杨梅(Myrica rubar Sieb. et Zucc.)为杨梅科(Myricaceae)杨梅属(Myrica Lour.)的常绿小乔木或灌木植物,果实初夏成熟,是我国长江以南地区重要的经济作物。但其优良品种大多数为中熟及晚熟品种[1],晚熟品种易受到南方“梅雨”危害而造成严重的经济损失。为此,浙江省农业科学院园艺研究所以培育早熟、优质、抗逆为育种目标,开展了早熟新品种选育工作,2008年在杭州萧山区进化镇早色杨梅种植区发现成熟期早且一致、果实均匀、风味独特的变异株,经过多年植物学、生物学、果实经济性状观察鉴定,表现稳定、一致,经分子生物学亲缘关系鉴定确认其与早色亲缘关系较近[2]。2019 年1 月获农业农村部植物新品种权证书(品种权号:CNA20170495.9),品种定名为早鲜(图1)。
1 选育过程
早鲜是2008 年在杭州萧山区进化镇的梅山休闲农庄杨梅种植区发现的早熟优良变异单株。2010年在早色大枝上采用全树嫁接方式高接该变异株;2016—2018年对母树及高接树观测,进行植物学特征、生物学特性和果实经济性状的调查。经过多年系统观察鉴定,早鲜杨梅早熟性好,成熟期一致,平均单果质量比早色增大9.64%,果实均匀,风味独特。
2 主要性状
2.1 果实主要经济性状
成熟期早,比早色提早5~7 d。果实圆球形,无果蒂凸环,完全成熟时果梗与果实易分离、果梗留枝,果面呈深红色,肉柱先端为圆钝形,缝合线浅。果型大,平均单果质量13.99 g,最大可达16.06 g,果形指数1.02,可食率91.17%;可溶性固形物含量(w,后同)12.54%,总糖含量8.46%,可滴定酸含量1.09%,柠檬酸含量1.05%,维生素C 含量59.88 mg·100 g-1,黄酮含量1.52 mg·g-1,多酚含量1.82 mg·g-1,果实味甜中带酸,带有其独特的鲜味(表1)。
表1 早鲜与早色杨梅品种的果实性状比较
Table 1 Comparison of fruit characters between Zaoxian and Zaose
品种Cultivar成熟期Mature period可食率Flesh recov -ery/%w(柠檬酸)Citric acid content/%w(维生素C)Vitamin C content/(mg·100 g-1)w(黄酮)Flavonoids content/(mg·g-1)w(多酚)Polyphenols content/(mg·g-1)风味Flavor早鲜Zaoxian 6月6日June 6th平均单果质量Average fruit weight/g 13.9991.17 w(可溶性固形物)Solid soluble content/%12.54 w(总糖)Total sugar content/%8.46 w(可滴定酸)Tiratable acid content/%1.091.0559.881.521.82早色Zaose 6月11-13日June 11-13 12.7690.519.306.290.880.7527.961.581.41味甜中带酸,具独特鲜味Tastes sweet and sour,with unique freshness甜酸Tastes sweet and sour
