草莓(Fragaria × ananassa Duch.)是一种多年生草本作物,具有较高的营养价值和经济价值。草莓适应能力强,在世界各地均有种植。近年来,随着现代都市农业的发展,中国草莓种植面积呈逐年上升趋势[1],但植物病害的频繁发生也严重制约着草莓产业的健康发展。草莓褐色叶斑病是新发现的一种真菌病害,目前在中国、巴西、比利时、美国、伊朗和韩国等地均有报道[2-7]。该病是由Pilidium concavum 和P.lythri 引起的病害,主要危害草莓叶片和果实,严重影响草莓的产量和品质。发病初期,叶片的中央出现圆形褐色病斑,随着病害的加重,病斑逐渐扩大形成褐色的同心轮纹症状。当前,草莓褐色叶斑病的防治研究还较少,常用化学药剂对其防效尚不清楚。另外,随着人们对食品安全问题的重视,以及长期使用化学农药造成环境污染等问题的出现,生物防治手段受到越来越多的关注。
利用拮抗菌防治植物病害是生物防治的重要手段之一。芽胞杆菌具有拮抗效果好、繁殖速度快、抗逆性强等特点,在植物病害防治方面表现出良好的应用前景[8]。贝莱斯芽胞杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)是芽胞杆菌中的一个种,在自然界中普遍存在。已有研究表明,贝莱斯芽胞杆菌中的部分菌株具有广谱拮抗活性,同时还能对作物产生促生的作用,在生产中表现出很好的应用潜力[9-10]。贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1 是从苹果枝干中分离获得,对苹果轮纹病菌(Botryosphaeria dothidea)、苹果腐烂病菌(Valsa mali)、苹果炭疽病菌(Colletotrichum gloeosporioides)和梨腐烂病菌(V.pyri)均表现强烈的拮抗活性,并且该内生细菌的使用不影响苹果的果实品质[11]。
笔者在本研究中分析了贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1 对草莓褐色叶斑病的防治效果,以及对草莓促生作用,为该拮抗菌在草莓病害生物防治中的应用奠定了基础。
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料
草莓褐色叶斑病菌(P.concavum)菌株CM2-4、贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1[11]均保存于中国农业科学院郑州果树研究所。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 拮抗活性鉴定 采用平板对峙实验[11],测定内生细菌贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1 对草莓褐色叶斑病菌生长抑制效果。