月中旬;枯叶夜蛾1 年发生2~3代,发生时间为6—10 月,不同杨梅品种间2 种吸果夜蛾发生危害差异明显,一般危害率为5%~10%,严重的可超过30%。
吸果夜蛾在国外也大量发生,几乎遍布整个太平洋地区,在部分高海拔地区也有吸果夜蛾的踪迹[16]。日本鸟取县吸果夜蛾主要发生在7—9 月,8月是危害高峰期,不同年份被害果率在10%~60%之间,不同品种、不同的果园被害率亦有所差异,主要优势种为枯叶夜蛾和鸟嘴壶夜蛾[21]。在澳大利亚东北部,柑橘在采摘前8 周开始就陆续受到吸果夜蛾的危害,2 月下旬至3 月下旬达到危害高峰期,主要优势种为艳叶夜蛾和嘴壶夜蛾[22]。在印度马哈拉施特拉邦,吸果夜蛾主要发生在柑橘、木瓜和石榴等水果的成熟期,一般在9—10月,主要优势种有艳叶夜蛾、苹果鹰夜蛾等[23]。
2 吸果夜蛾防控技术
2.1 农业防控
吸果夜蛾农业防控包括各类农业技术和管理措施,通过调整和改善果树生长环境、果实品种和灌溉方式等,错开吸果夜蛾危害高峰期;或通过消灭部分吸果夜蛾成虫或越冬代吸果夜蛾幼虫,预防大规模暴发,减轻来年防控压力;或通过合理的农业管理技术增强果树对吸果夜蛾及其他病虫害的抵抗力[5]。
在果树的选种和规划配置方面,应不种植或少种植早熟品种,尤其是在山地或近山地果园,避免混栽不同成熟期的品种或不同种的果树,错开果实成熟期与吸果夜蛾危害高峰期;同时要尽可能连片种植,不要过于分散,水果采收期也尽快一次性完成采收,减少吸果夜蛾危害的时间;落果与腐烂果实要及时清理,否则气味挥发物可能会吸引来更多吸果夜蛾[24-25]。
通过根除果园周围1 km 内的吸果夜蛾幼虫寄主也可以压低虫口密度,但需要投入大量人力成本。也可以反过来在果园周围混植一定量的幼虫寄主或对成虫引诱力强的植物、成熟水果,形成诱集圃,减轻吸果夜蛾对目标作物的危害[26-27],Kamala等[28]研究发现,部分吸果夜蛾具有飞行超过25 km的能力,根除幼虫寄主植物作用有限,而在果园内混植香蕉、番石榴等对吸果夜蛾引诱力更强的植物,可显著减少其危害需要保护的经济水果。
2.2 物理防控
吸果夜蛾物理防控是通过机械工具或物理因素达到防治目的,包括水果套袋、架设防护网、人工捕捉和灯光防控等。水果套袋可以一定程度降低吸果夜蛾的危害,但是传统纸袋效果较差,部分嗜好果类吸果夜蛾口器尖锐且坚硬,可以轻松扎透纸袋。聚乙烯袋的效果与前景最好,但可能会使果实腐烂或延迟成熟[25]。套袋法需要投入大量时间和人力成本,更适合小规模或经济价值高的水果或兼防其他害虫时采用[29]。
在果园中架设尼龙网可以保护水果免受吸果夜蛾、鸟类和果蝠等危害,国外许多果园利用此法均取得了不错的成效,但是其安装和维护成本非常昂贵,且在面对自然灾害时需要及时进行拆卸,也要避免网的重量对果树造成损害,需要根据果园的实际情况考虑安装[16]。
利用灯光也是防控吸果夜蛾的主要手段之一。吸果夜蛾的眼睛在夜晚光线照射下会反光,可以利用这一特性在晴朗无风的夜晚,通过强光手电照射吸果夜蛾的眼睛确定方位,吸果夜蛾在吸食果实时会保持不动,很容易进行人工捕捉[17,25]。光照度会直接影响吸果夜蛾的活动与取食,不同的波段可以起到驱避或诱杀的作用,580 nm左右的黄色和500 nm左右的绿色灯光对吸果夜蛾有较大的驱避作用,且光照度越大、辐射范围越广效果越好[16,30-31]。周华光等[32]研究表明,在果树周围布置黄色灯光可以减少吸果夜蛾的危害,驱虫灯距离果树越近,防治效果越好,在30 m 内防治效果达70%。灯光诱杀方面,裴艳等[33]研究表明新型太阳能电击式和风吸式杀虫灯对柑橘上的吸果夜蛾具有良好的诱杀效果。中国也有许多报道黑光灯对吸果夜蛾具有引诱效果,并已进行推广应用。但也有研究发现,田间许多吸果夜蛾在黑光灯周围活动,而被捕获的却很少,且对雌蛾的引诱能力较低,效果并不理想,可能与吸果夜蛾的种群和果园地理位置相关,因此生产上更推荐以黄光灯驱避的方式对吸果夜蛾进行防控[16,25]。
2.3 生物防控
吸果夜蛾生物防控是利用生物学特性和生态学现象,将吸果夜蛾控制在经济阈值以下,主要防控方式包括性诱剂、食诱剂、天敌防控和生物源驱避剂等。利用生物防控措施可以减少甚至替代化学农药的使用,具有极大的发展潜力。