2.2 植物学特征
长势健壮,树势较弱,圆头形或开心形,枝梢分布稀疏,以中、短果枝结果为主。叶片长10.1 cm、宽3.0 cm、厚0.18 mm,叶色浓绿,呈窄倒卵圆形,先端形状为钝,叶缘全缘。葇荑花序,淡黄褐色,花序长1.54 cm、粗2.45 mm,花朵为羊角形。该品种具有耐低温特点,2018 年在浙江中部、北部地区普遍降雪的环境下,枝干未出现明显的冻害;2019 年通过对不同杨梅种质耐低温生理指标的测定,结合主成分分析和聚类分析,发现早鲜具备较强的耐低温能力[2];与早色相比,低温胁迫下枝条可溶性糖提高32.1%、相对电导率下降12.5%,适合浙北地区栽培,促进了杨梅种植区域北移。
2.3 生物学特性
在浙北地区,早鲜杨梅的初花期在3月上旬,盛花期在3月中下旬,终花期在4月初。每年抽梢2~3次,即春梢、夏梢或秋梢,春梢始于4 月上旬、长度11.88 cm,夏梢始于6 月中旬、长度7.23 cm,果实成熟始于6月初,成熟期比早色提早5~7 d。
2.4 生长结果习性与产量
以春梢为主要结果枝,花序坐果率30.1%,生理落果较轻;采摘时,一般果柄留在树上。果实成熟期一致,采摘期短,便于集中采收;结果均匀,无大小年结果现象。一般高接后6~8 a即进入盛产期,丰产稳产,平均666.7 m2产量可达800 kg。
2.5 分子鉴定
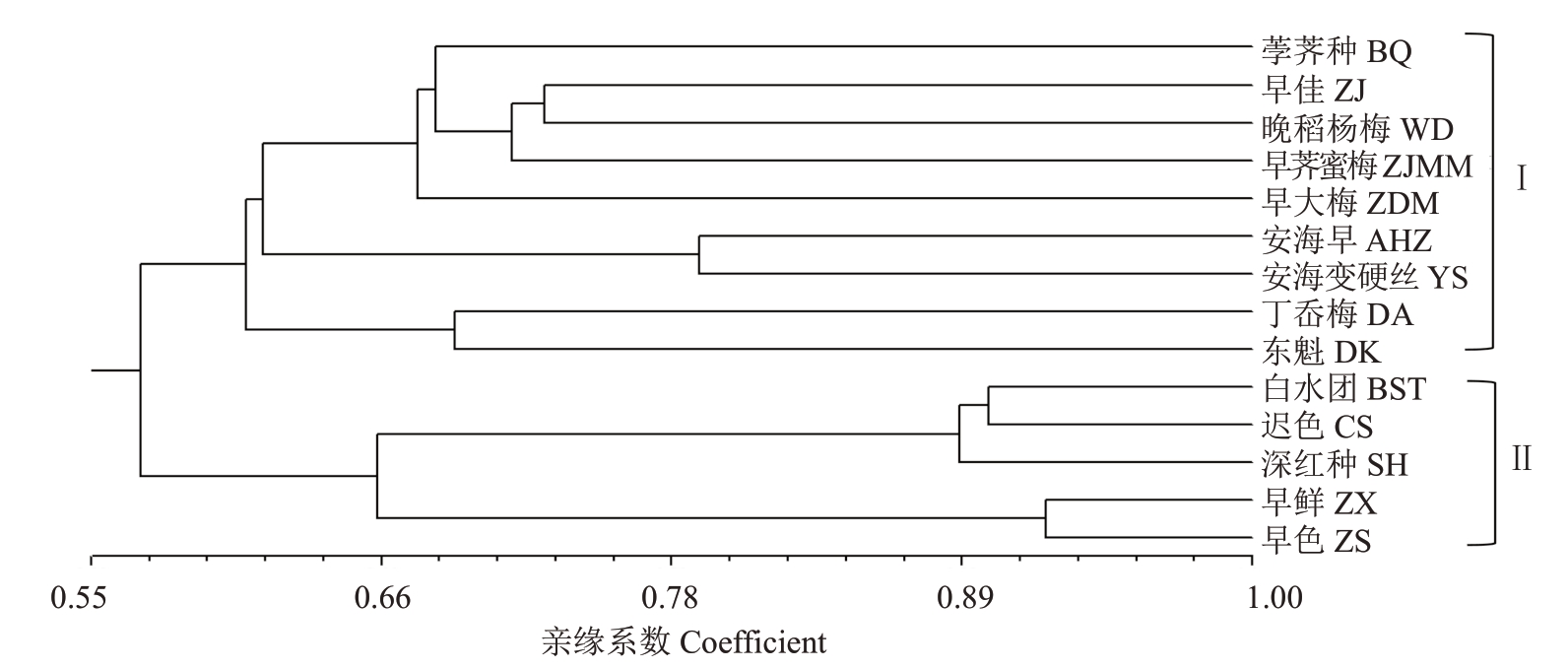
利用自主设计的59对gSSR引物和筛选到的40对MrEST-SSR引物,对14份杨梅主栽品种进行分子鉴定(图2):荸荠种(BQ)、丁岙梅(DA)、东魁(DK)、早鲜(ZX)、早色(ZS)、早大梅(ZDM)、早荠蜜梅(ZJMM)、白水团(BST)、迟色(CS)、安海早(AHZ)、安海变硬丝(YS)、深红种(SH)、晚稻杨梅(WD),引物zaas053可将早鲜与其他样品区分开,从分子水平证实早鲜没有与其他品种存在同物异名现象。
通过对早鲜及其他13 份杨梅材料进行聚类分析发现(图3):99 对标记可有效将14 份杨梅材料区分开来,并将其分为2 个群体,早鲜位于第Ⅱ亚群,并与其他13 个材料均存在差异,其中早鲜与早色的亲缘关系最为密切,亲缘系数为0.92,为新种质。
3 栽培技术要点
3.1 适栽区域
适宜在长江以南地区和气候相似的地区栽培,尤其适合浙北地区栽培。应尽量选择在富含石砾的酸性红壤或黄壤土上种植,园地土壤管理宜用自然生草法。