在平板中央接种直径为0.5 cm的草莓褐色叶斑病菌饼,在距中央位置2 cm 四周各接种3 μL 贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1(OD600 =0.8)。每次接种3 个平皿,3 次重复。对照组不接种内生细菌。于25 ℃下黑暗培养10 d 后,采用十字交叉法测量草莓褐色叶斑病菌菌落直径,计算抑制率。抑制率(%)=(对照菌落直径-处理菌落直径)/(对照菌落直径)×100。同时,利用超景深三维立体显微镜观察草莓褐色叶斑病菌丝形态特征,并测量菌丝直径。
1.2.2 菌株P2-1 分泌酶活性分析 蛋白酶活性检测[12]:在脱脂牛奶培养基中心位置接种3 μL(OD600=0.8)的P2-1 菌株细胞悬液,25 ℃培养48 h后观察消解圈。
纤维素酶活性检测[12]:在CMC 培养基中心位置接种3 μL(OD600=0.8)的P2-1 菌株细胞悬液,25 ℃培养48 h 后,加入5 mL 刚果红染料染色30 min。倒掉染料,再加入5 mL 1 mol·L-1 NaCl 溶液脱色15 min,观察消解圈。
β-1,3-葡聚糖酶活性检测[13]:在苯胺蓝培养基中心位置接种3 μL(OD600 = 0.8)的P2-1 菌株细胞悬浮液,25 ℃培养48 h 后观察消解圈。
1.2.3 菌株P2-1 对草莓的促生作用 草莓(香野)移栽7 d 后,将5 mL P2-1 细胞悬浮液(108个·mL-1)灌根处理草莓,处理30 d 后调查植株株高、根长、鲜质量和干质量,水处理作为对照。每个处理20 棵苗,3 次重复。
1.2.4 菌株P2-1 在草莓叶片上定殖动态研究 参照Yuan 等[11]的方法,具体步骤如下:用菌株P2-1 细胞悬浮液(108 个·mL-1)喷施处理草莓叶片,分别于处理后0(处理后3 h)、1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9 和10 d取叶片组织(0.1 g),置于2 mL 离心管中,再加入1 mL 无菌水,利用研磨仪将其研磨均匀。取上清液梯度稀释后涂布于NA 平板上,28 ℃培养24 h 后进行菌落计数,最后将菌落数量乘以相应的稀释倍数,换算成0.1 g 叶片中含有的菌落数量。3 次重复。
1.2.5 菌株P2-1 对草莓褐色叶斑病的防治作用利用离体草莓叶片鉴定菌株P2-1 对草莓褐色叶斑病的防治作用,具体方法如下:选取健康、长势一致草莓叶片,经无菌水清洗干净后,用75%(φ)乙醇擦拭消毒,再用无菌水清洗,晾干。用菌株P2-1 细胞悬浮液(108 个·mL-1)喷施处理叶片,接种草莓褐色叶斑病菌饼(直径为0.5 cm),无菌水处理作为阴性对照(CK),戊唑醇(86 μg·mL-1)(安徽省银山药业有限公司)处理作为阳性对照。处理后用蘸无菌水的脱脂棉缠绕叶柄保湿,置于25 ℃下光照培养箱中培养,分别于5 d 和7 d 后测量病斑直径,并拍照。每次接种10 个斑,3 次重复。发病率(%)=(总接种点数-无病症的接种点数)/总接种点数×100。
