柑橘(Citrus reticulata Blanco)属芸香科柑橘亚科,为世界第一大类水果,因其色香味兼优且营养价值高而深受消费者喜爱[1]。柑橘果实富含糖类、有机酸、维生素、膳食纤维、矿物质及酚类物质(类黄酮、酚酸等),研究表明酚类物质具有抗炎[2]、抗氧化[3]、抗癌[4]等功效。中国是柑橘的重要原产地之一,资源丰富[5]。目前,我国主要柑橘产区有广西、湖南、湖北、广东、江西、浙江、福建、四川、重庆和云南等10个省份[6],品种繁多,生产上主要栽培的有宽皮柑橘、甜橙、杂柑、柠檬等[7]。2021 年我国柑橘面积278.8多万hm2,产量约5 595.61万t。
柑橘果实品质包括色泽、果形、糖、酸、维生素C(Vc)、类黄酮、酚酸等外观品质、营养品质及风味品质[8]。果实品质是决定柑橘市场竞争力的重要因素,而品种特性对柑橘果实品质起决定性作用[9]。因此,客观、准确、科学地分析和评价柑橘果实品质,对品种选育、改良及结构调整极为重要。目前柑橘果实品质评价方面的研究大多利用简单的统计方法[10-11],而综合评价方法的应用主要集中于优新品种的品质评价,李勋兰等[12]对6 个晚熟杂柑新品种果实品质指标进行检测分析,并采用因子分析法进行综合评价,但未考察柑橘果皮酚类物质。有研究[13]报道对11个柑橘品种8种常规果实品质指标及果肉中20种酚类物质含量进行比较分析,利用因子分析法评价果实品质,但研究的品种相对较少。聚类分析是将数据进行分类,同类中的样本间相似,而不同类的样本间差异很大。热图分析是对数据分布情况进行分析的直观可视化方法,而热图聚类分析是将两者结合起来的分析方法,通过颜色深浅来反映样本中相应含量高低,更直观地呈现数据结果。王贵一等[14]利用PCA分析法,建立杧果品质综合评价方法。姜璐等[15]采用PCA 分析法及可视化热图聚类分析法对蓝靛果的品质进行综合评价,并对蓝靛果进行分类。PCA 分析法及聚类分析法已广泛用于梨[16]、猕猴桃[17]、蓝莓[18]、樱桃[19]、榴莲[20]、西瓜[21]等农产品品质差异的分析,但热图聚类分析法对柑橘品质的评价鲜见报道。笔者在本研究中对33 个不同柑橘品种(系)的常规品质指标、糖酸组分含量、总黄酮含量、总酚含量及抗氧化性能进行检测,采用相关性分析、PCA 分析、热图聚类分析等多元统计方法对果实品质进行综合评价,以期摸清不同柑橘品种的品质特性,丰富数据库,为柑橘品种结构调整、新品种选育及功能性成分的开发利用提供理论依据。
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料
试验共选取椪柑、胡柚、葡萄柚、红美人等33个不同柑橘品种(系)(见表1),样品均采自浙江省柑橘研究所种质资源圃,管理水平一致,采样时间为2021 年10 月27 日至2022 年4 月10 日,各个品种(系)样品均处于商业成熟期。每个品种(系)选取长势良好、树龄相似的果树3 株。每株树冠外围东南西北方向随机采集大小一致、无病虫害、无机械损伤的柑橘果实12 个,共36 个果实,随机分成3 组。果实采后立即运回浙江省柑橘研究所农产品检测实验室,清水洗净,用纱布擦干,去皮、籽,果肉榨汁取果汁进行理化品质测定。果皮置于50 ℃烘箱中烘干,粉碎过60目筛(0.25 mm),装入塑料瓶并密封,贮藏于-20 ℃冰箱中备用。
表1 样品采集信息
Table 1 Information of citrus samples

编号Number Z01编号Number Z18 Z02 Z19 Z03 Z20品种Cultivar胡柚Huyou明日见Asumi 123-1 Z04 Z21 Z05 Z22 Z06 Z23 Z07 Z24 Z08 Z25 Z09 Z26津之香Tsunokaori Tangor春香Haruka沃柑Orah刘本橙Liubencheng脐橙Navel orange 439 Z10 Z27 Z11 Z28 Z12 Z29 Z13 Z30 Z14 Z31 Z15 Z32 Z16 Z33品种Cultivar鸡尾葡萄柚Cocktail grapefruit火焰葡萄柚Flame grapefruit青岛44 Aoshima No.44 unshu瓯柑Ougan青瓯柑Green Ougan椪柑Ponkan贡柑Gonggan茶枝柑Chachi Gan默科特Murcott槾橘Manju早橘Sokitsu媛小春Himekoharu兴津60 Okitsu No.60红美人Hongmeiren甜橘柚Sweet Spring高橙Gaocheng清峰Seihou类别Classification葡萄柚Grapefruit葡萄柚Grapefruit宽皮柑橘Mandarin宽皮柑橘Mandarin宽皮柑橘Mandarin宽皮柑橘Mandarin宽皮柑橘Mandarin宽皮柑橘Mandarin宽皮柑橘Mandarin宽皮柑橘Mandarin宽皮柑橘Mandarin杂柑Citrus hybrid杂柑Citrus hybrid杂柑Citrus hybrid杂柑Citrus hybrid杂柑Citrus hybrid杂柑Citrus hybrid采样时间Sampling date 12月10日December 10th 3月10日March 10th 12月10日December 10th 12月10日December 10th 12月10日December 10th 12月10日December 10th 12月27日December 27th 12月27日December 27th 2月27日February 27th 12月10日December 10th 10月27日October 27th 2月10日February 10th 2月10日February 10th 12月10日December 10th 12月10日December 10th 12月10日December 10th 2月10日February 10th夏橙Valencia orange脐血橙Washington Sanguine塔罗科血橙Tarocco blood orange雪柑Xuegan锦橙Jincheng摩洛血橙Moro blood orange莱檬Lime类别Classification杂柑Citrus hybrid杂柑Citrus hybrid杂柑Citrus hybrid杂柑Citrus hybrid杂柑Citrus hybrid杂柑Citrus hybrid杂柑Citrus hybrid甜橙Sweet orange甜橙Sweet orange甜橙Sweet orange甜橙Sweet orange甜橙Sweet orange甜橙Sweet orange甜橙Sweet orange甜橙Sweet orange莱檬Lime采样时间Sampling date 12月10日December 10th 2月10日February 10th 11月20日November 20th 2月27日February 27th 12月27日December 27th 2月10日February 10th 12月10日December 10th 12月10日December 10th 12月10日December 10th 4月10日April 10th 2月10日February 10th 2月27日February 27th 12月27日December 27th 12月27日December 27th 1月10日January 10th 12月10日December 10th Z17
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 果实品质测定 外观品质:单果质量、果皮厚(果实赤道部)、果实横径和纵径,采用游标卡尺和电子天平测定,果形指数:果实纵径/果实横径。
可溶性固形物(TSS)含量用手持糖酸计(Atago PAL-1)法测定;TA含量用酸碱滴定法测定;固酸比:TSS/TA;维生素C 含量用2,6-二氯酚靛滴定法测定。糖组分含量参照郑丽静等[22]的方法略有改进,采用ICS5000离子色谱仪测定,色谱条件:色谱柱为PA10离子交换柱(4 mm×250 mm)和同款保护柱;流动相:H2O 和NaOH(200 mmoL·L-1),梯度洗脱;流速1.0 mL·min-1;柱温30 ℃;进样量10 μL;酸组分含量参照姚改芳等[23]的方法略有改进,采用10A高效液相色谱紫外分光光度法测定,色谱条件:LP-C18色谱柱(4.6 mm×300 mm,5 μm)和同款保护柱;流动相:KH2PO4缓冲液(pH:2.65);流速0.5 mL·min-1;柱温40 ℃;进样量10 μL;检测波长210 nm;采集时间35 min;总糖:蔗糖、葡萄糖和果糖的总和;总酸:柠檬酸、苹果酸、酒石酸、草酸和莽草酸的总和;糖酸比:总糖/总酸。
1.2.2 果皮测定 活性物质:利用超声辅助乙醇法制备供试样品果皮的提取液,总黄酮含量采用三氯化铝比色法测定,结果以芦丁计;提取物总酚含量采用Folin-Ciocalteu比色法测定,结果以没食子酸计。
抗氧化性能:采用boxbio 试剂盒测定果皮提取物DPPH 自由基清除能力、ABTS+自由基清除能力及FRAP 还原能力,DPPH 法和ABTS 法结果以维生素C 摩尔表示,FRAP 法结果以FeSO4 摩尔表示。参考李楠等[24]的方法计算抗氧化综合评价值:Yi=∑(Xij-Xjmin)/(Xjmax-Xjmin),其中Xij:第i 种柑橘,第j个抗氧化值;Xjmin和Xjmax分别为第i 种柑橘,第j 个抗氧化值的最小值和最大值。
1.3 数据处理与分析
每个指标均重复测定3次取平均值,采用Excel 2010、SPSS 22和Origin 2022b对试验数据进行统计分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 不同柑橘品种(系)果实品质
2.1.1 外观品质分析 由表2 可知,各品种(系)柑橘果实外观品质指标存在不同程度差异。果形指数变化范围0.64~1.27,其中莱檬的最大,较早橘(最小)大了98.4%。除莱檬、摩洛血橙、塔罗科血橙和123-1外,其余品种(系)果形指数均小于1。果实纵径和横径均值分别为66.56 mm和74.71 mm,单果质量均值为184.99 g。葡萄柚类中鸡尾葡萄柚单果质量最大,达422.50 g,其果实纵径和横径也均较大。葡萄柚类果皮厚均值为4.64 mm,火焰葡萄柚的相对较厚。宽皮柑橘类(Z03~Z11)果实单果质量均值为134.62 g,变化范围为90.57~167.20 g,果实纵径和横径均值分别为58.58 mm和70.23 mm,果皮厚均值为3.36 mm。杂柑类(Z12~Z24)果实单果质量变化范围为104.03~340.80 g,均值为193.92 g,其中胡柚的最大,果实纵径、横径及果皮厚差异均较大,其中胡柚的纵径(86.93 mm)、横径(94.75 mm)和果皮厚(8.02 mm)均最大,而媛小春的纵径(49.53 mm)和果皮厚(2.25 mm)均为最小,123-1 的横径(59.50 mm)最小。甜橙类单果质量范围为120.70~340.40 g,其中最大的为夏橙,果实纵径差异相对较小,其中锦橙的最大(82.40 mm),而果实横径差异较大,其中夏橙的最大(92.67 mm),摩洛血橙的最小(60.83 mm),果实果皮厚均值为4.72 mm,其中脐血橙的果皮最厚(6.21 mm),摩洛血橙的最薄(3.59 mm)。莱檬的果实纵径较大,而果皮相对较薄。
表2 不同柑橘品种(系)果实外观品质
Table 2 Exterior quality of different citrus varieties(strains)

注:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(p<0.05)。下同。
Note:Different lowercase letters in the same column indicate significant difference at 0.05 level.The same below.
