核桃(Juglans regia L.)别名胡桃、羌桃和万岁子[1],国外称波斯核桃(Persian walnut)、英国核桃(English walnut)或欧洲核桃(European walnut)[2],是世界上重要的坚果树种,位居全球四大干果(核桃、扁桃、腰果、榛子)之首,享有“大力士食品”、“万岁子”之美誉,其坚果具有极高的营养价值和良好的医疗保健效果,同时具有重要的环境保护和生态维护价值。核桃是我国主要的经济林树种之一,在我国退耕还林的国家战略中发挥着重要作用。综合性状优良的核桃品种是核桃产业现代化的重要基础。长期以来,我国核桃单位面积产量低、品质差,主要原因之一就是优良品种普及率低,这严重制约了我国核桃产量和品质的进一步提高[3-5]。为了更好地开发利用核桃资源,国内外已做了大量的研究工作,但目前仅见有国内核桃育种、栽培和生物技术的综述[5-8]。笔者针对十多年来核桃品种选育方面的国内外进展做一综述,为今后核桃科研和生产应用提供参考。
1 国内外核桃品种应用概况
1.1 我国核桃品种应用现状
我国是世界第一大核桃生产国和重要的出口国,据联合国粮食及农业组织(Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations,FAO)资料,我国2020 年核桃种植面积为28.44 万hm2,核桃产量为110 万t[9]。20 世纪20 年代我国核桃出口量达3000余t,20 世纪60 年代开始出口英国和联邦德国,20世纪70—80 年代我国出口的核桃总量占世界贸易量的50%以上。但从1986年开始,我国出口的核桃被优质的美国核桃取代,出口量急剧下降,到20 世纪90年代以后带壳核桃几乎全被挤出欧洲市场,没有品种化、质量差是我国核桃被国际市场淘汰的主要原因[10]。
1.2 国外核桃生产及品种应用概况
核桃在全世界的分布和栽培遍及全球六大洲的50 多个国家和地区,2020 年全球核桃种植面积为102.14万hm2,总产量为332.4万t,产量达万t以上的国家有22个,其中中国、美国、伊朗、土耳其、墨西哥和智利为世界核桃六大主产国[9]。国外以美国为代表,自20世纪70年代后美国就开始了大规模的品种改良,选育了以强特勒(Chandler)为代表的新品种作为主栽品种,完全实现了良种化栽植[11-12]。因此,美国核桃产量和质量得到了很大程度的提高,从而成为世界核桃生产大国和强国,以及世界核桃出口大国。
1.3 国内外核桃品种应用的差距
与发达国家相比,我国核桃产业存在的问题表现在多方面,但在品种选育及应用方面的主要问题是品种混杂。自改革开放以来,我国选育的优良品种很多,但在推广应用中没有广泛繁育的优良品种,或者栽植的植株良莠不齐,苗木质量差,甚至采用实生苗建园[11]。产生这些问题的主要原因有三:一是从业人员专业素质不高;二是自然环境条件较差;三是应用品种的体制(公司或农户)不完善。但是,随着我国经济的发展,这些差距将会逐步缩小。
2 核桃品种选育研究
2.1 核桃育种目标
纵观国内外的核桃育种计划可以看出,丰产、早实、品质优和抗逆是核桃育种的主要目标。直接构成产量的主要因素有结果枝密度、雌花数量、坐果率高低和坚果大小等,主要由品种的遗传特性决定[13]。但是,不同立地条件下具体的育种目标也有区别。如美国加州核桃的育种目标为发芽晚而避开晚霜;早实且侧芽结实率高,树势健壮;雌花脱落率低,无大小年结果现象;高产,抗病虫害;坚果壳面光滑、缝合严密;出仁率大于50%,坚果个大仁饱满,色浅;单果仁质量7~8 g,且取仁容易[2,14]。
有关国内核桃品种选育的指标, 主要有以下2类:一是树体生物学特性,如物候期、坐果情况、产量及抗病虫害能力等;二是坚果经济性状,如坚果纵横径、平均坚果质量、坚果壳厚、坚果出仁率、核仁质量和核仁颜色等[13]。在具体的育种实践中,不同的育种者对各指标均进行了调整,如以最低温-28 ℃下枝梢不受冻害、雌花期能通过晚霜危害作为核桃抗寒性的选优标准,选出了西扶1 号、西扶2 号等早实核桃优良品种[15];也有把每平方米投影面积产量作为核桃的选优指标[16];罗秀钧等[17]则把母枝抽生果枝数、果枝率、果枝平均坐果数、坐果率、株产量、株产仁质量、种壳色泽、壳面光滑程度、内隔膜厚度、取仁难易、种仁饱满度和种仁颜色等果实品质指标作为选种的指标,丰富了选种的内容,改善了中选品种的综合经济性状。
2.2 核桃的杂交育种
2.2.1 杂交育种概况 核桃属树种资源多,野生类型多,基因资源丰富,杂交育种是提高核桃产量和改良核桃品质的重要手段[18]。由于核桃属内各树种的染色体数目相同,遗传背景相似,因此不同种间均能互相杂交结实,从而形成了通过种间远缘杂交来改良核桃品种的重要途径[13]。这方面成功的例子有2个:一是河北核桃(麻核桃),它是普通核桃(J.regia L.)与核桃楸(J.mandshurica)通过种间天然杂交获得的种间杂种;二是美国核桃的砧木奇异核桃(Paradox),也是以北加州黑核桃(J.hindssi)为母本、普通核桃为父本,通过自然杂交而来。
2.2.2 国内核桃杂交育种 我国的核桃杂交育种工作始于20世纪60年代中后期,先后涉及的单位有辽宁经济林研究所、山东省果树研究所、中国林业科学研究院和云南林业科学院经济林研究所等科研单位。我国的核桃杂交育种标志性的成果是1990 年经林业部鉴评出16个我国首批早实核桃新品种,成为我国主要的推广品种(表1)[3,19]。
表1 我国杂交育成的首批早实类核桃品种
Table 1 The early-fruit walnut varieties from breeding firstling in China