3.2 种植技术
育苗以嫁接繁殖为主,穗条采自该品种的花枝,用杨梅本砧进行枝接。每年3—4月、选择1~2年生根径粗度0.8~1.0 cm 的本砧苗嫁接花枝;嫁接苗移栽后及时遮阳、防止干旱。栽培株行距以5 m×5 m或5 m×6 m为宜。
3.3 整形修剪及花果管理
该品种以2 年生春梢为主要结果母枝,树体枝梢分布稀疏,生产上无需过多人工整枝与疏花疏果,省工省力。对部分徒长枝进行压枝、吊枝,剪去细弱枝、重叠枝、交叉枝、病虫枯枝[3]。
3.4 肥料管理
种植前3 a,采取逐年扩穴深施方法,每年上半年追肥约4次,每次每株施入复合肥约0.1 kg。进入结果期,每年春、夏、秋共施肥3次,每次每株施入纯硫酸钾1~2 kg,成年树的氮磷钾质量配比为1∶0.3∶4。秋冬季以施入生物有机肥为主,每次每株施入15~25 kg。重视硼、锌、钼等微量元素施用。
3.5 病虫害防治
加强常规性栽培管理,保持树冠通风透光,重视冬季清园。病虫危害较少,冬季及时对枝干进行涂白处理,雪后及时摇雪,防止树冠积雪损伤或压断枝条。
参考文献:
[1]张跃建,缪松林. 我国杨梅品种资源及利用[J]. 中国南方果树,1999,28(4):24-25.ZHANGYuejian,MIAO Songlin. Variety resources of red bayberry and their utilization in China[J].South China Fruits,1999,28(4):24-25.
[2]张淑文,梁森苗,朱婷婷,任海英,郑锡良,戚行江.不同杨梅品种间的耐低温能力比较[J].浙江农业学报,2020,32(10):1772-1779.ZHANG Shuwen,LIANG Senmiao,ZHU Tingting,REN Haiying,ZHENG Xiliang,QI Xingjiang. Cold tolerance of different Chinese bayberry varieties[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2020,32(10):1772-1779.
[3]梁森苗,郑锡良,陈新炉,张启,王华新,戚行江,任海英.早熟杨梅新品种‘早佳’的选育[J].果树学报,2016,33(2):249-253.LIANG Senmiao,ZHENG Xiliang,CHEN Xinlu,ZHANG Qi,WANG Xinhua,QI Xingjiang,REN Haiying.A new early-ripening bayberry cultivar‘Zaojia’[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2016,33(2):249-253.
