砀山酥梨(Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.‘Dangshansuli’)是中国栽培面积最大的梨品种,以果形端正、黄亮美观、皮薄多汁、口感酥脆和耐贮等特点而著称,具有润肺止咳和清喉降火等功效。但在贮藏中后期易发生虎皮病,严重影响贮藏品质。二苯胺(diphenylamine,DPA)和乙氧基喹可有效防止果实虎皮病的发生,但由于DPA残留产生潜在致癌物和乙氧基喹毒害问题,在许多国家已被禁止使用[1]。近年来,广谱、低毒和高效的天然提取物是果蔬保鲜行业研究的热点领域,多数研究表明香辛料提取物、植物精油(作为植物组织的次生代谢产物)和中草药类植物提取物有抗菌防腐和调节果蔬生理功能的作用[2],而且绿色安全环保,具有开发植物源保鲜剂的巨大潜力。
紫檀芪(pterostilbene,Pte)是一种天然的植物抗毒素,属于酚类化合物的二苯乙烯家族[3],是白黎芦醇的甲基化衍生物。最初从檀香中分离得到,其后在血竭、蜂胶、蓝莓和葡萄等中均有发现。Pte具有与白藜芦醇相似的药理活性,如抗氧化、抗病原微生物、抗肿瘤和保护神经等功能[4]。白藜芦醇防治苹果和梨的虎皮病和改善果品品质的研究已有报道[5-8]。与其他二苯乙烯化合物类似,与白藜芦醇相比,Pte 在A-苯环上多2 个甲氧基,表现出更高的生物活性、稳定性和利用性[4,9]。据报道,Pte在抑制果实病害方面发挥重要作用。徐丹丹[10]研究发现,Pte 处理能显著抑制荔枝霜疫霉和葡萄灰霉病,同时抑制荔枝褐变。杨佳瑶等[11]研究提到,葡萄叶提取物中含有白藜芦醇和Pte,且均对葡萄霜霉病具有防治效果,且Pte的抑菌活性要优于白藜芦醇,这与Pezet 等[12]的结果一致。此外,Koh 等[13]研究表明,Pte 是一种有效的杀菌剂和杀孢子剂,能够显著抑制油菜茎基溃疡病的发生。Qi 等[14]研究发现,Pte 及其衍生物还可以作为针对植物细菌疾病的生物膜的抗菌剂。但Pte在果品保鲜和虎皮病防治方面尚未见报道。
笔者实验室前期研究发现Pte 对苹果和梨的采后品质保持和虎皮病防治有明显效果,但处理时由于缺少乳化剂导致溶液不稳定,有固体析出;同时由于果皮蜡质层的影响,Pte 水溶液很难在果实表面充分展着和吸附,导致原药在果实上滞留时间短,从而影响药效的发挥。因此,笔者在本研究中旨在探究紫檀芪乳油制剂(pterostilbene emulsifiable,Pte EC)的最佳配方,并通过其与Pte、DPA 对采后砀山酥梨果实贮藏品质和虎皮病的控制效果,探究紫檀芪乳油制剂Pte EC 能否提高药效以替代DPA 在生产上的应用,并为今后虎皮病的调控提供一定的理论依据。
1 材料和方法
1.1 紫檀芪乳油制剂的配方研究
1.1.1 供试试剂 原药:紫檀芪(纯度≥99.0%)购自西安晶博生物科技有限公司。
溶剂:无水乙醇、菜籽油、碳酸二甲酯、乙酸乙酯和甘油。
乳化剂:双乙酰酒石酸单双甘油酯、硬脂酰乳酸钠、聚甘油单硬脂酸和酪蛋白乳酸钠(食品级);吐温20、吐温40、吐温80、司盘20、EL-40(分析纯)和大豆磷脂。
以上药品均购自西安晶博生物科技有限公司,中国。
1.1.2 乳油的配方 (1)溶剂的选择。参照郭武棣[15]的方法进行筛选。向试管中加入1.2 g原药,用移液管吸取2 mL的溶剂加入试管中,观察其溶解情况,如不能完全溶解可用涡旋震荡仪或微热加以溶解。如还不能溶解,继续用移液管吸取2 mL的溶剂加到试管中,重复此操作。直至溶剂加到10 mL 时仍未完全溶解,则舍弃该溶剂。将溶解度大于10%,且在冰箱中(0 ℃)中贮藏3 d 后无沉淀或结晶的溶剂用作后续试验。
(2)乳化剂的选择。参照江志利[16]的方法。在精油中加入一定量(10%)的乳化剂,混合均匀后,在室温静置1 d,然后根据制剂的外观、乳化性能及冷贮(0 ℃,3 d)稳定性选择乳化剂,能形成透明均一的单相液体,乳化性能好,且在冷贮中无结晶析出的乳化剂入选。
1.1.3 乳油的质量检测方法(1)乳化分散性。乳化分散性试验参照GB/T 32775—2016测定,并对乳油乳化分散性的划分等级进行观察和记录,乳化分散性为1~3级为合格,4~5级为不合格[16]。
(2)乳液稳定性、热贮稳定性和冷贮稳定性测定方法。参考GB/T 1603—2001测定乳液的稳定性。
参考GB/T 19136—2003 测定乳液的热贮稳定性。
参照江志利[16]的方法,用注射器吸取10.0 g 乳油试样注入离心管,将离心管在0 ℃冰箱中静置1 h,在此期间每隔15 min 搅拌1 次,并观察和记录是否有沉淀或油状物析出。将离心管放回0 ℃冰箱静置7 d,随后取出拭净,静置3 h 后,离心15 min。如无离析物或离析小于0.3 g为合格。