品种Cultivar Z01 Z02 Z03 Z04 Z05 Z06 Z07 Z08 Z09 Z10 Z11 Z12 Z13 Z14 Z15 Z16 Z17 Z18 Z19 Z20 Z21 Z22 Z23 Z24 Z25 Z26 Z27 Z28 Z29 Z30 Z31 Z32 Z33均值Average CV/%纵径Vertical diameter/mm 86.67±1.53 a 79.47±2.54 cd 55.87±1.80 op 61.80±1.85 lm 59.60±1.93 mn 63.73±2.05 kl 55.87±1.80 op 62.00±2.17 lm 58.20±1.85 no 66.13±2.20 hijk 44.00±2.17 r 49.53±2.14 q 56.97±2.11 no 71.53±1.25 fg 74.83±2.25 e 72.67±2.75 ef 65.67±1.61 ijk 86.93±1.90 a 57.23±1.60 no 59.63±1.89 mn 64.67±2.25 jkl 78.20±1.85 d 53.03±2.11 p 67.20±1.28 hij 68.70±1.93 ghi 60.00±1.70 mn 73.10±1.85 ef 79.00±1.67 d 69.17±1.96 gh 65.80±1.93 ijk 82.40±2.35 bc 63.60±2.25 kl 83.33±1.65 b 66.56±10.70 16.08横径Horizontal diameter/mm 95.67±1.15 a 90.33±2.19 cd 77.33±2.52 h 66.67±1.67 klm 68.54±1.57 jkl 77.78±2.55 gh 63.00±1.73 nop 65.00±1.67 mno 68.44±1.68 jkl 76.27±2.58 hi 69.06±2.02 jk 60.83±0.83 pq 69.72±2.10 j 77.57±1.19 h 85.00±1.67 f 90.58±1.88 cd 73.58±1.51 i 94.75±1.64 ab 68.00±1.22 jkl 59.50±1.69 q 88.33±1.91 de 80.72±2.15 g 62.22±2.10 opq 67.61±2.34 jklm 75.00±1.67 hi 61.50±2.49 pq 92.67±2.52 abc 86.89±1.68 ef 67.22±1.27 jklm 67.11±2.36 jklm 92.06±1.25 bc 60.83±1.48 pq 65.56±0.96 lmn 74.71±11.35 15.20果形指数Fruit shape index 0.91±0.03 hijk 0.88±0.01 jklmn 0.72±0.00 r 0.93±0.00 fgh 0.87±0.01 klmn 0.82±0.01 opq 0.89±0.04 hijklm 0.95±0.01 efg 0.85±0.01 mno 0.87±0.01 lmn 0.64±0.02 s 0.81±0.03 opq 0.82±0.01 opq 0.92±0.02 ghi 0.88±0.02 ijklm 0.80±0.03 pq 0.89±0.01 hijklm 0.92±0.00 ghij 0.84±0.02 nop 1.00±0.06 cd 0.73±0.02 r 0.97±0.01 def 0.85±0.01 mno 0.99±0.02 cde 0.91±0.02 hij 0.98±0.06 de 0.79±0.04 q 0.91±0.00 hijk 1.03±0.05 bc 0.98±0.03 de 0.90±0.03 hijkl 1.05±0.01 b 1.27±0.03 a 0.90±0.11 12.57单果质量Single fruit mass/g 422.50±5.70 a 308.43±5.35 c 150.53±5.16 l 133.53±4.18 m 124.67±3.45 no 160.47±5.22 jk 114.07±4.04 pq 126.00±5.10 no 144.53±2.48 l 167.20±2.45 ij 90.57±2.84 s 104.03±4.19 r 126.47±5.48 no 250.83±7.47 e 252.77±6.33 e 282.40±8.39 d 172.27±3.66 i 340.80±3.30 b 148.30±2.21 l 112.10±1.73 q 232.07±2.83 f 229.97±1.89 f 111.03±2.00 q 157.97±3.17 k 188.43±3.33 h 124.43±3.91 no 340.40±4.39 b 187.83±3.06 h 147.20±2.51 l 129.13±2.51 mn 211.97±2.84 g 120.70±2.25 op 190.97±6.64 h 184.99±79.55 43.00果皮厚Peel thickness/mm 3.65±0.07 k 5.63±0.12 e 4.27±0.16 hi 4.26±0.11 hij 3.28±0.12 mn 3.20±0.16 mno 2.75±0.09 p 3.39±0.12 lm 3.07±0.11 no 4.04±0.20 j 2.02±0.12 r 2.25±0.18 q 3.40±0.14 lm 2.61±0.06 p 5.63±0.10 e 6.31±0.19 b 4.67±0.16 g 8.02±0.15 a 2.74±0.08 p 4.19±0.17 ij 4.10±0.20 ij 6.03±0.17 cd 2.58±0.17 p 4.51±0.11 g 4.62±0.13 g 4.14±0.13 ij 4.95±0.14 f 6.21±0.13 bc 3.80±0.13 k 4.45±0.12 gh 5.96±0.14 d 3.59±0.15 kl 2.98±0.14 o 4.16±1.35 32.54
2.1.2 内在品质分析 由表3可知,各品种(系)柑橘果实维生素C含量(w,后同)均值为34.30 mg·100 g-1,宽皮柑橘类果实维生素C含量均低于均值,而甜橙类除夏橙外,均高于均值,且甜橙类的普遍高于杂柑。维生素C含量最高的为123-1(63.98 mg·100 g-1),显著高于其他品种(系)(p<0.05),是早橘(最低,11.64 mg·100 g-1)的5.5倍。TSS含量的均值为10.9%,变化范围为8.1%~15.3%,其中兴津60(最高)是青岛44(最低)的1.9倍。葡萄糖和果糖含量的均值分别为20.97 mg·g-1和28.02 mg·g-1,变化范围分别为12.03~41.04 mg·g-1和16.17~53.60 mg·g-1。兴津60的葡萄糖和果糖含量均最高,瓯柑的葡萄糖含量最低,津之香的果糖含量最低。葡萄糖/果糖的比值为0.62~1.19,除清峰外,葡萄糖/果糖的比值均小于1,说明果糖含量普遍高于葡萄糖。蔗糖含量均值为47.89mg·g-1,其中早橘最高为87.35 mg·g-1,莱檬最低为5.21 mg·g-1,最高为最低的16.8 倍。总糖含量变化范围为43.95~145.71 mg·g-1,变异系数为22.93%,兴津60(最高)为莱檬(最低)的3.3 倍。3 种糖占总糖的比值结果见图1-A,蔗糖占总糖含量的11.86%~69.12%,其在不同品种(系)果实中的积累存在一定的差异,其中甜橙类除脐血橙外,蔗糖含量均低于50%,果糖和葡萄糖的含量总和超过50%,由此说明甜橙类以己糖(葡萄糖和果糖)和蔗糖共同积累。宽皮柑橘类除青岛44 和贡柑外,蔗糖含量高于50%,说明宽皮柑橘类以积累蔗糖为主。而莱檬葡萄糖和果糖的含量总和达88.14%,说明以积累己糖为主。

图1 果实中各糖组分与总糖的比值及各酸组分与总酸的比值
Fig. 1 The proportion of each sugar component and the proportion of each acid component in fruits
表3 不同柑橘品种(系)果实内在品质
Table 3 Fruit quality of different citrus varieties (strains)

糖Sugar/Acid比酸21.95±0.54 a 4.88±0.13 pq 5.28±0.09 op 9.29±0.28 fgh 9.47±0.18 fg 11.18±0.20 e 12.71±0.60 cd 6.07±0.20 mn 7.37±0.16 k 9.20±0.23 gh 14.74±0.65 b 9.06±0.07 gh 8.24±0.18 j 11.29±0.52 e 12.34±0.47 d 4.60±0.06 q 8.78±0.21 i 9.66±0.22 f 8.99±0.16 hi 5.69±0.08 no 7.20±0.12 k 11.35±0.22 e 13.08±0.14 c 7.57±0.14 k 6.68±0.13 l 7.44±0.16 k 4.81±0.10 q 7.16±0.14 k 6.32±0.09 lm 8.94±0.19 hi 5.41±0.05 o 8.94±0.15 hi 1.16±0.01 r 8.69±3.69 42.49酸)w(总Total acid/(mg·g-1)6.36±0.11 u 15.29±0.20 g 12.46±0.31 l 8.34±0.15 qrs 8.60±0.15 pqr 8.82±0.11 p 8.06±0.33 s 16.33±0.53 f 13.61±0.29 ij 8.24±0.16 rs 8.59±0.38 pqr 14.75±0.18 h 17.69±0.28 e 8.51±0.31 pqr 8.35±0.32 qrs 23.23±0.42 b 10.88±0.33 n 8.78±0.14 pq 14.04±0.32 i 18.20±0.36 d 10.19±0.29 o 7.27±0.12 t 9.76±0.19 o 11.73±0.16 m 12.19±0.28 l 15.22±0.28 g 19.02±0.30 c 13.54±0.19 j 12.95±0.25 k 11.48±0.28 m 13.72±0.21 ij 11.54±0.12 m 37.93±0.42 a 12.90±5.88 45.62酸)石w(酒Tartaric acid/(mg·g-1)0.41±0.05 r 