桃(Prunus.persica L.),蔷薇科,李属,多年生自花授粉落叶果树。因其染色体数目少(2n=16),基因组小(227 Mb),童期短,被认为是蔷薇科果树研究的模式植物[1]。中国是桃的起源中心,种质资源遗传多样性丰富。观赏桃是桃种质资源的重要类型。其花型主要分为铃形、蔷薇形和菊花形(图1),在三大花型的基础上,通过育种技术的不断更新,花型、花色、树形、枝形和叶色的交叉组合,赋予桃花更多的表现形式[2-3]。
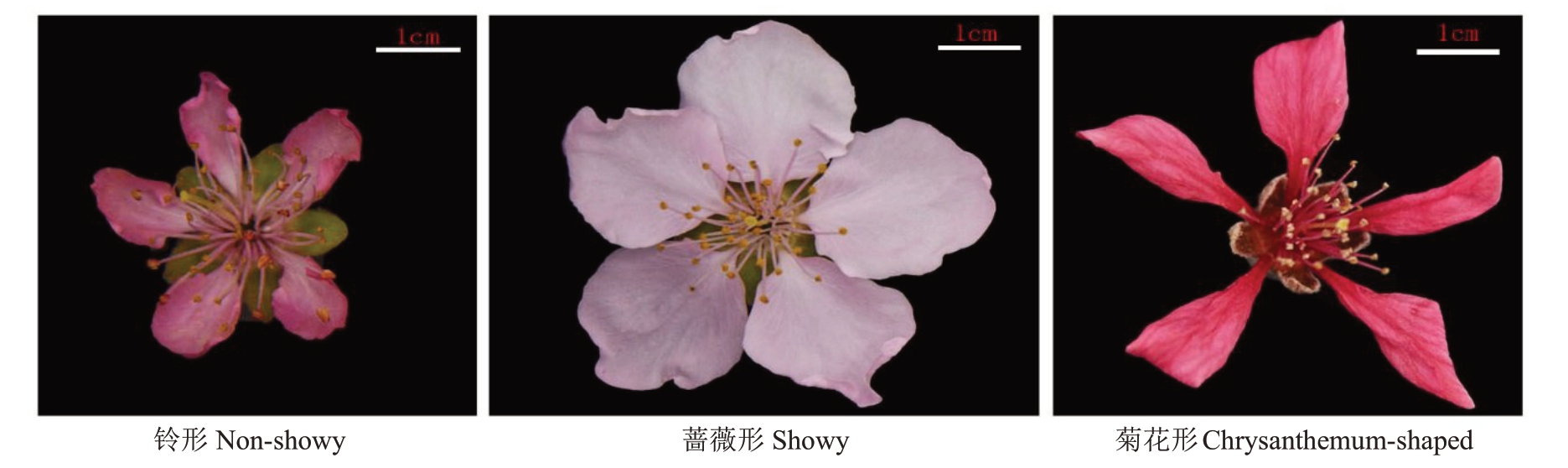

图1 桃花三大花型性状
Fig.1 Three major flower type traits of peach flower
铃形和蔷薇形是一对等位基因控制的质量性状。铃形花冠直径小,花瓣细长,完全开放时形似铃铛;蔷薇形花冠直径大,花瓣肥硕,开放时花瓣展开,在外观上容易区分表型,且该性状属于质量性状,定位分析相对简单,因此前人对此做了大量的研究,例如,在2009 年Ogundiwin 等[4]利用罐桃品种Dr. Davis和鲜食桃品种Georgia Belle的F1群体,构建了一个包含211个标记的遗传连锁图谱Pop-DG,将铃形/蔷薇形关联位点定位于8号染色体34.4 cM处;2010年Fan等[5]利用QTL定位将桃花铃形/蔷薇形定位在8 号染色体上的CPPT006 与PacC13 两个标记之间。之后随着GWAS 定位技术在果树分子育种上的发展,2015 年Micheletti 等[6]基于9K SNP 芯片对1580 份桃种质资源进行GWAS 分析,发现8 号染色体18 个SNP 标记与铃形/蔷薇形关联紧密,范围大小为4.3 Mb;2016 年Cao 等[7]利用129 份桃种质材料,在8号染色体13 740 117 bp处发现的1个SNP位点与铃形/蔷薇形关联度较高;2021 年孟歌等[8]利用199 份桃种质,将铃形/蔷薇形定位在8 号染色体14 484 624 bp处,并开发了相应的分子标记;2022年Lian等[9]利用黄水蜜×中油桃14杂交后代81株,在8号染色体PpB3-1 基因启动子区发现了1 个与表型关联度极高的SNP。目前开展的花型定位分析绝大多数利用的数据是SNP基因型,将控制桃花型的候选基因范围锁定在8 号染色体14 Mb~16 Mb 之间,但是基于SNP的GWAS结果定位区间往往较大,区间内的变异位点较多,开展关键基因挖掘工作仍具挑战性。而变异的SV(Structure Variantions)较SNP而言,更能影响基因的功能[10]。因此笔者利用本课题组前期发表的327 份桃种质材料的重测序结果,利用鉴定到的SV 位点进行全基因组关联分析(GWAS),将候选基因的范围锁定在14.4 Mb~14.6 Mb之间,并挖掘到1 个与表型相关性极高的SNP 位点Pp08:14 484 624 bp,利用KASP 基因分型技术验证了该位点的准确性,同时在与表型的验证过程中首次提出纯合铃形/杂合铃形之分,为进一步克隆关键基因提供理论支持。
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料
用于本试验GWAS分析的材料主要源于327份桃种质材料,具体品种参考Guo等[11],用于转座子验证的材料主要来源于1个192株的自交群体,2个96株的杂交群体,自交群体为中蟠17 号,杂交群体为瑞光39号×08-9-106和晴朗×中油蟠7号,用于IGV可视化分析的145 份桃种质材料(表1),其中有59份为GWAS 已有重测序数据,86 份新增重测序数据。以上种质资源及自交和杂交群体后代均来自国家园艺种质资源库和中国农业科学院郑州果树研究所桃种质资源圃。
表1 用于IGV 比对的145 份桃种质资源
Table 1 145 peach germplasm resources used for IGV comparison

编号Number品种名称Variety name表型Phenotype花冠直径Corolla diameter/cm编号Number品种名称Variety name表型Phenotype花冠直径Corolla diameter/cm 123456789 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy 5.0 3.9 4.5 4.2 4.0 5.1 4.2 3.9 4.2 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy 3.6 4.4 4.2 4.3 3.0 4.0 4.0 4.2 4.0 4.4 3.7 3.8 3.7 3.5 4.2吊枝白Diaozhibai大雪桃Daxuetao黑布袋Heibudai肥城红里6号Feichenghongli 