2 结果与分析
2.1 贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1 对草莓褐色叶斑病菌的抑制活性
平板对峙实验结果显示,贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1 对草莓褐色叶斑病菌具有强烈的抑菌活性(图1)。当对照组的草莓褐色叶斑病菌落直径达到5.11 cm 时,对峙实验中的草莓褐色叶斑病菌仅有1.72 cm。统计结果显示,P2-1 对草莓褐色叶斑病菌的抑制率达到66.38%,抑菌带约为0.76 cm。
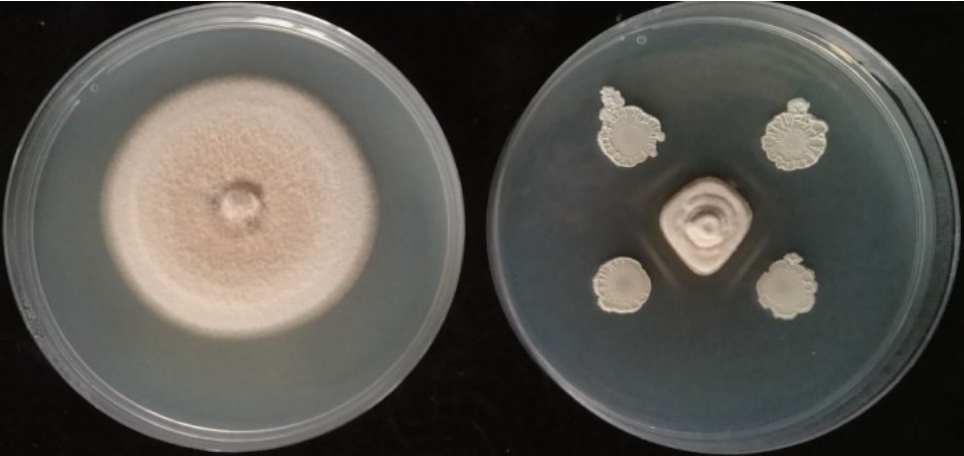
图1 贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1 对草莓褐色叶斑病菌的抑制作用
Fig.1 Inhibition effect of B.velezensis strain P2-1 on P.concavum
进一步观察菌丝形态特征,发现野生型草莓褐色叶斑病菌光滑通透,粗细均匀,而经P2-1 拮抗处理的菌丝出现断裂、消解、纤细、透明等畸形现象(图2-A~B)。菌丝直径测量结果显示,对照菌丝直径约为7.71 μm,而拮抗处理后菌丝直径仅为4.12 μm(图2-C)。这些结果表明,贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1 能显著影响草莓褐色叶斑病菌菌丝形态特征。

图2 贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1 对草莓褐色叶斑病菌菌丝的抑制作用
Fig.2 Effect of B.velezensis strain P2-1 on mycelia of P.concavum
2.2 菌株P2-1分泌酶活性
菌株P2-1 在脱脂牛奶培养基和CMC 培养基中能形成明显的透明圈,但在苯胺蓝培养基中不能形成明显的透明圈(图3),表明菌株P2-1 代谢产物中含有蛋白酶和纤维素酶活性,但不具有β-1,3-葡聚糖酶活性。
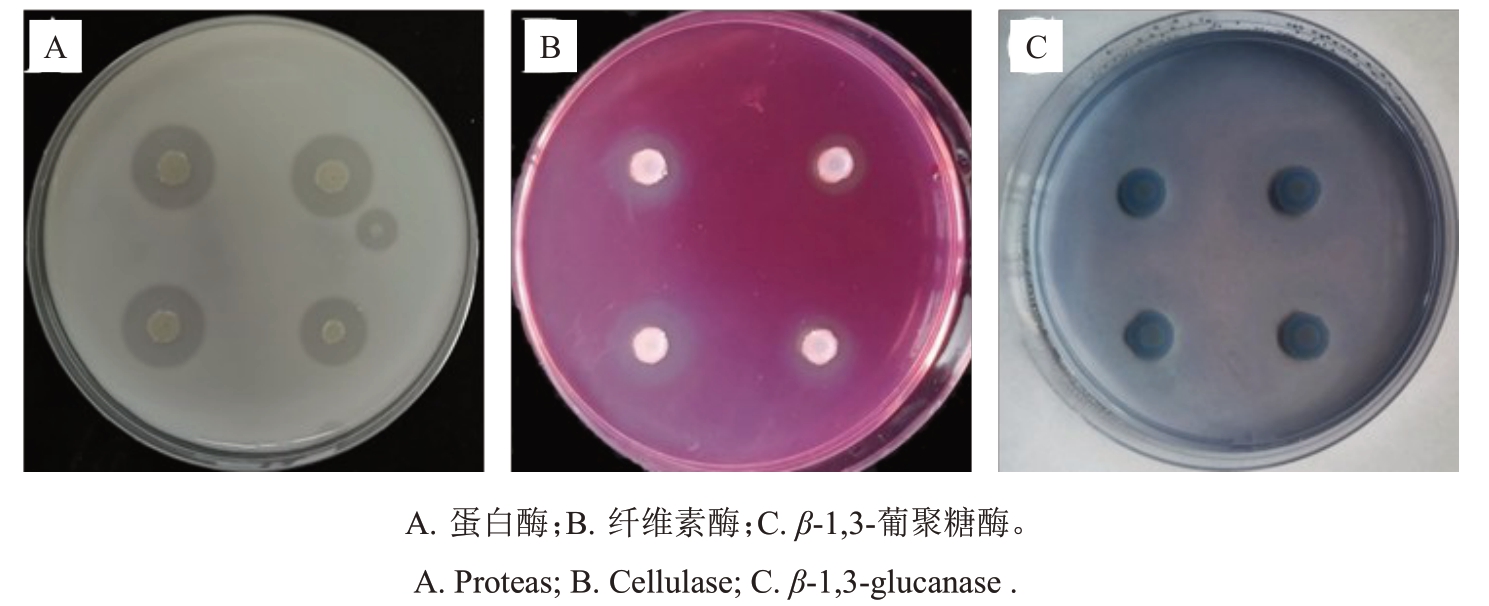
图3 贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1 分泌酶活性测定
Fig.3 Detection of secretase activity of B.velezensis strain P2-1