序号Number 1品种名Variety辽宁1号Liaoning No.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 0京861 Jing861中林5号Zhonglin No.5香玲Xiangling绿波Lvbo辽宁3号Liaoning No.3扎343 Zha 343中林1号Zhonglin No.1温185 Wen185辽宁4号Liaoning No.4 11 12 13 14 15 16善光Shanguang丰辉Fenghui新早丰Xinzaofeng西扶1号Xifu No.1西林2号Xilin No.2陕核1号Shanhe No.1亲本来源Source of parent河北昌黎大薄皮晚实优株10103×新疆纸皮核桃早实单株11001 Changli thin-skinned walnut10103×Zhipi walnut11001新疆核桃子代实生选出Xinjiang walnut涧9-11-12×涧9-11-15(选自山西祁县新疆核桃实生园)Jian9211212×Jian9211215(From Shanxi)上宋5号(早实)×阿克苏9号Shangsong No.5(early-fruiting)×Aksu No.9新疆核桃子代实生选出Xinjiang walnut河北昌黎大薄皮晚实优株10103×新疆纸皮核桃早实单株11001 Changli thin-skinned walnut 10103×Xinjiang walnut11001新疆林业科学院扎木台实生园Institute of Forestry, Xinjiang Academy of Forestry涧9-7-3(早实;山西祁县)×汾阳串子(晚实;山西汾阳)Jian92723(early-fruiting;Qixian)×Fenyang chuanzi(late fruiting;Fenyang)新疆温宿卡卡孜实生后代Xinjiang Wensu Kakazi辽宁朝阳大麻核桃(晚实)×新疆纸皮核桃(早实)Liaoning Chaoyang-dama(Late fruiting)×Xinjiang walnut11001(early-fruiting)新疆卡卡孜×上宋6号Kakazi×Shangsong No.6上宋5号(早实)×阿克苏9号Shangsong No.5(early-fruiting)×Aksu No.9新疆温宿土木秀克乡Xinjiang Wensu Tumuxiuke township陕扶风县隔年核桃实生选育Shanxi Fufeng-genian walnut新疆核桃实生选育Xinjiang walnut陕扶风县隔年核桃44号母树子代苗Shanxi Fufeng-genian walnut No.44
(1)品种选育研究。叶茂富等[20]率先开展核桃属间杂交育种研究,用核桃和山核桃(Carya cathayensis Sarg.)、核桃和薄壳山核桃[Carya illinoinensis(Wangenh.) K. Koch]进行核桃的种(属)间杂交,但未获得杂交品种。辽宁经济林研究所、中国林科院经济林研究所、山东果树所等先后开展了以普通核桃为杂交亲本的大规模杂交育种工作,培育出辽宁系、中林系和鲁光等众多新品种(系)[5-7]。周兰英等[21]研究表明,核桃与铁核桃(J.sigllata Dode)杂交亲和力较低,杂交结实率仅5%,为提高结实率要特别重视第1次授粉。王国安等[22]发现新疆早实核桃二次果的实生群体变异严重,种质类型丰富,认为利用核桃二次果的实生群体进行良种选育,可期望选育出矮化类型植株。自2000年以来,国内由杂交育成的核桃新品种名录见表2。
表2 2000 年以来我国杂交育成的主要核桃新品种
Table 2 The walnut varieties from breeding in China

品种(品系)Varieties鲁香Luxiang云新系列Yunxi series 90301、90303 90301、90303鲁丰Lufeng岱香Daixiang元林Yuanlin云辉1号Yunhui No.1研究者Breeder张美勇Zhang Meiyong方文亮Fang Wenliang范志远Fan Zhiyuan张美勇Zhang Meiyong张美勇Zhang Meiyong侯立群、王均毅Hou Liqun、Wang Junyi于菲Yu Fei亲本Parents上宋6号×新疆早熟丰产Shangsong No.6×Xinjiang early-fruiting walnut云南薄壳核桃×新疆核桃Yunnan thin-skinned walnut×Xinjiang walnut三台核桃×新早13号Santai walnut×Xinzao No.13上宋6号×阿克苏9号Shangsong No.6×Aksu No.9辽核1号×香玲Liaohe No.1×Xiangling元丰×强特勒Yuanfeng×Chandler新疆核桃×漾濞泡核桃Xinjiang walnut×Julans sigillata年份Year 2001 2001 2002 2003 2003 2007 2012鲁果9号Luguo No.9中宁强Zhongningqiang相昆Xiang Kun张俊佩Zhang Junpei早实核桃自然杂交亲本不详Early-fruting walnut魁核桃×洛宁县核桃Juglans major×Luoning walnut 2012 2013美香Meixiang郝艳宾Hao Yanbin香玲×云新34号Xiangling×Yunxin No.34 2015雪凝红Xueninghong洛核1号Luohe No.1张忠祥Zhang Zhongxiang马贯羊Ma Guanyang泡核桃×新疆核桃Julans sigillata×Xinjiang walnut彼特罗×中林5号Pedro×Zhonglin No.5 2015 2018鲁锦Lujin鲁绵2号Lumian No.2孙超Sun Chao王翠香Wang Cuiuxiang育种单位Breeding institution山东省果树研究所Shandong Institute of Pomology云南省林业和草原科学院Yunan Academy of Forestry and Grassland云南省林业和草原科学院Yunan Academy of Forestry and Grassland山东省果树研究所Shandong Institute of Pomology山东省果树研究所Shandong Institute of Pomology山东省林业科学研究院Shandong Academy of Forestry云南省农业科学院园艺作物研究所Institute Horticulture,Yunnan Academy of Agricultural Sciences山东省果树研究所Shandong Institute of Pomology中国林业科学研究院林业研究所Research Institute of Forestry Chinese Academy of Forestry北京市农林科学院林业果树研究所IFP,Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences贵州省林业科学研究院Guizhou Academy of Forestry洛阳农林科学院Luoyang Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences山东省林业科学研究院Shandong Academy of Forestry山东省林业科学研究院Shandong Academy of Forestry绿香×香玲Lüxiang×Xiangling鸡爪绵×香玲Jizhuanmian×Xiangling 2018 2021
