葡萄为葡萄科(Vitaceae)葡萄属(Vitis L.)多年生藤本植物,具有适应性强、用途广、产业链长等特点,是世界性重要的经济果树之一[1]。葡萄也是我国的重要果树树种,面积和产量均居世界前列,在我国农村经济结构调整、美丽乡村建设和农民脱贫致富过程中均发挥着重要作用。回顾我国葡萄产业的发展历程,每次的快速发展都离不开新品种的选育和引进[2]。葡萄是世界上品种类型最多的树种之一,据国际葡萄品种名录VIVC(Vitis International Variety Catalogue)统计,截止到2021 年全世界至少有23000 个品种(http://www.vivc.de/)[3]。同时葡萄品种间同物异名或同名异物以及苗木市场滥用品种名称等不良现象时有发生,极大地损害了育种者的权益,不利于产业的健康可持续发展[4]。建立完善的植物新品种保护制度可以提高对育种人新品种权的保护能力、调动育种者育种积极性、避免侵权行为的发生,维持良好的种苗交易市场,以促进产业经济的稳步发展[5]。
我国于1999年正式加入UPOV,成为其第39个成员国,经过20 余年的发展,我国植物新品种保护工作取得显著成绩。2022年新种子法开始实施,进一步加大了植物新品种知识产权的保护力度。开展植物特异性(Distinctness)、一致性(Uniformity)和稳定性(Stability)(简称DUS)测试是新品种保护的技术基础和品种能否授权的科学依据,DUS测试指南是指导测试单位开展DUS测试工作的技术标准,也是审批机关开展新品种实质性审查的技术规范[6]。我国于2014 年发布了葡萄DUS 测试指南,极大地推进和规范了我国葡萄新品种的申请与保护工作。随着近年来测试品种的不断增多,笔者在实践工作中发现一些需要调整和完善的内容,通过对UPOV、日本和我国的葡萄品种DUS 测试指南进行比较分析,结合田间实践,总结三者的异同和优缺点,为我国葡萄品种DUS测试指南的修订提供参考思路,提高我国葡萄品种保护效率,加快我国葡萄新品种走出去的国际进程。
1 葡萄品种DUS测试指南概况
UPOV于2008年发布了葡萄DUS测试指南,版本号为TG/50/9[7]。日本葡萄品种DUS 测试指南代号为1654。我国于2014 年以行业标准的形式发布了《植物新品种特异性、一致性和稳定性测试指南葡萄(NY/T 2563—2014)》,以下简称NY/T 2563[8]。3 个指南均适用于所有葡萄属(Vitis L.)新品种特异性、一致性和稳定性测试的结果判定。
2 葡萄品种DUS 测试指南的比较分析
2.1 测试材料
3 个指南提交的繁殖材料质量要求基本一致:枝条健壮、芽眼饱满、无病虫侵害,繁殖材料形式为自根苗、嫁接苗或插条[9]。但是三者对提交材料的数量要求不同,其中,TG/50/9 要求提交材料的最少数量为5株,或足够产生5株植株的苗木或者插条,1654要求提交的种苗数量为7株,NY/T 2563要求提交的自根苗数量不少于10株或插条不少于50个芽。
2.2 测试方法
葡萄品种测试指南测试方法主要对测试周期、测试地点、试验设计等做了具体说明。
3 个测试指南对测试周期的要求与苹果、桃等多数果树一致,均要求至少为2 个独立的生长结果周期[10-11],以减少测试过程中的误差,保证测试结果的可靠性。对测试地点进行了明确的规定,测试通常在同一个地点进行,如果某些性状在该地点不能充分表达,可在其他符合条件的地点对其进行观测。
2.3 三性判定标准
对于特异性的判定,3个指南基本一致,申请品种应明显区别于所有已知品种。在测试中,当申请品种至少在一个性状上与近似品种具有明显且可重现的差异时,即可判定申请品种具备特异性。
对于一致性的判定,TG/50/9、1654 和NY/T 2563均采用1%的群体标准和至少95%的接受概率,但所取样本大小不同。TG/50/9、1654 样本大小为5株,不允许有异型株;NY/T 2563 样本大小为10 株,最多允许有1个异型株。
对于稳定性的判定,TG/50/9 和NY/T 2563 在“一般不对稳定性进行测试,如果一个品种具备一致性,则可认为该品种具有稳定性”方面的论述是相同的。此外,TG/50/9 还作了另外的要求:在适当的情况下,或在有疑问的情况下,可以通过再测试1个周期或者在新的地点测试,以确保其显示出与最初提供材料具有相同的特性。
2.4 测试性状
性状是DUS测试审查的基础,是指能够准确识别、区分和描述可遗传表达的植物特征或特性[6]。
2.4.1 性状的功能分类及数量 测试性状按照功能和要求分为5类,包括基本性状、带星号(*)性状、分组性状、选测性状和技术问卷性状。性状表中列出的TG/50/9 测试性状有44 个,NY/T 2563 测试性状有51个,1654测试性状有52个(表1)。
表1 葡萄品种DUS 测试指南性状的功能分类及数量
Table 1 Functional classification and number of traits in different DUS test guidelines for Vitis L.
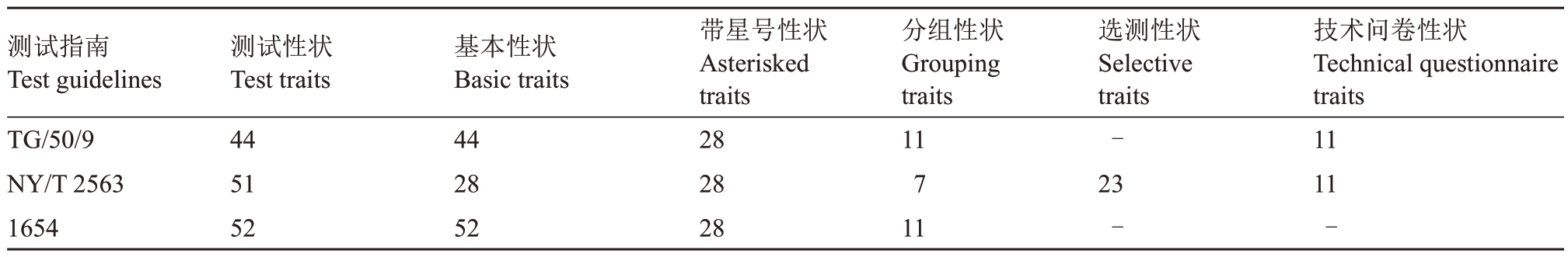
注:“-”表示在测试指南中此类性状未体现和说明。
Note:“-”indicates that such characters are not reflected and explained in the test guidelines.