1.1.4 乳油制剂的配方研究(1)溶剂的筛选。本试验选用无水乙醇、95%乙醇、菜籽油、碳酸二甲酯、乙酸乙酯和甘油溶剂溶解Pte,按照1.1.2(1)进行筛选,观察不同溶剂对紫檀芪的溶解情况。
(2)乳化剂的筛选。在最佳实验条件下,按照1.1.2(2)对Pte的乳化剂进行初步筛选,评价乳化结果并记录冷贮后的现象。
(3)乳化分散性的测定。选择最佳溶剂和初步筛选的乳化剂制备Pte EC并进行乳化分散性试验,观察最佳溶剂和不同乳化剂组合下Pte EC 的乳化分散效果。
(4)乳液稳定性、热贮稳定性和冷贮稳定性的测定。确定最佳配方后,按照1.1.3(2)对乳液的稳定性、热贮稳定性和冷贮稳定性进行检测和结果评价。
1.2 紫檀芪制剂与DPA 对砀山酥梨虎皮病的控制效果研究
1.2.1 采收和处理 2020-09-18 于陕西省铜川市商业果园采收砀山酥梨,采收时选取成熟度一致、大小相近、无病虫害和机械损伤的果实。采收当天运回陕西华圣果业有限公司,次日进行各处理:2500 µL·L-1 DPA 水溶液浸泡2 min(在实验室前期研究中,2500 µL·L-1是抑制虎皮病的最佳体积分数);10 mg·L-1 Pte水溶液处理2 min;10%Pte EC稀释成10 mg·L-1水溶液处理2 min;对照组(CK)不做任何处理。处理后用发泡网包装箱入库冷藏[贮藏条件:(-1±0.5)℃,RH为90%~95%]。贮藏期间每隔30 d随机取10个梨果实,每个处理3次重复。取出立即带回实验室测定果实品质指标后,用液氮研磨果皮(厚度约0.5 mm)取样保存于-80 ℃下,以供后续试验。
1.2.2 指标测定(1)品质指标的测定。硬度:每个处理组取10个果实,使用FT-327型硬度计测定果肉硬度,将梨靠近果体赤道部位对称的2个部位去皮,将直径为1.1 cm 的探头刺入梨果肉深0.8 cm,读数显示果肉硬度值,单位为kg·cm-2。
可溶性固形物(soluble solids content,SSC)含量:使用PAL-1 型数显手持糖度计测定单果赤道两对称面果汁SSC含量,单位为%。
可滴定酸(titratable acid,TA)含量:每个处理随机取10 个果实,均匀取100 g 果肉采用酸碱指示剂滴定法进行测定。
(2)丙二醛含量、DPPH自由基清除能力和过氧化氢含量的测定。丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)含量参照许婷婷等[17]的方法,采用硫代巴比妥酸比色法测定,单位为nmol·g-1。
过氧化氢(H2O2)含量测定参照许婷婷等[17]的方法,单位为nmol·g-1。
1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl,DPPH)自由基清除能力参照陈玮琦等[18]方法测定。
(3)α-法尼烯和共轭三烯含量的测定。参考Zhao等[19]的方法测定α-法尼烯、共轭三烯含量,单位为nmol·g-1。
(4)虎皮病发病率和病情指数的测定。虎皮病发病率计算公式:发病率(%)=(发病果个数/总果个数)×100。每处理组随机选取40 个果实,3 次重复。虎皮病病情指数参照Zanella[20]的方法测定。
1.2.3 数据分析 采用Excel 软件进行数据统计和作图,运用SPSS 26.0 软件进行方差分析,Duncan’s多重比较进行显著性分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 紫檀芪乳油制剂的配方研究
2.1.1 溶剂的选择 结果显示,无水乙醇、碳酸二甲酯和乙酸乙酯均能完全溶解Pte,Pte 在无水乙醇中溶解度达到0.3 g·mL-1。而95%乙醇、菜籽油、甘油不能将其溶解。无水乙醇、碳酸二甲酯、乙酸乙酯溶解Pte 后,均形成均一透明黄色的溶液,且在0 ℃放置3 d后无固体析出。根据绿色安全、对环境无污染等原则,最终选择无水乙醇作为Pte的溶剂。
2.1.2 乳化剂的选择 如表1 所示,吐温20、吐温80、司盘20和EL-40在冰箱(0 ℃)放置3 d后均为均一透明溶液,可作为进一步筛选的乳化剂。
表1 紫檀芪乳油乳化剂筛选结果
Table 1 Screening results of pterostilbene EC emulsifier

注:乳化剂的溶剂均为无水乙醇。下同。
Note:The solvent of emulsifier is absolute ethanol.The same below.