(2)遗传规律研究。我国北方的普通核桃种群是在自然授粉的实生后代中长期自然选择和人工选择的结果,总体表现出核壳较薄、取仁容易的特性[13,23]。核桃品质的优劣受多对数量性状基因的控制[18],各性状的变异很大。壳薄、果大、出仁率高、取仁易和缝合线窄等现代经济性状在实生子代的变异较大,且性状的品质越优、经济价值越高,子代变异程度就越大;壳厚、缝合线宽、出仁率低和取仁难等原始的野生性状,子代的变异程度较小[22]。这也验证了野生性状遗传力强的观点[13]。云南核桃和新疆核桃种间杂交F1代的主要性状的遗传分析表明,杂种F1代主要性状分离广泛,为多基因控制的数量性状遗传,其坚果出仁率、坚果大小、仁质量等均表现出趋中变异的特点,而仁色、壳厚等表现出一定程度的杂种优势[23]。
2.2.3 美国的核桃杂交育种(1)美国核桃的主栽品种。美国加州是核桃的主产地,在生产上应用的有30 余个品种,但仅Chandler和Hartley 这2个品种就占核桃总产量的60%,排前10位的品种还有Ashley、Franquette、Howard、Payne、Serr、Tehama、Tulare和Vina。
(2)最近选育的新品种。美国新选育出的优良品种被专利保护然后发表,前5 a 品种只提供给加州的栽培者,5 a 后可以在国际上交流。近年来美国核桃品种的选择开始注重更早熟的品种,已获得72 个优系/品种,其中91-077-6 和95-011-14 等5 个优系有希望进行品种选育。美国加州大学的核桃育种计划起始于1948 年,诸如Chandler、Howard、Vina、Tulare 和Serr 等众多的新品种均来自于该计划,这些优良品种的主要特点是早期高产、抗病、仁色浅;该计划还应用杂交和回交的方式培育抗病及线虫的品种[14,24]。较早发布的世界上首个红仁核桃品种Robert Livermore,种皮鲜红引人注目[25],最新发布的品种还有Ivanhoe、Solano 和Durham 等[26]。
2.2.4 其他国家的核桃育种 Poirier[27]在法国中部对7 个品种(Chandler、Franquette、Fernor、Fernette、Lara、Pedro 和Serr)的抗寒性进行了测定,结果发现杂交种NG38(Juglans regia×Juglans nigra)抗性突出。英国的育种计划从广泛收集资源开始,选育果用和材用品种[28]。土耳其为改善果实品质,培育高产、抗枯萎病的品种,2008 年使用土耳其品种(Şebin、Akça1等)和法国品种(Franquette)进行了13次杂交,从中获得了1340 个杂交株系,之后通过筛选发布了3 个优良品种[29]。伊朗以7 个优良品种为亲本,与8个其他国家品种(包括Serr、Hartley等)进行杂交育种,并对后代进行评估,2010年发布了2个品种Jamal 和Damavand[30-32]。表3 为近些年国外发表的杂交品种[33-38]。
表3 近些年国外发表的核桃杂交品种
Table 3 Hybrid varieties published abroad in recent years
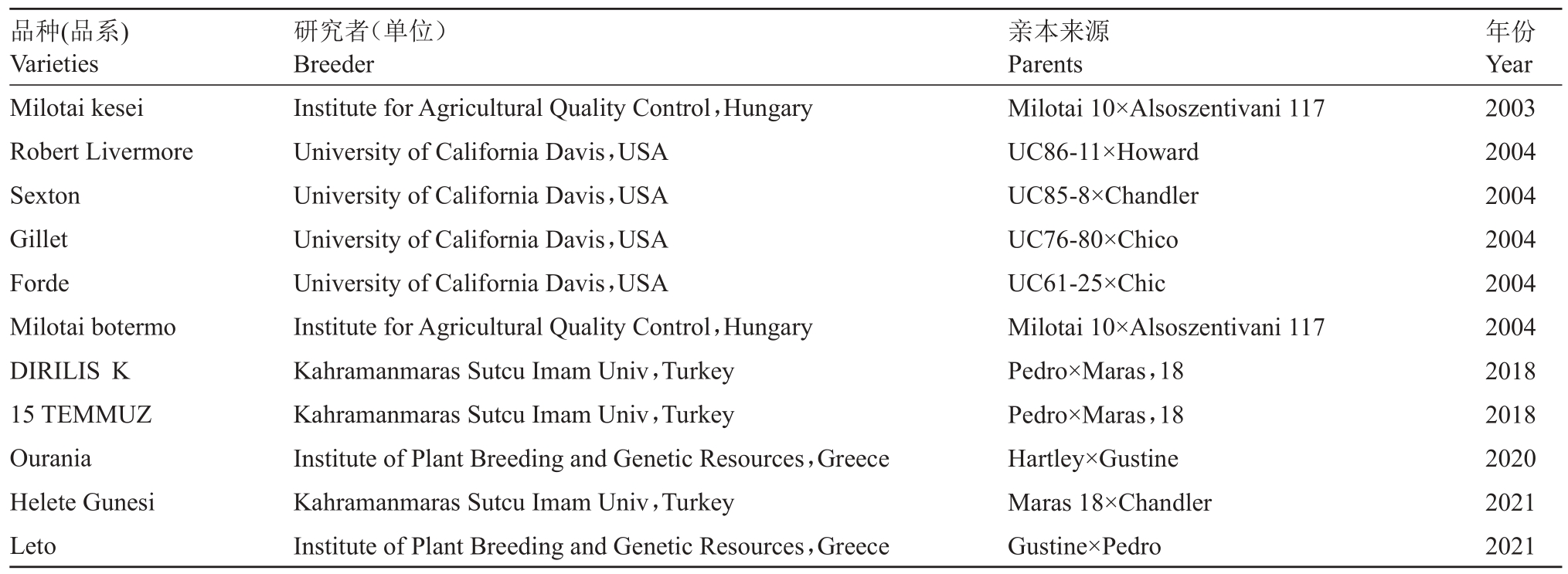
品种(品系)Varieties Milotai kesei Robert Livermore Sexton Gillet Forde Milotai botermo DIRILIS K 15 TEMMUZ Ourania Helete Gunesi Leto Institute for Agricultural Quality Control,Hungary University of California Davis,USA University of California Davis,USA University of California Davis,USA University of California Davis,USA Institute for Agricultural Quality Control,Hungary Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam Univ,Turkey Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam Univ,Turkey Institute of Plant Breeding and Genetic Resources,Greece Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam Univ,Turkey Institute of Plant Breeding and Genetic Resources,Greece Milotai 10×Alsoszentivani 117 UC86-11×Howard UC85-8×Chandler UC76-80×Chico UC61-25×Chic Milotai 10×Alsoszentivani 117 Pedro×Maras,18 Pedro×Maras,18 Hartley×Gustine Maras 18×Chandler Gustine×Pedro 2003 2004 2004 2004 2004 2004 2018 2018 2020 2021 2021研究者(单位)Breeder亲本来源Parents年份Year
2.3 核桃的实生选种
核桃的良种选育起始于单株选择,但早期主要是利用集团选择法[39]。在核桃的选育中,综合评分法是应用最广的方法;经过多年发展,主成分分析法、综合指数法等在核桃的良种选择中也得到了广泛应用[40-41]。