6山东四月半Shandongsiyueban青丝桃Qingsitao晚湖景蜜露Wanhujingmilu红李光Hongliguang金凤Jinfeng红叶桃Hongyetao帚形山桃Zhouxingshantao光核桃Guanghetao红花山桃Honghuashantao甜仁桃Tianrentao青州白皮蜜桃Qingzhoubaipimitao早熟黄甘Zaoshuhuanggan肥城白里10号Feichengbaili 10南山甜桃Nanshantiantao喀什1号Kashi 1新疆蟠桃1号Xinjiangpantao 1新疆蟠桃2号Xinjiangpantao 2白花Baihua兴津油桃Xingjingyoutao大久保Dajiubao天津水蜜Tianjinshuimi鹰嘴桃Yingzuitao扁桃Biantao金塔油蟠桃Jintayoupantao五月鲜扁干Wuyuexianbiangan肉蟠桃Roupantao青桃Qingtao晚白花Wanbaihua大红袍Dahongpao乌黑鸡肉桃Wuheijiroutao石头桃Shitoutao曙光Shuguang丽格兰特Legrand瑞光2 号Ruiguang 2莺歌桃Yinggetao洒红桃Sahongtao瑞光3 号Ruiguang 3麦黄蟠桃Maihuangpantao 52 53 54蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy 4.4 3.8 3.8蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy 4.1 3.4 18 19 20蔷薇形Showy 4.4蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy 4.6 4.7 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42蔷薇形Showy 4.6蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy铃形Non-showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy铃形Non-showy蔷薇形Showy 4.5 4.1 4.7 3.7 4.6 4.3 4.8 4.8 3.1 4.5 4.4 4.2 3.5 4.2 4.2 3.5 1.8 4.5 5.8 2.1 3.9 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy铃形Non-showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy铃形Non-showy蔷薇形Showy 3.2 4.2 4.6 4.5 5.1 4.4 4.7 1.5 4.8 4.9 4.7 3.8 4.7 4.8 3.2 4.2 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy 5.1 5.3 5.3 4.4 6.1 4.8 4.2 4.0 4.2 80 81 82 83 84 85黄金蟠桃Huangjinpantao雨花露Yuhualu砂子早生Shazizaosheng沙红桃Shahongtao龙华水蜜Longhuashuimi有明白桃Youmingbaitao鸡嘴白Jizuitao齐桃Qitao深州离核水蜜Shenzhouliheshuimi深州白蜜Shenzhoubaimi阳泉肉桃Yangquanroutao青州红皮蜜桃Qingzhouhongpimitao叶县冬桃Yexiandongtao敦煌冬桃Dunhuangdongtao肥城白里17号Feichengbaili 17张白5号Zhangbai 5临白3号Linbai 3石桃Shitao五月白Wuyuebai卡里南Cullinan早黄金Zaohuangjin丰黄Fenghuang连黄Lianhuang江村4号Jiangcun 4农神蟠桃Nongshenpantao奉化蟠桃Fenghuapantao中油蟠1号Zhongyoupan 1平顶油蟠桃Pingdingyoupantao早红2号Zaohong 2人面桃Renmiantao绛桃Jiangtao黄李光Huangliguang粉红碧桃Fenhongbitao六月空Liuyuekong武汉大红袍Wuhandahongpao湖景蜜露Hujingmilu南方红花早Nanfanghonghuazao春蕾Chunlei春时Springtime朝晖Zhaohui玉露Yulu秦王Qinwang锦绣Jinxiu蔷薇形Showy铃形Non-showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy 4.5 2.6 4.5 4.5 5.4 4.2