乳化剂Emulsifier双乙酰酒石酸单双甘油酯Monodiglyceride diacetyl tartrate硬脂酰乳酸钠Sodium stearoyl lactate聚甘油单硬脂酸Polyglycerol Monostearate酪蛋白乳酸钠Casein sodium lactate吐温20 Tween 20吐温40 Tween 40吐温80 Tween 80司盘20 Span 20 EL-40大豆磷脂Soyabean lecithin冷贮后的现象Phenomenon after cold storage 1 d均一透明Transparent and homogeneous均一透明Transparent and homogeneous白色沉淀White precipitate乳白溶液Opal solution均一透明Transparent and homogeneous乳白溶液Opal solution均一透明Transparent and homogeneous均一透明Transparent and homogeneous均一透明Transparent and homogeneous黄色沉淀Yellow precipitate 2 d乳白溶液Opal solution乳白溶液Opal solution白色沉淀White precipitate乳白溶液Opal solution均一透明Transparent and homogeneous乳白溶液Opal solution均一透明Transparent and homogeneous均一透明Transparent and homogeneous均一透明Transparent and homogeneous黄色沉淀Yellow precipitate 3 d乳白溶液Opal solution乳白溶液Opal solution白色沉淀White precipitate乳白溶液Opal solution均一透明Transparent and homogeneous乳白溶液Opal solution均一透明Transparent and homogeneous均一透明Transparent and homogeneous均一透明Transparent and homogeneous黄色沉淀Yellow precipitate
2.1.3 乳化剂的分散性 如表2 所示,选用吐温20作为制备Pte的乳化剂时乳化分散效果较好,乳油呈云雾状自动分散,搅拌后呈蓝色透明乳状液,上无浮油,下无沉淀的乳化分散状态符合国家标准。最终确定吐温20为制备Pte EC的乳化剂。
表2 紫檀芪乳油乳化剂的乳化分散性测定结果
Table 2 Determination result of emulsifying and dispersing property of pterostilbene EC emulsifier
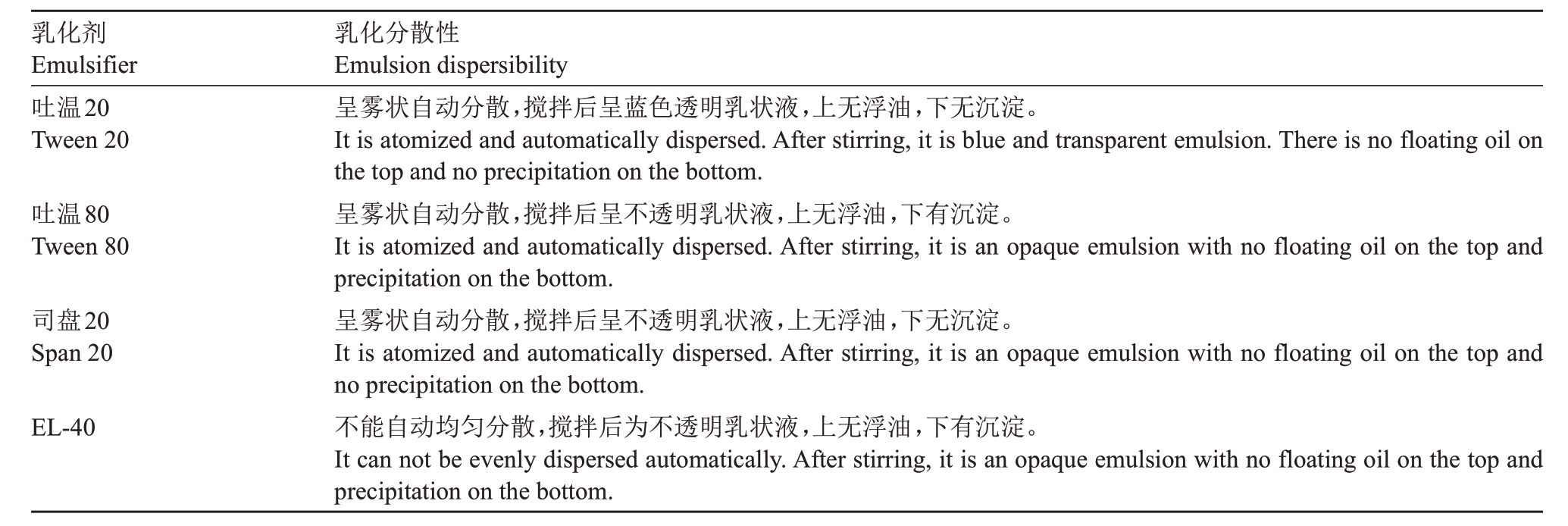
乳化剂Emulsifier吐温20 Tween 20吐温80 Tween 80司盘20 Span 20 EL-40乳化分散性Emulsion dispersibility呈雾状自动分散,搅拌后呈蓝色透明乳状液,上无浮油,下无沉淀。It is atomized and automatically dispersed.After stirring,it is blue and transparent emulsion.There is no floating oil on the top and no precipitation on the bottom.呈雾状自动分散,搅拌后呈不透明乳状液,上无浮油,下有沉淀。It is atomized and automatically dispersed.After stirring, it is an opaque emulsion with no floating oil on the top and precipitation on the bottom.呈雾状自动分散,搅拌后呈不透明乳状液,上无浮油,下无沉淀。It is atomized and automatically dispersed.After stirring, it is an opaque emulsion with no floating oil on the top and no precipitation on the bottom.不能自动均匀分散,搅拌后为不透明乳状液,上无浮油,下有沉淀。It can not be evenly dispersed automatically.After stirring,it is an opaque emulsion with no floating oil on the top and precipitation on the bottom.
2.1.4 最佳配方 通过对多种溶剂和乳化剂的比较和试验,确定Pte EC 的溶剂为无水乙醇,乳化剂为吐温20。其中Pte 占10%,乳化剂占10%,溶剂占80%。