利用食诱剂是常见的绿色生物防控技术。吸果夜蛾食诱剂多以基于花香、发酵糖水气味的鳞翅目害虫广谱型食诱剂为主,糖醋酒液是其中代表,具有诱虫范围广、不受昆虫性别影响、操作简单、配置便捷、绿色无公害等特点,目前在田间广泛应用,但诱集效果受到比例影响,且不能有针对性地引诱嗜好果类吸果夜蛾[18-20]。利用水果本身的挥发性气味成分制作食诱剂有较大的应用潜力。Izumi 等[34]提取了桃果实成熟过程中的7种挥发性气味成分对鸟嘴壶夜蛾进行试验,结果表明丁酸乙酯和乙酸乙酯可以引起鸟嘴壶夜蛾触角电位反应。在田间诱捕试验中,丁酸乙酯和乙酸乙酯均可以诱捕到吸果夜蛾,而乙酸乙酯、丁酸乙酯和含5 种脂类的混合物单独诱捕效果均不如成熟桃果实,但含乙酸乙酯、丁酸乙酯等7种脂类的混合物混合后诱捕效果高于成熟桃果实。Fay 等[35]研究表明在琼脂中添加成熟或过熟果实挥发物可以吸引到特定的吸果夜蛾。因此,通过研究对目标吸果夜蛾引诱力较强的水果并基于其挥发性气味成分开发吸果夜蛾新型食诱剂具有极大的研究价值。
性诱剂是以昆虫性信息素制作的生物诱捕剂,具有高效、专一及无污染的特性,应用性诱剂是一种可持续发展的绿色生物防控技术,目前已被广泛应用于鳞翅目害虫绿色防控中[36]。Fay等[6]通过长期监测发现,果园中危害的吸果夜蛾超过三分之二为雄蛾,值得研究开发性诱剂。Yoshihisa 等[37]从鸟嘴壶夜蛾雌蛾腺体中成功鉴定并分离到了2种化学物质组分,通过人工合成,证实其对鸟嘴壶夜蛾雄蛾有良好的田间诱捕效果,并确定了主要组分为顺-9,10-环氧-(Z)-6-二十一碳烯,次要组分为顺-9,10-环氧-(Z,Z)-3,6-二十一碳双烯。Mallikarjun 等[38]研究表明,Eudocima materna Linnaeus(艳叶蛾属的一种)性信息素主要组分为(Z,E)-9,11-十四碳二烯-1-醇乙酸酯,次要组分为Z-9-二十三烯和Z-9-十二碳烯醇乙酸酯。吸果夜蛾许多种类的性信息素组分还未被鉴定,且未见中国吸果夜蛾性信息素鉴定的相关报道,具有广阔的研究空间。
天敌防控是生物防控的重要组成部分。吸果夜蛾有多种天敌,包括赤眼蜂、姬蜂等寄生性天敌和螳螂等捕食性天敌。其中,草蛉黑卵蜂(Telenomus sp.)和卵跳小蜂(Ooencyrtus sp.)2 种寄生蜂对某些吸果夜蛾卵寄生具有特异性[39],在天敌发生盛期应减少或避免施用广谱化学杀虫剂,以此保护天敌。赤眼蜂是防治鳞翅目害虫时广泛应用的天敌生物,卵寄生死亡率可达95%。若在危害高峰前2个月做好放蜂工作,可以有效抑制虫源,降低危害率[40-42]。姬蜂科(Ichneumonidae)、寄蝇科(Tachinidae)和部分茧蜂科(Braconidae)天敌可以寄生吸果夜蛾幼虫,但在野外环境中对吸果夜蛾数量影响较小[5]。Muniappan 等[43]曾在美国关岛引入吸果夜蛾幼虫寄生蜂,但该种群并未在生态系统中持续存在,即使表现活跃也难以在吸果夜蛾危害高峰期有效控制其数量[44]。有学者发现蝙蝠和壁虎是吸果夜蛾的潜在捕食者,且蝙蝠的超声波会引发吸果夜蛾的躲避行为,也许可以利用声波技术对吸果夜蛾进行防控[45-48]。
生物源驱避剂是具有某种特殊气味可驱散或忌避害虫的信息化合物,本身几乎无杀虫活性,一般不会危害环境或破坏生态平衡。吸果夜蛾嗅觉器官较发达,可以从很远的地方接受气味刺激。驱避剂的特殊气味可以驱散或忌避吸果夜蛾,并掩盖水果的挥发性气味,从而起到良好的防治效果,具有绿色环保、安全高效及不会产生抗药性等优点[5]。郑雪良等[49]利用香茅油在山地柑橘园防控吸果夜蛾,试验结果显示悬挂香茅油对吸果夜蛾的防控效果超50%,且优于常规化学农药防控,可以显著降低果实被害率。Jayanthi 等[50]对8 种植物源驱避剂对吸果夜蛾的驱避效果进行了对比,结果表明麻藤、香茅、罂粟和印楝等植物油对吸果夜蛾均有驱避作用。卫生丸的特殊气味也可以有效防控吸果夜蛾,降低落果率[51-52]。
生物源杀虫剂主要包括各类生物碱、生防菌等。生物碱已经广泛应用于鳞翅目幼虫的防控中[53-55],但部分吸果夜蛾如鸟嘴壶夜蛾的幼虫寄主本身含有天然生物碱[56],可能会对其产生抗药性,因此在防控过程中需要多种生物碱混用。Kulkarni 等[57]研究表明苏云金芽孢杆菌对吸果夜蛾幼虫有效。但是,吸果夜蛾幼虫寄主通常是果园外山地的杂草,仅以成虫飞入果园危害,所以采用针对幼虫的杀虫剂对吸果夜蛾进行防控具有难度。
2.4 化学防控
吸果夜蛾化学防控目前以拟除虫菊酯类杀虫剂为主。周晓音等[58]研究表明,5.7%百树得乳油1500~2000倍液,10-15 d喷施1次可取得良好效果;同时试验观察到打药初期果园内未见吸果夜蛾,但随着药效时长结束,吸果夜蛾开始在果园外飞舞并重新危害水果,猜测百树得防治吸果夜蛾的机制主要为驱避作用。笔者认为百树得主要成分为氟氯氰菊酯,无特殊气味,挥发性较差,是否起驱避作用仍需严谨的试验验证。