表1 (续) Table 1(Continued)
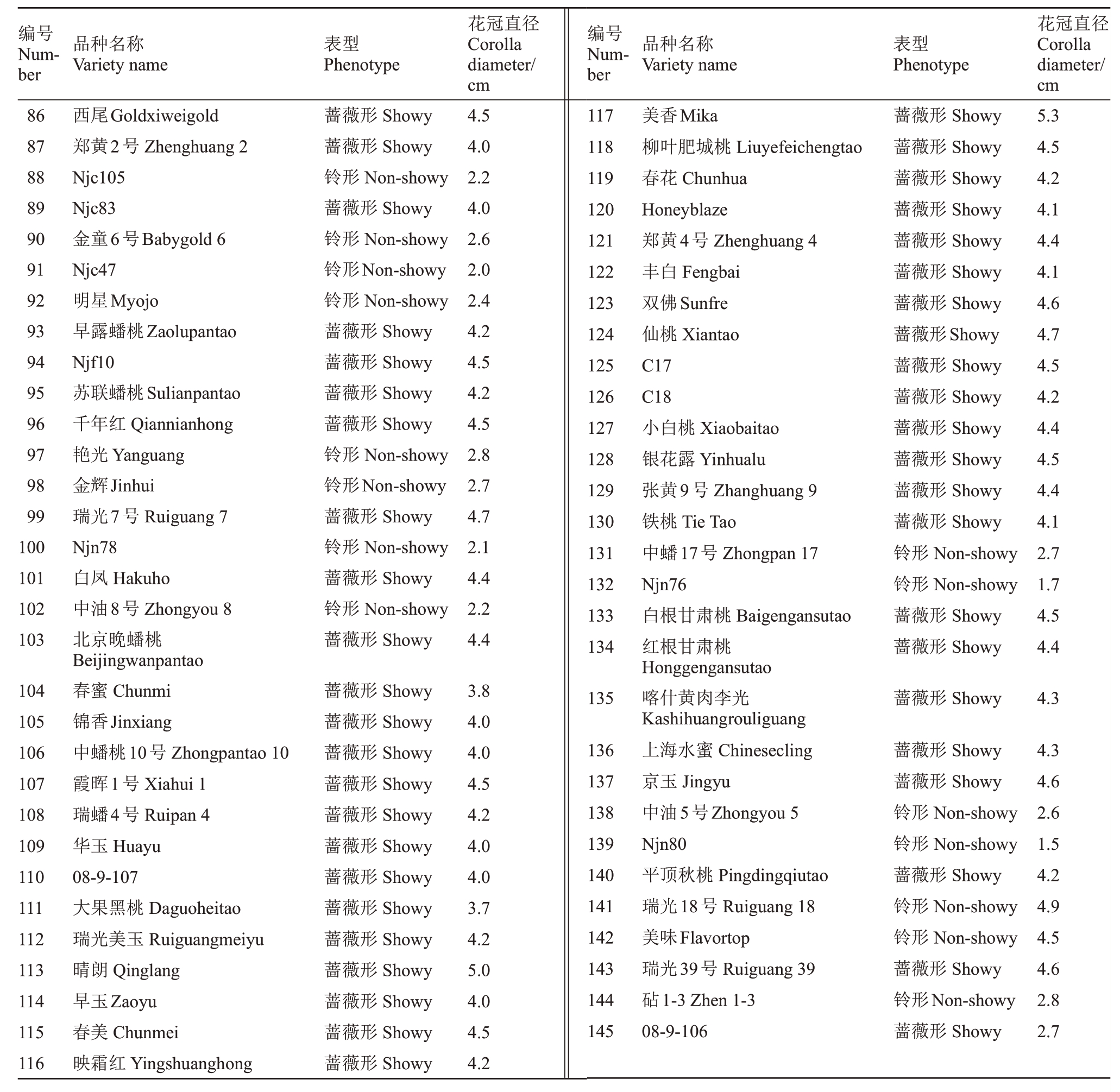
编号Number品种名称Variety name表型Phenotype花冠直径Corolla diameter/cm编号Number品种名称Variety name表型Phenotype花冠直径Corolla diameter/cm 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy铃形Non-showy蔷薇形Showy铃形Non-showy铃形Non-showy铃形Non-showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy铃形Non-showy铃形Non-showy蔷薇形Showy铃形Non-showy蔷薇形Showy铃形Non-showy蔷薇形Showy 4.5 4.0 2.2 4.0 2.6 2.0 2.4 4.2 4.5 4.2 4.5 2.8 2.7 4.7 2.1 4.4 2.2 4.4 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy铃形Non-showy铃形Non-showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy 5.3 4.5 4.2 4.1 4.4 4.1 4.6 4.7 4.5 4.2 4.4 4.5 4.4 4.1 2.7 1.7 4.5 4.4 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116西尾Goldxiweigold郑黄2号Zhenghuang 2 Njc105 Njc83金童6号Babygold 6 Njc47明星Myojo早露蟠桃Zaolupantao Njf10苏联蟠桃Sulianpantao千年红Qiannianhong艳光Yanguang金辉Jinhui瑞光7号Ruiguang 7 Njn78白凤Hakuho中油8号Zhongyou 8北京晚蟠桃Beijingwanpantao春蜜Chunmi锦香Jinxiang中蟠桃10号Zhongpantao 10霞晖1号Xiahui 1瑞蟠4号Ruipan 4华玉Huayu 08-9-107大果黑桃Daguoheitao瑞光美玉Ruiguangmeiyu晴朗Qinglang早玉Zaoyu春美Chunmei映霜红Yingshuanghong蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy 3.8 4.0 4.0 4.5 4.2 4.0 4.0 3.7 4.2 5.0 4.0 4.5 4.2 135蔷薇形Showy 4.3 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145美香Mika柳叶肥城桃Liuyefeichengtao春花Chunhua Honeyblaze郑黄4号Zhenghuang 4丰白Fengbai双佛Sunfre仙桃Xiantao C17 C18小白桃Xiaobaitao银花露Yinhualu张黄9号Zhanghuang 9铁桃Tie Tao中蟠17号Zhongpan 17 Njn76白根甘肃桃Baigengansutao红根甘肃桃Honggengansutao喀什黄肉李光Kashihuangrouliguang上海水蜜Chinesecling京玉Jingyu中油5号Zhongyou 5 Njn80平顶秋桃Pingdingqiutao瑞光18号Ruiguang 18美味Flavortop瑞光39号Ruiguang 39砧1-3 Zhen 1-3 08-9-106蔷薇形Showy蔷薇形Showy铃形Non-showy铃形Non-showy蔷薇形Showy铃形Non-showy铃形Non-showy蔷薇形Showy铃形Non-showy蔷薇形Showy 4.3 4.6 2.6 1.5 4.2 4.9 4.5 4.6 2.8 2.7
1.2 表型数据的调查
2022年3、4月对自然群体及杂交群体的表型进行调查。具体调查结果如表2所示。
表2 桃花型表型调查结果
Table 2 Statistical of peach flower-type phenotype

注:Q1 为自交群体中蟠17 号,Q2,Q3 分别为杂交群体瑞光39号×08-9-106,晴朗×中油蟠7 号。
Note:Q1 is the inbreeding population Zhongpan 17,Q2 and Q3 are respectively the hybrid population Ruiguang 39×08-9-106 and Qinglang×Zhongyoupan 7.