2.1.5 乳液的稳定性 Pte EC的乳液稳定性检测结果见表3,乳液上无浮油、下无沉油和沉淀为合格,符合GB/T 1603—2001。
表3 紫檀芪乳油乳液稳定性结果
Table 3 Emulsion stability results of pterostilbene emulsifiable concentrate

乳油名称The name of the EC 10%紫檀芪乳油10%Pte EC乳液稳定性Emulsion stability上无浮油、下无沉淀There is no floating oil on the top and no sediment on the bottom评价Estimate合格Qualified
2.1.6 热贮稳定性 根据GB/T 19136—2003 将密封乳油的橡皮塞试管置于54 ℃的水浴锅中,14 d后取出,把试管外部擦净后分别称量质量,发现3支试管前后的质量均未发生明显变化,结果如表4 所示。于24 h内对其乳化分散性和乳液稳定性进行检测,发现其乳化分散性和乳液稳定性均合格。
表4 10%紫檀芪乳油热贮稳定性结果
Table 4 Heat storage stability results of 10%pterostilbene EC
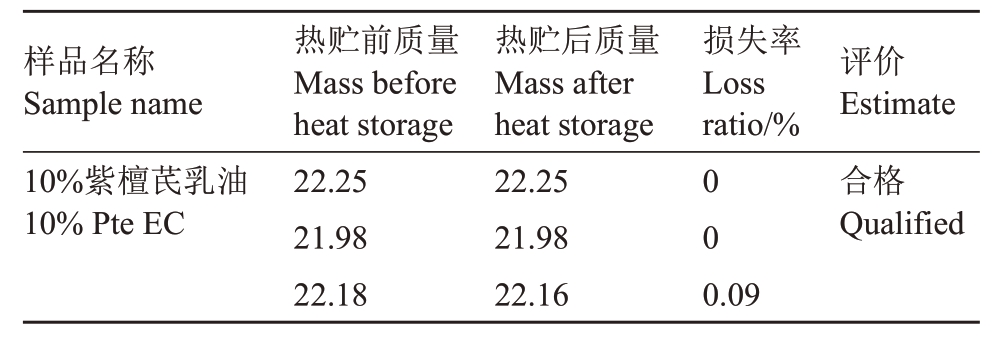
样品名称Sample name 10%紫檀芪乳油10%Pte EC热贮前质量Mass before heat storage 22.25 21.98 22.18热贮后质量Mass after heat storage 22.25 21.98 22.16损失率Loss ratio/%00评价Estimate合格Qualified 0.09
2.1.7 冷贮稳定性 由表5 可知,10%紫檀芪乳油在规定条件下离心后,无离析物。于24 h内对其乳化分散性和乳液稳定性进行检测,发现其乳化分散性和乳液稳定性均合格。故10%紫檀芪乳油冷贮稳定性合格。
表5 紫檀芪乳油冷贮稳定性检测结果
Table 5 Test results of cold storage stability of pterostilbene EC
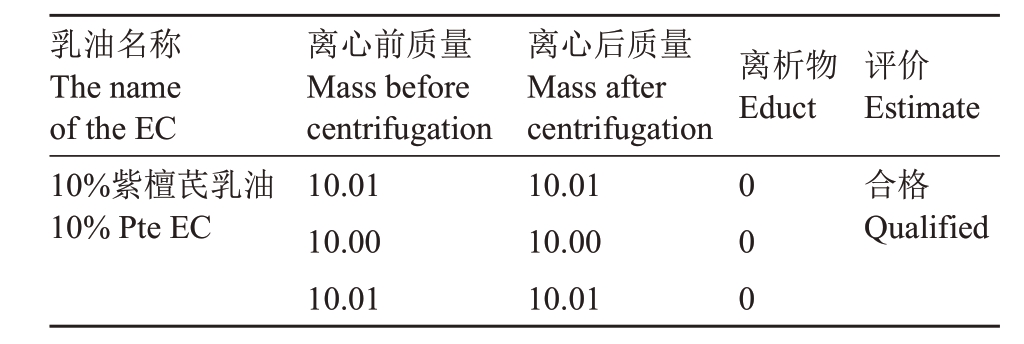
乳油名称The name of the EC 10%紫檀芪乳油10%Pte EC离心前质量Mass before centrifugation 10.01 10.00 10.01离心后质量Mass after centrifugation 10.01 10.00 10.01离析物Educt 000评价Estimate合格Qualified
2.2 不同处理对砀山酥梨硬度、SSC和可滴定酸含量的影响
如图1所示,果实硬度和SSC随着贮藏时间的延长逐渐下降。由图1-A可知,刚收获时,梨果实硬度为5.82 kg·cm-2,冷藏至210 d时,CK、DPA、Pte、Pte EC果实的硬度分别降至2.83、3.27、3.04、3.09 kg·cm-2。冷藏初期(60~90 d)各处理组果实硬度显著高于对照组(p<0.05),但在贮藏中后期(90~210 d)差异不显著。由图1-B 可知,贮藏过程中,DPA、Pte 和Pte EC 处理组的SSC 与对照差异不显著。由此可知,DPA、Pte 和Pte EC 能保持梨果实的硬度,但并不能显著延缓果实SSC的下降。
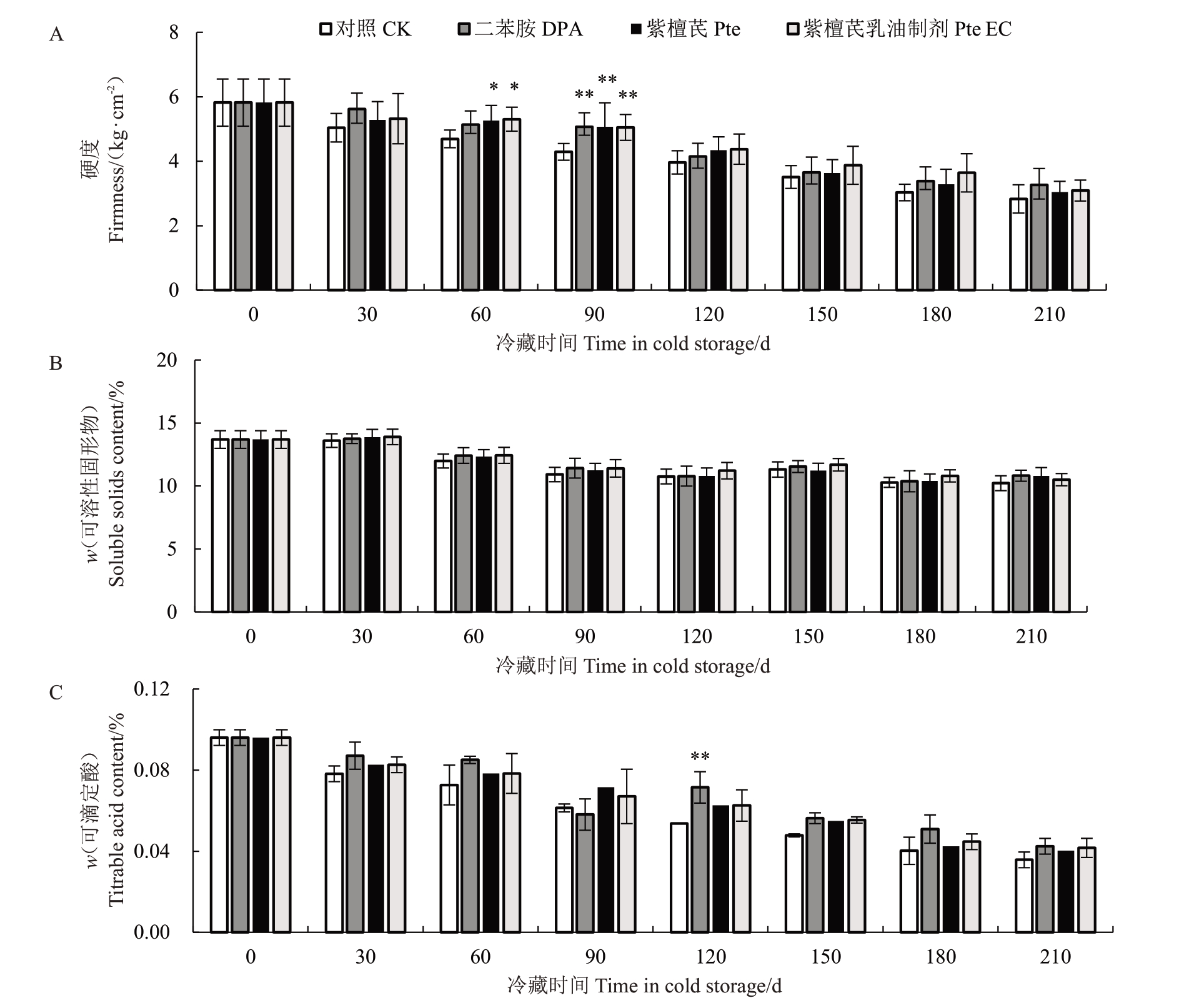
图1 不同处理对冷藏期间砀山酥梨硬度(A)、可溶性固形物含量(B)和可滴定酸含量(C)的影响
Fig.1 Effects of different treatments on the firmness(A),SCC(B)and TA(C)of Dangshansuli pears during cold storage
数据以3 个重复的(平均值±标准误)表示,星号表示所在时间点处理组和对照组相比显著差异。*、**、***、****分别表示在0.05、0.01、0.001、0.000 1 水平上的显著性。下同。
Data are presented as the (mean ± SE) of three replicates. The * indicates significant difference between two treatment and control groups at the time point.*,**,***,****indicate significance at the level of 0.05,0.01,0.001,and 0.000 1,respectively.The same below.