核桃良种选育最为关注的性状是丰产性,具体指标为结果母枝平均抽生果枝数2 个以上,结果母枝3 a连续结果率80%以上,每果枝平均坐果1.5 个以上。坚果品质指标包括果大壳薄,壳面光滑、刻纹浅而少、果实饱满,能出整仁或半仁,壳厚1.5 mm以下,出仁率50%以上,含油率65%以上,核仁浅黄色,风味香酥,单果质量l0 g以上或每千克100个以下[16]。
我国核桃的选优工作开始于20 世纪60 年代。自20 世纪80 年代以来,参照核桃丰产与坚果品质的国家标准(GB 7907—1987)[42],各地利用丰富的种质资源全面开展实生选种工作,选育出84 个新品种,涉及到全国32 个教学科研单位,对提高我国核桃的坚果品质、促进我国核桃的良种化生产起到了积极的推动作用[3,43]。这些核桃良种以早实类品种居多,主要特点体现在短枝、结果穗状、早结实、丰产性强、薄壳及品质优良等方面,其中仅有晋龙1 号成为全国第1 个通过省级鉴定的晚实核桃新品种[44]。
国外在核桃实生选种方面也进行了调查研究。欧洲的核桃坚果质量分布在3.8~21.1 g,仁质量分布在1.85~9.8 g,出仁率为32.6%~63.8%,脂肪含量在42.0%~71.5%[45]。在对19个核桃单系的坚果性状评价后发现,核桃单系总体分成3 类,即大果型、多果型及普通型[45]。表4为近些年国外实生选种获得的主要品种[46-51]。
表4 近些年国外实生选种获得的主要品种
Table 4 Main varieties obtained in recent years from seedling selection overseas
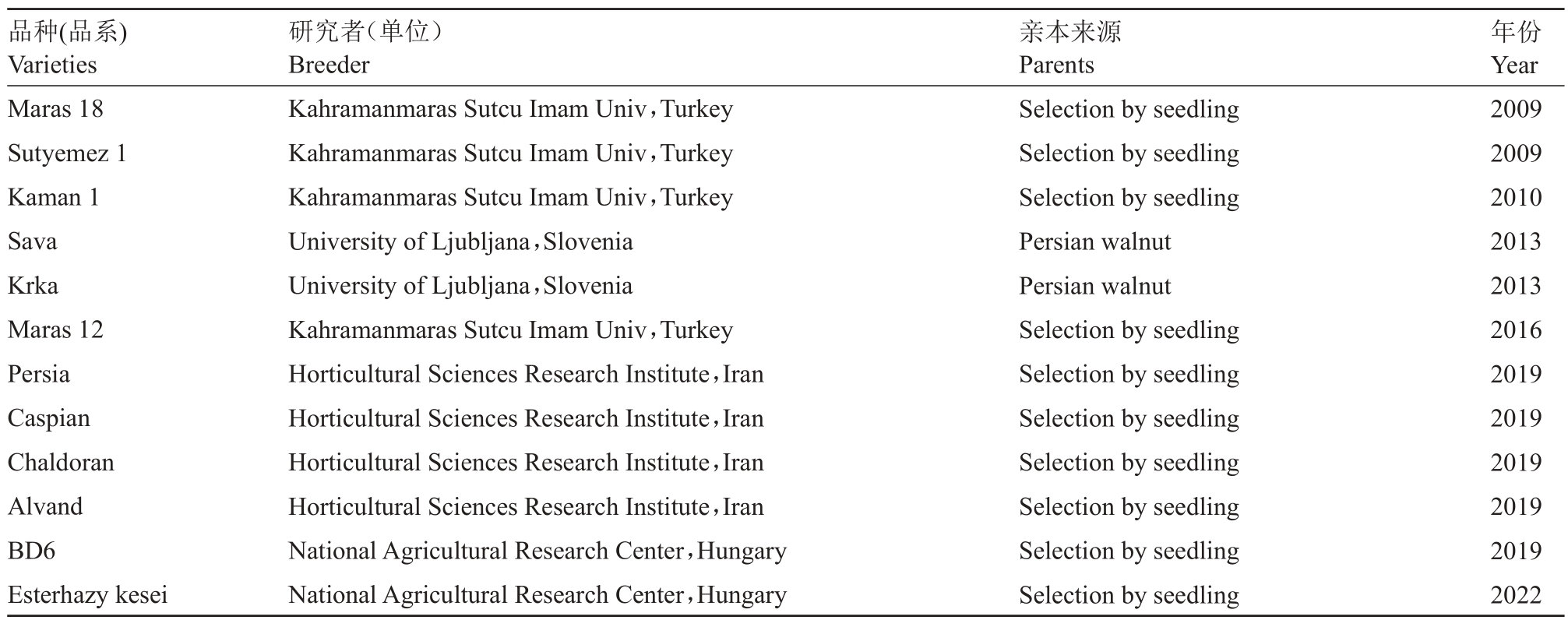
品种(品系)Varieties Maras 18 Sutyemez 1 Kaman 1 Sava Krka Maras 12 Persia Caspian Chaldoran Alvand BD6 Esterhazy kesei研究者(单位)Breeder Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam Univ,Turkey Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam Univ,Turkey Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam Univ,Turkey University of Ljubljana,Slovenia University of Ljubljana,Slovenia Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam Univ,Turkey Horticultural Sciences Research Institute,Iran Horticultural Sciences Research Institute,Iran Horticultural Sciences Research Institute,Iran Horticultural Sciences Research Institute,Iran National Agricultural Research Center,Hungary National Agricultural Research Center,Hungary亲本来源Parents Selection by seedling Selection by seedling Selection by seedling Persian walnut Persian walnut Selection by seedling Selection by seedling Selection by seedling Selection by seedling Selection by seedling Selection by seedling Selection by seedling年份Year 2009 2009 2010 2013 2013 2016 2019 2019 2019 2019 2019 2022
2.4 核桃的引种
核桃良种引进是实现栽培良种化的最有效途径,主要分为国外核桃良种引进和国内不同生态区间的核桃品种引进。
2.4.1 从国外引进的核桃品种 早在20 世纪50 年代初,武汉植物园曾从美国、苏联和东欧的一些国家引进多个核桃品种和类型。此后,国内各主要核桃科研和教学单位广泛开展了优良品种的引进工作,先后从国外引进多个核桃优良品种。自1980年起,中国林业科学研究院核桃基因库已引进各国核桃优良品种20 多个,砧木资源7 种[52]。中国林业科学研究院经济林研究所等陆续引进Vina、Chandler 和Tehama 等12 个美国加州主栽核桃品种,以及黑核桃、魁核桃(J. major)、小黑核桃(J. microcarpa)、北加州黑核桃及其种间杂种(奇异核桃)等5 个树种[53]。山西农业大学和山西林业科学研究院分别于20 世纪80 年代初和20 世纪90 年代中期从意大利、罗马尼亚引入优良品种的种子及接穗10多份[54],对其生态适应性进行研究的同时从中选出了1 个优系[55]。此后,我国的核桃引种工作扩大至一些公司,内容也扩展至薄壳山核桃等,这些工作均极大拓展了我国核桃产业内容,丰富了品种资源[56-58](表5)。
表5 中国从国外引进的主要核桃品种
Table 5 The walnut varieties from abroad in China

品种(品系)Varieties福兰克蒂,马勃,艾瑞克,维纳塞瑞托,鲁泡克,帕瑞森安娜Franquette,Marbo,Enreke,Vina Serrento,Lopoc,Parisiana清香Qingxiang特哈玛,爱米格,彼德罗,强特勒Tehama,Amigo,Pedro,Chandler塞比塞尔,塞比塞尔44奥热斯蒂,乔杰尤65,吉米塞热Sibisel precoce,Sibisel 44 Orastia,Geoagiu65,Germisara美国红仁核桃Robert Livermore引种者(单位)Introduceder山西农业大学Shanxi Agricultural University郗荣庭XI Rongting奚声珂XI Shengke山西省林业科学院Shanxi Academy of Forestry Sciences陕西盛大公司Shaanxi Shanda Company材料来源Source意大利Italy日本Japan美国USA罗马尼亚România美国USA年份Year 1982 1983 1984 1996 2017