2.3 菌株P2-1在草莓叶片上的定殖动态分析
统计结果显示,喷施处理草莓叶片后,菌株P2-1菌落数量迅速上升,7 d 后达到最大值,菌落数量为1.15×1010 CFU。随后,菌落数量呈下降趋势,处理10 d 后,菌落数量趋于稳定,维持在4.07×108CFU 左右(图4)。
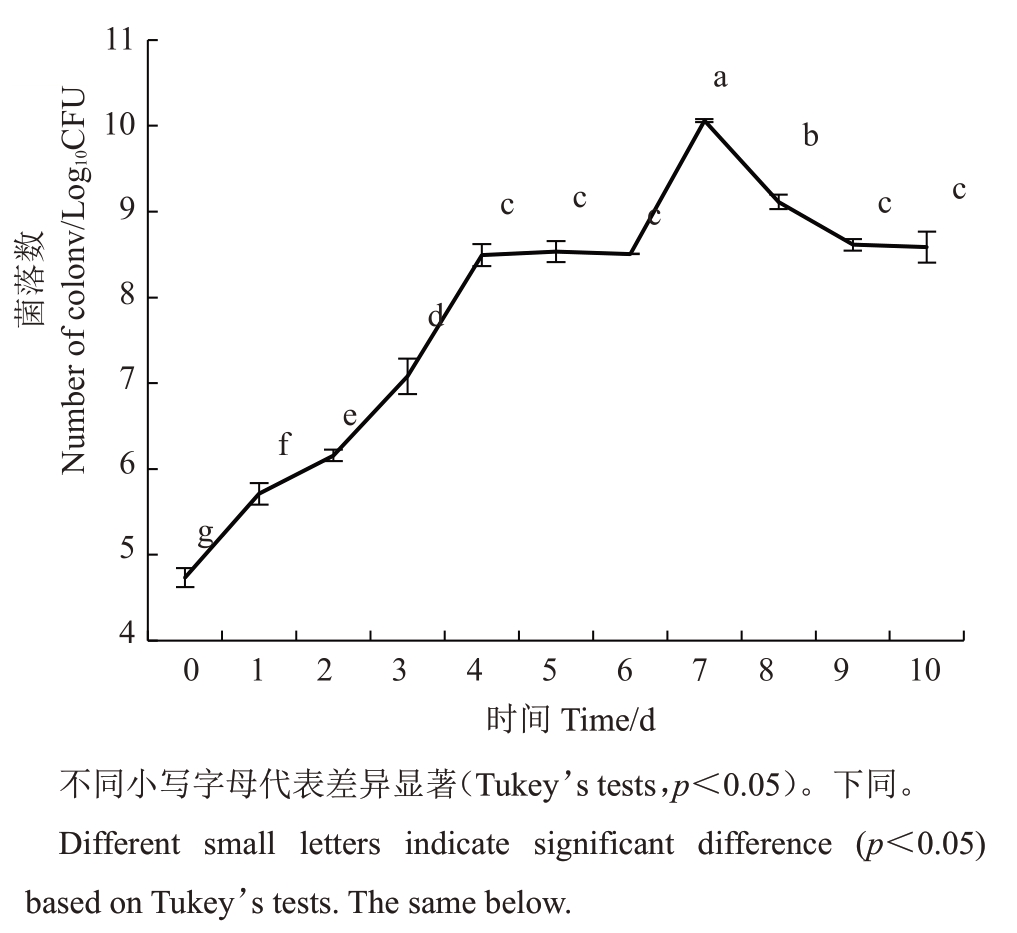
图4 贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1 在草莓叶片定殖动态
Fig.4 Colonization dynamics of B.velezensis strain P2-1 in leaves of strawberry
2.4 菌株P2-1对草莓褐色叶斑病的防治作用
为了明确菌株P2-1 对草莓褐色叶斑病的防治效果,利用离体草莓叶片进行鉴定。鉴定结果显示,与CK 处理相比,菌株P2-1 细胞悬浮液处理能显著抑制草莓褐色叶斑病的发病程度(图5-A)。进一步统计结果显示,与CK 处理相比,菌株P2-1 处理后草莓褐色叶斑病的发病率和病斑直径均显著降低(图5-B~C)。接种5 d 后,菌株P2-1 处理的草莓叶片发病率约为33.33%,平均病斑直径为1.63 cm,显著低于CK 处理(图5-B~C)。与接种5 d 相比,接种7 d 后各种处理的病斑直径均增加,但菌株P2-1 处理和阳性对照戊唑醇(Tebuconazole)处理仍均显著低于CK(图5-C)。以上结果表明,菌株P2-1 对草莓褐色叶斑病具有较好的防治潜力。

图5 贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1 对草莓褐色叶斑病发病程度的影响
Fig.5 Effect of B.velezensis strain P2-1 on inhibition of tan-brown leaf spot of strawberry
2.5 菌株P2-1对草莓的促生作用
菌株P2-1 细胞悬浮液能显著促进草莓的生长。统计结果显示,与对照草莓相比,经菌株P2-1细胞悬浮液处理后草莓的株高、根长、湿质量和干质量均显著提高(表1),分别提高24.83%、40.74%、28.88%和37.40%。
表1 贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1 对草莓生长量的影响
Table 1 Effect of B.velezensis strain P2-1 on plant growth of strawberry
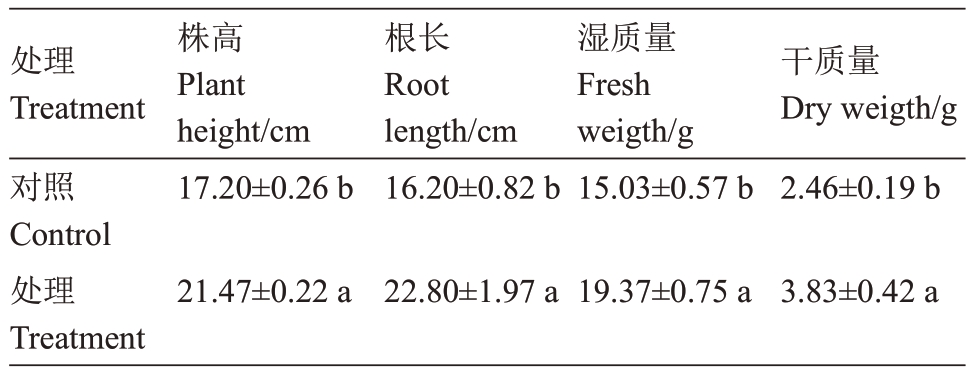
注:表中数据为平均值±标准误。
Note:Date are mean±SE.