测试指南Test guidelines TG/50/9 NY/T 25631654技术问卷性状Technical questionnaire traits 1111-测试性状Test traits 445152基本性状Basic traits 442852带星号性状Asterisked traits 282828分组性状Grouping traits 11711选测性状Selective traits-23-
基本性状是指DUS 测试中UPOV 接受的性状以及UPOV成员能够从中选择适合于特定环境的性状[12]。TG/50/9基本性状有44个,NY/T 2563基本性状有28 个,1654 基本性状有52 个(表1)。带星号(*)性状是UPOV 用于统一品种描述所需要的重要性状,除非受环境条件限制性状的表达状态无法测试,否则所有UPOV成员都应使用这些性状[12]。TG/50/9、NY/T 2563以及1654的带星号性状均有28个,分别占基本性状的63.64%、100%和53.85%。
分组性状可作为选择近似品种的依据,在特异性测试中将那些不相关的已知品种排除在种植试验之外,同时用于种植试验分组,以便将近似品种种在一起[13]。适于分组的性状应为不变异或变异极小,而且这些性状的差异明显,在全部收集的品种中应该均匀分布。其中TG/50/9有11个分组性状,NY/T 2563有7个分组性状,1654有11个分组性状(表1),详细对比见表2。对于选测性状,TG/50/9与1654并无相关说明,在NY/T 2563 中,除了带星号性状,其余皆为选测性状,共23个。
表2 葡萄品种DUS 测试指南分组性状对比
Table 2 Grouping characteristics in different DUS test guidelines for Vitis L.

注:QL.质量性状;QN.数量性状;PQ.假质量性状;-表示对应的性状在该指南中不作为分组性状。下同。
Note:QL.Qualitative traits;QN.Quantitative traits;PQ.Pseudo-qualitative traits;-.The corresponding trait is not used as a grouping trait in this guideline.The same below.
序号Serial number NY/T 2563性状编号/性状名称Number/Characteristics类型Type 123456789----QN TG/50/9性状编号/性状名称Number/Characteristics 2*嫩梢:梢尖开合程度Young shoot:openness of tip 6*幼叶:正面颜色Young leaf:color of upper side 7*幼叶:背面主脉间匍匐茸毛密度Young leaf:prostrate hairs between main veins on lower side 16*花序:花器类型Flower:floral organs 20*成龄叶:裂片数Mature leaf:number of lobes 31*浆果始熟期Time of verasion 36*果粒:形状Berry:shape 37*果粒:颜色Berry:color of skin 40*果粒:果肉花青甙显色强度Berry:anthocyanin coloration of flesh 42*果粒:香型Berry:particular flavor 43*果粒:种子的形成Berry:formation of seeds-PQ QN QL 11*成龄叶:裂片数Mature leaf:number of lobes 19*浆果始熟期Time of beginning of berry ripening 24*果粒:形状Berry:shape 25*果粒:颜色Berry:color of skin-QN/QN/PQ QN PQ PQ QN 1011 PQ QL 1227*果粒:香型Berry:particular flavor 28*果粒:种子Berry:formation of seeds 30幼叶:背面主脉上直立茸毛密度Young leaf:erect hairs on main veins on lower side of blade 1654性状编号/性状名称Number/Characteristics 2*嫩梢:梢尖开合程度Young shoot:openness of tip 6*幼叶:正面颜色Young leaf:color of upper side 7*幼叶:背面主脉间匍匐茸毛密度Young leaf:prostrate hairs between main veins on lower side 17*花序:花器类型Flower:Floral organs 21*成龄叶:裂片数Mature leaf:number of lobes 32*浆果始熟期Time of verasion 38*果粒:形状Berry:shape 39*果粒:颜色Berry:color of skin 44*果粒:果肉花青甙显色强度Berry:anthocyanin coloration of flesh 49*果粒:香型Berry:particular flavor 50*果粒:种子的形成Berry:formation of seeds-QN
技术问卷性状是在DUS 测试指南技术问卷中列出的性状,旨在通过育种人提供的性状信息了解品种基本情况、初步筛选近似品种[6]。1654 中没有体现出技术问卷性状,而TG/50/9和NY/T 2563的11个技术问卷性状一致,为“嫩梢:梢尖开合程度、幼叶:正面颜色、幼叶:背面主脉间匍匐茸毛密度、花序:花器类型、成龄叶:裂片数、浆果始熟期、果粒:形状、果粒:颜色、果粒:果肉花青甙显色强度、果粒:香型、果粒:种子”。
2.4.2 性状的内容分类及数量 对3 个测试指南的性状进行综合分析,可将测试性状归纳为芽性状、枝条性状、叶性状、花性状、果实性状、种子性状6类(表3)。表3表明,这3个指南的测试性状以叶性状和果实性状居多,叶性状占所有测试性状的32.69%~39.22%,果实性状占所有测试性状的29.55%~34.62%。
表3 葡萄品种DUS 测试指南性状的内容分类及数量
Table 3 Content classification and number of traits in different DUS test guidelines for Vitis L.