0.32±0.03 s 0.77±0.05 f 0.83±0.03 e 0.75±0.03 fg 0.56±0.04 no 0.63±0.02 klm 0.65±0.03 ijkl 0.84±0.02 de 0.54±0.02 op 0.66±0.04 hijk 0.94±0.04 b 0.64±0.03 jkl 0.67±0.03 hijk 0.50±0.02 pq 0.42±0.02 r 0.88±0.03 de 0.93±0.04 bc 0.70±0.05 ghij 0.66±0.04 hijk 0.59±0.04 mno 0.60±0.03 lmn 0.71±0.06 gh 1.07±0.05 a 0.62±0.03 klm 0.83±0.04 de 0.26±0.03 t 0.71±0.04 gh 0.60±0.03 lmn 0.89±0.04 cd 0.70±0.02 ghi 0.88±0.03 de 0.45±0.03 qr 0.67±0.18 27.45酸)果w(苹Malic acid/(mg·g-1)0.19±0.03 s 0.62±0.06 o 0.25±0.03 rs 2.11±0.04 c 1.35±0.06 de 0.88±0.09 lm 1.00±0.08 ij 1.09±0.07 gh 1.31±0.04 e 1.07±0.05 ghi 2.15±0.05 c 0.21±0.03 s 0.42±0.07 p 1.41±0.09 d 0.39±0.03 pq 0.27±0.02 rs 0.60±0.04 o 1.35±0.09 de 0.78±0.07 n 0.97±0.05 jk 1.12±0.04 g 3.82±0.07 a 2.61±0.04 b 1.21±0.04 f 1.00±0.05 hij 0.81±0.06 mn 0.31±0.03 qr 0.46±0.04 p 0.84±0.03 lmn 0.90±0.04 kl 1.33±0.07 e 1.22±0.04 f 0.84±0.06 lmn 1.06±0.75 70.52酸)檬w(柠Citric acid/(mg·g-1)5.67±0.14 op 14.26±0.28 e 11.34±0.27 h 5.27±0.15 p 6.40±0.13 m 7.30±0.12 l 6.32±0.28 mn 14.48±0.44 e 11.37±0.32 h 6.56±0.17 m 5.67±0.28 op 13.47±0.19 f 16.50±0.31 d 5.94±0.18 no 7.39±0.30 l 22.42±0.41 b 9.27±0.33 j 6.38±0.25 m 12.42±0.31 g 16.43±0.28 d 8.39±0.25 k 2.75±0.16 q 6.32±0.21 mn 9.32±0.22 j 10.45±0.31 i 13.45±0.20 f 18.40±0.31 c 12.28±0.24 g 11.41±0.23 h 9.58±0.27 j 11.59±0.20 h 9.35±0.16 j 36.59±0.44 a 11.05±6.24 56.50糖)74.52±0.99 t 65.80±0.55 u 77.44±1.21 r 81.41±0.51 q 98.58±0.55 k 98.97±0.84 jk 75.88±0.85 s 95.94±0.84 lm 95.46±0.54 m 84.76±0.67 p 73.34±0.87 t 82.45±0.92 q 88.84±0.52 o 81.47±0.30 q 91.36±0.43 n 96.99±0.44 l 81.86±0.63 q 74.19±0.56 t 43.95±0.55 v 96.88±22.21 22.93 w(总Total sugar/(mg·g-1)139.57±1.19 b 102.33±0.63 i 100.14±0.92 j 126.37±0.66 e 133.66±0.70 c 145.71±0.94 a 102.98±0.73 hi 106.85±0.57 g 126.09±0.87 e 103.6±0.61 h 127.63±1.05 d 113.23±0.54 f 102.54±0.63 hi 103.12±0.64 hi糖)w(果Fructose/34.73±0.98 f 22.81±0.57 no 20.52±0.40 p 19.11±0.38 q 20.67±0.56 p 26.64±0.47 l 30.55±0.44 i 25.60±0.50 m 27.00±0.74 kl 16.67±0.42 r 22.83±0.49 no 40.02±0.69 c 53.60±0.44 a 23.45±0.80 n 28.62±0.54 j 35.64±0.55 e 22.73±0.50 no 20.07±0.40 p 46.05±0.34 b 34.17±0.48 f 16.17±0.31 r 18.95±0.39 q 29.82±0.62 i 32.56±0.33 g 25.65±0.49 m 36.69±0.36 d 29.79±0.31 i 26.86±0.37 kl 27.56±0.50 k 31.41±0.27 h 22.12±0.46 o 32.75±0.56 g 22.86±0.31 no 28.02±8.20 29.27(mg·g-1)糖)萄w(葡Glucose/(mg·g-1)24.27±0.62 fg 17.52±0.58 no 13.50±0.31 r 12.03±0.35 t 15.55±0.45 p 19.81±0.49 l 22.15±0.48 j 19.59±0.51 l 18.74±0.42 m 13.09±0.33 rs 16.19±0.32 p 31.66±0.46 c 41.04±0.34 a 21.20±0.91 k 22.17±0.30 ij 27.30±0.44 d 27.08±0.51 d 14.44±0.34 q 35.66±0.57 b 24.82±0.53 ef 12.40±0.35 st 13.55±0.25 r 22.71±0.54 hij 22.96±0.26 h 18.25±0.42 mn 25.52±0.42 e 23.82±0.35 g 19.49±0.36 l 17.22±0.59 o 22.90±0.35 hi 15.75±0.45 p 23.72±0.50 g 15.87±0.33 p 20.97±6.57 31.31糖)w(蔗Sucrose/(mg·g-1)80.57±0.85 b 34.19±0.65 s 31.78±0.53 u 46.30±0.55 lm 45.18±0.38 no 52.13±0.38 f 49.63±0.51 j 53.78±0.46 e 54.41±0.39 e 46.12±0.28 lm 87.35±0.35 a 61.98±0.63 d 51.06±0.73 gh 51.29±0.87 g 52.19±0.21 f 43.91±0.41 p 45.66±0.52 mn 50.25±0.59 hij 44.38±0.33 op 44.62±0.55 op 44.77±0.56 o 49.94±0.36 ij 75.10±0.41 c 33.32±0.25 t 37.57±0.60 q 51.02±0.58 gh 37.75±0.55 q 50.64±0.57 ghi 37.08±0.53 qr 48.23±0.40 k 36.32±0.49 r 46.66±0.50 l 5.21±0.19 v 47.89±14.37 30.00 C)素生w(维Vc/(mg·100 g-1)32.20±0.56 mn 40.56±0.61 i 20.44±0.43 v 30.11±0.57 o 28.37±0.52 q 24.97±0.37 s 22.54±0.45 u 28.98±0.41 pq 25.28±0.24 s 26.89±0.38 r 11.64±0.28 y 35.58±0.48 k 31.55±0.20 n 28.4±0.98 q 23.69±0.19 t 43.19±0.68 g 32.86±0.50 lm 29.68±0.40 op 33.18±0.31 l 63.98±0.38 a 38.54±0.34 j 17.72±0.22 w 20.89±0.36 v 41.45±0.44 h 49.07±0.10 f 61.57±0.29 b 23.85±0.63 t 54.31±0.36 d 55.81±0.47 c 50.93±0.67 e 42.8±0.47 g 48.4±0.46 f 12.51±0.34 x 34.30±13.35 38.91固TSS/TA比酸15.0±0.6 fg 6.6±0.1 n 8.2±0.2 m 15.3±0.2 fg 15.6±0.5 f 16.6±0.3 e 18.2±0.6 d 8.3±0.2 m 11.6±0.1 i 14.4±0.8 g 25.7±1.8 a 11.6±0.1 i 10.0±0.2 l 19.4±1.2 bc 18.0±0.8 d 6.3±0.2 n 15.1±0.6 fg 18.4±0.7 cd 11.5±0.4 i 8.0±0.2 m 11.3±0.2 ij 19.6±1.3 b 19.4±0.3 b 12.9±0.6 h 9.9±0.3 l 10.9±0.3 ijk 6.3±0.1 n 10.4±0.4 jkl 10.0±0.4 kl 12.9±0.3 h 8.1±0.2 m 13.0±0.3 h 2.3±0.0 o 12.8±4.9 38.70酸)定滴w(可TA/(g·100 mL-1)0.78±0.02 n 1.29±0.02 f 0.99±0.02 j 0.60±0.01 pq 0.54±0.02 r 0.62±0.02 p 0.57±0.01 qr 1.33±0.02 e 0.92±0.02 l 0.70±0.02 o 0.49±0.04 s 1.17±0.01 g 1.54±0.03 d 0.66±0.03 o 0.57±0.02 qr 2.01±0.04 b 0.78±0.02 n 0.50±0.02 s 1.18±0.03 g 1.53±0.02 d 0.81±0.02 mn 0.48±0.03 s 0.69±0.02 o 0.79±0.02 n 0.93±0.02 lk 1.16±0.04 g 1.64±0.03 c 1.19±0.02 g 1.04±0.03 i 0.97±0.01 jk 1.10±0.01 h 0.83±0.02 m 3.58±0.02 a 1.03±0.58 56.68性溶物)w(可形固TSS/%11.7±0.2 h 8.5±0.2 p 8.1±0.1 q 9.2±0.3 no 8.4±0.2 p 10.2±0.2 lm 10.5±0.2 kl 11.0±0.2 i 10.7±0.2 jk 10.1±0.2 m 12.7±0.2 def 13.7±0.2 b 15.3±0.2 a 12.8±0.2 d 10.3±0.2 lm 12.6±0.1 defg 11.8±0.1 h 9.3±0.2 m 13.5±0.2 bc 12.3±0.2 g 9.1±0.2 no 9.3±0.2 m 13.3±0.2 c 10.2±0.2 lm 9.2±0.2 m 12.7±0.2 de 10.3±0.2 lm 12.4±0.2 fg 10.4±0.2 l 12.5±0.2 efg 8.9±0.2 o 10.9±0.1 ij 8.3±0.2 pq 10.9±1.8 16.72品Cultivar种Z01 Z02 Z03 Z04 Z05 Z06 Z07 Z08 Z09 Z10 Z11 Z12 Z13 Z14 Z15 Z16 Z17 Z18 Z19 Z20 Z21 Z22 Z23 Z24 Z25 Z26 Z27 Z28 Z29 Z30 Z31 Z32 Z33值均Average CV/%i