2.4.2 国内核桃品种引进 我国北方核桃主产区的代表树种是普通核桃,而西南产区中最大的云南产区代表树种是铁核桃(泡核桃)。在漫长的栽培实践中品种的性状出现了明显分化,存在着华北产区主产的结果较晚的晚实类核桃及新疆和陕西分布的早果性突出的早实类品种等[43]。
20世纪50年代,北京林业大学首次将新疆早实核桃引入北京地区栽培。自此之后,我国许多省份开始引种新疆核桃,各地相继从其实生后代中选出了适宜于当地生态环境的优良品种或优株,如云南的云新、山东的香玲、山西的晋龙及河南的薄丰等。近年来,随着我国核桃产业的迅速发展,核桃优良品种在省际之间相互引种开展频繁,极大促进了优良品种的普及[59-62]。国内外重要的主栽品种果实性状见图1。

图1 国内主栽核桃品种及特色品种资源
Fig.1 Domestic main varieties and distinctive characteristics of walnut varieties
3 问题及展望
3.1 问题
我国在核桃育种工作中取得了一定成就,各地充分利用当地的核桃种质资源选育出了众多的优良核桃品种,但与发达国家相比,在核桃育种领域还存在以下三方面问题:一是特色资源开发程度远远适应不了产业发展需求,急需深入开展工作;二是利用分子生物学等手段在抗病品种选育工作中的应用较为落后;三是针对育种实践周期长的特点,未能制定长期有效的计划并一以贯之,导致育种效率低下。
3.2 展望
随着人民生活水平的提高,对核桃营养保健价值和医疗功效认识的加深,以及核桃系列产品的开发利用,人们对核桃的需求量将不断上升,对核桃的品质也提出了更高的要求。展望未来,核桃品种选育领域将会展现出如下趋势。
趋势1:深化种质资源开发利用,培育兼用型品种为产业发展服务,培育特色品种以满足消费者的多元化要求。笔者团队参加的2016 年启动的国家核桃种质资源调查与编目项目已完成,该项目充分利用了现代大数据技术及处理手段强化了对资源的动态掌握及后续利用研究。在我国丰富的核桃种质资源中,存在大量特异类型,如果材兼用核桃品种[63]、专用鲜食核桃品种[64-65]、观赏用核桃品种[66-67]、具有无融合生殖特性的核桃资源[68]以及传统仁用核桃中的美国红瓤核桃[56]、中国彩色核桃[69]和四川茂汶香核桃等[43],均是宝贵的种质材料和品种资源。只有发掘这些特色资源才可满足核桃生产、消费的全面需求,进一步巩固核桃产业基础。
趋势2:分子生物学手段将辅助新品种选育,助力传统技术提高育种效率。自McGranhan 等[70-71]获得核桃的转基因再生植株以来,相关研究已多有报道,而国内在核桃属植物的基础理论研究[72-73]、生物技术及转基因研究[74-75]和特定基因调控机制等方面也获得一定进展[76-77],这些工作为利用生物技术转入抗病虫基因进行核桃抗病虫害育种及优质新品种改良打下了一定基础。在今后的核桃育种工作中,虽然常规育种在一定时期内仍是核桃品种改良的主要手段,但是现代生物技术的主要内容如基因(蛋白质、酶、细胞)工程等生物新技术育种将是强有力的支撑技术。生物技术在核桃品种的鉴定和保存方面已得到应用,在育种研究中则能够有效弥补核桃常规育种的不足,从而展示了核桃育种工作的美好前景。
趋势3:进一步重视种质资源对品质育种的贡献作用。我国在核桃育种工作中取得了一定成就,这得益于各地充分利用当地的种质资源[78-80]。如铁核桃和核桃的种间杂交获得的品种既耐寒冷霜冻,又弥补了北方核桃在南方高温多湿环境下栽培易衰老、多病虫害等缺陷[81-82]。此外,目前早实核桃新品种受病虫危害普遍较重,因此资源评价与抗病虫育种将成为未来核桃育种的重要内容[83-84]。针对核桃产业的发展,轻简高效栽培是以后的方向,这对品种的要求包括2 个方面:一是在保证品质的前提下树体生长习性适应机械化修剪的类型;二是中厚壳品种:现在推广的绝大多数品种为早实类核桃,其壳较薄不利于机械加工。核桃产业的现代化离不开机械化,这又要求主栽品种必须满足机械采收要求。这个变化从国家标准对壳厚的要求也可反映出来,即淡化对壳厚的要求,从有壳厚指标演变为无要求[42,85]。
在培育选用良种的同时,还要重视科学合理综合的配套栽培经营技术体系的研究,将良种良法配套,才能实现高产、优质、高效的目的,促进我国核桃产业的可持续发展。
致谢:感谢为本文提供品种图片的王贵研究员、曹尚银研究员、范志远研究员、赵宝军研究员、辛国高级工程师和孙红川高级工程师。
[1]郗荣庭,张毅萍.中国果树志·核桃卷[M].北京:中国林业出版社,1996.XI Rongting,ZHANG Yiping. Chinese fruit annals·Walnut[M].Beijing:China Forestry Publishing House,1996.
[2]JANICK J,JAMES N M. Fruit breeding. Volume Ⅲ[M]. New York:John Wiley&Sons Inc,1996:241-242.
[3]侯立群.中国核桃产业发展报告:1949—2007[M].北京:中国林业出版社,2008.HOU Liqun.China walnut development report:1949—2007[M].Beijing:China Forestry Publishing House,2008.
[4]吴国良,刘群龙,王丽萍,宋宇琴.21 世纪中国核桃产业发展思路的探讨[C]//中国核桃大会.国家林业局,西北农林科技大学,2008.WU Guoliang,LIU Qunlong,WANG Liping,SONG Yuqin.Study on the development of walnut industry in the 21st centu-ry[C]//China Walnut Congress. State Forestry Administration,Northwest A&F University,2008.
[5]韩华柏,何方.我国核桃育种的回顾和展望[J].经济林研究,2004,22(3):45-50.HAN Huabo,HE Fang.Retrospect and prospect of walnut breeding in China[J]. Economic Forest Researches,2004,22(3):45-50.