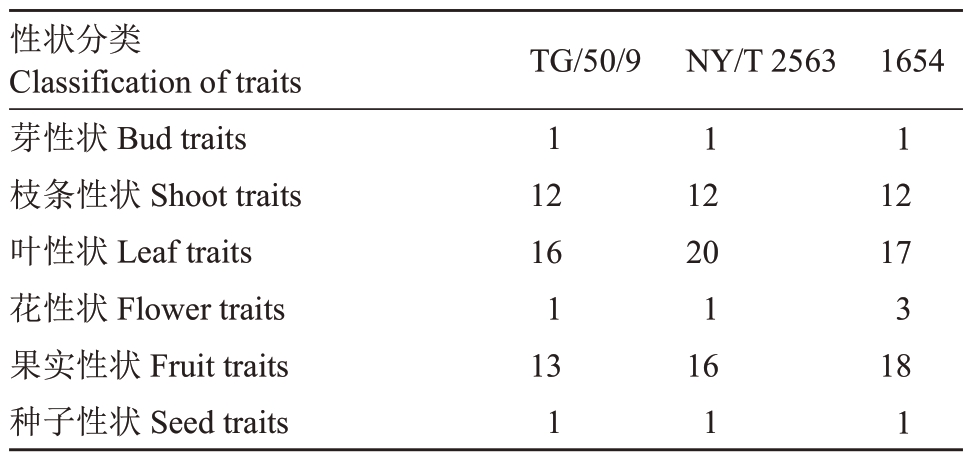
性状分类Classification of traits芽性状Bud traits枝条性状Shoot traits叶性状Leaf traits花性状Flower traits果实性状Fruit traits种子性状Seed traits TG/50/911216 1131 NY/T 256311220 11611654 112173 181
2.4.3 测试性状差异分析 TG/50/9有44个测试性状,其中质量性状2个、数量性状35个、假质量性状7个。NY/T 2563有51个测试性状,其中质量性状3个、数量性状33个、假质量性状15个。1654有52个测试性状,其中质量性状2个、数量性状40个、假质量性状10个(表4)。从表4可以看出,TG/50/9、NY/T 2563与1654测试性状完全相同的性状有21个,分级数不同的性状有10 个,表达状态不同的性状有2个,性状类型不同的性状有5个,观测部位不同的性状有1个,分级数及性状类型不同的性状有2个,表达状态及性状类型不同的性状有1 个,表达状态和代码对应不一致的性状有2个。
表4 葡萄品种DUS 测试指南测试性状对比
Table 4 Tested in different DUS test guidelines for Vitis L.

序号Serial number TG/50/9性状编号/性状名称Number/traits NY/T 2563性状编号/性状名称Number/traits 1654性状编号/性状名称Number/traits性状差异Differences in traits差异说明Difference in description 12341*1*1*萌芽始期Time of bud burst 2*嫩梢:梢尖开合程度Young shoot:openness of tip 3*嫩梢:梢尖匍匐茸毛密度Young shoot:density of prostrate hairs on tip 4*嫩梢:梢尖匍匐茸毛花青甙显色强度Young shoot:anthocyanin coloration of prostrate hairs on tip 5 嫩梢:梢尖直立茸毛密度Young shoot:density of erect hairs in shoot tip 6*幼叶:正面颜色Young leaf:color of the upper side 7*幼叶:背面主脉间匍匐茸毛密度Young leaf:prostrate hairs between main veins on lower side of blade 8 幼叶:背面主脉上直立茸毛密度Young leaf:erect hairs on main veins on lower side 9 新梢:姿态(引绑前)Shoot:form(before tying)XT 2*2*XT 3*3*XT 4*4*XT----5295 FJ TG/50/9 和1654 此性状分为9 级,NY/T 2563 此性状分为5 级。In TG/50/9 and 1654,this trait is divided into 9 levels,and in NY/T 2563 it is divided into 5 levels.67895*6*XT 6*7*XT--308 FJ TG/50/9 和1654 此性状分为9 级,NY/T 2563 此性状分为5 级。In TG/50/9 and 1654, this trait is divided into 9 levels, and in NY/T 2563,it is divided into 5 levels.319 FJ XZ 103210 XZ TG/50/9 和1654 此性状为数量性状,分为9 级;NY/T 2563 此性状为假质量性状,分为5 级。In TG/50/9 and 1654, this trait is a quantitative trait and divided into 9 levels;In NY/T 2563,this trait is a pseudo-qualitative trait and divided into 5 levels.TG/50/9 和1654 此性状为数量性状,NY/T 2563 此性状为假质量性状。TG/50/9 and 1654 define this trait as a quantitative trait,while NY/T 2563 defines it as a pseudo-qualitative trait.117*11*XZ TG/50/9 和1654 此性状为数量性状,NY/T 2563 此性状为假质量性状。TG/50/9 and 1654 define this trait as a quantitative trait,while NY/T 2563 defines it as a pseudo-qualitative trait.1210 新梢:节间背侧颜色Shoot:color of dorsal side of internodes 11*新梢:节间腹侧颜色Shoot:color of ventral side of internodes 12 新梢:节背侧颜色Shoot:color of dorsal side of nodes 3412 XZ TG/50/9 和1654 此性状为数量性状,NY/T 2563 此性状为假质量性状。TG/50/9 and 1654 define this trait as a quantitative trait,while NY/T 2563 defines it as a pseudo-qualitative trait.