大量研究[1-2,5,11,58-59]指出,吸果夜蛾成虫在果实上停留的时间并不长,且以口针刺吸水果危害,接触果面较小,化学农药对吸果夜蛾触杀效果有限。吴荣宗等[25]研究表明,利用化学农药制成毒果诱饵对嗜好果类吸果夜蛾的效果很差,大部分被毒杀的吸果夜蛾为嗜坏果类,无法对优势种进行有效防治。部分小宗作物如杨梅上尚无登记防治吸果夜蛾的农药[20]。同时,果实成熟期前30 d 严格禁止使用化学农药,因此要在吸果夜蛾危害初期结合其他防控方式做好预防工作。
3 研究展望
中国的水果产业是继粮食、蔬菜之后的第三大农业种植产业,具有广阔的国内外市场前景和较强的竞争优势,是农民收入的重要来源。2022 年开始,中国严格落实“长牙齿”的耕地保护硬措施,将引导新发展林果业上山上坡,不与粮食争地,这是乡村振兴战略的重要内容,未来会有越来越多的山地或近山地果园,这也对如何科学、高效、环保监测和防控吸果夜蛾提出了新的挑战。
目前,生产上利用化学农药防控吸果夜蛾存在诸多弊病,灭活效果较差,持效期短,且吸果夜蛾危害高峰通常在严禁使用化学农药的果实成熟期,若初期防控不到位,吸果夜蛾在果实成熟期暴发将会造成严重的经济损失。同时,大量的化学农药使用会造成“3R”问题(Resistance 抗性、Resurgence 再增猖獗、Residue 残留)等[58-59]。因此,生产上迫切需要更成熟高效的吸果夜蛾新型绿色综合防控技术,从而减少甚至代替化学农药的使用,确保水果的品质与安全。
在生物学和生态学研究方面,进行吸果夜蛾智能化精准识别和长期监测预报可以明确果园内吸果夜蛾主要优势种与发生规律。吸果夜蛾种类繁多,不同地区、不同水果的吸果夜蛾存在地理和种群的差异,同一果园不同时期的吸果夜蛾种类组成也不尽相同,同时山地果园还存在灯蛾、螟蛾等多种蛾类昆虫,利用计算机技术对蛾类害虫进行智能识别,并自动将其中吸果夜蛾的种类、发生数量、发生时期进行统计和分析,建立区域性吸果夜蛾种群模型,可以为果园全年的防控策略提供数据支撑,并大大减少人力调查成本。沈志杰等[60]研究发现,同一地区不同生境果园害虫的发生代数不同,明确当地发生规律可以更好地为防控提供依据,因地制宜地选择防控措施,贯彻“预防为主、综合防治”的植保方针。目前,基于昆虫的图像、声音和飞行模式已开发了相应的自动识别技术,未来计算机技术与植物保护相结合,逐步实现果园害虫种群识别和动态监测的数据化和可视化是绿色防控重要的发展趋势之一[61-62]。
在天敌防控方面,赤眼蜂的鳞翅目寄主昆虫最多,同时中国是世界上赤眼蜂防治害虫面积最大的国家之一,相关技术较为成熟,拥有极大的应用潜力。但由于吸果夜蛾种类繁多,不同赤眼蜂种类具有的寄生潜力不同,在防控时要结合实际情况,明确吸果夜蛾发生的优势种,选用合适的赤眼蜂,从而起到良好的防治效果[42]。同时,要注意化学药剂对天敌昆虫的影响,施药避开放蜂时期或选用对天敌友好的药剂。
在驱避防控方面,利用灯光或驱避剂是未来防控模式的重点研究方向之一。吸果夜蛾成虫通常白天在果园外的山地休息,仅在夜晚飞入果园进行危害,利用灯光可以有效驱避吸果夜蛾进入果园,并且LED灯相比荧光灯和白炽灯更加省电,成本更低。但山地果园地形复杂,在使用时要注意灯光照射的有效距离[29-33]。由于化学农药难以针对幼虫进行防控,对成虫的触杀效果并不理想,主要起驱避作用,因此,研究开发相关的生物源驱避剂可以减少甚至代替化学药剂的使用,也可以更好保护环境与天敌[51-54,58-59]。
在性诱剂防控方面,夜蛾科作为鳞翅目物种最多的科包含了多种性信息素,不同种之间的性信息素可能结构相近,但在具体比例或关键官能团上具有差异,因此性信息素具有高度专一性。Deng等[63]研究表明,不同地理种群的亚洲玉米螟Ostrinia furnacalis(Guenée)的性信息素组分具有差异,根据地域配置相应的性诱剂可以提高诱捕量。目前,对于吸果夜蛾性信息素相关的研究较少,许多种类还未明确其性信息素的组分,也未见吸果夜蛾地理种群性信息素鉴定相关的报道,市面上也缺乏有针对性的相关产品;吸果夜蛾种类繁多,单一的性信息素可能无法兼顾所有防控对象,部分吸果夜蛾性信息素组分复杂、合成难度较大、成本较高;因此,对于吸果夜蛾优势种单一且明确的果园,性信息素具有极大的应用潜力,但对于具有多种吸果夜蛾优势种的果园,则无法兼顾所有防控对象,存在局限性,其应用价值值得进一步研究[34-36]。