[6]冯连芬,吕芳德,张亚萍,和红晓.我国核桃育种及其栽培技术研究进展[J].经济林研究,2006,24(2):69-73.FENG Lianfen,LÜ Fangde,ZHANG Yaping,HE Hongxiao.Literature review of researches on breeding and cultivation techniques of Chinese walnut[J]. Nonwood Forest Research,2006,24(2):69-73.
[7]赵登超,侯立群,韩传明.我国核桃新品种选育研究进展[J].经济林研究,2010,28(1):118-121.ZHAO Dengchao,HOU Liqun,HAN Chuanming. Advances in research on new variety breeding of walnut in China[J]. Nonwood Forest Research,2010,28(1):118-121.
[8]汤浩茹,王永清,任正隆.核桃体细胞胚发生与转基因研究进展[J].林业科学,2000,36(3):102-110.TANG Haoru,WANG Yongqing,REN Zhenglong.An overview of progress on somatic embryogenesis and transformation in walnut[J].Scientia Silvae Sinicae,2000,36(3):102-110.
[9]Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations[DB/OL].[2022-04-18].https://www.fao.org/home/en.
[10]史相玉,程旭,刘英.我国核桃出口状况及其对策[J].农产品加工,2004(12):48.SHI Xiangyu,CHENG Xu,LIU Ying. Walnut export status and countermeasures in China[J]. Farm Products Processing,2004(12):48.
[11]张毅萍.世界及我国核桃生产概况和几个问题[C]//中国园艺学会干果分会成立大会暨第二届全国干果生产与科研进展学术研讨会论文集.北京:中国农业出版社,2001:9-13.ZHANG Yiping.General situation and some problems of walnut production in the world and in china[C]//Proceedings of the Founding Conference of the Dry Fruit Branch of the Chinese Horticultural Society and the Second National Symposium on Dry Fruit Production and Scientific Research Progress. Beijing:China Agriculture Press,2001:9-13.
[12]方文亮.美国的核桃业[J].云南林业科技,1999,28(2):47-51.FANG Wenliang.Walnut industry of the United States of America[J].Yunnan Forestry Science and Technology,1999,28(2):47-51.
[13]沈德绪.果树育种学[M].北京:农业出版社,1992:313-315.SHEN Dexu. Fruit tree breeding[M]. Beijing:China Agriculture Publishing House,1992:313-315.
[14]MCGRANAHAN G,LESLIE C.Advances in genetic improvement of walnut at the university of California,Davis[J]. Acta Horticulturae,2006,705:117-122.
[15]高绍棠,刘晓愚,杨吉安.扶风隔年核桃优树选择研究[J].果树科学,1990,7(1):37-40.GAO Shaotang,LIU Xiaoyu,YANG Ji’an. Study on selection of Fufeng alternate year walnut[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,1990,7(1):37-40.
[16]杨俊霞,郭宝林,张卫红,古芹霞.核桃主要经济性状的主成分分析及优良品种选择的研究[J].河北农业大学学报,2001,24(4):39-42.YANG Junxia,GUO Baolin,ZHANG Weihong,GU Qinxia.The studies of principal component analysis on the main economic character and superior variety selection of walnut[J]. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei,2001,24(4):39-42.
[17]罗秀钧,王汉涛,武显维.河南省核桃良种选育研究[J].武汉植物学研究,1990,8(4):365-373.LUO Xiujun,WANG Hantao,WU Xianwei.Studies on the selection and breeding of fine strains in walnut in Henan Province[J].Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research,1990,8(4):365-373.
[18]方文亮,杨振邦. 核桃杂交育种研究报告[J]. 经济林研究,1987,5(S1):228-233.FANG Wenliang,YANG Zhenbang. Research report on cross breeding of walnut[J].Economic Forest Researches,1987,5(S1):228-233.
[19]马庆国,齐静,裴东.16 个早实核桃良种遗传多样性的FISHAFLP 分析[J].林业科学研究,2010,23(5):631-636.MA Qingguo,QI Jing,PEI Dong.FISH-AFLP analysis of genetic diversity of early- fruiting walnut cultivars[J]. Forest Research,2010,23(5):631-636.
[20]叶茂富,吴厚钧.山核桃与薄壳山核桃杂交的研究[J].林业科学,1965,1(1):50-56.YE Maofu,WU Houjun. Studies on hybridization of Carya cathayensis and C. illinoensis[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae,1965,1(1):50-56.
[21]周兰英,肖千文,胡庭兴,陈礼清,张尚杰,向永宗,王品邦.核桃杂交育种试验[J].林业实用技术,2004(9):7-8.ZHOU Lanying,XIAO Qianwen,HU Tingxing,CHEN Liqing,ZHANG Shangjie,XIANG Yongzong,WANG Pinbang. Walnut cross breeding experiment[J]. Forest Science and Technology,2004(9):7-8.
[22]王国安,艾力,虎海防.核桃二次果是遗传育种的新型试材[J].北方果树,2004(1):13-14.WANG Guo’an,AI Li,HU Haifang.Walnut secondary fruit is a new test material for genetic breeding[J]. Northern Fruits,2004(1):13-14.
[23]张雨,方文亮,杨杨,范志远,习学良.核桃杂交F1代坚果品质主要性状遗传分析[J].西南农业学报,2004,17(S1):461-466.ZHANG Yu,FANG Wenliang,YANG Yang,FAN Zhiyuan,XI Xueliang. Genetic analysis on main characters of nut quality of F1 generation of hybrization of Juglans[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2004,17(S1):461-466.
[24]CLARK J R,FINN C.Register of new fruit and nut cultivars list 44[J].HortScience,2008,43(5):1321-1343.
[25]MCGRANAHAN G,LESLIE C. `Robert Livermore',a Persian walnut cultivar with a red seedcoat[J].Hortscience,2004,39(7):1772.
[26]BERNARD A,LHEUREUX F,DIRLEWANGER E. Walnut:past and future of genetic improvement[J].Tree Genetics & Genomes,2017,14(1):1-28.
[27]POIRIER M,BODET C,PLOQUIN S,SAINT J B,LACOINTE A,AMEGLIO T.Walnut cultivar performance of cold resistance in south central France[J]. Acta Horticulturae,2004,705:281-285.
[28]HEMERY G E,RUSSELL K.Advances in walnut breeding and culture in the United Kingdom[J]. Acta Horticulturae,2006,705:95-101.
[29]AKCA Y,M SUTYENEZ,YILMAZ S,KARADAG H. The new walnut variety breeding program in Turkey[C]//VIIth International Scientific Agricultural Symposium,2016:461-466.
[30]SUTYEMEZ M. New walnut cultivars:Maras 18,sutyemez 1,and kaman 1[J].HortScience,2016,51(10):1301-1303.