表4 (续) Table 4 (Continued)

序号Serial number TG/50/9性状编号/性状名称Number/traits NY/T 2563性状编号/性状名称Number/traits 1654性状编号/性状名称Number/traits性状差异Differences in traits差异说明Difference in description 133313 XZ TG/50/9 和1654 此性状为数量性状,NY/T 2563 此性状为假质量性状。TG/50/9 and 1654 define this trait as a quantitative trait,while NY/T 2563 defines it as a pseudo-qualitative trait.1413 新梢:节腹侧颜色Shoot:color of ventral side of nodes 14 新梢:节间直立茸毛密度Shoot:erect hairs on internodes 3514 FJ 153615 XT TG/50/9 和1654 此性状为数量性状,分为9 级;NY/T 2563 此性状为假质量性状,分为5 级。In TG/50/9 and 1654, this trait is a quantitative trait and divided into 9 levels; in NY/T 2563 it is a pseudo-qualitative trait and divided into 5 levels.-1615 新梢:卷须长度Shoot:length of tendrils 16*花序:花器类型Flower:sexual organs 8*17*FJ 179*18*XT TG/50/9 和1654 此性状分为4 级,表达状态为雄花/雄花和弱化的雌花/两性花/雌花;NY/T 2563 此性状分为3 级表达状态为雄花/雌能花/两性花。In TG/50/9 and 1654, this trait is divided into 4 levels, including fully developed male flower, male flower with weak development of female organs, bisexual flower and female flower;In NY/T 2563,this trait is divided into 3 levels,male flower/female flower/hermaphroditic flower.-1817*成龄叶:大小Mature leaf:size of blade 18*成龄叶:形状Mature leaf:shape of blade 10*19*BD 193920 XT TG/50/9 和1654 此性状表达状态为心形/楔形/近五角形/近圆形/肾形;NY/T 2563 此性状表达状态为心形/近三角形/近五角形/近圆形/肾形。TG/50/9 and 1654 describe this trait as cordate, wedgeshaped, pentagonal, circular, or kidney-shaped; NY/T 2563 describes it as cordate, triangular, pentagonal, circular, or kidney-shaped.-2019 成龄叶:泡状突起Mature leaf:blistering of upper side of blade 20*成龄叶:裂片数Mature leaf:number of lobes 11*21*BD XZ 214022 XT TG/50/9 此性状为数量性状,表达状态为一裂/三裂/五裂/七裂/多于七裂;NY/T 2563 此性状为数量性状,表达状态为无/三裂/五裂/七裂/多于七裂;1654 此性状为假质量性状,表达状态为一裂/三裂/五裂/七裂/多于七裂。In TG/50/9, this trait is a quantitative trait and described as one, three, five, seven, and more than seven lobes; In NY/T 2563,it is also a quantitative trait including none,three,five,seven and more than seven lobes;in 1654,this trait is a pseudo-qualitative trait, including one, three, five, seven and more than seven lobes.-2221 成龄叶:上裂刻深度Mature leaf:depth of upper lateral sinuses 22 成龄叶:上裂刻裂片开叠类型Only varieties with lobed leaves:Mature leaf:arrangement of lobes of upper lateral sinuses 4123 FJ TG/50/9 和1654 此性状分为4 级,表达状态为开张/闭合/轻度重叠/高度重叠;NY/T 2563 此性状分为3 级,表达状态为开张/闭合/重叠。In TG/50/9 and 1654, this trait is divided into 4 levels, including open, closed, slightly overlapped and strongly overlapped; in NY/T 2563 it is divided into 3 levels, open,closed,and overlapped.,
表4 (续) Table 4 (Continued)

序号Serial number TG/50/9性状编号/性状名称Number/traits NY/T 2563性状编号/性状名称Number/traits 1654性状编号/性状名称Number/traits性状差异Differences in traits差异说明Difference in description 2323*成龄叶:叶柄洼开叠类型Mature leaf:arrangement of lobes of petiole sinus 12*24*FJ XZ 2413*25*FJ 2514*26*XT TG/50/9 此性状为数量性状,分为9 级,表达状态为极开张/高度开张/半开张/轻度开张/闭合/轻度重叠/中度重叠/高度重叠/极重叠;NY/T 2563 此性状为数量性状,分为7级,表达状态为极开张/开张/半开张/闭合/轻度重叠/中度重叠/高度重叠;1654 此性状为假质量性状,分为9 级,表达状态为极开张/高度开张/半开张/轻度开张/闭合/轻度重叠/中度重叠/高度重叠/极重叠。In TG/50/9,this trait is a quantitative trait and divided into 9 levels: very wide open, wide open, half open, slightly open,closed, slightly overlapped, half overlapped, strongly overlapped, and very strongly overlapped; in NY/T 2563 it is a quantitative trait divided into 7 levels: very wide open, wide open, half open, closed, slightly overlapped, half overlapped,and strongly overlapped;in 1654 it is a pseudo-qualitative trait and divided into 9 levels: very wide open, wide open, half open, slightly open, closed, slightly overlapped,half overlapped,strongly overlapped,and very strongly overlapped.TG/50/9 和1654 此性状分为9 级,NY/T 2563 此性状分为5 级。In TG/50/9 and 1654, this trait is divided into 9 levels, and in NY/T 2563,it is divided into 5 levels.-2615*27*SC -2724*成龄叶:锯齿长度Mature leaf:length of teeth 25*成龄叶:锯齿长度/锯齿宽度之比Mature leaf:ratio length/width of teeth 26*成龄叶:锯齿形状Mature leaf:shape of teeth 27*成龄叶:正面主脉上花青甙显色强度Mature leaf:proportion of main veins on upper side of blade with anthocyanin coloration 16*28*BW 2817*29*XT TG/50/9 和1654 此性状观测花青甙着色的主脉总长度的比例,花青甙显色的中断不包括在该比例中。NY/T 2563此性状观测正面主脉上花青甙显色强度,观察叶片上表面的主要叶脉从基部到中部的花青甙显色强度。In TG/50/9 and 1654, this trait is recorded according to the proportion of colored main vein portion against the total length of the main vein, and the interruption of anthocyanin coloration was not included in this proportion. In NY/T 2563, the trait is observed as the color intensity on the frontal main veins and the color intensity on the upper surface of the leaves observed from the base to the middle of the main vein.-2918*30*XT -3028*成龄叶:背面主脉间匍匐茸毛密度Mature leaf:prostrate hairs between main veins on lower side of blade 29*成龄叶:背面主脉上直立茸毛密度Mature leaf:erect hairs on main veins on lower side of blade 30 成龄叶:叶柄长度/中脉长度之比Mature leaf:length of petiole compared to length of middle vein 3731 XT -