表型Phenotype Q3 96 0 96铃形Non-showy蔷薇形Showy总计Total种质资源Germplasm GWAS 72 255 327 IGV 18 127 145遗传群体Genetic group KASP Q1 135 57 192 Q2 52 44 96
1.3 DNA提取与测序
样品DNA的提取采用改良的CTAB法,具体方法参考张南南等[12]的方法,DNA 质量用NanoDrop 1000 spectrophotometer(Themo Scientific)紫外分光光度仪检测。用于KASP 基因分型的样品DNA 质量浓度调整至50~100 ng·μL。用于GWAS定位分析的DNA纯化后构建文库和测序,文库大小为350 bp,测序平台选用Hiseq X Ten(Illumina),测序任务由安诺优达基因科技有限公司(北京)完成。经数据质控后(FastQC),每个样本产生至少5 Gb的数据[11]。
1.4 全基因组关联分析
利用SV数据开展GWAS分析,最终产生181 381个变异位点,定位出铃形/蔷薇形相关的变异位点,并曼哈顿(Manhattan)图显示关联位点。
1.5 IGV可视化分析
利用IGV可视化查看基因组重测序结果,比对文件为下机的bam文件,导入IGV的bam文件附加samtools 文件,生成3 个相关的tracks,Alignment Track,Coverage Track,Splice Junction Track,对145份桃品种基因组序列进行比对。
1.6 KASP标记分型
竞争性等位基因特异性PCR(KASP)扩增体系:5 μL 2×KASP master mix(广州固德生物技术有限公司,广州,中国),1 μL DNA 样品,0.5 μL混合引物以及3.5 μL水,添加混合试剂前加入等体积石蜡油封体系。KASP 扩增程序如下:95 ℃预变性15 min;95 ℃变性20 s,61~55 ℃复性延伸60 s,10 个循环,每个循环复性延伸温度降低0.6 ℃;95 ℃变性20 s,55 ℃复性延伸60 s,32个循环。荧光数据读取和分析仪器为Roche LC96 Ⅱ(Roche Diagnostics,USA),读取温度为37 ℃,读取时间为60 s,所用荧光为羧基荧光素(FAM,carboxy fluorescein)和六氯荧光素(HEX,hexachlorouorescein)。KASP 引物序列信息见表3。
表3 KASP 分型所用引物序列信息
Table 3 Primer sequence information used for KASP typing

位点名称Loci name Pp08:14484624引物名称Prmer name Primer-FA M Primer-HEX Primer-Common引物序列Primer sequences GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTATACGTGTACAATAGATAGTCCAC GAAGGTCGGAGTCAACGGATTTATACGTGTACAATAGATAGTCCAA CTACTGATTTGGTCTGTTGGGTAACACCT
2 结果与分析
2.1 铃形/蔷薇形性状关键位点全基因组关联分析
笔者在本研究中通过对327份桃材料进行重测序分析,利用SV变异定位铃形/蔷薇形候选区间,在桃全基因组中共获得181 381 个高质量SV 位点。GWAS 结果发现在Pp08:14 518 604~14 521 291 处有一个2866 bp转座子(TE)与花型显著相关(图2),缩短了前人的定位区间。PCR扩增该转座子后,用1%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳在23份种质资源(图3)和384份杂交群体后代中进行验证(表4)。发现在23份桃种质中没有差异,在384 份杂交群体后代中虽然存在分离,但x2检验结果却表明转座子的插入与缺失与花型无显著的相关性。
表4 用于转座子鉴定的384 份遗传群体及x2检验结果
Table 4 Results of x2test and 384 genetic populations used for transposon identification

注:x2<0.05,表示具有显著相关性。下同。