各品种(系)柑橘果实均含有柠檬酸、苹果酸、酒石酸、草酸和莽草酸。除春香外,柠檬酸含量最高,其次为苹果酸和酒石酸,而草酸(0.036~0.093 mg·g-1)和莽草酸(0.013~0.091 mg·g-1)含量极低未列入表中。柠檬酸的含量范围为2.75~36.59 mg·g-1,变异系数为56.50%,其中莱檬的柠檬酸含量最高,显著高于其他品种(系)(p<0.05),是最低(春香)的13.3倍。苹果酸的均值为1.06 mg·g-1,其中春香最高为3.82 mg·g-1,显著高于其他品种(系)(p<0.05),鸡尾葡萄柚最低为0.19 mg·g-1。酒石酸的均值为0.67 mg·g-1,变异系数为27.45%,刘本橙最高为1.07 mg·g-1,夏橙最低为0.26 mg·g-1。总酸含量的变异系数为45.62%,变化范围为6.36~37.93 mg·g-1,莱檬(最高)含量为最低(鸡尾葡萄柚)的6.0倍。可滴定酸含量均值为1.03 g·100 mL-1,莱檬最高为3.58 g·100 mL-1。TSS/TA 最高和最低分别为早橘(25.7)和莱檬(2.3),而糖酸比最高和最低分别为鸡尾葡萄柚(21.95)和来檬(1.16)。有机酸组分占总酸含量的比值见图1-B,其中草酸和莽草酸含量极低,未列入图中。除春香(37.89%)外,柠檬酸的比值为63.21%~96.70%,前三的依次为夏橙、高橙和莱檬,而春香的苹果酸占比高达52.63%,为最高。
2.1.3 果皮活性物质分析 由表4可知,各品种(系)果实中总黄酮和总酚含量存在差异,总黄酮含量均值为35.76 mg·g-1,其中宽皮柑橘类和大多杂柑类总黄酮含量均高于均值,甜橙类均低于均值。说明宽皮柑橘类和杂柑类总黄酮含量普遍较高。总黄酮含量为21.71~65.30 mg·g-1,变异系数28.29%,最高为青瓯柑65.30 mg·g-1,次高为茶枝柑56.30 mg·g-1,最低为鸡尾葡萄柚21.71 mg·g-1,最高是最低的3.0 倍。总酚含量均值为27.22 mg·g-1,大多宽皮柑橘类和杂柑类总酚含量高于均值,而甜橙类大多低于均值,说明宽皮柑橘类和杂柑类总酚含量相对较高,而甜橙类含量较低。总酚含量为15.43~41.07 mg·g-1,其中排在前三的依次为清峰(41.07 mg·g-1)、青瓯柑(36.30 mg·g-1)和茶枝柑(35.93 mg·g-1),最高为最低(春香)的2.7倍。
表4 不同柑橘品种(系)总黄酮和总酚含量
Table 4 The contents of total flavonoids and phenolics in citrus of different varieties(strains)
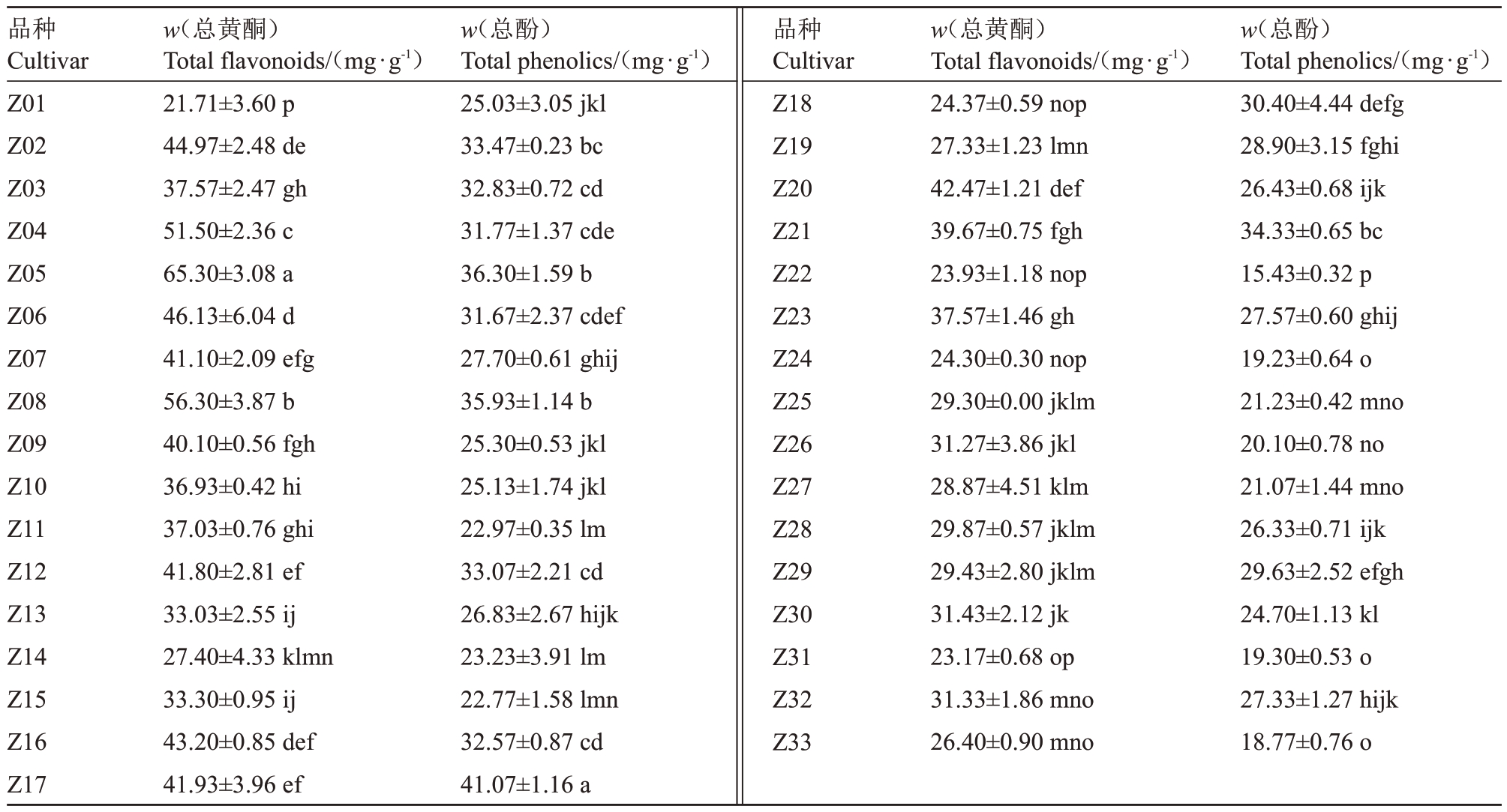
品种Cultivar Z01 Z02 Z03 Z04 Z05 Z06 Z07 Z08 Z09 Z10 Z11 Z12 Z13 Z14 Z15 Z16 Z17 w(总黄酮)Total flavonoids/(mg·g-1)21.71±3.60 p 44.97±2.48 de 37.57±2.47 gh 51.50±2.36 c 65.30±3.08 a 46.13±6.04 d 41.10±2.09 efg 56.30±3.87 b 40.10±0.56 fgh 36.93±0.42 hi 37.03±0.76 ghi 41.80±2.81 ef 33.03±2.55 ij 27.40±4.33 klmn 33.30±0.95 ij 43.20±0.85 def 41.93±3.96 ef w(总酚)Total phenolics/(mg·g-1)25.03±3.05 jkl 33.47±0.23 bc 32.83±0.72 cd 31.77±1.37 cde 36.30±1.59 b 31.67±2.37 cdef 27.70±0.61 ghij 35.93±1.14 b 25.30±0.53 jkl 25.13±1.74 jkl 22.97±0.35 lm 33.07±2.21 cd 26.83±2.67 hijk 23.23±3.91 lm 22.77±1.58 lmn 32.57±0.87 cd 41.07±1.16 a品种Cultivar Z18 Z19 Z20 Z21 Z22 Z23 Z24 Z25 Z26 Z27 Z28 Z29 Z30 Z31 Z32 Z33 w(总黄酮)Total flavonoids/(mg·g-1)24.37±0.59 nop 27.33±1.23 lmn 42.47±1.21 def 39.67±0.75 fgh 23.93±1.18 nop 37.57±1.46 gh 24.30±0.30 nop 29.30±0.00 jklm 31.27±3.86 jkl 28.87±4.51 klm 29.87±0.57 jklm 29.43±2.80 jklm 31.43±2.12 jk 23.17±0.68 op 31.33±1.86 mno 26.40±0.90 mno w(总酚)Total phenolics/(mg·g-1)30.40±4.44 defg 28.90±3.15 fghi 26.43±0.68 ijk 34.33±0.65 bc 15.43±0.32 p 27.57±0.60 ghij 19.23±0.64 o 21.23±0.42 mno 20.10±0.78 no 21.07±1.44 mno 26.33±0.71 ijk 29.63±2.52 efgh 24.70±1.13 kl 19.30±0.53 o 27.33±1.27 hijk 18.77±0.76 o
2.1.4 体外抗氧化能力 酚类物质因含酚羟基而可清除自由基[25]。由表5可知,不同品种(系)果皮提取物的3种体外抗氧化能力(清除ABTS+自由基能力、FRAP还原能力、清除DPPH自由基能力)存在明显差异。清除ABTS+自由基能力均值为94.13 μmol·g-1,其中清峰最高为159.12 μmol·g-1,次高火焰葡萄柚为149.37 μmol·g-1。甜橙类除夏橙和摩洛血橙外,清除ABTS+自由基能力均低于均值,而宽皮柑橘类除青岛44、默科特和早橘外,均高于均值。DPPH自由基清除能力均值为5.96 mg·g-1,宽皮柑橘类和杂柑类大多高于均值,而甜橙类均低于均值。DPPH自由基清除能力前三的依次为椪柑、高橙和青瓯柑,分别为8.72 mg·g-1、8.54 mg·g-1和8.35 mg·g-1,三者间差异不显著(p>0.05),最低为春香3.03 mg·g- 1。FRAP还原能力的变化范围为99.66~406.24 μmol·g-1,均值为222.64 μmol·g-1,宽皮柑橘类除默科特、槾橘和早橘外,FRAP还原能力均高于均值,而甜橙类均低于均值,说明宽皮柑橘类普遍较高。媛小春FRAP 还原能力为最高,是最低火焰葡萄柚的4.1倍。综上表明,宽皮柑橘类3 种抗氧化能力普遍较高。此外,3 种不同抗氧化能力测定方法评价同一品种果皮提取物的抗氧化能力存在一定的差异,因此利用综合评价法得到抗氧化综合评价值。果皮抗氧化综合评价值的变化范围为0.09~2.32,排在前三的依次为清峰、青瓯柑和媛小春。
表5 不同柑橘品种(系)果实抗氧化能力
Table 5 Antioxidant capacities in different varieties(strains)of citrus
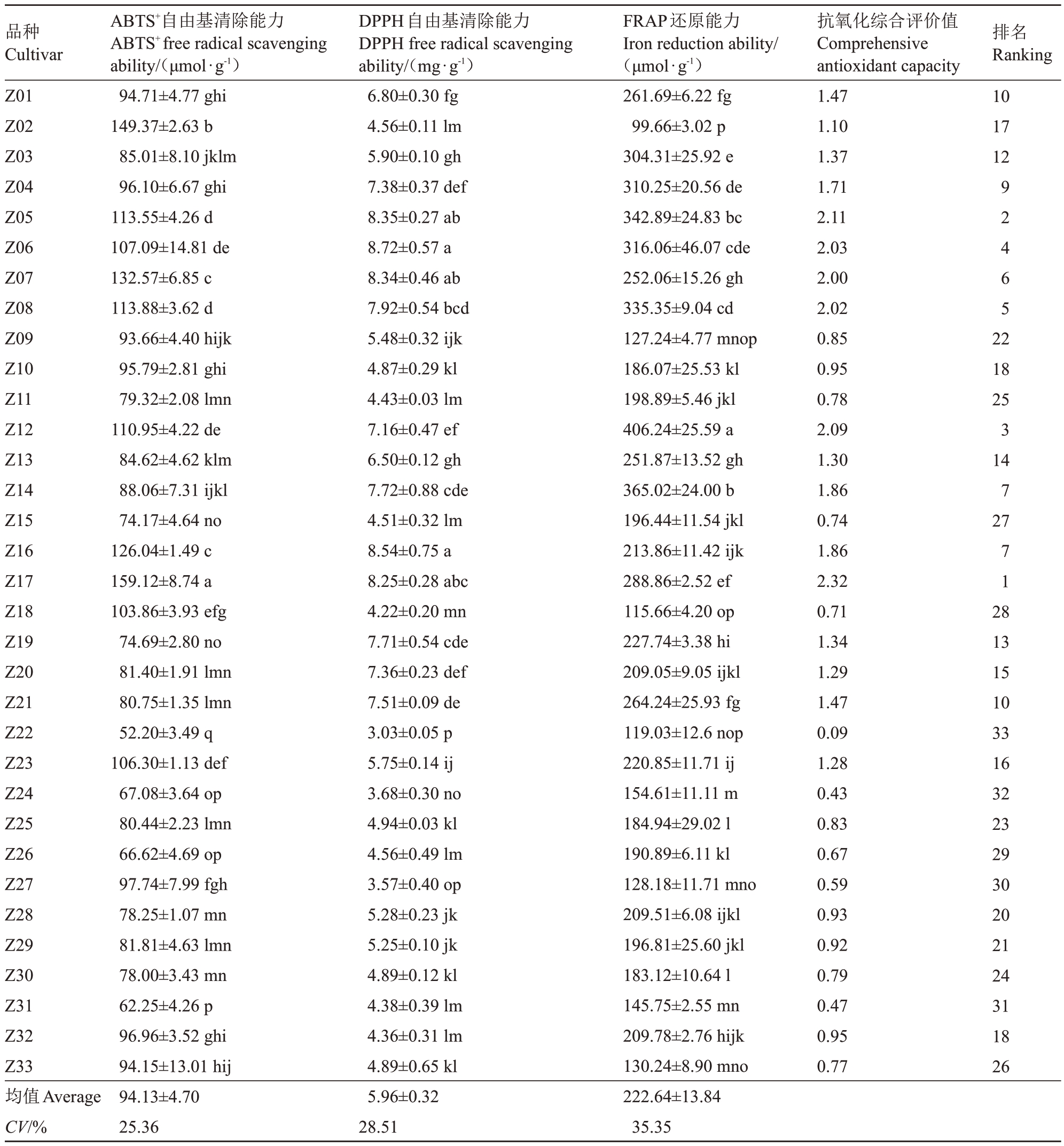
品种Cultivar Z01 Z02 Z03 Z04 Z05 Z06 Z07 Z08 Z09 Z10 Z11 Z12 Z13 Z14 Z15 Z16 Z17 Z18 Z19 Z20 Z21 Z22 Z23 Z24 Z25 Z26 Z27 Z28 Z29 Z30 Z31 Z32 Z33均值Average CV/%ABTS+自由基清除能力ABTS+free radical scavenging ability/(μmol·g-1)94.71±4.77 ghi 149.37±2.63 b 85.01±8.10 jklm 96.10±6.67 ghi 113.55±4.26 d 107.09±14.81 de 132.57±6.85 c 113.88±3.62 d 93.66±4.40 hijk 95.79±2.81 ghi 79.32±2.08 lmn 110.95±4.22 de 84.62±4.62 klm 88.06±7.31 ijkl 74.17±4.64 no 126.04±1.49 c 159.12±8.74 a 103.86±3.93 efg 74.69±2.80 no 81.40±1.91 lmn 80.75±1.35 lmn 52.20±3.49 q 106.30±1.13 def 67.08±3.64 op 80.44±2.23 lmn 66.62±4.69 op 97.74±7.99 fgh 78.25±1.07 mn 81.81±4.63 lmn 78.00±3.43 mn 62.25±4.26 p 96.96±3.52 ghi 94.15±13.01 hij 94.13±4.70 25.36 DPPH自由基清除能力DPPH free radical scavenging