表4 (续) Table 4 (Continued)

序号Serial number TG/50/9性状编号/性状名称Number/traits NY/T 2563性状编号/性状名称Number/traits 1654性状编号/性状名称Number/traits性状差异Differences in traits差异说明Difference in description 31323334 35363738 39404142 31*浆果始熟期Time of beginning of berry ripening 32*果穗:大小(花序梗除外)Bunch:size(peduncle excluded)33*果穗:密度Bunch:density 34*果穗:穗梗长度Bunch:length of peduncle of primary bunch 35*果粒:大小Berry:size 36*果粒:形状Berry:shape 37*果粒:果皮颜色(未开花)Berry:color of skin(without bloom)38 果粒:果粒与果柄分离难易程度Berry:ease of detachment from pedicel 39 果粒:果皮厚度Berry:thickness of skin 40*果粒:果肉花青甙显色强度Berry:anthocyanin coloration of flesh 41果粒:果肉硬度Berry:firmness of flesh 42*果粒:香型Berry: particular flavor 19*20*21*22*23*24*25*474826*4927*32*33*34*35*37*38*39*414244*4549*XT XT XT XT XT BD FJ SC FJ XT XZ FJ-----TG/50/9 和1654 此性状表达状态为扁圆形/圆形/宽椭圆形/长椭圆形/圆柱形/钝卵圆形/卵圆形/倒卵圆形/弯形/手指形;NY/T 2563 此性状表达状态为圆柱形/长椭圆形/椭圆形/圆形/扁圆形/卵圆形/钝卵圆形/倒卵圆形/弯形/束腰形。TG/50/9 and 1654 describe this trait as obloid, globose,broad ellipsoid, narrow ellipsoid, cylindrical, obtuse ovoid,ovoid, obovoid, horn-shaped, or finger-shaped; NY/T 2563 as cylindrical, narrow ellipsoid, ellipsoid, globose, obolid,ovoid,obtuse ovoid,obovoid,horn-shaped and waist-shaped.TG/50/9 和1654 此性状分为9 级,表达状态为绿色/黄绿色/黄色/红黄色/淡红色/红色/灰红色/深紫红色/蓝黑色NY/T 2563 此性状分为8 级,表达状态为绿色/黄绿色/黄色/粉红色/红色/暗红色/紫黑色/蓝黑色。TG/50/9 and 1654 divide this trait into 9 levels: green, yellow green, yellow, yellow rose, rose, red, grey red, dark red violet, and blue black; NY/T 2563 divides it into 8 levels:green, yellow green, yellow, pink, red, dark red, purpleblack or blue-black.-TG/50/9 和NY/T 2563 此性状分为3 级,1654 此性状分为9 级。TG/50/9 and NY/T 2563 this characteristic is divided into 9 levels,and 1654 this characteristic is divided into 5 levels.-TG/50/9 和1654 此性状为数量性状,NY/T 2563 此性状为假质量性状。In TG/50/9 and 1654, this trait is a quantitative trait; in NY/T 2563 it is a pseudo-qualitative trait.TG/50/9和1654此性状分为5级,表达状态为无/玫瑰香型/狐香型/青草型/其他;NY/T 2563 此性状分为6 级,表达状态为无/玫瑰香型/草莓香型/狐香型/青草型/其他。In TG/50/9 and 1654, this trait is divided into 5 levels: none,muscat, foxy, herbaceous and other odor than muscat, foxy or herbaceous;in NY/T 2563 it is divided into 6 levels:none,muscat,strawberry flavor,foxy,herbaceous and other odors.;
表4 (续) Table 4 (Continued)

序号Serial number TG/50/9性状编号/性状名称Number/traits NY/T 2563性状编号/性状名称Number/traits 1654性状编号/性状名称Number/traits性状差异Differences in traits差异说明Difference in description 4343*果粒:种子的形成Berry:formation of seeds 28*50*FJ 445151 XT TG/50/9 和1654 此性状分为3 级,表达状态为无/有败育痕迹/有;NY/T 2563 此性状分为4 级,表达状态为无/败育类型Ⅰ/败育类型Ⅱ/正常。In TG/50/9 and 1654, this trait is divided into 3 levels: none,rudimentary and complete; in NY/T 2563 it is divided into 4 levels:none,fertile type Ⅰ,fertility type Ⅱ,and normal.-4544 成熟枝条:主要色泽Woody shoot:main color----46----47----48495051 38 成龄叶:叶柄洼受叶脉限制类型Mature leaf:petiole depressions are limited by the type of leaf veins 42 成龄叶:下裂刻裂片开叠类型Mature leaf:arrangement of lobes of lower lateral sinuses 43 成龄叶:横截面形状Mature leaf:cross-sectional shape 44果穗:形状Bunch:shape 45果穗:歧肩Bunch:shoulders 46果粒:质量Berry:weight 50果粒:果皮涩味Berry:the peel is astringent----52535455 565758------------------16花序:花穗长度Flower:length of flower clusters 36果穗:穗梗颜色Bunch:color of peduncle 40果粒:果粉Berry:bloom 43果粒:果肉与果皮分离难易程度Berry:separation of skin and flesh 46果粒:果肉的特性Berry:character of flesh 47果粒:果汁的甜度Berry:Sweetness of flesh juice 48果粒:果汁的多少Berry:juiciness of flesh----------------------
表4 (续) Table 4 (Continued)
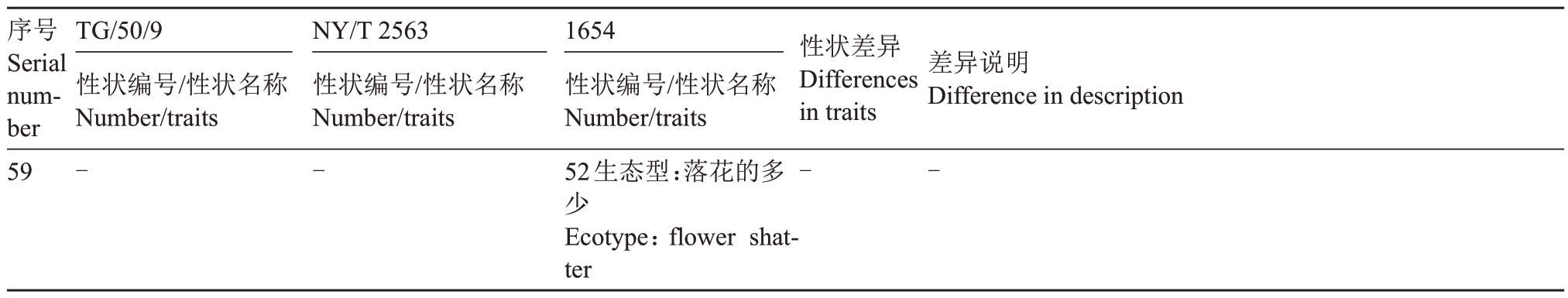
注:FJ.分级数不同;XT.无差异;BD.表达状态不同;XZ.性状类型不同;BW.观测部位不同;SC.表达状态和代码对应不同;TG/50/9、NY/T 2563 以及1654 性状名称相同时将NY/T 2563、1654 性状名称省略。
Note: FJ. different grades; XT. no difference; BD. different expression status; XZ. different trait type; BW. different observation site; SC. different expression status and code correspondence;TG/50/9,NY/T 2563 and 1654 Omit the names of NY/T 2563 and 1654 traits when the trait names are the same.