Note:x2<0.05,Indicates a significant correlation.The same below.
项目Item数值Value位点信息Loci name ms179810物理位置Position Pp08:14 518 604~14 521 291 bp铃形Non-showy 0蔷薇形Showy 1 x2值正确率Accuracy/%68.75 x2value 147.310-log10(p)值-log10(p)value 6.71
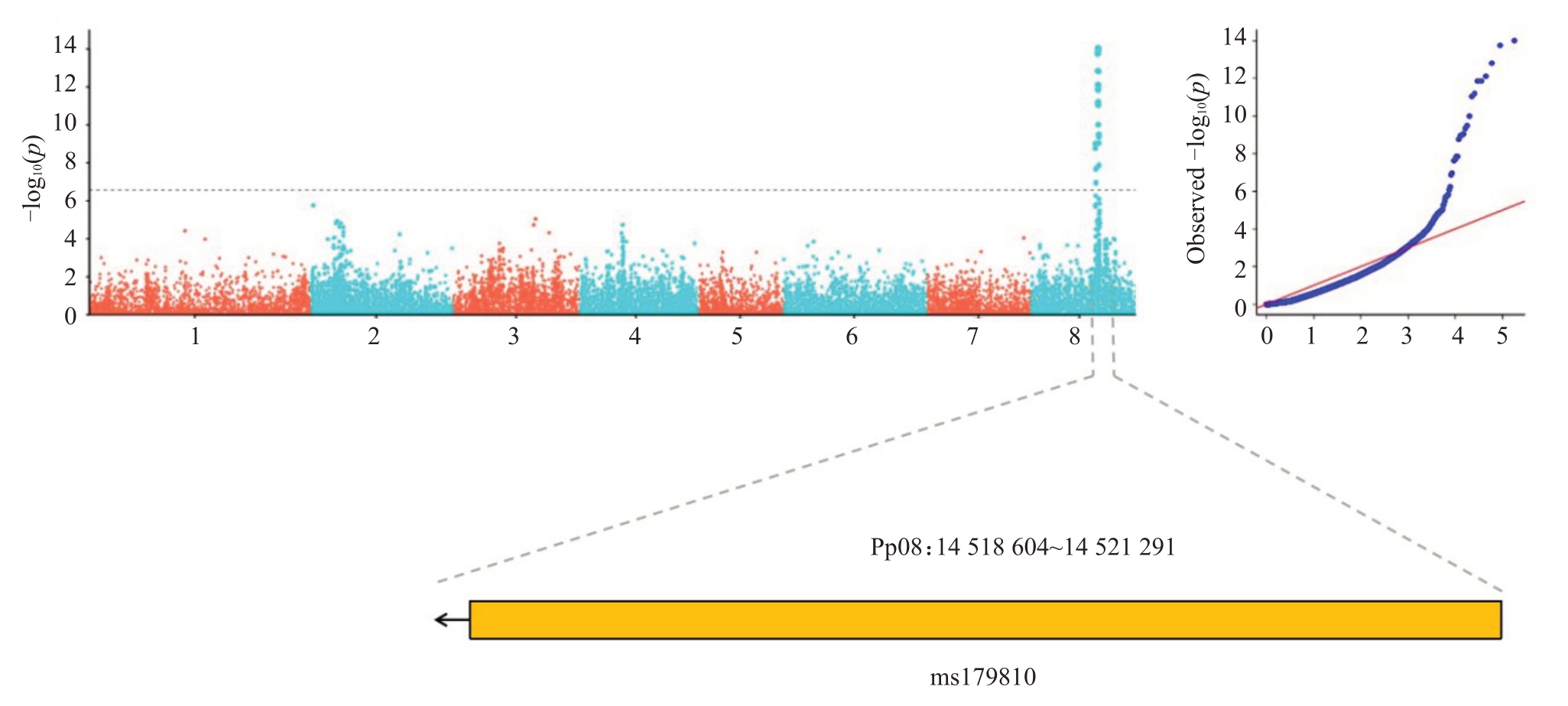
图2 基于CMLM 模型的铃形/蔷薇形花型性状SV 关联分析曼哈顿图和QQ-plot 图
Fig.2 Manhattan diagram and QQ-plot of SV-based GWAS of Showy/Non-showy flower shape traits using CMLM model

图3 转座子鉴定的23 份桃品种琼脂糖凝胶图
Fig.3 Agarose gel result of 23 peach varieties identified by transposon
NJF7. NJF7(Sh);HY. 红叶桃(Sh);NS. 南山甜桃(Sh);ZYP4. 中油蟠4 号(sh);SX. 双喜红(sh);ZHP. 早黄蟠桃(Sh);GQ. Golden Queen(Sh);ZH9.张黄9 号(Sh);QT.青桃(Sh);SH.上海水蜜(Sh);TJ.天津水蜜(Sh);SZ.深州水蜜(Sh);R.肉蟠桃(Sh);DZB.吊枝白(Sh);BJ.北京晚蟠桃(Sh);MG.美国蟠桃(Sh);QZ.青州白皮蜜桃(Sh);ZYP2.中油蟠2 号(sh);ZY9.中油9 号(sh);NJC77(sh);CH.Grest Haven(sh);NJC17(sh);ZY5.中油5 号(sh)。
NJF7(Sh);HY.Hongyetao(Sh);NS.Nanshantiantao(Sh);ZYP4.Zhongyoupan 4(sh);SX.Shuangxihong(sh);ZHP.Zaohuangpantao(Sh);GQ.Goldenqueen(Sh);ZH9.Zhang Huang 9(Sh);QT.Qingtao(Sh);SH.Chinese Cling(Sh);TJ.Tianjinshuimi(Sh);SZ.Shenzhoushuimi(Sh);R.roupantao(Sh);DZB.Diaozhibai(Sh);BJ.Beijingwanpantao(Sh);MG.Meiguopantao(Sh);QZ.Qingzhoubaipimitao(Sh);ZYP2.Zhongyoupan 2(sh);ZY9.Zhongyou 9(sh);NJC77(sh);GH.Grest Haven(sh);NJC17(sh);ZY5.Zhongyou 5(sh).
2.2 IGV可视化分析挖掘变异关键位点
由于转座子的插入与花型之间没有显著性关系,且该定位区间附近基因数量较少,从而在原有的定位基础上,扩大定位区间,在定位区间前后100 kb的范围内,利用IGV软件,以Prunuspersica-genome.v2.0.a1作为参考基因组,在145份桃种质材料重测序数据中比对分析,发现在转座子上游33 980 bp处存在一个变异的SNP(C→A),该位点为Pp08:14 484 624 bp,经比对发现,该位点存在3种变异类型,如图4-a~c所示,图4-a位点为CC时,表现为铃形花,图4-b位点为AC时,表现依然为铃形花,图4-c位点为AA时,表现为蔷薇形花。但是通过与表型比对发现,位点为CC时的铃形花冠直径比位点为AC的更小,位点为CC时花冠直径为(1.54±0.46)cm,位点为AC时花冠直径为(2.61±0.4)cm。因此笔者认为,在花型的分类中,铃形花又可以分为纯合铃形和杂合铃形。

图4 145 份桃资源IGV 比对结果
Fig.4 IGV comparison results of 145 peach resources
a.纯合铃形比对结果;b.杂合铃形比对结果;c.蔷薇形比对结果。
a.Results of homozygous Non-showy alignment;b.Results of heterozygous Non-showy alignment;c.Results of Showy alignment.