在食诱剂防控方面,以糖醋酒液为代表的鳞翅目害虫广谱型食诱剂不能有针对性引诱嗜好果类吸果夜蛾,通常引诱到大量嗜坏果类吸果夜蛾,没有真正解决生产实际问题,市面上也缺乏成熟的产品。不同种类或不同新鲜程度的水果气味成分对吸果夜蛾不同种类的引诱效果存在差异,通过筛选对嗜好果类吸果夜蛾具有良好引诱效果的水果挥发性气味成分,人工合成并模拟成熟水果的气味从而开发能引诱多种嗜好果类吸果夜蛾食诱剂具有良好的发展前景[18-20,37-38]。笔者在田间调查过程中发现成熟的杧果对嘴壶夜蛾、鸟嘴壶夜蛾等引诱效果较其他桃、梨等水果更强,可以作为挥发性气味筛选的水果之一。完善其对不同种类和不同新鲜程度的水果的选择机制,可以为其种群分类和开发新型食诱剂提供重要依据。
将多种绿色防控措施相结合可能产生“1+1>2”的协同效果。万霞等[64]研究表明性信息素与LED协同使用相比单一使用性诱剂对美国白蛾引诱的效果有显著提升作用。Mallikarjun 等[38]研究表明,在吸果夜蛾性信息素中添加石榴挥发物2-乙基己醇,可以显著增强雄蛾对性信息素的触角电位反应和增加田间诱捕量。同时,植物挥发物对蛾类昆虫信息素合成、释放与行为调控也有一定的影响,拥有与性诱剂协同防治的应用潜力[65-67]。孙媛等[68]研究表明,桃潜叶蛾Lyonetia clerkella 和梨小食心虫Grapholitha molesta(Busck)可以互相感知对方的性信息素,且2 种性信息素混合使用时对二者的田间诱捕效果无影响。邓建宇等[69]研究表明,梨小食心虫和桃蛀螟Conogethes punctiferalis(Guenée)可以互相感知对方的性信息素,且2 种性信息素混合使用时可以显著提高二者的田间诱捕效果。吸果夜蛾后续还可以研究多种绿色防控方式的协同或推拉作用,如吸果夜蛾不同种性信息素引诱协同作用、植物源挥发物与食诱剂或性诱剂的引诱协同作用、特定波段具有驱避效果的LED 灯与生物源驱避剂的驱避协同作用、驱避防控与引诱防控的推拉作用等。
吸果夜蛾在许多方面仍有大量值得研究的内容,如不同种类的基因组测序、喙部形态构造、嗅觉感受机制及植物源挥发物与信息素协同等。相关研究不仅要完善吸果夜蛾基础分类与生物生态学理论,更要积极探索吸果夜蛾绿色防控的新途径,开发更成熟、高效的绿色防控技术,提高水果产业的社会效益、经济效益和生态效益。
[1] KLEM C C,ZASPEL J. Pest injury guilds,Lepidoptera,and placing fruit-piercing moths in context:A review[J]. Annals of the Entomological Society of America,2019,112(5):421-432.
[2] RAMKUMAR J,SWAMIAPPAN M,RAGURAMAN S,SADASAKTHI A. Larval host specificity and proboscis morphology of fruit piercing moths[J]. Journal of Biopesticides,2010,3:428-431.
[3] NGAMPONGSAI A,BARRETT B,PERMKAM S,SUTHAPRADIT N,NILLA-OR R.A preliminary study on some ecological aspects of the fruit piercing moths in Songkhla Province of southern Thailand[J]. Songklanakarin Journal of Science and Technology,2005,27(6):1135-1145.
[4] 吴荣宗,杜佩璇,邹曾健.柑桔吸果夜蛾的研究:Ⅰ.生物学特性及发生规律[J].华南农学院学报,1984,5(1):60-71.WU Rongzong,DU Peixuan,ZOU Cengjian. Studies on the citrus fruit-piercing noctuids:Ⅰ.The biology and regularity of the outbreak of the fruit-piercing noctuids[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University,1984,5(1):60-71.