序号Serial number TG/50/9性状编号/性状名称Number/traits NY/T 2563性状编号/性状名称Number/traits 1654性状编号/性状名称Number/traits性状差异Differences in traits差异说明Difference in description 59--52生态型:落花的多少Ecotype:flower shatter--
除此之外,TG/50/9、1654 和NY/T 2563 在萌芽始期、始花期、浆果始熟期的观测时期以及在新梢性状和成龄叶性状上的观测部位不同。TG/50/9 和1654萌芽始期的观测时期为“当50%的植株处于芽萌发阶段”,NY/T 2563 为“当约5%的芽眼萌发时为萌芽开始期”。TG/50/9 和1654 始花期的观测时期为“10%花帽脱落”,NY/T 2563 为“5%花帽脱落”。TG/50/9 和1654 浆果始熟期的观测时期为“当50%的植株上约50%的浆果开始变软,用手指轻轻按压会变形”,NY/T 2563 为“当有色品种果粒开始显浅色,黄色、绿色品种开始变软为果粒始熟期,5%的果粒始熟”。TG/50/9 新梢的观测部位为“在嫩枝的三分之一处”,1654 和NY/T 2563 为“在树体中部的枝条上”。TG/50/9 和1654 成龄叶的观测部位为“在花序正上方枝条中间三分之一的叶片上”,NY/T 2563为“在新梢的第7~9枚叶片上”。
3 讨论与分析
国际植物新品种保护联盟,简称UPOV(International Union For The Protection Of New Varieties Of Plants),它是一个政府间的国际组织,主要协调和促进成员国之间在行政和技术上的合作[14]。UPOV是由《保护植物新品种国际公约》建立的,该公约于1961 年在巴黎通过,并进行了3 次修订呈现3 个版本,分别为1972 年文本、1978 年文本和1991 年文本[15]。我国于1999 年4 月23 日正式加入UPOV,执行1978 年文本,从此开始实施植物新品种保护制度,并不断研制和修订相应的DUS 测试指南,以促进我国植物新品种保护事业的快速发展。
品种登记、品种权申请等工作的关键环节是进行DUS 测试,而开展DUS 测试的重要依据是DUS测试指南,因此,研制科学合理的DUS 测试指南具有重要意义[16-17]。迄今为止,UPOV 已发布337 份DUS 测试指南(https://www.upov.int/test_guidelines/en/),在指导和统一各成员国DUS 测试和品种描述等方面发挥了重要作用[18]。同时,UPOV 鼓励各个成员国承担标准的修订工作,以更好地满足产业和育种人的需求。随着国家对植物知识产权保护的日益重视和对新品种选育工作的稳定支持,国内育成品种日益增多,每年报道审定登记葡萄品种30 余个,新的性状类型不断出现,建议加快推进葡萄品种测试指南的修订,结合田间实践的同时也要与国际葡萄DUS测试指南接轨,制定出更加完善且适于我国的葡萄品种DUS测试指南,为我国葡萄品种的选育和保护提供有力的保障。
通过上述比较分析,表明了3 个指南在提交繁殖材料的质量要求、测试周期、附加测试、带星号性状上是一致的,但由于三者在一些方面的要求不一致或者在中国、UPOV 和日本葡萄DUS 测试指南中的某1 个或某2 个指南中并未对某方面的要求进行陈述,所以三者在提交繁殖材料的质量和形式要求、测试周期、测试地点、附加测试、带星号性状等方面基本一致,在提交繁殖材料的数量要求、DUS 判定标准、测试性状、基本性状、分组性状、选测性状、技术问卷性状等方面的要求不尽相同。笔者通过系统比对、分析TG/50/9、NY/T 2563与1654的异同,并结合实际对葡萄品种DUS测试提出以下修订建议(表5)。
表5 NY/T 2563 修订建议
Table 5 NY/T 2563 revision suggestions

序号Serial number原文Original修改意见Revise opinion修改理由Reason for revision 1建议提交的植物材料的最低数量为5株The minimum amount of recommended plant material to be submitted is 5 plants适当减少提交的材料数量不会给试验结果造成影响,材料过多造成工作量大增Appropriately reducing the number of submitted materials will not affect the test results, and the excessive amount of materials will greatly increase the workload 2建议修改为;应采用1%的群体标准和至少95%的接受概率,在样本大小为5 株时,不允许有异型株It is recommended to amend to: a population standard of 1% and a probability of at least 95% acceptance should be used, and no deformed plants are allowed when the sample size is 5 strains减小样本大小,减少工作量,提高测试效率Reduce sample size, reduce workload, and improve test efficiency 3繁殖材料的要求:提交的自根苗数量不少于10株,或插条不少于50芽Requirements for propagation material: the number of self-rooted seedlings submitted is not less than 10 plants,or the cuttings not less than 50 buds一致性的判定:采用1%的群体标准和至少95%的接受概率,当样本大小为10 株时,最多可以允许有1 个异型株Determination of uniformity: Using a population standard of 1% and a probability of at least 95% acceptance, when the sample size is 10 plants, a maximum of 1 heterotypic strain can be allowed性状8“花序:花器类型”表达状态为“雄花/雌能花/两性花”Characteristic8“Flower: sexual organs”the expression state is male flower/female flower/hermaphroditic flower建议将表达状态修改为“雄花/雄花和弱化的雌花/两性花/雌花”It is recommended to change the expression state to“male/male flowers and weakened female flowers/hermaphroditic flowers/female flowers”4建议将表达状态修改为“一裂/三裂/五裂/七裂/多于七裂”It is recommended to change the expression state to“one/three/five/seven/more than sevens”花器类型中除了雄花、雌能花、两性花之外还有另外一种花器类型的存在,即雄花和弱化的雌花并存In addition to male flowers,female flowers,and hermaphroditic flower , there is another type of sexual organs , that is, the coexistence of male flowers and weakened female flowers无裂片即无裂刻的成龄叶,为在表述上与国际测试指南统一,建议将“无”改为“一裂”For mature leaves without splits, it is recommended to change“none”to“one split”in order to be consistent with the international test guidelines.5性状11“成龄叶:裂片数”表达状态为“无/三裂/五裂/七裂/多于七裂”Characteristic11“Mature leaf: number of lobes”the expression state is“none/three/five/seven/more than sevens”性状15“成龄叶:锯齿形状”分为5级,表达状态为“两侧凸/两侧直/两侧凹/一侧凸,一侧凹/两侧直与两侧凸混合型”Characteristic15 “Mature leaves:shape of teeth”is divided into 5 levels, and the expression status is“both sides convex/both sides straight/both sides concave/one side convex, one side concave/mixture of both sides straight and both sides convex”建议增加1个表达状态“两侧直一侧凸一侧凹混合型”It is recommended to add 1 expression state“both sides straight, one side convex, one side concave mixed type”成龄叶的锯齿形状中存在“两侧直一侧凸一侧凹混合型”There is a“ both sides straight, one side convex,one side concave mixed type ”in the sawtooth shape of mature leaves