2.3 KASP基因分型技术鉴定纯合铃形种质
由于铃形/蔷薇形是由一对等位基因控制的质量性状,根据孟德尔遗传规律,变异位点为AC的铃形花自交后代应该出现以上3种花型的分型。因此采用该位点基因型为AC的中蟠17号,利用其自交群体后代192株,对Pp08:14 484 624 bp进行KASP基因分型验证,发现中蟠17号自交群体有3种基因型(图5),分离比为41∶94∶54,接近1∶2∶1。对中蟠17号自交群体的花冠直径进行了调查统计(图6),花冠直径被分为(1.54±0.46)cm、(2.61±0.4)cm、大于3.7 cm 3种类型,分别为纯合铃形、杂合铃形、蔷薇形,与基因型比对正确率在98.44%(表5)。对所得结果进行聚类分析(图7),发现纯合铃形和杂合铃形关系更近,较蔷薇形关系较远。
表5 基因型与表型比对结果
Table 5 Comparison of genotype and phenotype for flower type

位点信息Loci name Pp08:14 484 624物理位置Position Pp08:14 484 624纯合铃形Non-showy(C)CC杂合铃形Non-showy(Z)AC蔷薇形Showy AA x2值x2 value 0.007 p值p value 0.001 3正确率Accuracy/%98.44%
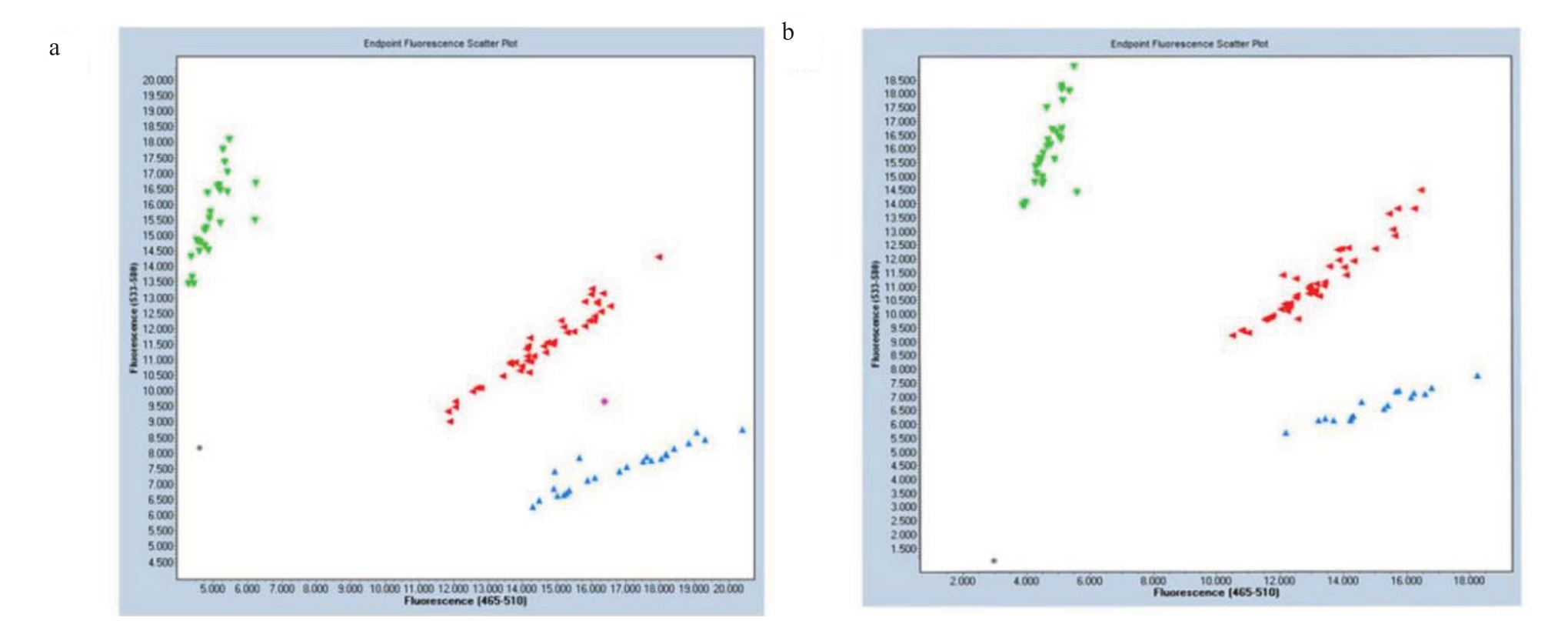
图5 中蟠17 号自交群体的KASP 标记基因分型图
Fig.5 Genotyping map of KASP marker in self-crossing population of Zhongpan 17
绿色荧光代表蔷薇形(AA);红色荧光代表杂合铃形(AC);蓝色荧光代表纯合铃形(CC)。
Green fluorescence represents Showy(AA);Red fluorescence represents heterozygous Non-showy(AC);Blue fluorescence represents the homozygous Non-showy(CC).
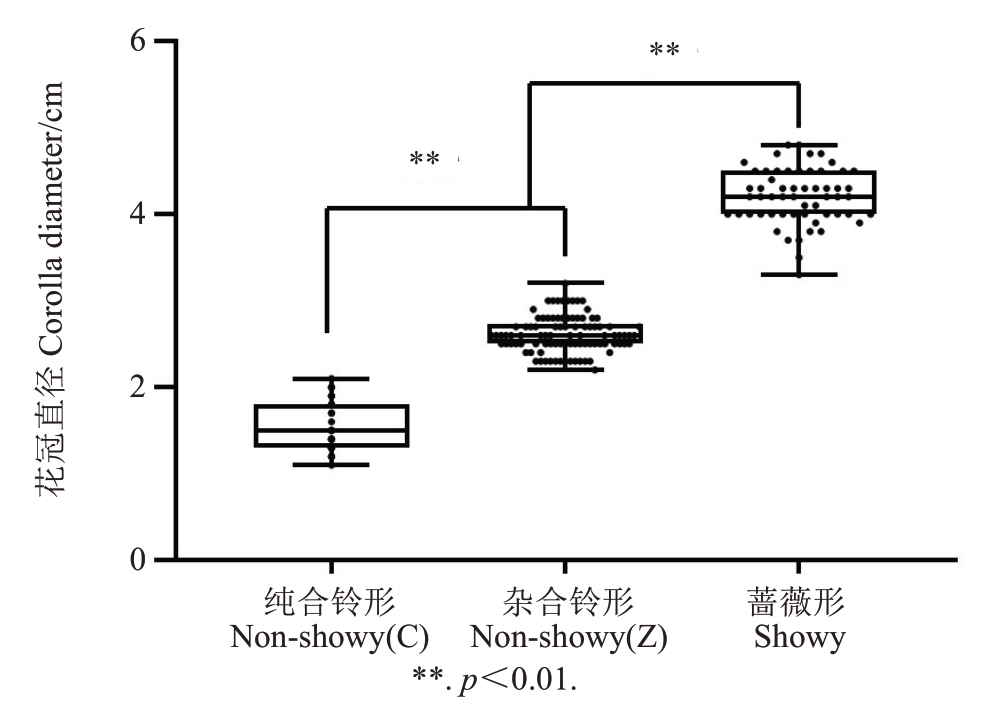
图6 中蟠17 号自交群体花冠直径箱型图
Fig. 6 Box plot of flower diameter in the offsprings of Zhongpan 17

图7 中蟠17 号自交群体花冠直径聚类分析
Fig.7 Cluster analysis of flower diameter in offsprings of Zhongpan 17
3 讨 论
在花型分类中,育种家更倾向于培育花冠直径大且重瓣的蔷薇形花,比如:洒红龙柱、报春、迎春、满天红等[13-16]。花冠直径大小也一直被认为是区分铃形/蔷薇形的标准之一,因此开发控制花型的分子标记,对观赏桃花分子育种具有重要指导意义。
有研究推断花的大小进化轨迹是从小花到大花,此过程要经过多年的遗传变异和自然选择[17-18]。Landis 等[19]的研究发现,黄花菜种群的花从种质的起源到现在变大了2.5 倍;Mojica 等[20]的研究发现,在自然变异中,大的菊花需要花费2000年的时间才能从小的菊花突变而来。花型是影响交配系统进化和繁殖成功的一个关键生态性状,传粉者、天敌和非生物环境是花型变异的驱动力,花型差异通常与不同的传粉者有关,形成传粉综合征[21],花型一直被认为是操控传粉者的一种适应方式[22-23],促进花型向着大花型的方向进化,更有利于传粉者授粉。但是一些物种花形态的差异往往不符合这一推断,有研究发现,自交群体的起源是和他们祖先非常接近的杂交群体,从异花授粉到自花授粉伴随着花的形态学向“自交综合征”的显著变化,其特征就是花的大小缩小,花的性状大多数变异是由群体遗传变异而来,但是花形态上的某些差异可能归因于一个单独的进化史[24]。桃就是典型的自花授粉植物,虽然铃形对蔷薇形为显性,但是上海水蜜作为栽培桃的祖先[25-26],其花型为蔷薇形,并且有研究报道GF677(蔷薇形)与红根甘肃桃1号(蔷薇形)杂交,后代出现了广泛的分离,F1代出现了铃形花,因此铃形花可能是桃、扁桃与甘肃桃种间杂交而来的[27]。综合桃花的发展和进化史,从而推断铃形花可能从蔷薇形花中突变而来。研究桃花型的进化史,首先需明确控制花型的关键基因,尽管此前对于铃形/蔷薇形的定位做了大量研究,将关键基因定位在8 号染色体14 Mb~16 Mb 之间,但具体位置一直存在差异。笔者在本研究中利用基于SV 的GWAS 分析,最显著的信号位于8 号染色体ms179810 转座子,x2检验结果却表明转座子的插入与缺失与花型没有显著的相关性,但在该定位区间挖掘到一个与表型相关度极高的SNP(Pp08:14 484 624 bp),经查阅文献资料,孟歌等[8]利用199份桃资源,筛选到1 042 687个SNP标记,利用GWAS 分析找到同样的位点,经鉴定与表型的准确率在93.46%。笔者通过改进引物、增加验证群体,提出并验证了纯合铃形的存在,因此该标记在桃自然群体中表型符合率在98.62%,在杂交群体中表型准确率在98.44%,证明该位点不仅可作为区分铃形/蔷薇形的分子标记,还可以作为区分纯合铃形/杂合铃形的分子标记。