[5] BHUMANNAVAR B S,VIRAKTAMATH C A. Biology,ecology and management of fruit piercing moths(Lepidoptera:Noctuidae)[J].Pest Management in Horticultural Ecosystems,2013,18(1):1-18.
[6] FAY H,HALFPAPP K.Activity of fruit-piercing moths,Eudocima spp. (Lepidoptera:Noctuidae),in North Queensland crops:Some effects of fruit type,locality and season[J]. Australian Journal of Entomology,1999,38(1):16-22.
[7] 邹曾健,杜佩璇,吴荣宗.吸果夜蛾的生物学特性及其幼虫等形态的识别[J].华南农学院学报,1980,1(2):86-100.ZOU Cengjian,DU Peixuan,WU Rongzong. On the biology and habits of eleven fruit-piercing noctuids and the morphology of the immature stages[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University,1980,1(2):86-100.
[8] 陈一心.中国动物志:昆虫纲,第16 卷:鳞翅目:夜蛾科[M].北京:科学出版社,1999.CHEN Yixin. Fauna sinicaInsecta,Vol. 16. Lepidoptera,Noctuidae[M].Beijing:Science Press,1999.
[9] 吴荣宗,邹曾健.柑桔吸果夜蛾的头部内骨骼、肌肉系统和口器构造与成虫取食习性的关系[J].昆虫学报,1985,28(2):165-172.WU Rongzong,ZOU Cengjian. Studies on the cephalic endoskeleton,musculature and proboscis of citrus fruit-piercing noctuid moths in relation to their feeding habits[J].Acta Entomologica Sinica,1985,28(2):165-172.
[10] 冯波,胡武新,潘华,杜永均.嘴壶夜蛾的形态、生活史及昼夜节律[J].昆虫学报,2013,56(12):1440-1451.FENG Bo,HU Wuxin,PAN Hua,DU Yongjun. Morphology,life history and circadian rhythm of the fruit-piercing moth,Oraesia emarginata(Lepidoptera:Noctuidae)[J]. Acta Entomologica Sinica,2013,56(12):1440-1451.
[11] 刘先琴,张祥万.武汉地区吸果夜蛾种群及为害特点与口器结构观察初报[J].中国南方果树,2001,30(4):16-17.LIU Xianqin,ZHANG Xiangwan.Preliminary report on the population,damage characteristics and mouthparts structure of fruitsucking moth in Wuhan area[J]. South China Fruits,2001,30(4):16-17.
[12] LEONG S C T,KUEH R J H. Seasonal abundance and suppression of fruit-piercing moth Eudocima phalonia(L.)in a citrus orchard in Sarawak[J]. The Scientific World Journal,2011,11:2330-2338.
[13] ZASPEL J M,WELLER S J,BRANHAM M A.A comparative survey of proboscis morphology and associated structures in fruit-piercing,tear-feeding,and blood-feeding moths in Calpinae (Lepidoptera:Erebidae)[J]. Zoomorphology,2011,130(3):203-225.
[14] KRENN H W. Feeding mechanisms of adult Lepidoptera:structure,function,and evolution of the mouthparts[J]. Annual Review of Entomology,2010,55:307-327.
[15] ZAHIRI R,HOLLOWAY J D,KITCHING I J,LAFONTAINE J D,MUTANEN M,WAHLBERG N. Molecular phylogenetics of Erebidae (Lepidoptera:Noctuidea)[J]. Systematic Entomology,2012,37(1):102-124.
[16] LEROY L,MILLE C,FOGLIANI B. The common fruit-piercing moth in the Pacific region:A survey of the current state of a significant worldwide economic pest,Eudocima phalonia (Lepidoptera:Erebidae),with a focus on new Caledonia[J]. Insects,2021,12(2):117.
[17] 王希,何兴财,王旭明,李文君,钟玲.江西省橘园吸果夜蛾发生情况调查[J].湖北植保,2021(2):49-50.WANG Xi,HE Xingcai,WANG Xuming,LI Wenjun,ZHONG Ling. Investigation on the occurrence of fruit-sucking moth in orange orchards in Jiangxi Province[J]. Hubei Plant Protection,2021(2):49-50.
[18] 苏燕钿,高松峰,陈盖洵.潮州饶平柑橘吸果夜蛾的优势种调查和防治方法[J].中国热带农业,2016(5):42-43.SU Yandian,GAO Songfeng,CHEN Gaixun. Investigation on dominant species of Citrus fruit sucking moth in Raoping,Chaozhou and its control methods[J]. China Tropical Agriculture,2016(5):42-43.
[19] 姜英,胡淼,张伟平,刘玉惠,孙秋平.赣榆县黑莓桥夜蛾的发生为害及其防治方法[J].中国植保导刊,2009,29(5):30.JIANG Ying,HU Miao,ZHANG Weiping,LIU Yuhui,SUN Qiuping.Occurrence,damage and control methods of Noctuidae in Ganyu County[J].China Plant Protection,2009,29(5):30.