处理Treatment对照Control处理Treatment株高Plant height/cm 17.20±0.26 b根长Root length/cm 16.20±0.82 b湿质量Fresh weigth/g 15.03±0.57 b干质量Dry weigth/g 2.46±0.19 b 21.47±0.22 a 22.80±1.97 a 19.37±0.75 a 3.83±0.42 a
3 讨 论
草莓褐色叶斑病是近几年在草莓上出现的一种新的真菌病害,在世界范围内普遍发生,严重威胁草莓产业的健康发展。然而,当前有关草莓褐色叶斑病生物防治的研究还很少,可利用草莓褐色叶斑病生防菌也很有限。贝莱斯芽胞杆菌是一种重要的生防菌资源,对多种植物病原细菌和真菌都具有较强的抑制活性,并且具有促进植物生长的特性,在生产中表现出巨大的应用前景。仇月等[14]报道了贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株SDTB038 对草莓枯萎病具有较好的防治效果。姚锦爱等[15]报道了贝莱斯芽胞杆菌株ZZBV-3 对草莓根腐病具有较好的防治效果。冯江鹏等[16]发现贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株JK3 对草莓胶孢炭疽菌具有较好的抑制活性。目前,尚无贝莱斯芽胞杆菌防治草莓褐色叶斑病的相关报道。笔者在本研究中发现,贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1 对草莓褐色叶斑病菌具有强烈的拮抗活性,是一种潜在的草莓褐色叶斑病拮抗菌资源,该研究结果拓宽了拮抗菌株P2-1 潜在的应用范围。
生防菌可通过分泌抗菌化合物发挥拮抗活性。贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株AR1 能够通过次级代谢产物5-N-tyrosinylornithine 直接抑制病原真菌的生长[17]。贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株HC6 能分泌3 种具有拮抗活性的脂肽化合物,包括伊枯草菌素A、表面活性素和丰原素[18]。笔者在本研究中发现,经贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1 处理后,草莓褐色叶斑病菌出现断裂、消解、纤细、透明等畸形现象。进一步结果显示,菌株P2-1 可能通过其代谢产物的蛋白酶和纤维素酶活性,降解草莓褐色叶斑病菌细胞壁,使菌丝表现出畸形现象,从而拮抗菌丝的生长。黄艺烁等[12]同样发现,多粘类芽胞杆菌菌株(Paenibacillus polymyxa)ZF197 也是通过代谢产物中的蛋白酶和纤维素酶破坏立枯丝核菌(Rhizoctonia solani)细胞壁,导致菌丝产生畸形。
生防菌定殖能力与其防治效果及稳定性紧密相关[19-20]。菌株P2-1 是从苹果枝干中分离获得,但它在草莓叶片上同样表现出很好的定殖能力,处理10 d后菌落数量仍可维持较高的定殖密度,展示了良好的应用潜力。进一步的草莓褐色叶斑病防效实验结果显示,菌株P2-1 能有效降低草莓褐色叶斑病的发病率和发病程度,其防治效果与化学农药戊唑醇相当,表现出潜在的应用潜力,为后续发开生防菌剂奠定了基础。
贝莱斯芽胞杆菌不仅具有广谱的拮抗活性,还具有植株促生作用。Liu 等[21]发现,贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株D4 通过分泌铁载体以及溶磷作用促进番茄的生长。贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株NKG-2 同样能明显促进番茄的生长[22]。本研究得出类似的结果,即菌株P2-1 能显著促进草莓植株的生长,但其具体促生机制还有待深入的研究。总体而言,贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1 是一株草莓病害生防及促生菌。
4 结 论
贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株P2-1 对草莓褐色叶斑病菌具有强烈的抑制活性,并对草莓褐色叶斑病菌表现出较好的防治效果,是一种潜在的草莓褐色叶斑病生防菌资源。同时,菌株P2-1 能促进草莓植株生长。
致谢:感谢中国农业科学院郑州果树研究所张慧蓉老师和于巧丽老师在公共仪器和试剂使用方面提供的帮助。
[1]王鸣谦,薛莉,赵珺,代汉萍,雷家军.世界草莓生产及贸易现状[J].中国果树,2021(2):104-108.WANG Mingqian,XUE Li,ZHAO Jun,DAI Hanping,LEI Jiajun. Strawberry production and trade in the world[J]. China Fruits,2021(2):104-108.