A new early-ripening and low temperature resistant Chinese bayberry cultivar Zaoxian
LIANG Senmiao1,ZHANG Shuwen1,WANG Shifu2,ZHENG Xiliang1,QI Xingjiang1*
(1Institute of Horticultural Sciences, Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Hangzhou 310021, Zhejiang, China;2The Hangzhou Xiaoshan District Agriculture(Forestry)Technology Promotion Center,Xiaoshan 311202,Zhejiang,China)
Abstract:Zaoxian is a new early-ripening Chinese bayberry cultivar bred from an excellent variant individual plant found in the planting area of Zaose.The fruit is spherical,without a pedunculated convex ring. The fruit is dark red when fully ripe, and the flesh column is round and blunt. The average fruit weight is 13.99 g and can reach up to16.06 g. Flesh recovery is 91.17%. Soluble solid content is 12.54%,and total sugar content 8.46%.Titratable acid content is 1.09%;citric acid content 1.05%,and vitamin C content 59.88 mg·100 g-1.Therefore, the fruit of Zaoxian are sweet and sour, with a unique umami taste and high quality. The tree vigor is weak with few and sparse branches, and therefore the canopy has good ventilation and light transmission.The leaves are dark green, narrowly obvate, obtuse at the apex,with an entire leaf margin.Medium and short fruit branches dominate the fruit tree,thus the number of fruit on the branches is relatively uniform. The stalk and the pulp are easy to separate after maturity, and the cultivar is early bearing and has no alternative bearing phenomenon. Generally, it enters the peak production period 6-8 years after top grafting.It is productive with an average yield of 800 kg·666.7 m-2.In Xiaoshan district,Hangzhou,Zhejiang,Zaoxian fruit matures in early June 6,about 5-7 days earlier than Zaose. The cultivar has low-temperature tolerance. Under low-temperature stress,the soluble sugar content in the shoots increased by 32.1%, and the relative electric conductivity decreased by 12.5%. Therefore, Zaoxian is suitable for cultivation in northern Zhejiang and enables the northward expanding of bayberry planting area. Molecular identification using 99 gSSR and MrESTSSR markers showed that there were differences between Zaoxian and other 13 main cultivars of Chinese bayberry,and the relationship coefficient with Zaose was the largest,which was 0.92,proving Za-oxian a new variety.And Primer zaas 053 can distinguish Zaoxian from the other 12 varieties.It is suitable for cultivation in the south of the Yangtze River and areas with similar climate.It should be planted on acid red soil or yellow soil rich in gravel, and sod culture should be used for orchard soil management. Seedlings are mainly obtained via grafting propagation, and the scions are collected from the flowering branches of Zaoxian. From March to April every year, 1 to 2 year old rootstock seedlings with a stock diameter of 0.8-1.0 cm are selected for grafting.The grafted seedlings should be shaded in time after transplanting to prevent desiccation.The recommended spacing of planting is 5 m×5 m or 5 m×6 m.The spring shoot is the main fruit bearing branch of this variety.As the branches and shoots of the tree are sparsely distributed,there is no need for much manual pruning,flower thinning and fruit thinning in production. Some bare branches should be bent, and weak branches, overlapping branches and diseased shall be thinned out.In the first three years after planting,planting hole expansion and deep application of fertilizer is adopted.The top dressing is carried out 4 times in the first half of each year,and about 0.1 kg of compound fertilizer is applied to each plant each time.In the fruiting period,1-2 kg of pure potassium sulfate fertilizer is applied three times in spring,summer and autumn to each plant each time,and the ratio of nitrogen,phosphorus and potassium for adult trees is 1∶0.3∶4.Bioorganic fertilizer is mainly applied in autumn and winter,with 15-25 kg per plant each time.It is necessary to strengthen routine cultivation management, maintain reasonable ventilation and light transmission of tree crown,and pay attention to clearing the orchard in winter.There are few diseases and insect pests.In winter,the branches and stems shall be painted Lime-Sulphur-Synthetic-Solution in time,to prevent the freezing damage and the snow shall be shaken off from thee tree crown in time after snow to prevent branch crush.
Key words:Chinese bayberry;New cultivar;Zaoxian;Early-ripening;Low temperature resistance