表5 (续) Table 5 (Continued)

序号Serial number原文Original修改意见Revise opinion修改理由Reason for revision 6性状20“果穗:大小”Characteristic20“Bunch:size”建议将该性状拆分为“果穗:长度”和“果穗:宽度“2个数量性状It is recommended to split this characteristic intotwoquantitativecharacteristics:“Bunch:Length”and“Bunch:Width”7建议将该性状增加一个表达状态“窄指形”It is recommended to add an expression state to the characteristic"narrow finger shape"果穗大小是用投影面积表示的,果穗大小(cm²)=穗长(cm)(不包括穗梗)×穗宽(cm),用此方法计算的面积不够准确,并且在已知穗长和穗宽的情况下再计算出面积比较繁琐,原本的穗长和穗宽已经可以作为判定新品种的2个性状并且更加准确实用Panicle size is expressed in terms of projected area,panicle size (cm²) = panicle length (cm) (excluding panicle stem)×panicle width(cm),the area calculated by this method is not accurate enough, and it is more cumbersome to calculate the area under the condition of known panicle length and panicle width, the original panicle length and panicle width can already be used as two characteristics to determine the new variety and more accurate and practical束腰形为较宽的手指形,增加一个窄指形更有利于品种的区分The corset waist shape is a wider finger shape, and adding a narrow finger shape is more conducive to the differentiation of varieties 8性状24“果粒:形状”分为10 级,表达状态为“圆柱形/长椭圆形/椭圆形/圆形/扁圆形/卵圆形/钝卵圆形/倒卵圆形/弯形/束腰形”Characteristic 24“Berry: shape”is divided into 10 levels,and the expression status is”cylindrical/ narrow ellipsoid/ ellipsoid/ globose/ obloid/ovoid/ obtuse ovoid/ obovoid/hornshaped/waist-shaped”性状36“新梢:卷须长度”Characteristic 36“Shoot: length of tendrils”建议将该性状删除It is recommended that the characteristic be removed 9增加性状Increases the characteristics “果粒:酒窝凹陷的有无”“Berry:presence of a dimple”1011萌芽始期:当约5%的芽眼萌发时为萌芽开始期Time of bud burst: The bud- onset phase occurs when about 5% of the buds germinate选测性状中数量性状的代码表示为“1/2/3/4/5”The code for the quantitative characteristics in the additional characteristics is expressed as“1/2/3/4/5”建议修改为“当50%的植株处于芽萌发阶段为萌芽开始期”Suggested revision to“When 50% of the plants are in the bud germination stage for the germination stage”建议将选测性状中数量性状的代码表示为“1/3/5/7/9”It is recommended that the code of the quantitative characteristic in the selected characteristic be expressed as“1/3/5/7/9”在实际应用中很少通过测量卷须的长度来判别品种,在测试指南中也未给出测量卷须具体部位和长度等级划分In practical applications, it is rare to determine the variety by measuring the length of the tendrils, and the specific parts of the measuring tendrils and the length grade are not given in the test guideline有些品种的果粒在未受到挤压等外界条件的影响下先天性存在凹陷,如IFG Six 等;无凹陷的品种如霞多丽Some varieties of fruit have congenital dimples without being affected by external conditions such as extrusion,such as IFG Six,etc.;varieties without dimples such as Chardonnay通过观察开始萌芽植株的百分比更方便萌芽始期的判定,并且更具有普遍性By observing the percentage of plants that begin to germinate, it is more convenient to determine the initial stage of germination and is more general在代码表示中,数量性状一般为“1/3/5/7/9”,同时也与国际DUS测试指南相统一In the code representation, the quantitative characteristic is generally“1/3/5/7/9”, which is also consistent with the international DUS test guidelines
[1] 王博,罗惠格,覃富强,陈祥飞,朱维,谢太理,曹雄军,白先进.葡萄花芽分化研究进展[J/OL].南方农业学报,2022:1-14[2022-07-04]http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/45.1381.S.20220406.1312.002.html.WANG Bo,LUO Huige,QIN Fuqiang,CHEN Xiangfei,ZHU Wei,XIE Taili,CAO Xiongjun,BAI Xianjin.Research progresses of grape floral differentiation[J/OL].Journal of Southern Agriculture,2022:1-14[2022-07-04]http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/45.1381.S.20220406.1312.002.html.