由图1-C可知,随着贮藏时间的延长,果实TA含量呈下降趋势。与对照组相比,DPA、Pte和Pte EC处理组果实的TA含量略高。冷藏至120 d时,DPA处理组果实TA含量显著高于对照组(p<0.01)。其他的贮藏时间,DPA、Pte和Pte EC处理可延缓冷藏期间梨果实酸度的下降,但与对照差异不显著。
2.3 不同处理对砀山酥梨MDA 含量、DPPH 自由基清除率和过氧化氢含量的影响
如图2-A所示,果实果皮MDA含量随着贮藏时间的延长呈上升趋势。刚采收时,梨果皮MDA含量(b,后同)为1.90 nmol·g-1,冷藏至210 d时,CK、DPA、Pte、Pte EC 处理组梨果皮MDA 含量分别上升至6.72、5.31、5.74、5.58 nmol·g-1。冷藏前期(0~90 d)对照组果皮MDA 含量呈缓慢上升,后期呈急速上升趋势。贮藏后期各处理组果皮MDA 含量显著低于对照组(p<0.05)。

图2 不同处理对冷藏期间砀山酥梨MDA 含量(A)、DPPH 自由基清除率(B)和H2O2含量(C)的影响
Fig.2 Effects of different treatments on the MDA content(A),and DPPH clearance(B)and content of H2O2(C) of Dangshansuli pears during cold storage
DPPH自由基清除率是反映果皮的抗氧化能力变化的重要指标。如图2-B 所示,贮藏期间梨果皮DPPH自由基清除率随着冷藏时间的延长大体呈下降趋势。刚收获时果皮DPPH 自由基清除率为96.50%,贮藏至210 d 时,CK、DPA、Pte、Pte EC 处理果皮DPPH 自由基清除率下降至84.94%、87.45%、86.22%、86.73%。整个贮藏过程中各处理组果皮DPPH自由基清除率均高于对照,但差异不显著。
如图2-C 所示,对照和各处理组梨果皮H2O2含量随着冷藏时间的延长逐渐增加,前中期缓慢上升,后期急速上升。刚收获时果皮H2O2 含量为25.98 nmol·g-1,冷藏至210 d 时,CK、DPA、Pte、Pte EC 处理组果皮H2O2含量分别上升至92.25、78.13、81.56、81.83 nmol·g-1。此时,各处理组梨果皮H2O2含量显著低于对照组(p<0.05)。由此可知,DPA、Pte、Pte EC 处理不能显著抑制冷藏期间梨果皮DPPH 自由基清除率的下降,但能显著抑制梨果皮MDA和H2O2的积累,DPA处理效果最佳。
2.4 不同处理对砀山酥梨α-法尼烯和共轭三烯含量的影响
如图3-A所示,果实果皮α-法尼烯含量随着冷藏时间的延长呈先上升后下降趋势,并在120 d时出现峰值,此时DPA、Pte 处理能显著降低α-法尼烯峰值(p<0.05)。由3-B可知,贮藏期间,各处理组和对照组梨果皮共轭三烯含量呈上升趋势。刚收获时,果皮共轭三烯含量为1.13 nmol·g-1,冷藏至210 d时,CK、DPA、Pte、Pte EC处理组果皮共轭三烯含量分别上升至98.46、76.52、87.07、87.19 nmol·g-1,此时,各处理组果皮共轭三烯含量极显著低于对照(p<0.01),其中DPA处理与对照组之间差异显著(p<0.000 1)。由此可知,DPA、Pte、Pte EC 处理能有效抑制α-法尼烯的氧化,减少果实共轭三烯的积累(p<0.05)。冷藏后期DPA处理效果最佳。
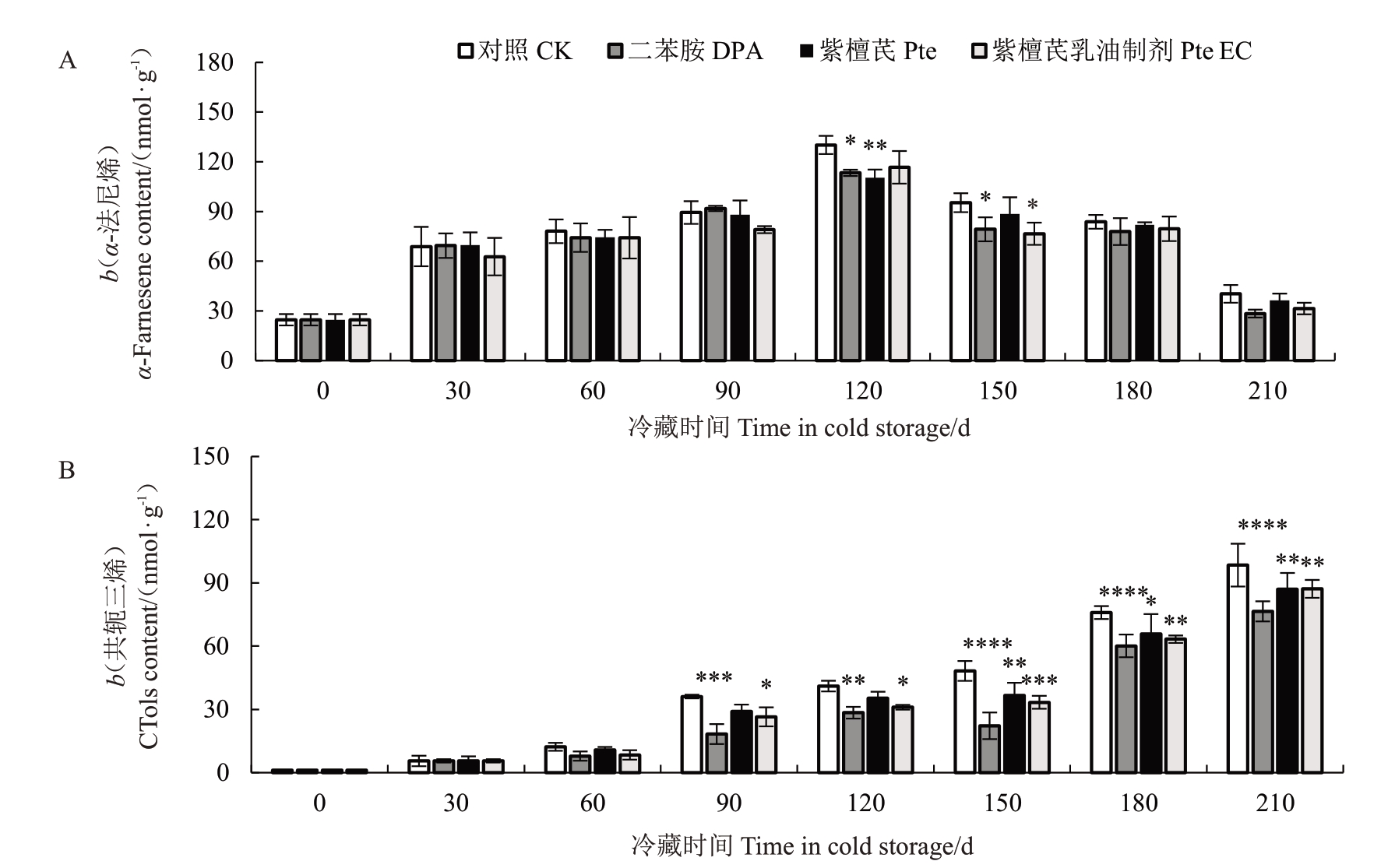
图3 不同处理对冷藏期间砀山酥梨α-法尼烯(A)和共轭三烯含量(B)的影响
Fig.3 Effects of different treatments on the content of α-farnesene(A)and CTols(B)in Dangshansuli pears during cold storage
2.5 不同处理对砀山酥梨虎皮病发病率、病情指数和发病状态的影响
如图4所示,冷藏期间梨果实的虎皮病发病率和病情指数均呈上升趋势。对照和各处理组果实在150 d 时开始发病,冷藏至210 d 时,CK、DPA、Pte、Pte EC 果实发病率和病情指数分别为51.58%、22.89%、39.39%、36.26% 和34.55%、20.73%、26.58%、23.60%,其中对照组果实发病率最高。DPA、Pte、Pte EC处理均能有效抑制砀山酥梨果实虎皮病的发生,Pte和Pte EC处理差异显著(p<0.01),DPA 处理效果极显著(p<0.000 1)。由此可知,DPA、Pte、Pte EC处理均能有效控制虎皮病的发生(见图4-C),以DPA 处理效果最佳,其次是Pte EC处理。