[31]HASSANI D,ATEFI J,HAGHJOOYAN R,DASTJERDI R,KESHAVARZI M,MOZAFFARI MR,SOLEIMANI A,RAHMANIAN A R,NEMATZADEH F,MALMIR A. Cultiverrelease:Jamal,a new Persian walnut cultivar for moderate-cold areas of Iran,cultivar release[J]. Seed and Plant Improvement Journal,2012,28(3):25-27.
[32]HASSANI D,ATEFI J,HAGHJOOYAN R,DASTJERDI R,KESHAVARZI M,SOLEIMANI A,MOZAFFARI M R,SOLEIMANI A,RAHMANIAN A R,NEMATZADEH F,MALMIR A. Cultiverrelease:Damavand,a new Persian walnut cultivar as a pollinizer for Iranian walnut cultivars and genotypes[J]. Seed and Plant Improvement Journal,2012,28(3):33-31.
[33]HASSANI D,DASTJERDI R,HAGHJOOYAN R,SOLEIMANI A,KESHAVARZI M,ATEFI J,MOZAFFARI M R,REZAEE R,FAHADAN A,RAHMANIAN A R. Genetic improvement of Persian walnut (Juglans regial.) in Iran[J]. Acta Horticulturae,2014,1050:95-102.
[34]BUJDOSÓ G,SZENTIVÁNYI P,TÓTH-MARKUS M.Organoleptic testing of new Hungarian walnut cultivars and cultivar candidates[C].5th International Walnut Symposium,2004.
[35]SUTYEMEZ M,OZCAN A,BUKUCU S B. Walnut cultivars through cross-breeding:'Dirili' and '15 Temmuz'[J]. Journal-American Pomological Society,2018,72(3):173-180.
[36]MANTHOS I,ROUSKAS D.‘Ourania’Walnut[J]. Hort-Science,2021,56(4):1-2.
[37]SÜTYEMEZ M,BÜKÜCÜ Ş B,ÖZCAN A.‘Helete Güneşi’,a new walnut cultivar with late leafing,early harvest date,and superior nut traits[J].Agriculture,2021,11(10):991.
[38]MANTHOS I,ROUSKAS D. Introduction of a new interesting walnut cultivar Leto[J].Plants,2021,10(12):2738.
[39]徐緯英,朱湘渝,胡长令,陶淳.用选择方法改良我国核桃品种:山西汾阳南偏城最优良单株的选择研究[J]. 林业科学,1965,1(1):18-36.XU Weiying,ZHU Xiangyu,HU Changling,TAO Chun. Improving my country's walnut varieties by selection method:Study on the selection of the best individual plant in Nanpiancheng,Fenyang,Shanxi[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae,1965,1(1):18-36.
[40]高焕章,吴楚,李申如,周瑞锋.综合指数法在核桃选种中的应用研究[J].林业科学,2002,38(3):171-176.GAO Huanzhang,WU Chu,LI Shenru,ZHOU Ruifeng.The application of synthetic index method on superior variety selection of walnut[J].Scientia Silvae Sinicae,2002,38(3):171-176.
[41]高焕章,吴楚,艾天成,鲍新梅.用主成分分析法决策湖北核桃优系核仁加工产品类型[J].湖北农业科学,2002,41(4):58-61.GAO Huanzhang,WU Chu,AI Tiancheng,BAO Xinmei. Plotting processing product types for kernels from excellent strains of Hubei walnut using principal component analysis method[J].Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2002,41(4):58-61.
[42]国家标准局. 核桃丰产与坚果品质:LY/T 1329—1999[S]. 北京:国家标准局,1999.National Bureau of Standards.Walnut yield and nut quality:LY/T 1329—1999[S].Beijing:National Bureau of Standards,1999.
[43]裴东,鲁新政. 中国核桃种质资源[M]. 北京:中国林业出版社,2011.PEI Dong,LU Xinzheng. Walnut germplasm resources in China[M].Beijing:China Forestry Publishing House,2011.
[44]王贵,高中山.核桃新品种:晋龙1 号[J].园艺学报,1992,19(3):287-288.WANG Gui,GAO Zhongshan. A new walnut variety-‘Jinlong No.1’[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,1992,19(3):287-288.
[45]ZENELI G,KOLA H,DIDA M. Phenotypic variation in native walnut populations of Northern Albania[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2005,105(1):91-100.
[46]BORISEVICH V A,LIPSKAYA S L.Quality signs of walnut[J].Plodovodstvo,2004,16:33-36.
[47]SOLAR A,VEBERIC R,STAMPAR F.‘Sava’and‘Krka’walnut cultivars[J].Hortscience,2014,49(8):1081-1082.
[48]SUTYEMEZ M,BUKUCU S B,OZCAN A. Mara 12:A walnut cultivar with cluster-bearing habit[J]. HortScience,2019,54(8):1437-1438.
[49]HASSANI D,MOZAFFARI M,SOLEIMANI A,DASTJERDI R,REZAEE R,KESHAVARZI M,VAHDATI K,FAHADAN A,ATEFI J. Four new Persian walnut cultivars of Iran:Persia,Caspian,Chaldoran,andAlvand[J].HortScience,2020,55(7):1-2.
[50]BUJDOSÓ G,FODOR A,KARACS-VÉGH A. BD6 walnut[J].HortScience,2020,55(8):1-2.
[51]BUJDOSÓ G,ERCIUFLI S,RATIU A,CSEKE K.Walnut‘Esterhazy kesei’for small-scale cultivation[J].HortScience,2022,57(4):523.
[52]韩振海. 落叶果树种质资源学[M]. 北京:中国农业出版社,1995.HAN Zhenhai.Germplasm resources of deciduous fruit trees[M].Beijing:China Agriculture Press,1995.
[53]XI S K,WANG Z L,YOU Y T. Introduction of American walnuts (Juglans L.)in China[J]. Rorest Research,1995,8(3):285-290.
[54]吴国良,常留印,陈国秀,赵梁军,史燕山.核桃实生苗叶性状与抗寒性关系[J].植物学通报,1998,33(S1):111-113.WU Guoliang,CHANG Liuyin,CHEN Guoxiu,ZHAO Liangjun,SHI Yanshan. The relationship between leaf characters of walnut seedling and its cold resistance[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany,1998,33(S1):111-113.
[55]吴国良,史燕山,常留印. 核桃优系:NY83-05[J].中国种业,1997(2):F003.WU Guoliang,SHI Yanshan,CHANG Liuyin. Walnut superior series:NY83-05[J].China Seed Industry,1997(2):F003.
[56]董兆斌,王根宪,王英宏.洛南县美国红仁核桃引种初报[J].陕西林业科技,2017(1):25-28.DONG Zhaobin,WANG Genxian,WANG Yinghong. Preliminary report on introduction of America red-kernel walnut in Luonan[J].Shaanxi Forest Science and Technology,2017(1):25-28.