[20] 王华弟,沈颖,颜丽菊,饶汉宗.浙东南山区杨梅嘴壶夜蛾和枯叶夜蛾的发生规律与综合防治研究[J]. 上海农业科技,2017(6):126-128.WANG Huadi,SHEN Ying,YAN Liju,RAO Hanzong.Study on the occurrence regularity and integrated control of Myrica rubra and Spodoptera litura in Nanshan district of East Zhejiang Province[J].Shanghai Agricultural Science and Technology,2017(6):126-128.
[21] 张学祖.日本鸟取县果树试验场的果虫防治[J].新疆农业科学,1981,18(2):48-49.ZHANG Xuezu. Control of fruit insects in fruit tree experimental field in tottori prefecture,Japan[J].Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences,1981,18(2):48-49.
[22] FAY H A C,HALFPAPP K H.Fruit maturity and soundness relevant to feeding choice by fruit-piercing moths (Lepidoptera:Noctuidae)in citrus crops in northeast Australia[J].International Journal of Pest Management,2006,52(4):317-324.
[23] PATHRE R F,JADHAV S D. Some fruit piercing moths (Lepidoptera:Heterocera)from Jalna district of Maharashtra,India[J].Journal of Entomological Research,2020,44(1):131.
[24] FAY H A C.Fruit piercing moths and fruitspotting bugs:Intractable pests of tree fruits in a reduced-insecticide environment[J].Acta Horticulturae,2002(575):485-493.
[25] 吴荣宗.柑桔吸果夜蛾的研究:Ⅰ.防治方法的探讨[J].华南农学院学报,1984,5(2):26-35.WU Rongzong. Studies on the citrus fruit-piercing noctuids:Ⅰ.Research on the control of the fruit-piercing noctuids[J].Journal of South China Agricultural University,1984,5(2):26-35.
[26] REDDY G V P,CRUZ Z T,MUNIAPPAN R.Attraction of fruitpiercing moth Eudocima phalonia (Lepidoptera:Noctuidae) to different fruit baits[J].Crop Protection,2007,26(4):664-667.
[27] KAMALA J P D,AURADE R M,KEMPRAJ V,VERGHESE A.Aromatic fruits as baits for the management of fruit-piercing moths in pomegranate:exploiting olfaction[J]. Current Science.2015,109(8):1476-1479.
[28] KAMALA J P D,VERGHESE A.Studies on feeding preference of adult fruit sucking moth,Eudocima(Othreis)materna(L.):A clue for devising trap cropping strategies[J].Pest Manage HorticEcosyst,2009,15:107-113.
[29] LEE S C,YOO J K,YOO C Y. Survey on the kinds of the fruit sucking moths and their damages in Korea(1)[J]. Korean Journal of Applied Entomology,1970,9(1):37-41.
[30] WHITEHEAD V B,RUST D J. Control of the fruit-piercing moth Serrodes parfifa (Fabr.) (Lepidoptera:Noctuidae)[J]. Phytophylactica,1972,4(1):9-12.
[31] SHIMODA M,HONDA K I. Insect reactions to light and its applications to pest management[J].Applied Entomology and Zoology,2013,48(4):413-421.
[32] 周华光,翟婧,庄君辉,虞世恩,赵丽稳,许燎原.驱虫灯对果树吸果夜蛾的驱避效果初探[J].浙江农业科学,2021,62(12):2493.ZHOU Huaguang,ZHAI Jing,ZHUANG Junhui,YU Shi’en,ZHAO Liwen,XU Liaoyuan.Preliminary study on repellent effect of pest-repelling lamp on fruit-piercing moth in fruit trees[J].Journal of ZhejiangAgricultural Sciences,2021,62(12):2493.
[33] 裴艳,邹金福,徐国祥,周小江,杨佑安,黄新明.太阳能电击式和风吸式杀虫灯在柑橘绿色防控中的应用[J].作物研究,2019,33(S1):96-98.PEI Yan,ZOU Jinfu,XU Guoxiang,ZHOU Xiaojiang,YANG You’an,HUANG Xinming. Application of solar electric shock and wind suction insecticidal lamp in citrus green prevention and control[J].Crop Research,2019,33(S1):96-98.
[34] IZUMI Y,TIAN R L,SONODA S,IMAYOSHI Y,IWABUCHI H,MIYASHITA Y,KANAZAKI S,TSUMUKI H. Analysis of peach fruit headspace volatiles and response by the fruit-piercing moth Oraesia excavata (Lepidoptera:Noctuidae)[J]. Applied Entomology and Zoology,2015,50(2):231-238.
[35] FAY H A C,HALFPAPP K H,ZALUCKI M P,DREWRA I,WHITEG G. Development of a baiting fruit piercing moths(Lepidoptera:Noctuidae) based on feeding attractants[C]// ZALUCKI M P,DREW R A I,WHITE G G. Proceedings of the Sixth Australasian Applied Entomological Research Conference,September 29–October 2,1998,Brisbane,(Australia):University of Queensland Printers,,1998.
[36] 向玉勇,杨茂发.昆虫性信息素研究应用进展[J].湖北农业科学,2006,45(2):250-256.XIANG Yuyong,YANG Maofa. Progress on study and application of insects sex pheromone[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2006,45(2):250-256.