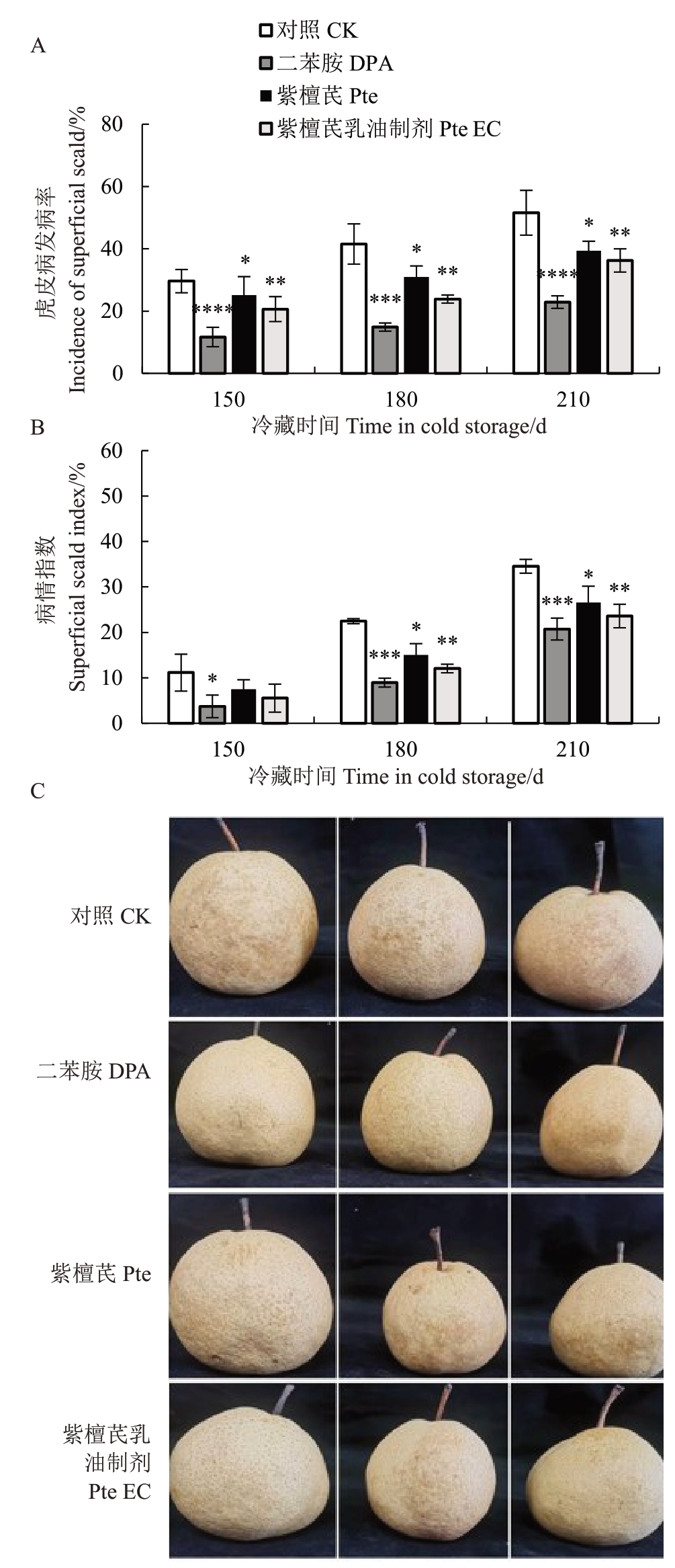
图4 不同处理对冷藏期间砀山酥梨虎皮病发病率(A)、病情指数(B)和冷藏210 d 后发病状态(C)的影响
Fig.4 Effects of different treatments on scald incidence(A),scald index(B)during cold storage and superficial scald state(C)of Dangshansuli pears during cold storage after 210 days
3 讨 论
传统乳油中含有较多的甲苯和二甲苯等有机溶剂,可以通过渗透作用进入植物果皮和动物皮肤,故在生产、运输和销售过程中对人体健康和食品安全构成威胁。笔者在本研究中通过对溶剂和乳化剂的筛选、理化性能的检测研制出了10% Pte EC,且各项性能均符合国家农药制剂标准[21],最终配方选用无水乙醇为溶剂,吐温20为乳化剂。与传统有机溶剂相比,该配方绿色环保,果实食用更安全。
在果品保鲜方面,Pte处理能够延缓梨果实硬度下降,使果实的SSC、TA、DPPH 自由基清除率高于对照组。但Pte 和Pte EC 处理在保持果实的品质指标以及提高果皮DPPH 效果方面差异不显著(p>0.05)。由此可知,Pte 处理可以在一定程度上改善果品的采后品质,延缓果实的衰老。在虎皮病防治方面,各处理都能够显著降低冷藏期间砀山酥梨虎皮病发病率和病情指数(p<0.05),其中DPA效果最佳,其次是Pte EC,最后是Pte。
可见Pte 制成乳油制剂后可以更好地控制砀山酥梨虎皮病的发生,并且Pte 与Pte EC 两处理组之间差异显著(p<0.05)。乳油制剂虽改善药效,但与DPA 处理效果仍有明显差距(p<0.01)。在抑制虎皮病相关指标方面,与Pte 相比,Pte EC 处理能更有效抑制冷藏期间砀山酥梨果皮H2O2和共轭三烯的积累(p<0.05),这可能是Pte 虎皮病控制效果低于Pte EC的原因。
大多数梨品种中黑皮病的发生与细胞内部α-法尼烯及其氧化产物共轭三烯在果实中的积累有关[22]。这种氧化分解和氧化还原的失衡导致细胞膜损伤,细胞区隔被破坏,多酚氧化酶通过邻苯二酚生成醌并最终形成棕色色素,介导大部分酶促褐变[23-24]。本研究中Pte EC 能抑制冷藏期间梨果皮α-法尼烯含量的增加,但其含量在峰值出现后开始下降,该变化趋势与虎皮病发病情况并不一致。与α-法尼烯相比,共轭三烯在虎皮病的发生中发挥更重要的作用[25-28]。与上述结论一致,本试验中Pte EC处理可以显著(p<0.05)抑制果实共轭三烯的积累,且其处理的果实在冷藏期间的发病率和病情指数显著(p<0.05)低于对照组。因此,本研究猜测共轭三烯是砀山酥梨虎皮病发生的诱因,Pte EC 处理可以显著降低其积累来抑制虎皮病的发生。
虎皮病是一种低温疾病,其发生与细胞内ROS诱发的氧化胁迫也密切相关。由于寒冷诱导的电子传递细胞色素途径受损,导致超氧自由基和H2O2累积相互作用形成羟基自由基,这些羟基自由基具有高度活性,并导致法尼烯氧化形成H2O2 等过氧化产物[29]。当病果抗氧化系统遭到破坏后,大量ROS 积累会诱发果皮发生膜脂过氧化,膜通透性增强,导致细胞膜系统损坏。MDA是膜脂过氧化的终产物,也是评价氧化胁迫的重要指标之一。本研究中冷藏后期果皮中H2O2含量的急速增加,加速了虎皮病病情的发展,而Pte EC处理能显著抑制果皮H2O2含量的增加和MDA的积累(p<0.05),减少活性氧的积累,减轻膜脂过氧化,保持细胞膜的完整性,从而抑制虎皮病的发生。
4 结 论
笔者在本研究中最终确定的10%Pte EC 的优选配方为10%紫檀芪+ 10%吐温20 + 80%无水乙醇,该制剂各项性能均符合国家农药制剂标准。配方绿色安全,且提高了药效,在一定程度上能改善果品品质,延缓果实衰老。同时Pte EC 还能有效控制砀山酥梨的虎皮病,防治效果仅次于DPA。笔者为虎皮病的防治提供了新的思路,也为Pte EC 进一步进行商业应用示范提供了理论依据。
[1] 李英丽,张少颖,董宇. 采前1-甲基环丙烯处理对货架期Bartlett 梨虎皮病和抗氧化特性的影响[J].食品科学,2021,42(1):250-256.LI Yingli,ZHANG Shaoying,DONG Yu.Effect of preharvest 1-methylcyclopene application on superficial scald and antioxidant capacity of Bartlett pears during shelf life[J].Food Science,2021,42(1):250-256.