ability/(mg·g-1)6.80±0.30 fg 4.56±0.11 lm 5.90±0.10 gh 7.38±0.37 def 8.35±0.27 ab 8.72±0.57 a 8.34±0.46 ab 7.92±0.54 bcd 5.48±0.32 ijk 4.87±0.29 kl 4.43±0.03 lm 7.16±0.47 ef 6.50±0.12 gh 7.72±0.88 cde 4.51±0.32 lm 8.54±0.75 a 8.25±0.28 abc 4.22±0.20 mn 7.71±0.54 cde 7.36±0.23 def 7.51±0.09 de 3.03±0.05 p 5.75±0.14 ij 3.68±0.30 no 4.94±0.03 kl 4.56±0.49 lm 3.57±0.40 op 5.28±0.23 jk 5.25±0.10 jk 4.89±0.12 kl 4.38±0.39 lm 4.36±0.31 lm 4.89±0.65 kl 5.96±0.32 28.51 FRAP还原能力Iron reduction ability/(μmol·g-1)261.69±6.22 fg 99.66±3.02 p 304.31±25.92 e 310.25±20.56 de 342.89±24.83 bc 316.06±46.07 cde 252.06±15.26 gh 335.35±9.04 cd 127.24±4.77 mnop 186.07±25.53 kl 198.89±5.46 jkl 406.24±25.59 a 251.87±13.52 gh 365.02±24.00 b 196.44±11.54 jkl 213.86±11.42 ijk 288.86±2.52 ef 115.66±4.20 op 227.74±3.38 hi 209.05±9.05 ijkl 264.24±25.93 fg 119.03±12.6 nop 220.85±11.71 ij 154.61±11.11 m 184.94±29.02 l 190.89±6.11 kl 128.18±11.71 mno 209.51±6.08 ijkl 196.81±25.60 jkl 183.12±10.64 l 145.75±2.55 mn 209.78±2.76 hijk 130.24±8.90 mno 222.64±13.84 35.35抗氧化综合评价值Comprehensive antioxidant capacity 1.47 1.10 1.37 1.71 2.11 2.03 2.00 2.02 0.85 0.95 0.78 2.09 1.30 1.86 0.74 1.86 2.32 0.71 1.34 1.29 1.47 0.09 1.28 0.43 0.83 0.67 0.59 0.93 0.92 0.79 0.47 0.95 0.77排名Ranking 10 17 12 92465 22 18 25 3 14 7 27 71 28 13 15 10 33 16 32 23 29 30 20 21 24 31 18 26
2.2 相关性分析
2.2.1 不同柑橘品种(系)品质指标的相关性分析由表6可知,柑橘果实品质指标之间存在相关性,其中总酸含量与柠檬酸含量的相关系数最高为0.993。TSS含量与蔗糖、果糖、葡萄糖、总糖含量及糖酸比呈极显著正相关(p<0.01)。TA含量与柠檬酸和总酸含量呈极显著正相关(p<0.01),相关系数分别为0.986和0.985;而TA含量与TSS/TA、蔗糖含量和糖酸比呈极显著负相关(p<0.01),相关系数分别为-0.780、-0.576和-0.640;维生素C与TSS/TA、苹果酸含量和糖酸比呈极显著负相关(p<0.01),而与果形指数和果皮厚呈极显著正相关(p<0.01)。总黄酮和总酚含量均与纵径和果形指数呈极显著负相关(p<0.01),而两者间也呈极显著正相关(p<0.01),相关系数为0.690。由此说明,各指标之间存在不同程度的相关性,即20项品质指标之间的信息存在重叠。
表6 柑橘果实品质相关性分析
Table 6 Correlation analysis of fruit quality of citrus

注:* 表示在0.05 水平下显著相关,** 表示在0.01 水平下极显著相关。下同。Note: *. Indicate significant correlation a
总Total phenolicscontent量含酚1酮黄量总含Total flavonoidscontent糖Sugar/Acid 10.690**比酸1-0.104-0.051酸量总含Total acidcontent 1-0.708**-0.066-0.127石量Tartaric acidcontent酸酒含1-0.282**0.033 0.018 0.110酸果量苹含Malic acidcontent 10.188-0.337**0.230*-0.012-0.290**酸檬量柠含Citric acidcontent 1-0.444**-0.320**0.993**-0.698**-0.060-0.088糖量Total sugarcontent总含1-0.211*-0.123 0.117-0.234*0.578**-0.042 0.042果含糖量Fructose content 10.760**0.269**-0.402**0.072 0.238*0.079-0.172-0.073糖10.937**0.759**0.243*0.074 0.208*0.081 0.066葡含萄量Glucose content-0.429**-0.115 10.182 0.175 0.765**0.235*0.105 0.812**0.085 0.076糖量Sucrose content蔗含-0.591**-0.593**果Peel thick-ness皮厚1-0.283**-0.253*-0.264**-0.355**-0.005-0.031-0.080-0.014-0.252*-0.259**-0.080果量单质Single fruitmass 10.560**-0.045-0.130-0.168-0.129 0.036-0.216*-0.531**-0.006 0.158-0.382**-0.117形数果指Fruit shapeindex 0.081 0.391**0.072 0.092 0.427**径Horizon-taldiameter 1-0.033-0.499**-0.066-0.007-0.345**-0.270**-0.259**-0.313**横0.870**0.670**0.074径Verticaldiameter 1-0.304**-0.028-0.246*-0.294**-0.199*-0.069-0.191-0.483**-0.114-0.283**-0.037纵10.712**0.446**0.788**0.692**-0.359**-0.275**-0.279**-0.417**0.181-0.099-0.362**0.167-0.090-0.466**-0.273**素量Vccontent生维C含10.099-0.093 0.269**-0.090 0.272**-0.154 0.215*0.287**0.070 0.086-0.308**0.216*0.060-0.285**-0.102 0.018比TSS/TA酸固1-0.388**-0.248*-0.069-0.308**-0.109-0.176 0.691**-0.145-0.199*0.331**-0.798**0.552**0.268**-0.766**0.781**0.003-0.049定量TAcontent滴含可酸1-0.780**0.056 0.230*-0.058 0.440**0.068-0.024-0.576**0.212*0.245*-0.220*0.986**-0.380**-0.359**0.985**-0.640**-0.106-0.137性物溶形可固含量TSScontent 10.024 0.163 0.210*-0.404**-0.306**-0.180-0.259**-0.344**0.535**0.805**0.758**0.863**0.025-0.155 0.163 0.016 0.275**-0.105 0.008量标Quality indices含物形含可TSS content 量量固酸TSS/TA C含量含量含含含Sugar/Acid量Total flavonoidscontent量量TA content Vc content纵Vertical diameter径Horizontal diameter数Fruit shape index单Single fruit mass果Peel thickness量Sucrose content量Glucose content果Fructose content量Totalsugarcontent量Citric acid content量Malic acid content酒Tartaric acid content量Total acid content含指性定比素指质厚含糖含含酸酸酸含比酮含质溶滴酸生径形果皮糖萄糖糖檬果石酸酸黄酚品可固维横果蔗葡总柠苹总糖总总Total phenolics content
2.2.2 果皮抗氧化性能与活性物质相关性分析 由表7可知,果皮总黄酮、总酚含量均与ABTS+、DPPH及FRAP 呈极显著正相关(p<0.01)。其中总酚含量与ABTS+、DPPH 和FRAP 的相关系数分别为0.669、0.671 和0.556,总黄酮含量与ABTS+、DPPH和FRAP 的相关系数分别为0.550、0.597 和0.514。说明酚类物质对抗氧化能力起非常重要的作用,其中总酚含量与抗氧化能力的相关性极显著。果皮抗氧化综合评价值与总黄酮和总酚含量的相关系数分别为0.671 和0.774,这进一步证实了以上结论。此外,3 种体外抗氧化评价方法两两之间均呈极显著正相关(p<0.01),说明各品种(系)柑橘果皮提取物清除DPPH自由基和ABTS+自由基以及FRAP 还原铁离子的效果基本一致。
表7 柑橘果皮抗氧化能力与总黄酮、总酚含量相关性分析
Table 7 Correlation analysis of antioxidant capacities and contents of total flavonoids and phenolics in citrus peel