[2]GENG W L,HU P,MA Z,ZHAO X Y,WEI Y M. First report of Pilidium concavum causing tan-brown leaf spot on strawberry in China[J].Plant Disease,2012,96(9):1377.
[3]LOPES U P,ZAMBOLIM L,LOPES U N,PEREIRA O L,COSTA H.First report of Pilidium concavum causing tan-brown rot in strawberry fruits in Brazil[J]. Plant Pathology,2010,59(6):1171-1172.
[4]DEBODE J,VAN HEMELRIJCK W,HEUNGENS K,MAES M,CREEMERS P. First report of Pilidium concavum causing tan-brown rot on strawberry fruit in Belgium[J]. Plant Disease,2011,95(8):1029.
[5]FERNÁNDEZ-ORTUÑO D,BRYSON P K,SCHNABEL G.First report of Pilidium concavum causing tan-brown rot on strawberry nursery stock in South Carolina[J]. Plant Disease,2014,98(7):1010.
[6]KARIMI K,ARZANLOU M,BABAI-AHARI A,PERTOT I.Biological and molecular characterisation of Pilidium lythri,an emerging strawberry pathogen in Iran[J].Phytopathologia Mediterranea,2016,55(3):366-379.
[7]PARK M J,BACK C G,PARK J H,HAN K S. Occurrence of tan-brown leaf spot caused by Pilidium concavum on Fragaria ananassa in Korea[J]. The Korean Journal of Mycology,2017,45(4):377-380.
[8]胡亚杰,韦建玉,卢健,胡志忠,王生才,谭永忠,蒋南,龚湛武,李迪秦.枯草芽孢杆菌在农作物生产上的应用研究进展[J].作物研究,2019,33(2):167-172.HU Yajie,WEI Jianyu,LU Jian,HU Zhizhong,WANG Shengcai,TAN Yongzhong,JIANG Nan,GONG Zhanwu,LI Diqin.Research progress of Bacillus subtilis application in crops production[J].Crop Research,2019,33(2):167-172.
[9]蔡高磊,张凡,欧阳友香,赵昌松,彭宣和,江爱明.贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)研究进展[J].北方园艺,2018(12):162-167.CAI Gaolei,ZHANG Fan,OUYANG Youxiang,ZHAO Changsong,PENG Xuanhe,JIANG Aiming.Research progress on Bacillus velezensis[J].Northern Horticulture,2018(12):167-172.
[10]郝芳敏,臧全宇,马二磊,丁伟红,王毓洪,黄云萍.甜瓜多种真菌病害拮抗细菌NBmelon-1 的鉴定及其促生和生防效果[J].中国瓜菜,2021,34(7):14-19.HAO Fangmin,ZANG Quanyu,MA Erlei,DING Weihong,WANG Yuhong,HUANG Yunping. Identification,biocontrol and growth promoting effects of antagonistic bacteria NBmelon-1 of various fungal diseases in melon[J]. Chinese Cucurbits and Vegetables,2021,34(7):14-19.
[11]YUAN H B,SHI B K,WANG L,HUANG T X,ZHOU Z Q,HOU H,TU H T. Isolation and characterization of Bacillus velezensis strain P2-1 for biocontrol of apple postharvest decay caused by Botryosphaeria dothidea[J/OL]. Frontier in Microbiology,2022,12:4148.DOI:10.3389/fmicb.2021.808938.