[37] OHMASA Y,WAKAMURA S,KOZAI S,SUGIE H,HORIIKE M,HIRANO C,MORI S. Sex pheromone of the fruit-piercing moth,[Oraesia excavata(Butler)](Lepidoptera:Noctuidae):Isolation and identification[J]. Applied Entomology and Zoology,1991,26(1):55-62.
[38] MALLIKARJUN K B,THIPPAIAH R M,RAGHAVENDRA A,SHARMA J,CHAKRAVARTHYA K. Role of fruit volatiles and sex pheromone components in mate recognition in fruit piercing moth Eudocima materna Linnaeus (Lepidoptera:Erebidae)[J].Journal of Entomol and Zoology Studies,2019,7(3):1381-1387.
[39] SANDS D,LIEBREGTS W. Biological control of fruit piercing moth[Eudocima Fullonia(Clerck)](Lepidoptera:Noctuidae)in the Pacific:exploration,specificity,and evaluation of parasitoid[C]//HODDLE M S. Second International Symposium on Biological Control of Arthropods,September,2005. Davos (Switzerland),2005:12-16.
[40] ALTIERI M A,ANNAMALAI S,KATIYAR K P,FLATH R A.Effects of plant extracts on the rates of parasitization of Anagasta kuehniella [Lep.:Pyralidae] eggs by Trichogramma pretiosum[Hym.:Trichogrammatidae]under greenhouse conditions[J].Entomophaga,1982,27(4):431-437.
[41] 向玉勇,张帆.赤眼蜂在我国生物防治中的应用研究进展[J].河南农业科学,2011,40(12):20-24.XIANG Yuyong,ZHANG Fan. Review of application research on Trichogramma westwood in biological control in China[J].Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences,2011,40(12):20-24.
[42] SMITH S M.Biological control with Trichogramma:Advances,successes,and potential of their use[J].Annual Review of Entomology,1996,41:375-406.
[43] MUNIAPPAN R,BAMBA J,CRUZ J,REDDY G V P.Biology,rearing and field release on Guam of Euplectrus maternus,a parasitoid of the fruit-piercing moth,Eudocima fullonia[J].BioControl,2004,49(5):537-551.
[44] BHUMANNAVAR B S,VIRAKTAMATH C A. Seasonal incidence and extent of parasitization of fruit piercing moths of the genus Othreis(Lepidoptera:Noctuidae)[J].Journal of Biological Control,2001,15(1):31-38.
[45] SVENSSON A M,RYDELL J. Mercury vapour lamps interfere with the bat defence of tympanate moths (Operophtera spp.;Geometridae)[J].Animal Behaviour,1998,55(1):223-226.
[46] YAGER D D.Predator detection and evasion by flying insects[J].Current Opinion in Neurobiology,2012,22(2):201-207.
[47] TER HOFSTEDE H M,GOERLITZ H R,RATCLIFFE J M,HOLDERIED M W,SURLYKKE A.The simple ears of noctuoid moths are tuned to the calls of their sympatric bat community[J].The Journal of Experimental Biology,2013,216(21):3954-3962.
[48] NAKANO R,IHARA F,MISHIRO K,TOYAMA M,TODA S.High duty cycle pulses suppress orientation flights of crambid moths[J].Journal of Insect Physiology,2015,83:15-21.
[49] 郑雪良,王登亮,黄振东,胡秀荣,蒲占湑,吴雪珍,陈骏.香茅油对柑橘吸果夜蛾的趋避试验[J]. 浙江农业科学,2019,60(7):1163-1164.ZHENG Xueliang,WANG Dengliang,HUANG Zhendong,HU Xiurong,PU Zhanxu,WU Xuezhen,CHEN Jun. Repellency of citronella oil against Oraesia excavate Butler[J].Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences,2019,60(7):1163-1164.
[50] JAYANTHI P K,VERGHESE A,NAGARAJV D. Studies on feeding preference of adult fruit sucking moth,Eudocima (Othreis)materna(L.):A clue for devising trap cropping strategies[J].Pest Management in Horticultural Ecosystems,2009,15(2):107-113.
[51] 玉波. 果树悬挂卫生球可减轻吸果夜蛾危害[J]. 现代农业,1992(8):13.YU Bo. Hanging sanitary balls on fruit trees can reduce the harm of fruit sucking moth[J].Modern Agriculture,1992(8):13.
[52] 蒋义民,吴孔官,蒋际清.萘忌避柑桔吸果夜蛾的试验初报[J].福建果树,1988(3):32-33.JIANG Yimin,WU Kongguan,JIANG Jiqing. Preliminary report on the experiment of naphthalene to avoid citrus fruit-sucking moth[J].Fujian Fruits,1988(3):32-33.
[53] CARPINELLA M C,DEFAGO M T,VALLADARES G,PALACIOS S M.Antifeedant and insecticide properties of a limonoid from Melia azedarach (Meliaceae) with potential use for pest management[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2003,51(2):369-374.
[54] ISMAN M B. Botanical insecticides,deterrents,and repellents in modern agriculture and an increasingly regulated world[J].Annual Review of Entomology,2006,51:45-66.