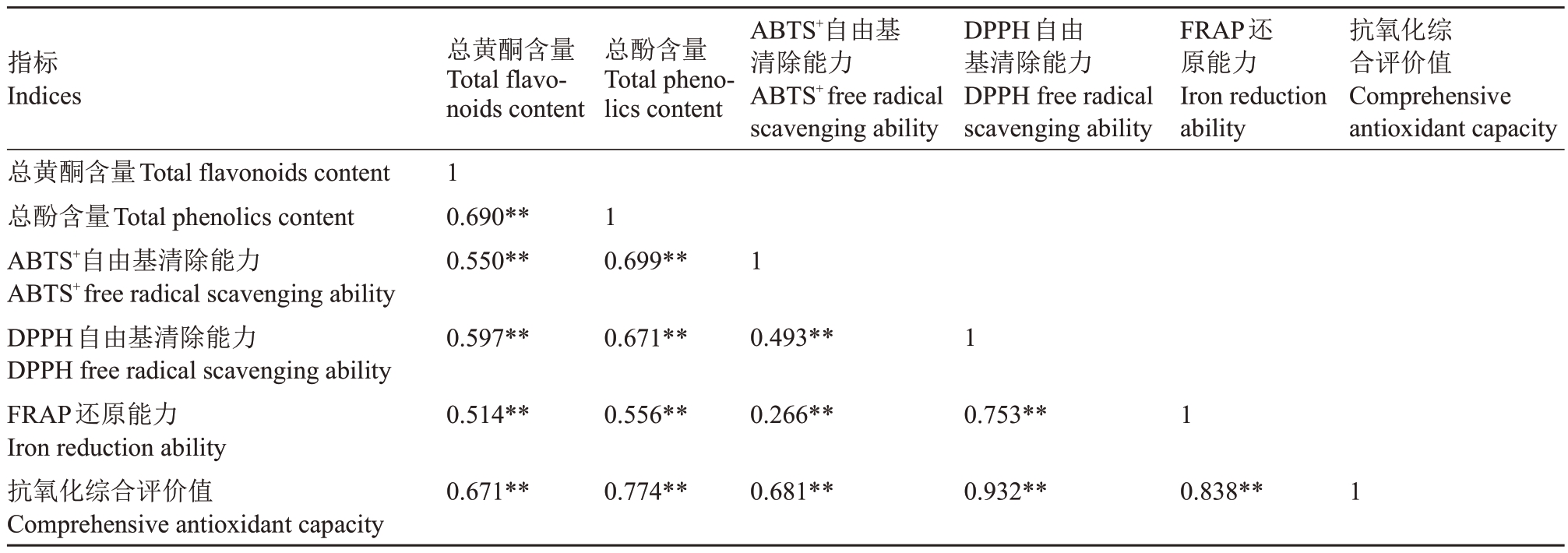
指标Indices总黄酮含量Total flavonoids content总酚含量Total phenolics content ABTS+自由基清除能力ABTS+free radical scavenging ability DPPH自由基清除能力DPPH free radical scavenging ability FRAP还原能力Iron reduction ability抗氧化综合评价值Comprehensive antioxidant capacity总黄酮含量Total flavonoids content 1 0.690**0.550**0.597**0.514**0.671**总酚含量Total phenolics content 1 0.699**0.671**0.556**0.774**ABTS+自由基清除能力ABTS+free radical scavenging ability 1 0.493**0.266**0.681**DPPH自由基清除能力DPPH free radical scavenging ability 1 0.753**0.932**FRAP还原能力Iron reduction ability 1 0.838**抗氧化综合评价值Comprehensive antioxidant capacity 1
2.3 不同柑橘品种(系)果实品质的主成分分析
由表8可知,PCA分析得到5个主成分特征值大于1,累计方差贡献率达85.120%,说明这5个主成分能反映20个指标的绝大部分信息。PC1方差贡献率为29.518%,贡献较大的为TSS/TA、蔗糖、糖酸比,其中以蔗糖的贡献最大,载荷值0.852,其次是TSS/TA,载荷值为0.842,与果实口感相关,PC1可命名为口感因子。而PC2方差贡献率为22.588%,贡献较大的为TSS、葡萄糖和果糖,与PC2 呈正载荷,果糖正载荷值最大为0.839,PC2主要反映果实甜味,可命名为甜味因子;PC3 方差贡献率为14.905%,贡献较大的为单果质量,载荷值为0.723,可命名为质量因子。而PC4 贡献最大的为果形指数,方差贡献率为10.034%,主要反映果实的外观形状,可命名为果形因子;第PC5方差贡献率为8.075%,贡献最大的为维生素C,载荷值为0.789,主要与果实的抗氧化品质相关,可命名为抗氧化因子。PC1和PC2累计贡献率达52.106%,反映了柑橘果实品质的主要信息,因此,PC1和PC2的代表性指标对果实品质的影响起主要作用。
表8 主成分载荷矩阵、特征值及贡献率
Table 8 Factor loading,coefficient eigenvalues and variance contribution rates of principal components

品质指标Quality indices可溶性固形物含量TSS content可滴定酸含量TA content固酸比TSS/TA维生素C含量Vc content纵径Vertical diameter横径Horizontal diameter果形指数Fruit shape index单果质量Single fruit mass果皮厚Peel thickness蔗糖含量Sucrose content葡萄糖含量Glucose content果糖含量Fructose content总糖含量Totalsugarcontent柠檬酸含量Citric acid content苹果酸含量Malic acid content酒石酸含量Tartaric acid content总酸含量Total acid content糖酸比Sugar/Acid总黄酮含量Total flavonoids content总酚含量Total phenolics content特征值Eigenvalues方差贡献率Rate of variance/%累计贡献率Rate of cumulative variances/%主成分1 PC1 0.420-0.815 0.842-0.194-0.570-0.248-0.512-0.310-0.391 0.852 0.141 0.110 0.633-0.817 0.361 0.368-0.807 0.787 0.182 0.153 5.904 29.518 29.518主成分2 PC2 0.732 0.451-0.339 0.275-0.527-0.605 0.074-0.501-0.516 0.042 0.822 0.839 0.580 0.486-0.406 0.159 0.470-0.190 0.097 0.096 4.518 22.588 52.106主成分3 PC3 0.374 0.020 0.010 0.113 0.500 0.639-0.150 0.723 0.357 0.300 0.433 0.425 0.479-0.003-0.337-0.383-0.057 0.378-0.575-0.271 2.981 14.905 67.011主成分4 PC4 0.081 0.001 0.196 0.147 0.167-0.332 0.620-0.181-0.003-0.071-0.027 0.081-0.024-0.057 0.480 0.353 0.013 0.089-0.645-0.768 2.007 10.034 77.045主成分5 PC5 0.021-0.301-0.153 0.789 0.094 0.027 0.085-0.072 0.473-0.138 0.084 0.080-0.035-0.241-0.247 0.532-0.270-0.198 0.020 0.289 1.615 8.075 85.120
2.4 不同柑橘品种(系)品质综合评价
PCA 分析中的5个主成分反映了柑橘品质指标原数据的大部分信息,因此,可用这5个主因子进行柑橘品质综合评价。PCA 分析得到的F1、F2、F3、F4、F5这5个主成分来代替20个指标对柑橘品质进行分析,根据各主成分模型获得得分,并以相应的相对方差贡献率为权重建立综合评价模型为F=0.347F1+0.265F2+0.175F3+0.118F4+0.095F5,获得各品种综合得分及排名,得分高低反映果实综合品质的高低。由表9 可知,综合得分排名前三的分别为兴津60、媛小春、明日见,表明这些品种果实风味相对较好,维生素C含量丰富。
表9 不同柑橘品种(系)主成分得分及综合得分
Table 9 Principal component score and comprehensive score of different varieties(strains)of citrus
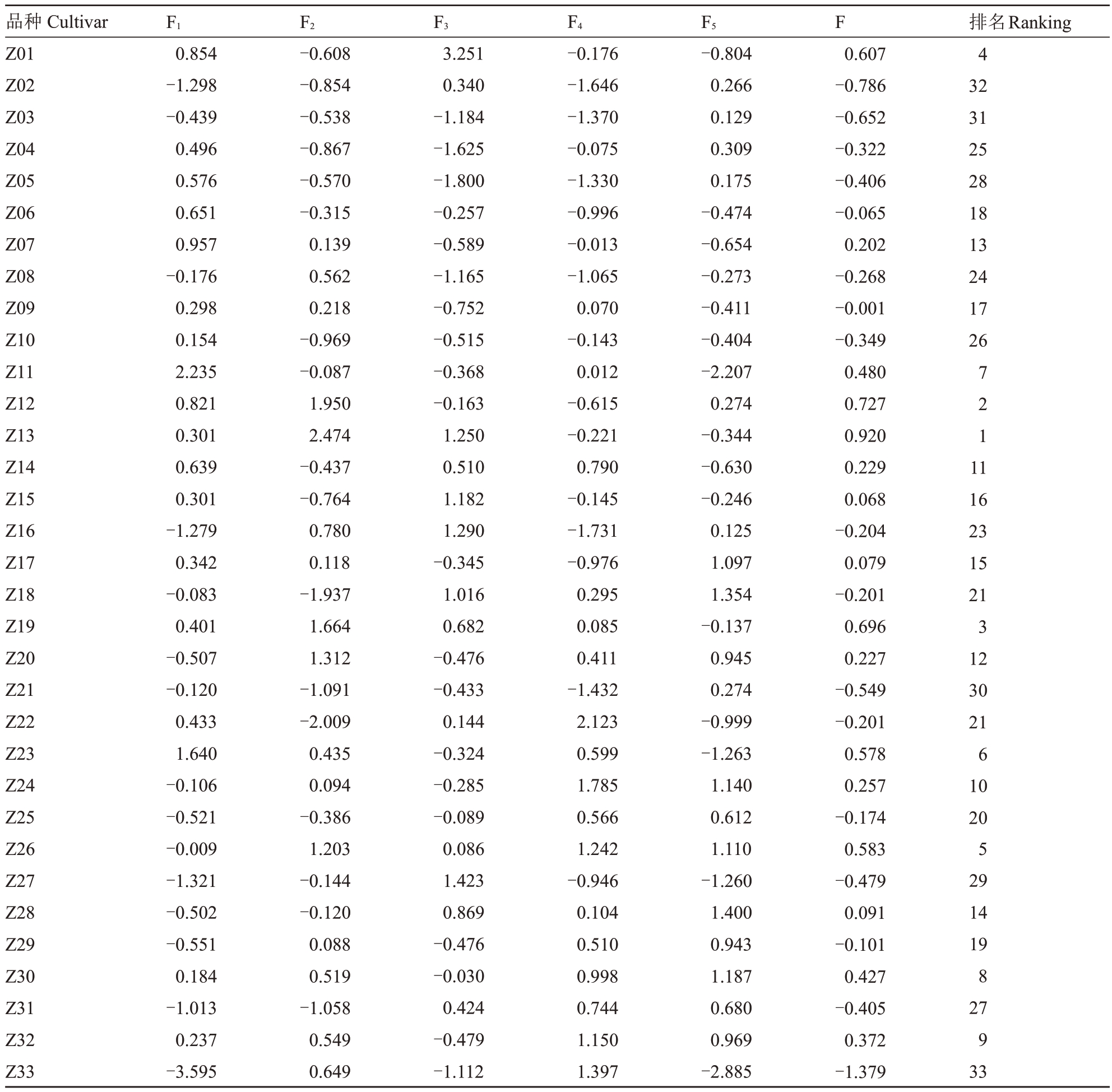
品种Cultivar Z01 Z02 Z03 Z04 Z05 Z06 Z07 Z08 Z09 Z10 Z11 Z12 Z13 Z14 Z15 Z16 Z17 Z18 Z19 Z20 Z21 Z22 Z23 Z24 Z25 Z26 Z27 Z28 Z29 Z30 Z31 Z32 Z33 F1 0.854-1.298-0.439 0.496 0.576 0.651 0.957-0.176 0.298 0.154 2.235 0.821 0.301 0.639 0.301-1.279 0.342-0.083 0.401-0.507-0.120 0.433 1.640-0.106-0.521-0.009-1.321-0.502-0.551 0.184-1.013 0.237-3.595 F2-0.608-0.854-0.538-0.867-0.570-0.315 0.139 0.562 0.218-0.969-0.087 1.950 2.474-0.437-0.764 0.780 0.118-1.937 1.664 1.312-1.091-2.009 0.435 0.094-0.386 1.203-0.144-0.120 0.088 0.519-1.058 0.549 0.649 F3 3.251 0.340-1.184-1.625-1.800-0.257-0.589-1.165-0.752-0.515-0.368-0.163 1.250 0.510 1.182 1.290-0.345 1.016 0.682-0.476-0.433 0.144-0.324-0.285-0.089 0.086 1.423 0.869-0.476-0.030 0.424-0.479-1.112 F4-0.176-1.646-1.370-0.075-1.330-0.996-0.013-1.065 0.070-0.143 0.012-0.615-0.221 0.790-0.145-1.731-0.976 0.295 0.085 0.411-1.432 2.123 0.599 1.785 0.566 1.242-0.946 0.104 0.510 0.998 0.744 1.150 1.397 F5-0.804 0.266 0.129 0.309 0.175-0.474-0.654-0.273-0.411-0.404-2.207 0.274-0.344-0.630-0.246 0.125 1.097 1.354-0.137 0.945 0.274-0.999-1.263 1.140 0.612 1.110-1.260 1.400 0.943 1.187 0.680 0.969-2.885 F 0.607-0.786-0.652-0.322-0.406-0.065 0.202-0.268-0.001-0.349 0.480 0.727 0.920 0.229 0.068-0.204 0.079-0.201 0.696 0.227-0.549-0.201 0.578 0.257-0.174 0.583-0.479 0.091-0.101 0.427-0.405 0.372-1.379排名Ranking 4 32 31 25 28 18 13 24 17 26 7211 1 16 23 15 21 3 12 30 21 6 10 20 5 29 14 19 8 27 9 33
2.5 聚类分析