[2] 郑贺云,张翠环,耿新丽,再吐娜·买买提,廖新福.果蔬天然保鲜剂研究进展[J].黑龙江农业科学,2018(7):158-162.ZHENG Heyun,ZHANG Cuihuan,GENG Xinli,Zaituna·Maimaiti,LIAO Xinfu. Research progress of natural preservative for fruits and vegetables[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences,2018(7):158-162.
[3] WASZCZUK M,BIANCHI S E,MARTINY S,PITTOL V,LACERDA D S,ARAUJO A S D,BASSANI V L. Development and validation of a specific-stability indicating liquid chromatography method for quantitative analysis of pterostilbene:Application in food and pharmaceutical products[J]. Analytical Methods,2020,12(35):4310-4318.
[4] LIU Y J,YOU Y Y,LU J,CHEN X,YANG Z H.Recent advances in synthesis,bioactivity,and pharmacokinetics of pterostilbene,an important analog of resveratrol[J]. Molecules,2020,25(21):5166.
[5] 孙丽娜.白藜芦醇对砀山酥梨黑皮病控制效果与发病机理的研究[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2014.SUN Lina.Study on the control effect and pathogenesis of resveratrol on Dangshansuli pears superficial scald[D]. Xi’an:Shaanxi Normal University,2014.
[6] NIU J P,HOU Z,OU Z F,HUI W.Comparative study of effects of resveratrol,1-MCP and DPA treatments on postharvest quality and superficial scald of Starkrimson apples[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2018,240:516-521.
[7] NIU J P,MA M,GAO X,GUAN J F,WANG X,LI L Q,WANG Y,LI C,HUI W. Physiological and biochemical mechanism of resveratrol inhibiting superficial scald in Dangshansuli pears[J]. New Zealand Journal of Crop and Horticultural Science,2022,50(2/3):118-130.
[8] 石淼.MHO 与苹果虎皮病发生和活性氧代谢关系的研究[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2014.SHI Miao. Study on the relationship between MHO and the occurrence of apples superficial scald and reactive oxygen species metabolism[D].Xi’an:Shaanxi Normal University,2014.
[9] WANG P,SANG S M.Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of resveratrol and pterostilbene[J].Biofactors,2018,44(1):16-25.