[2] 刘崇怀,孔庆山,潘兴.我国鲜食葡萄育种的种质基础与种质创新[J].果树学报,2002,19(4):256-261.LIU Chonghuai,KONG Qingshan,PAN Xing.Germplasm background of the grape varieties bred in China and its innovation[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2002,19(4):256-261.
[3] 王富强,张建,温常龙,樊秀彩,张颖,孙磊,刘崇怀,姜建福.基于KASP 标记的葡萄品种鉴定[J].中国农业科学,2021,54(13):2830-2846.WANG Fuqiang,ZHANG Jian,WEN Changlong,FAN Xiucai,ZHANG Ying,SUN Lei,LIU Chonghuai,JIANG Jianfu.Identification of grape cultivars based on KASP makers[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2021,54(13):2830-2846.
[4] 王富强,李贝贝,樊秀彩,张颖,刘崇怀,姜建福. 葡萄品种SSR 分子鉴定体系的建立及应用[J].果树学报,2020,37(9):1281-1293.WANG Fuqiang,LI Beibei,FAN Xiucai,ZHANG Ying,LIU Chonghuai,JIANG Jianfu. Establishment and application of SSR molecular identification system in grapevine[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2020,37(9):1281-1293.
[5] 樊欣欣.中国农业植物新品种权保护的法律研究[J/OL].分子植物育种,2022,1-11[2022-07-04].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220505.1037.003.html.FAN Xinxin. Legal research on protection of new variety rights of agricultural plants in China[J/OL].Molecular Plant Breeding,2022,1-11[2022-07-04].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220505.1037.003.html.
[6] 唐浩.植物品种特异性、一致性、稳定性测试总论[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2017.TANG Hao.General discussion of plant variety distinctness,uniformity,and stability tests[M].Beijing:China Agriculture Press,2017.
[7] UPOV.TG/50/9. Guidelines for the conduct of tests for distinctness,uniformity and stability of Grapevine[S].Geneva,2008.
[8] 农业部. 植物新品种特异性、一致性和稳定性测试指南:葡萄:NY/T 2563—2014[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2014.Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China.Guidelines for the conduct of tests for distinctness,uniformity and stability:Grapevine (Vitis L.):NY/T 2563—2014[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China,2014.
[9] 张峰.环塔里木盆地几种特色果树繁殖技术研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆农业大学,2009.ZHANG Feng. Study on propagation technique of several characteristic fruit trees around tarim basin in Xinjiang[D]. Wlumuqi:Xinjiang Agricultural University,2009.
[10] UPOV.TG/14/9. Guidelines for the conduct of tests for distinctness,uniformity and stability of apple[S].Geneva,2005.
[11] UPOV.TG/53/7 Rev. Guidelines for the conduct of tests for distinctness,uniformity and stability of peach[S]. Geneva,2010/2014.
[12] 杨旭红,杨扬.UPOV 测试指南研制程序和主要方法[J].中国种业,2013(1):16-18.YANG Xuhong,YANG Yang. UPOV test guideline development procedure and main method[J]. China Seed Industry,2013(1):16-18.
[13] 王汝锋,崔野韩,吕波,杨旭红,杨杨,杨坤. GB/T 19557.1—2004.植物新品种特异性、一致性和稳定性测试指南总则[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2004.WANG Rufeng,CUI Yehan,LÜ Bo,YANG Xuhong,YANG Yang,YANG Kun. GB/T19557. 1-2004. General directives for the conduct of tests of distinctness,uniformity and stability for new varieties of plants[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China,2004.
[14] 佚名.国际植物新品种保护联盟[J].烟台果树,2017(3):17.Anon. International union for the protection of new varieties of plants[J].Yantai Fruits,2017(3):17.
[15] 郭瑞华,崔野韩.“国际植物新品种保护联盟”简介[J].上海农业学报,2002(1):6.GUO Ruihua,CUI Yehan. Introduction to the“International union for the protection of new varieties of plants”[J].Acta Agriculturae Shanghai,2002(1):6.
[16] 单飞彪,闫文芝,杜瑞霞,王永行,杨钦方,刘春晖,白立华,刘静,贾静.中国和UPOV 向日葵品种DUS 测试指南比较分析[J].中国种业,2020(6):4-9.SHAN Feibiao,YANN Wenzhi,DU Ruixia,WANG Yongxing,YANG Qinfang,LIU Chunhui,BAI Lihua,LIU Jing,JIA Jing.Comparative analysis of test guidelines for distinctness,uniformity and stability of Sunflowers(Helianthus annuus L.) formulated by China and UPOV[J]. China Seed Industry,2020(6):4-9.
[17] 王斐,欧春青,张艳杰,姜淑苓,马力,赵亚楠.中国和UPOV梨品种DUS 测试指南比较分析[J].果树学报,2018,35(10):1271-1276.WANG Fei,OU Chunqing,ZHANG Yanjie,JIANG Shuling,MA Li,ZHAO Yanan. Comparative analysis of test guidelines for distinctness,uniformity and stability of pear (Pyrus L.) formulated by China and UPOV[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2018,35(10):1271-1276.
[18] 邓姗.我国茄子测试指南与UPOV 测试指南的比较分析[J].上海农业科技,2021(1):17-18.DENG Shan.Comparative analysis of test guidelines for distinctness,uniformity and stability of Solanum melongena L. formulated by China and UPOV[J].Shanghai Agricultural Science and Technology,2021(1):17-18.