[55] RANI P U,RAJASEKHARREDDY P.Toxic and antifeedant activities of Sterculia Foetida (L.) seed crude extract against Spodoptera litura (F.) and Achaea Janata (L.)[J]. Journal of Biopesticides,2009,2:161-164.
[56] WADA K,MANAKATA K. Naturally occurring insect control cheive measurement of heptachlor in the soil and certain products of animal and plant origin.ang[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,1968,16(3):471-474.
[57] KULKARNI S R,PATIL S K,GURU P N. Host specificity and bioratonal management of fruit sucking moth,Eudocima (Othreis) materna L.[J]. Pest Management in Horticultural Ecosystems,2017,23(1):12-16.
[58] 周晓音,黄顺,敏梁红,朱廷才,黄玉松,周岳良.应用“百树得”防治柑桔吸果夜蛾的研究[J].中国南方果树,1997,26(4):13-14.ZHOU Xiaoyin,HUANG Shun,MIN Lianghong,ZHU Tingcai,HUANG Yusong,ZHOU Yueliang. Study on the application of“Baishude”to control citrus fruit-sucking moth[J]. South China Fruits,1997,26(4):13-14.
[59] HENG R K J,TECK S L C,KUNDAT F R. Biology and ecology of fruit piercing moth Eudocima phalonia (L.) in a citrus orchard in Sarawak,Malaysia[J]. Journal of Tropical Biology and Conservation.2012,9:176-182.
[60] 沈志杰,房明华,洪文英,刘涛,沃林峰,孙媛,蓝陈仪航,邓建宇.不同生境果园梨小食心虫各代成虫高峰期差异[J].植物保护,2021,47(3):222-225.SHEN Zhijie,FANG Minghua,HONG Wenying,LIU Tao,WO Linfeng,SUN Yuan,LAN Chenyihang,DENG Jianyu. Differences of adult peak periods of each generation of male oriental fruit moth,Grapholita molesta (Busck) in different habitat orchards[J].Plant Protection,2021,47(3):222-225.
[61] 封洪强,姚青.农业害虫自动识别与监测技术[J].植物保护,2018,44(5):127-133.FENG Hongqiang,YAO Qing. Automatic identification and monitoring technologies of agricultural pest insects[J].Plant Protection,2018,44(5):127-133.
[62] 赵紫华,马建华,高峰,张蓉.害虫种群区域性生态调控的系统策略[J].中国生物防治学报,2021,37(5):855-862.ZHAO Zihua,MA Jianhua,GAO Feng,ZHANG Rong. Systematic strategy of ecologically based pest management of insect pest population at landscape scales[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control,2021,37(5):855-862.
[63] DENG J Y,LAN C Y H,ZHOU J X,YAO Y B,YIN X H,FU K Y,DING X H,GUO W C,LIU W,WANG N,WANG F M.Analysis of sex pheromone production and field trapping of the Asian corn borer (Ostrinia furnacalis Guenée) in Xinjiang,China[J].Journal of Integrative Agriculture,2023,22(4):1093-1103.
[64] 万霞,邓建宇,王义平.不同诱捕器和不同波段LED 灯对美国白蛾的引诱效果[J].植物保护,2021,47(1):103-107.WAN Xia,DENG Jianyu,WANG Yiping. Effects of different trap types and fluorescent tubes at different bands on capture of Hyphantria cunea(Drury)[J].Plant Protection,2021,47(1):103-107.
[65] 杨真,张宏瑞,李正跃.植物挥发物对蛾类昆虫行为影响的研究进展[J].南方农业学报,2015,46(3):441-446.YANG Zhen,ZHANG Hongrui,LI Zhengyue. Advances in effects of plant volatiles on phalaenae behaviors[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture,2015,46(3):441-446.
[66] 张秀歌,李祥,孙小旭,李思翰,董文霞.植物挥发物对蛾类昆虫性信息素的影响[J].应用昆虫学报,2015,52(6):1333-1344.ZHANG Xiuge,LI Xiang,SUN Xiaoxu,LI Sihan,DONG Wenxia.Effect of plant volatiles on moth sex pheromone[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology,2015,52(6):1333-1344.
[67] THÖMING G. Behavior matters-future need for insect studies on odor-mediated host plant recognition with the aim of making use of allelochemicals for plant protection[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2021,69(36):10469-10479.
[68] 孙媛,蓝陈仪航,施程程,沈志杰,房明华,洪文英,沃林峰,刘涛,邓建宇.桃潜叶蛾与梨小食心虫性信息素互作效应[J].果树学报,2021,38(9):1563-1568.SUN Yuan,LAN Chenyihang,SHI Chengcheng,SHEN Zhijie,FANG Minghua,HONG Wenying,WO Linfeng,LIU Tao,DENG Jianyu. Interaction effect between Lyonetia clerkella and Grapholitha molesta sex pheromones[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2021,38(9):1563-1568.
[69] DENG J Y,SHEN Z J,WANG F M,LIU T,HONG W Y,FANG M H,WO L F,CHU S J.Enhancement of attraction to sex pheromone of Grapholita molesta (Busck) (Lepidoptera:Tortricidae)by structurally unrelated sex pheromone compounds of Conogethes Punctiferalis(Guenée)(Lepidoptera:Crambidae)[J].Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology,2022,25(1):101859.