[10] 徐丹丹. 植物多酚对两种果实病害的抑制作用及其机理研究[D].北京:中国农业大学,2018.XU Dandan. Inhibitory effect of plant polyphenols on two kinds of fruit diseases and its mechanism[D]. Beijing:China Agricultural University,2018.
[11] 杨佳瑶,张敏,申红妙,甄志先,毕秋艳,冉隆贤.葡萄叶提取物对葡萄霜霉病的防治作用及有效成分分析[J].植物保护学报,2018,45(5):1121-1128.YANG Jiayao,ZHANG Min,SHEN Hongmiao,ZHEN Zhixian,BI Qiuyan,RAN Longxian. Control of grape downy mildew with extracts of grape leaves and analysis of its effective components[J].Journal of Plant Protection,2018,45(5):1121-1128.
[12] PEZET R,GINDRO K,VIRET O,RICHTER H. Effects of resveratrol,viniferins and pterostilbene on Plasmopara oviticola zoospore mobility and disease development[J]. Vitis,2004,43(3):145-148.
[13] KOH J C O,BARBULESCU D M,SALISBURY P A,SLATER A T.Pterostilbene is a potential candidate for control of blackleg in canola[J/OL].PLoS One,2016,11(5):e0156186.DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0156186.
[14] QI P Y,ZHANG T H,FENG Y M,WANG M W,SHAO W B,ZENG D,JIN L H,WANG P Y,ZHOU X,YANG S. Exploring an innovative strategy for suppressing bacterial plant disease:Excavated novel isopropanolamine-tailored pterostilbene derivatives as potential antibiofilm agents[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2022,70(16):4899-4911.
[15] 郭武棣.液体制剂[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2004.GUO Wudi. Liquid pharmaceutical preparations[M]. Beijing:Chemical Industry Press,2004.
[16] 江志利.植物精油杀虫作用及制剂研究[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2013.JIANG Zhili. Studies on insecticidal action and preparation of plant essential oil[D].Yangling:Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University,2013.
[17] 许婷婷,张婷婷,姚文思,朱慧文,金鹏,郑永华.热处理对低温胁迫下黄瓜活性氧代谢和膜脂组分的影响[J].核农学报,2020,34(1):85-93.XU Tingting,ZHANG Tingting,YAO Wensi,ZHU Huiwen,JIN Peng,ZHENG Yonghua. Effects of heat treatment on reactive oxygen species metabolism and membrane lipid fractions in cucumber under low temperature stress[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2020,34(1):85-93.
[18] 陈玮琦,郭玉蓉,张娟,窦姣,张晓瑞.苹果幼果中酚类物质抗氧化活性研究[J].食品工业科技,2015,36(1):115-118.CHEN Weiqi,GUO Yurong,ZHANG Juan,DOU Jiao,ZHANG Xiaorui.Antioxidative activities in vitro of polyphenols from unripe apple pomace[J].Science and Technology of Food Industry,2015,36(1):115-118.
[19] ZHAO J,XIE X B,SHEN X,WANG Y.Effect of sunlight-exposure on antioxidants and antioxidant enzyme activities in‘d’Anjou’pear in relation to superficial scald development[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,210:18-25.
[20] ZANELLA A. Control of apple superficial scald and ripening:A comparison between 1-methylcyclopropene and diphenylamine postharvest treatments initial low oxygen stress and ulter low oxygen storage[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2003,27(1):69-78.
[21] 王开运.农药制剂学[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2009.WANG Kaiyun. Pesticide preparation science[M]. Beijing:China Agriculture Press,2009.
[22] GAGO C,GUERREIRO A,CRUZ S,MARTINS N,CABRITA M J,MIGUEL M G,FALEIRO M L,ANTUNES M D.1-Methylcyclopropene and lemongrass essential oil nanocoatings effect on the preservation of cold stored Rocha pear[J/OL]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2022,192:111992.DOI:10.1016/j.postharvbio.2022.111992.
[23] DIAS C,AMARO A,FONSECA A,FERRANTE A,SILVESTRE A,ROCHA S M,ISIDORO N,PINTADO M. β-Farnesene exogenous application as a novel damage induction model to fast explore the effectiveness of postharvest strategies:The case study of the Rocha pear dop[J]. Horticulturae,2022,8(2):93.
[24] XIANG F X,GAO R,CHEN Y,PANG J W,LIU S S,LINGHU T,RUI Z,WANG Z G,XU L F.Exogenous putrescine and 1-methylcyclopropene prevent soft scald in Starkrimson pear[J/OL].Postharvest Biology and Technology,2022,193:112035. DOI:10.1016/j.postharvbio.2022.112035.
[25] HE J G,FENG Y X,CHENG Y D,KARUPPANAPANDIAN T,WANG J X,GUAN J F. Changes in α-Farnesene and phenolic metabolism and the expression of associated genes during the development of superficial scald in two distinct pear cultivars[J/OL]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2022,23(20):12088.DOI:10.3390/ijms232012088.
[26] LARRIGAUDIERE C,CANDAN AP,GINE-BORDONABA J,CIVELLO M,CALVO G. Unravelling the physiological basis of superficial scald in pears based on cultivar differences[J].Scientia Horticulturae,2016,213:340-345.
[27] BUSATTO N,GINE-BORDONABA J,LARRIGAUDIERE C,LINDO-GARCIAV,FARNETI B,BIASIOLI F,VRHOVSEK U,COSTA F.Molecular and biochemical differences underlying the efficacy of lovastatin in preventing the onset of superficial scald in a susceptible and resistant Pyrus communis L. cultivar[J/OL].Postharvest Biology and Technology,2021,173:111435. DOI:10.1016/j.postharvbio.2020.111435.
[28] 田改妮.1-MCP 处理对不同采收期砀山酥梨贮藏生理和黑皮病的影响[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2009.TIAN Gaini. Effects of 1-MCP treatment on storage physiology and melanosis of Dangshansuli pear with different harvest stage[D]. Yangling:Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University,2009.
[29] GONG Y H,SONG J,PALMER L C,VINQVISTTYMCHUK M,FILLMORE S,TOIVONEN P,ZHANG Z Q.Tracking the development of the superficial scald disorder and effects of treatments with diphenylamine and 1-MCP using an untargeted metabolomic approach in apple fruit[J/OL]. Food Chemistry,Molecular Sciences,2021,2:100022.DOI:10.1016/j.fochms.2021.100022.