不同品种(系)柑橘20 个品质指标的热图分析结果见图2,将33个品种(系)划分为6类。第1类是莱檬,得分最低,果实TA、柠檬酸、总酸含量高且果形指数大,说明莱檬与其他品种(系)差异显著。第2类为春香和胡柚,果实TSS/TA较高,纵径较大,且果皮相对较厚,得分较低。第3类为沃柑和早橘,蔗糖、总糖、糖酸比及苹果酸含量相对较高,得分相对较高。第4类为明日见,兴津60和媛小春,综合得分排名前三,果实TSS、葡萄糖、果糖和总糖含量较高,这几个品种均属于杂柑类,亲本间存在一定的关联。第6类为鸡尾葡萄柚,果实蔗糖、总糖含量及糖酸比较高,纵、横径及单果质量较大,得分排名第四。其余24 个品种(系)柑橘均为第5 类,说明杂柑类、宽皮柑橘类及甜橙类间关联性较强。结合PCA分析可知,第4类样本的果实品质最佳,第3类和第6 类的果实品质较好。由此说明明日见,兴津60 和媛小春果实品质相似,品质佳。沃柑和早橘的品质相近,品质较佳。

图2 不同柑橘品种(系)聚类分析热图
Fig.2 Cluster analysis heat maps of different varieties(strains)of citrus
3 讨 论
随着人们对健康的日益关注,富含生物活性物质的柑橘品种将越来越受消费者青睐。本研究结果表明,甜橙类果实中维生素C 含量高于杂柑,这与李勋兰等[13]、朱丽莎等[10]、洪林等[11]的研究结果一致。柑橘果皮富含酚类物质,且不同品种(系)间含量存在差异,总黄酮和总酚含量变化范围分别为21.71~65.30 mg·g-1和15.43~41.07 mg·g-1。宽皮柑橘类果实总黄酮和总酚含量均普遍高于甜橙类和莱檬,这与左龙亚等[26]和郑洁等[27]的研究结果基本一致。甜橙类品种间果实总黄酮、总酚及维生素C含量差异较宽皮柑橘和杂柑品种间的含量差异小,这可能由于样本中的甜橙类品种亲本具有相似性,而杂柑类亲本来源相对较复杂。青瓯柑和茶枝柑果皮的总黄酮和总酚含量明显高于其他品种(系),可作为功能性成分开发的原料。近年来,柑橘果实酚类物质的抗氧化活性是研究热点。高炜等[28]和李娟等[29]研究发现柑橘果皮对清除DPPH自由基、ABTS+自由基以及还原铁离子均有一定的促进作用,本研究结果与之一致。但3种抗氧化能力检测方法评价同一品种果实的抗氧化活性存在一定的差异,这可能是由于抗氧化机制不同造成的。此外,结果还表明,柑橘果实抗氧化活性与酚类物质含量呈正相关,与前人研究结果一致[30],这可能与多酚是起抗氧化作用的主要物质有关。
糖、酸是柑橘果实风味物质的主要成分,其含量和构成比例决定果实甜、酸味[31-32]。本研究通过对33个柑橘品种(系)的糖、酸组分及含量进行分析测定,结果表明,柑橘果实中可溶性糖主要为蔗糖、果糖和葡萄糖。莱檬、明日见和兴津60中果糖占总糖含量比值为最高,其余品种(系)果实中蔗糖比值最高,这与前人研究结果基本一致[33]。此外,本研究还发现宽皮柑橘类以积累蔗糖为主,甜橙类、7个杂柑及火焰葡萄柚以己糖(葡萄糖和果糖)和蔗糖共同积累,而莱檬以积累己糖为主,该结果与孙达[9]、林媚等[34]、吴孔杰等[35]、Echeverria等[36]的基本一致。柑橘果实中含有柠檬酸、苹果酸、酒石酸、草酸等多种组分,但大多数品种以其中的1~2种为主[9,37]。本研究中春香的苹果酸含量很高(占总酸含量的比值为52.63%),其余品种(系)均以柠檬酸和苹果酸为主,其中柠檬酸比值为63.21%~96.70%,这与前期研究结果基本一致[9,34,38]。
本研究中对20 个柑橘果实品质指标进行PCA分析,得到5个主成分,累计贡献率达85.120%,蔗糖含量、果糖含量、单果质量、果形指数和维生素C含量是综合评价果实品质的主要指标。建立综合评价模型为F=0.347F1+0.265F2+0.175F3+0.118F4+0.095F5,得到各品种(系)的综合得分及排名,得分越高说明果实综合品质越好。兴津60、媛小春、明日见、鸡尾葡萄柚、439、沃柑、早橘排名前7,果实品质优良,可作为品种选育及推广种植的材料。总体上,杂柑综合得分较甜橙和宽皮柑橘高,说明杂柑果实品质更好,该结果与李勋兰等[12]的不一致,可能是由供试材料及综合评价中所选用的果实品质指标不同所造成的。通过热图聚类分析将33个柑橘品种(系)分为6类,其中果实品质最佳的是第4类,由明日见、兴津60和媛小春组成,这3个品种有相同的亲本(清见);较好的是第6类的鸡尾葡萄柚;而相对较好的为沃柑和早橘组成的第3类。从热图聚类结果可看出,多数样本亲缘关系相近的品种聚为一类,说明遗传因素在影响柑橘果实品质的因素中起决定性作用。第5类的青瓯柑和茶枝柑得分排名靠后,品质较差,而果皮生物活性物质含量很高,可能由于本研究选取的大多与鲜食相关的品质指标还不够全面,后续应结合种植及消费需求,筛选出如功能因子、加工因子、特征因子等品质评价指标,建立更全面系统的评价体系。
4 结 论
通过对33个柑橘品种(系)20个品质指标进行检测分析,结果表明,品种间果实品质存在差异,而品质评价指标间有交叉性,蔗糖含量、果糖含量、单果质量、果形指数和维生素C 含量是综合评价果实品质的主要指标。甜橙类果实维生素C含量较高,而宽皮柑橘类和杂柑类果皮酚类物质含量较高,抗氧化性较强,其中综合抗氧化评价值排名前3的依次为清峰、青瓯柑和媛小春。热图聚类分析与PCA分析结果基本一致,两者结合可更系统、科学地评价不同品种柑橘果实品质的优劣。本研究结果可为柑橘品种结构调整、新品种选育及功能性成分的开发利用提供理论依据。
[1] 邓秀新.世界柑橘品种改良的进展[J].园艺学报,2005,32(6):1140-1146.DENG Xiuxin.Advances in world wide citrus breeding[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2005,32(6):1140-1146.
[2] CHEN X M,TAIT A R,KITTS D D. Flavonoid composition of orange peel and its association with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities[J].Food Chemistry,2017,218:15-21.
[3] 姚旭,郦萍,顾青.4 种甜橙皮黄酮类化合物体外抗氧化活性及降糖降脂功能研究[J].中国食品学报,2022,22(1):49-57.YAO Xu,LI Ping,GU Qing.Studies on antioxidant activity,hypoglycemic and lipid-lowering capacity of flavonoids in sweet orange peels in vitro[J].Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2022,22(1):49-57.
[4] SONG M Y,WU X,CHAROENSINPHON N,WANG M Q,ZHENG J K,GAO Z L,XU F,LI Z Z,LI F,ZHOU J Z,XIAO H. Dietary 5- demethylnobiletin inhibits cigarette carcinogen NNK induced lung tumorigenesis in mice[J]. Food & Function,2017,8(3):954-963.
[5] 单杨.我国柑橘工业现状及发展趋势[J].农业工程技术(农产品加工业),2014(4):13-17.SHAN Yang. Present situation and development trend of citrus industry in China[J].Agricultural Engineering Technology(Agricultural Products Processing Industry),2014(4):13-17.
[6] 伊华林,刘慧宇.我国柑橘品种分布特点及适地适栽品种选择探讨[J].中国果树,2022(1):1-7.YIN Hualin,LIU Huiyu.Distribution characteristics of citrus varieties and selection of varieties suitable for planting in China[J].China Fruits,2022(1):1-7.
[7] 黄振东,王鹏,徐建国,鹿连明,陈国庆,温明霞,林媚.浙东地区红美人杂柑果实品质与土壤和叶片养分的关系[J].果树学报,2020,37(1):88-97.HUANG Zhendong,WANG Peng,XU Jianguo,LU Lianming,CHEN Guoqing,WEN Mingxia,LIN Mei. Relationship between fruit quality and nutrients in soil and leaves of‘Hongmeiren’citrus hybrid cultivated in eastern Zhejiang province[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2020,37(1):88-97.
[8] 曾秀丽.不同生境下甜橙果实的质地研究[D].成都:四川农业大学,2007.ZENG Xiuli. Studies on the effects of habitats to sweet orange[Citrus sinesis(L.) Osbeck] fruit texture[D]. Chengdu:Sichuan Agriculture University,2007.
[9] 孙达.不同柑橘种质资源中可溶性糖和有机酸含量的评价[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2013.SUN Da. Soluble sugar and organic acid contents evalution of different citrus germplasm resources[D]. Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University,2013.
[10] 朱丽莎,董超,赵静,江东,王成秋,焦必宁.重庆主栽甜橙品种果实品质比较分析[J].中国南方果树,2018,47(5):128-135.ZHU Lisha,DONG Chao,ZHAO Jing,WANG Dong,WANG Chengqiu,JIAO Bining.Comparative analysis of fruit quality of main sweet orange varieties in Chongqing[J]. South China Fruits,2018,47(5):128-135.