[12]黄艺烁,谢学文,石延霞,柴阿丽,李磊,李宝聚.多粘类芽胞杆菌ZF197 对白菜茎基腐病防治效果[J].园艺学报,2020,47(6):1059-1071.HUANG Yishuo,XIE Xuewen,SHI Yanxia,CHAI A’li,LI Lei,LI Baoju. Biocontrol effect of Paenibacillus polymyxa strain ZF197 against base stem rot of Chinese cabbage[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2020,47(6):1059-1071.
[13]ZHAI Y,ZHU J X,TAN T M,XU J P,SHEN A R,YANG X B,LI J L,ZENG L B,WEI L. Isolation and characterization of antagonistic Paenibacillus polymyxa HX-140 and its biocontrol potential against Fusarium wilt of cucumber seedlings[J]. BMC Microbiology,2021,21(1):75.
[14]仇月,孙守民,李鑫荣,杨帅,王红艳. 贝莱斯芽胞杆菌SDTB038 与化学药剂协同防治草莓枯萎病的研究[J].中国生物防治学报,2021,37(5):989-996.QIU Yue,SUN Shoumin,LI Xinrong,YANG Shuai,WANG Hongyan. Synergistic effects of Bacillus velezensis SDTB038 and chemical pesticides on strawberry Fusarium wilt[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control,2021,37(5):989-996.
[15]姚锦爱,黄鹏,赖宝春,余德亿.贝莱斯芽胞杆菌ZZBV-3 的鉴定及其对草莓根腐病的防效[J].中国生物防治学报,2021,37(1):172-177.YAO Jin’ai,HUANG Peng,LAI Baochun,YU Deyi. Identification and control efficacy of Bacillus velezensis ZZBV-3 against strawberry root rot[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control,2021,37(1):172-177.
[16]冯江鹏,邱莉萍,梁秀燕,陈碧秀,夏海洋,彭春龙,钟永军.草莓胶孢炭疽菌拮抗细菌贝莱斯芽孢杆菌JK3 的鉴定及其抗菌活性[J].浙江农业学报,2020,32(5):831-839.FENG Jiangpeng,QIU Liping,LIANG Xiuyan,CHEN Bixiu,XIA Haiyang,PENG Chunlong,ZHONG Yongjun. Identification of antagonistic bacteria Bacillus velezensis JK3 against anthracnose of strawberry and its antipathogenic activity[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2020,32(5):831-839.
[17]BAYISARA,CHO JY,KIM KY.Purification and identification of a new antifungal dipeptide from Bacillus velezensis AR1 culture supernatant[J].Pest Management Science,2021,77(2):775-779.
[18]LIU Y,TENG K,WANG T,DONG E,ZHANG M,TAO Y,ZHONG J.Antimicrobial Bacillus velezensis HC6:Production of three kinds of lipopeptides and biocontrol potential in maize[J].Journal of Applied Microbiology,2020,128(1):242-254.
[19]申顺善,张涛,王娟,刘东平,张珊珊,孙治强,朴凤植.多粘类芽孢杆菌HK18-8 对辣椒炭疽病菌的抑制作用及其定殖能力[J].园艺学报,2019,46(3):499-507.SHEN Shunshan,ZHANG Tao,WANG Juan,LIU Dongping,ZAHNG Shanshan,SUN Zhiqiang,PIAO Fengzhi. Antifungal activity of Paenibacillus polymyxa HK18-8 against pepper anthracnose and its colonization ability[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2019,46(3):499-507.
[20]KLOEPPER J W,BEAUCHAMP C J.A review of issues related to measuring colonization of plant roots by bacteria[J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology,1992,38(12):1219-1232.
[21]LIU R H,LI J Y,ZHANG F R,ZHENG D A,CHANG Y L,XU L S,HUANG L L. Biocontrol activity of Bacillus velezensis D4 against apple Valsa canker[J/OL].Biological Control,2021,163:104760.DOI:10.1016/j.biocontrol.2021.104760.
[22]MYO E M,LIU B H,MA J J,SHI L M,JIANG M G,ZHANG K C,GE B B. Evaluation of Bacillus velezensis NKG-2 for biocontrol activities against fungal diseases and potential plant growth promotion[J].Biological Control,2019,134:23-31.