4 结 论
笔者根据桃基因组Pp08:14 484 624 bp 处的变异类型以及桃花型的调查结果,首次将铃形花细分为纯合铃形和杂合铃形,且开发了同时鉴定纯合铃形、杂合铃形及蔷薇形的分子标记。纯合铃形种质资源的鉴定,为鉴定与挖掘提供新的实验材料,推动了桃花型的研究进展。
[1] 王力荣,王蛟,朱更瑞,方伟超,王新卫,陈昌文,曹珂.桃若干重要特异性状的遗传趋向分析[J].园艺学报,2017,44(2):223-232.WANG Lirong,WANG Jiao,ZHU Gengrui,FANG Weichao,WANG Xinwei,CHEN Changwen,CAO Ke. Genetic analysis of some special traits in peach[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2017,44(2):223-232.
[2] 王力荣.我国桃产业现状与发展建议[J].中国果树,2021(10):1-5.WANG Lirong. Current situation and development suggestions of peach industry in China[J].China Fruits,2021(10):1-5.
[3] 张斌斌,蔡志翔,沈志军,严娟,马瑞娟,俞明亮.观赏桃种质资源表型性状多样性评价[J].中国农业科学,2021,54(11):2406-2420.ZHANG Binbin,CAI Zhixiang,SHEN Zhijun,YAN Juan,MA Ruijuan,YU Mingliang.Diversity analysis of phenotypic characters in germplasm resources of ornamental peaches[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2021,54(11):2406-2420.
[4] OGUNDIWIN E A,PEACE C P,GRADZIEL T M,PARFITT D E,BLISS F A,CRISOSTO C H. A fruit quality gene map of Prunus[J].BMC Genomics,2009,10(1):587.
[5] FAN S H,BIELENBERG D G,ZHEBENTYAYEVA T N,REIGHARD G L,OKIE W R,HOLLAND D,ABBOTT A G.Mapping quantitative trait loci associated with chilling requirement,heat requirement and bloom date in peach (Prunus persica)[J].The New Phytologist,2010,185(4):917-930.
[6] MICHELETTI D,DETTORI M T,MICALI S,ARAMINI V,PACHECO I,LINGE C D S,FOSCHI S,BANCHI E,BARRENECHE T,QUILOT-TURION B,LAMBERT P,PASCAL T,IGLESIAS I,CARBÓ J,WANG L R,MA R J,LI X W,GAO Z S,NAZZICARI N,TROGGIO M,BASSI D,ROSSINI L,VERDE I,LAURENS F,ARÚS P,ARANZANA M J. Wholegenome analysis of diversity and SNP-major gene association in peach germplasm[J].PLoS One,2015,10(9):e0136803.
[7] CAO K,ZHOU Z K,WANG Q,GUO J,ZHAO P,ZHU G R,FANG W C,CHEN C W,WANG X W,WANG X L,TIAN Z X,WANF L R. Genome-wide association study of 12 agronomic traits in peach[J].Nature Communications,2016,7(1):13246.
[8] 孟歌,朱更瑞,方伟超,陈昌文,王新卫,王力荣,曹珂.桃的花型性状相关SNP 位点挖掘与候选基因分析[J].植物遗传资源学报,2022,23(2):505-517.MENG Ge,ZHU Gengrui,FANG Weichao,CHEN Changwen,WANG Xinwei,WANG Lirong,CAO Ke.Genome-wide association study identified SNP alleles and candidate genes for flower shape trait in peach (Prunus persica)[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,2022,23(2):505-517.