[11] 洪林,李勋兰,杨蕾,王武,韩国辉,程昌凤,谭平.重庆5 个新引进晚熟杂柑品种品质表现初步评价[J]. 中国南方果树,2018,47(6):25-30.HONG Lin,LI Xunlan,YANG Lei,WANG Wu,HAN Guohui,CHENG Changfeng,TAN Ping.Preliminary evaluation of quality performance of five new introduced late-maturing mandarin cultivars in Chongqing[J].South China Fruits,2018,47(6):25-30.
[12] 李勋兰,洪林,王武,杨蕾,谭平.晚熟杂柑新品种果实品质综合评价[J].果树学报,2018,35(2):195-203.LI Xunlan,HONG Lin,WANG Wu,YANG Lei,TAN Ping.Comprehensive evaluation of fruit quality of new late-maturing mandarin cultivars[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2018,35(2):195-203.
[13] 李勋兰,洪林,杨蕾,王武,韩国辉,农江飞,谭平.11 个柑橘品种果实营养成分分析与品质综合评价[J].食品科学,2020,41(8):228-233.LI Xunlan,HONG Lin,YANG Lei,WANG Wu,HAN Guohui,NONG Jiangfei,TAN Ping.Analysis of nutritional components and comprehensive quality evaluation of citrus fruit from eleven varieties[J].Food Science,2020,41(8):228-233.
[14] 王贵一,孟嘉珺,许文静,陈昌琳,刘思琪,吕远平.不同品种芒果的营养成分及风味物质分析[J].食品工业科技,2022,43(1):71-79.WANG Guiyi,MENG Jiajun,XU Wenjing,CHEN Changlin,Liu Siqi,LÜ Yuanping.Analysis of nutritional components and flavor substances of different varieties of mangoes[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(1):71-79.
[15] 姜璐,包怡红,贾雨彤,赖章飞,徐福成.18 个品种蓝靛果营养成分分析及综合品质评价[J].农业工程学报,2022,38(7):326-335.JIANG Lu,BAO Yihong,JIA Yutong,LAI Zhangfei,XU Fucheng. Nutritional component analysis and comprehensive quality evaluation of 18 different varieties of Lonicera caerulea[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2022,38(7):326-335.
[16] 严鑫,吴巨友,贡鑫,焦玉茹,袁凯莉,鲁彬,王苗苗,陶书田,王然,张绍铃. 不同产地圆黄梨果实品质差异分析[J]. 果树学报,2021,38(12):2082-2090.YAN Xin,WU Juyou,GONG Xin,JIAO Yuru,YUAN Kaili,LU Bin,WANG Miaomiao,TAO Shutian,WANG Ran,ZHANG Shaoling. Analysis of fruit quality of Wonhwang pear from different regions[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2021,38(12):2082-2090.
[17] 付勋,张海彬,聂青玉,冯婷婷,刘丹,张艳,李翔.猕猴桃品质指标差异分析及GC-IMS 分析果汁中挥发性物质[J].食品科学,2022,43(10):247-254.FU Xun,ZHANG Haibin,NIE Qingyu,FENG Tingting,LIU Dan,ZHANG Yan,LI Xiang. Different varieties of kiwifruit:Analysis of differences in quality indexes and volatile components in juice by gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry[J].Food Science,2022,43(10):247-254.
[18] 许文静,陈昌琳,邓莎,刘怡君,吕远平.基于主成分分析和聚类分析的蓝莓品质综合评价[J].食品工业科技,2022,43(13):311-319.XU Wenjing,CHEN Changlin,DENG Sha,LIU Yijun,LÜ Yuanping. Comprehensive evaluation of blueberry quality based on principal component analysis and cluster analysis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(13):311-319.
[19] 吴澎,贾朝爽,范苏仪,孙玉刚.樱桃品种果实品质因子主成分分析及模糊综合评价[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(17):291-300.WU Peng,JIA Chaoshuang,FAN Suyi,SUN Yugang. Principal component analysis and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of fruit quality in cultivars of cherry[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2018,34(17):291-300.
[20] 陈妹姑,林兴娥,李新国,刘咲頔,高宏茂,明建鸿,戴敏洁,周兆禧.基于主成分分析和聚类分析的榴莲品质综合评价[J].食品工业科技,2023,44(7):278-286.CHEN Meigu,LIN Xing’e,LI Xinguo,LIU Xiaodi,GAO Hongmao,MING Jianhong,DAI Minjie,ZHOU Zhaoxi. Comprehensive evaluation of durian quality based on principal component analysis and cluster analysis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(7):278-286.
[21] 侯东颖,苏东涛,郝科星,张曼,张涛,侯富恩.基于主成分和聚类分析的无籽西瓜果实性状的综合评价[J].中国瓜菜,2022,35(5):37-41.HOU Dongying,SU Dongtao,HAO Kexing,ZHANG Man,ZHANG Tao,HOU Fuen. Comprehensive evaluation of fruit characters of seedless watermelon based on principal component and cluster analysis[J].China Cucurbits and Vegetables,2022,35(5):37-41.
[22] 郑丽静,聂继云,闫震,徐国锋,王昆,高源,叶孟亮.苹果可溶性糖组分及其含量特性的研究[J].园艺学报,2015,42(5):950-960.ZHENG Lijing,NIE Jiyun,YAN Zhen,XU Guofeng,WANG Kun,GAO Yuan,YE Mengliang. Studies on the characteristics of the composition and content of soluble sugars in apple fruit[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2015,42(5):950-960.
[23] 姚改芳,张绍铃,吴俊,曹玉芬,刘军,韩凯,杨志军.10 个不同系统梨品种的可溶性糖与有机酸组分含量分析[J].南京农业大学学报,2011,34(5):25-31.YAO Gaifang,ZANG Shaoling,WU Jun,CAO Yufen,LIU Jun,HAN Kai,YANG Zhijun.Analysis of components and contents of soluble sugars and organic acids in ten cultivars of pear by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University,2011,34(5):25-31.
[24] 李楠,杨欣,孙元琳,周素梅.20 种花茶黄酮、总酚及抗氧化活性分析[J].食品研究与开发,2021,42(18):34-39.LI Nan,YANG Xin,SUN Yuanlin,ZHOU Sumei. Flavones,total polyphenols and in vitro antioxidant activity in twenty kinds of herbal teas[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(18):34-39.
[25] ELENA G M,MORENO D A,CRISTINA G V. Comparison of‘Verna’lemon juice quality for new ingredients and food products[J].Scientia Horticulturae,2009,120:353-359.
[26] 左龙亚.柑橘亚属植物果皮多酚类物质提取及其抗氧化、抑菌活性检测[D].重庆:西南大学,2018.ZUO Longya. Polyphenols extraction and antioxidant,antifungal activities test of subgenus citrus[D]. Chongqing:Southwest University,2018.
[27] 郑洁,赵其阳,张耀海,焦必宁.超高效液相色谱法同时测定柑橘中主要酚酸和类黄酮物质[J]. 中国农业科学,2014,47(23):4706-4717.ZHENG Jie,ZHAO Qiyang,ZHANG Yaohai,JIAO Bining. Simultaneous determination of main flavonoids and phenolic acids in citrus fruit by ultra performance liquid chromatography[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2014,47(23):4706-4717.
[28] 高炜,刘剑波,朱明扬,朱冬香,李浪,丁胜华,单杨.4 种柠檬不同组织的酚类物质分布及其抗氧化特性[J].中国食品学报,2019,19(2):281-289.GAO Wei,LIU Jianbo,ZHU Mingyang,ZHU Dongxiang,LI Lang,DING Shenghua,SHAN Yang. Distribution of phenolics in different tissues of four kinds of lemon and their antioxidant activity[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2019,19(2):281-289.
[29] 李娟,牛泽宇,岳湘齐,谢璇,付鑫景,陆俊.不同产地甜橙果皮提取物抗氧化活性成分及能力研究[J].食品与机械,2019,35(9):156-162.LI Juan,NIU Zeyu,YUE Xiangqi,XIE Xuan,FU Xinjing,LU Jun. Study on antioxidant components and antioxidant activities of peels extracts from sweet orange in Hunan provice[J]. Food and Machinery,2019,35(9):156-162.
[30] ZHANG H,YANG Y F,ZHOU Z Q. Phenolic and flavonoid contents of mandarin (Citrus reticulate Blanco) fruit tissues and their antioxidant capacity as evaluated by DPPH and ABTS methods[J].Journal of Integrative Agriculture,2018,17(1):256-263.
[31] BALTAZARI A,MTUI H D,MWATAWALA M W,HOVE L M,MSOGOYA T,SAMWEL J,SUBRAMANIAN J. Effects of storage conditions,storage duration and post-harvest treatments on nutritional and sensory quality of orange[Citrus sinensis(L.)Osbeck] fruits[J]. International Journal of Fruit Science,2020,20(4):737-749.
[32] 沈胜男.伦晚和红肉脐橙果实发育过程中主要品质变化的研究[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2009.SHEN Shengnan. Study on the fruit quality changes during fruit development of Lane late and Cara cara navel orange[D]. Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University,2009.
[33] 杨阳,唐宁,李正国,黄涛江.5 个晚熟柑橘品种果实发育期品质变化研究[J].西南农业学报,2014,27(1):263-267.YANG Yang,TANG Ning,LI Zhengguo,HUANG Taojiang.Quality changes of five late- maturing citrus varieties during fruit development and maturity[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2014,27(1):263-267.
[34] 林媚,姚周麟,王天玉,徐阳,徐建国,张伟清.8 个杂交柑橘品种的糖酸组分含量及特征研究[J].果树学报,2021,38(2):202-211.LIN Mei,YAO Zhoulin,WANG Tianyu,XU Yang,XU Jianguo,ZHANG Weiqing. A study on the components and characteristics of sugars and acids in 8 hybrid citrus cultivars[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2021,38(2):202-211.
[35] 吴孔杰,胡承孝,谭启玲,孙学成,赵小虎,武松伟.柑橘果实糖积累特征及蔗糖转运机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报,2022,49(12):2543-2558.WU Kongjie,HU Chengxiao,TAN Qiling,SUN Xuecheng,ZHAO Xiaohu,WU Songwei. Research advanced on character of sugar accumulation and mechanism of sucrose transport in Citrus fruit[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2022,49(12):2543-2558.
[36] ECHEVERRIA E,GONZALEZ P C,BRUNE A. Characterization of proton and sugar transport at the tonoplast of sweet lime(Citrus limmetioides) juice cells[J]. Physiologia Plantarum,1997,101(2):291-300.
[37] 陈发兴,刘星辉,陈立松.果实有机酸代谢研究进展[J].果树学报,2005,22(5):526-531.CHEN Faxing,LIU Xinghui,CHEN Lisong. Advances in research on organic acid metabolism in fruits[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2005,22(5):526-531.
[38] 张伟清,林媚,孙立方,冯先桔,平新亮.不同产地‘红美人’杂柑的糖酸特征及品质比较[J]. 分子植物育种,2022,20(10):3386-3394.ZHANG Weiqing,LIN Mei,SUN Lifang,FENG Xianju,PING Xinliang. Comparison of sugar and acid characteristics and fruit quality of‘Hongmeiren’hybrid citrus from different habitats[J].Molecular Plant Breeding,2022,20(10):3386-3394.