[9] LIAN X D,ZHANG H P,JIANG C,GAO F,YAN L,ZHENG X B,CHENG J,WANG W,WANG X B,YE X,LI J D,ZHANG L L,LI Z Q,TAN B,FENG J C.De novo chromosomelevel genome of a semi-dwarf cultivar of Prunus persica identififies the aquaporin PpTIP2 as responsible for temperature-sensitive semi-dwarf trait and PpB3-1 for flflower type and size[J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2022,20(5):886-902.
[10] WANG X,GAO L,JIAO C,STRAVORAVDIS S,HOSMANI P S,SAHA S,ZHANG J,MAINIERO S,STRICKLER SR,CATALA C,MARTIN G B,MUELLER L A,VREBALOV J,GIOVANNONI J J,WU S,FEI Z J.Genome of Solanum pimpinellifolium provides insights into structural variants during tomato breeding[J].Nature Communications,2020,11(1):5817.
[11] GUO J,CAO K,Cecilia D,LI Y,ZHU G R,FANG W C,CHEN C W,WANG X W,WU J L,GUAN L P,WU S,GUO W W,YAO J L,FEI Z J,WANG L R.An integrated peach genome structural variation map uncovers genes associated with fruit traits.[J].Genome Biology,2020,21(1):258.
[12] 张南南,牛良,崔国朝,曾文芳,王志强,鲁振华.一种高通量提取桃DNA 方法的建立与应用[J].中国农业科学,2018,51(13):2614-2621.ZHANG Nannan,NIU Liang,CUI Guochao,ZENG Wenfang,WANG Zhiqiang,LU Zhenhua. Establishment and application of a high-throughout protocol for peach (Prunus persica) DNA extraction[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2018,51(13):2614-2621.
[13] 朱更瑞,王力荣,方伟超,曹珂,陈昌文,冯义彬,侯凯,刘端明,岳长平,靳月笑.观赏桃品种‘洒红龙柱桃’[C]//中国园艺学会桃分会第三届学术研讨会论文集.2011:27.ZHU Gengrui,WANG Lirong,FANG Weichao,CAO Ke,CHEN Changwen,FENG Yibin,HOU Kai,LIU Duanming,YUE Changping,JIN Yuexiao. Cultivation and promotion of a special ornamental peach variety‘Sa Hong Longzhu’[C]//Proceedings of the Third Academic Symposium of the Peach Branch of the Chinese Horticultural Society,Chinese Horticultural Society Peach Branch,2011:27.
[14] 朱更瑞,王力荣,方伟超,曹珂,陈昌文,李全红,冯义彬,凌国钧,岳长平.低需冷量早花观赏桃品种‘报春’[J].园艺学报,2011,38(10):2035-2036.ZHU Gengrui,WANG Lirong,FANG Weichao,CAO Ke,CHEN Chaowen,LI Quanhong,FENG Yibin,LING Guojun,YUE Changping.A low chilling and early blooming ornamental peach cultivar‘Baochun’[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2011,38(10):2035-2036.
[15] 朱更瑞,王力荣,方伟超,陈昌文,曹珂,王小丽,王新卫.低需冷量、早花观赏桃新品种‘迎春’的选育[J].果树学报,2016,33(6):770-772.ZHU Gengrui,WANG Lirong,FANG Weichao,CHEN Changwen,CAO Ke,WANG Xiaoli,WANG Xinwei.A new low chilling requirement ornamental flower peach cultivar‘Ying- chun’[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2016,33(6):770-772.
[16] 朱更瑞,王力荣,方伟超.花果两用观赏桃新品种满天红的选育[J].果树学报,2008,25(3):440-441.ZHU Gengrui,WANG Lirong,FANG Weichao.Selection and cultivation of a new peach variety Mantianhong both for ornamental and food[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2008,25(3):440-441.
[17] ELIZABETH C. Flowers of evil:Proserpina’s venomous plants in Ruskin’s botany[J].Pacific Coast Philology,2009,44(1):114-128.
[18] GALEN C.Molecular and immunologic pathology for the endoscopist:Special techniques[J].Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Clinics of North America,2000,10(4):573-593.
[19] LANDIS J B,SOLTIS D E,SOLTIS P S.Comparative transcriptomic analysis of the evolution and development offlower size in Saltugilia (Polemoniaceae).[J]. BMC Genomics,2017,18(1):475.
[20] MOJICA J P,KELLY J K. Viability selection prior to trait expression is an essential component of natural selection[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B,2010,277(1696):2945-2950.
[21] TAKAAKI N.Large flower size:Molecular basis and role of cytokinin[J]. Journal of the Japanese Society for Horticultural Science,2012,81(2):129-139.
[22] GONZALEZ N,VANHAEREN H,INZE D. Leaf size control:Complex coordination of cell division and expansion[J]. Trends in Plant Science,2012,17(6):332-340.
[23] KELLY J K,MOJICA J P.Interactions among flower-size QTL of Mimulus guttatus are abundant but highly variable in nature[J].Botan Ical Gazette,2011,189(4):1461-1471.
[24] KRIZEK B A,ANDERSON J T. Control of flower size[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany,2013,64(6):1427-1437.
[25] 左覃元,朱更瑞,王力荣.中国桃果产业的现状及展望[J].果树科学,1997,14(1):61-63.ZUO Qingyuan,ZHU Gengrui,WANG Lirong. Current situation and prospects of China’s peach fruit industry[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,1997,14(1):61-63.
[26] CAO K,YANG X W,LI Y,ZHU G R,FANG W C,CHEN C W,WANG X W,WU J L,WANG L R.New high-quality peach(Prunus persica L.Batsch)genome assembly to analyze the molecular evolutionary mechanism of volatile compounds in peach fruits[J].The Plant Journal,2021,108(1):281-295.
[27] 王力荣,朱更瑞,方伟超.中国桃遗传资源[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2012.WANG Lirong,ZHU Gengrui,FANG Weichao. Peach genetic resource in China[M].Beijing:China Agriculture Press,2012.