[57]刘朝斌,高绍棠,黄昌新.哈特勒品种核桃引种调查[J].西北林学院学报,2000,15(3):36-40.LIU Chaobin,GAO Shaotang,HUANG Changxin.An investigation of the introduction of“Hartley”walnut variety[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry College,2000,15(3):36-40.
[58]杨迪.沈阳地区美国山核桃引种适应性研究[D].沈阳:沈阳农业大学,2020.YANG Di.Study on the adaptability of Carya illinoinensis introduction in Shenyang area[D]. Shenyang:Shenyang Agricultural University,2020.
[59]刘文德,王贵,徐树文,陈维智,贺兴源.早实核桃新品种引种试验研究[J].经济林研究,1991,9(2):36-42.LIU Wende,WANG Gui,XU Shuwen,CHEN Weizhi,HE Xingyuan. Introduction trial with early walnut varieties[J]. Economic Forest Researches,1991,9(2):36-42.
[60]高绍棠,曹玉美,尹卫东,高林宝,王群.淳化泥河沟试区核桃引种小结[J].西北林学院学报,1993,8(2):58-66.GAO Shaotang,CAO Yumei,YIN Weidong,GAO Linbao,WANG Qun. Introduction of walnut in Chunhua County[J].Journal of Northwest Forestry University,1993,8(2):58-66.
[61]康宁,武显维,高福存.太行山低山丘陵区良种核桃引种结果[J].落叶果树,1994,26(4):23.KANG Ning,WU Xianwei,GAO Fucun. The results of the introduction of improved walnut varieties in the hilly area of Taihang Mountains[J].Deciduous Fruits,1994,26(4):23.
[62]王根宪,冀宏山,王善振,惠立清.早实核桃新品种在秦岭南麓低山丘陵区引种表现[J].山西果树,1998(4):25-26.WANG Genxian,JI Hongshan,WANG Shanzhen,HUI Liqing.Introduction of new early-bearing walnut varieties in the low mountain and hilly areas at the southern foot of the Qinling Mountains[J].Shanxi Fruits,1998(4):25-26.
[63]侯立群,王钧毅,赵登超,杨克强,韩传明.材果兼用型核桃新品种‘青林’[J].园艺学报,2010,37(2):333-334.HOU Liqun,WANG Junyi,ZHAO Dengchao,YANG Keqiang,HAN Chuanming. A new walnut cultivar‘Qinglin’used for wood and fruit[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2010,37(2):333-334.
[64]侯立群,赵登超,王钧毅,杨克强,韩传明,崔淑英.鲜食核桃新品种‘绿香’[J].园艺学报,2010,37(7):1193-1194.HOU Liqun,ZHAO Dengchao,WANG Junyi,YANG Keqiang,HAN Chuanming,CUI Shuying.A new fresh-eating walnut cultivar‘Lüxiang’[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2010,37(7):1193-1194.
[65]李好先,曹尚银,薛辉,赵弟广,牛娟,张富红,陈利娜.鲜食核桃新品种‘中核4 号’[J].园艺学报,2015,42(8):1619-1620.LI Haoxian,CAO Shangyin,XUE Hui,ZHAO Diguang,NIU Juan,ZHANG Fuhong,CHEN Lina.A new fresh-eating walnut cultivar‘Zhonghe 4'[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2015,42(8):1619-1620.
[66]郝艳宾,吴春林,陈永浩,董宁光,王维霞,齐建勋.麻核桃新品种‘京艺1 号’的选育[J].果树学报,2013,30(4):718-719.HAO Yanbin,WU Chunlin,CHEN Yonghao,WANG Weixia,QI Jianxun. Selection of a new Juglans hopeiensis cultivar‘Jingyi 1’[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2013,30(4):718-719.
[67]郝艳宾,齐建勋,吴春林,陈永浩,董宁光,王维霞.麻核桃新品种‘华艺1 号’[J].园艺学报,2012,39(12):2531-2532.HAO Yanbin,QI Jianxun,WU Chunlin,CHEN Yonghao,DONG Ningguang,WANG Weixia. A new cultivar of Juglans Hopeiensis‘Huayi 1’[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2012,39(12):2531-2532.
[68]WU G L,CHEN Y H,ZHANG P F,YANG J Q,SONG Y Q.Apomixis and new selections of walnut[J]. Acta Horticulturae,2007,760:541-548.
[69]刘永辉,孟海军,杨莹,赵伟,李琳,王磊,吴国良.彩色核桃品种资源及开发利用[J].果树资源学报,2021,2(2):90-94.LIU Yonghui,MENG Haijun,YANG Ying,ZHAO Wei,LI Lin,WANG Lei,WU Guoliang. Development and utilization of colorful walnut cultivars resources in China[J].Journal of Fruit Resources,2021,2(2):90-94.
[70]MCGRANAHAN G H,LESLIE C A,URATSU S L,MARTIN L A,DANDAKER A M. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of walnut somatic embryos and regeneration of transgenic plants[J].Biotechnology,1988,6(7):800-804.
[71]MCGRANAHAN H,LESLI C AE,URATSU S L,DANDAKER A M. Improved efficiency of the walnut somatic embryo gene transfer system[J].Plant Cell Reports,1990,8:512-516.
[72]ZHANG J P,ZHANG W T,JI F Y,QIU J,SONG X B,BU D C,PAN G,MA Q G,CHEN J X,HUANG R M,CHANG Y Y,PEI D. A high-quality walnut genome assembly reveals extensive gene expression divergences after whole- genome duplication[J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2020,18(9):1848-1850.
[73]武鹏雨,刘婷婷,包建平,虎海防,马凯,张锐.核桃基因组学研究进展[J].中国果树,2022(2):12-19.WU Pengyu,LIU Tingting,BAO Jianping,HU Haifang,MA Kai,ZHANG Rui. Research progress in Juglans genomics study[J].China Fruits,2022(2):12-19.
[74]方宏筠,王关林.黑核桃体细胞胚状体发生及其基因转化系统的建立[J].园艺学报,2000,27(6):406-411.FANG Hongjun,WANG Guanlin. Somatic embryogenesis of Juglans nigria l.and establishment of gene transformation system of walnut[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2000,27(6):406-411.
[75]汤浩茹,WALLBRAUN M,任正隆,REUSTLE G M,KRCZAL G.通过农杆菌介导法将哈兹木霉几丁质酶ThEn-42 基因导入核桃[J].园艺学报,2001,28(1):12-18.TANG Haoru,WALLBRAUN M,REN Zhenglong,REUSTLE G M,KRCZAL G. Genetic transformation of the Trichoderma endochitinase gene ThEn 42 to somatic embryos of English walnut[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2001,28(1):12-18.
[76]LI Y Z,LUO X,WU C Y,CAO S Y,ZHOU Y F,JIE B,CAO Y L,MENG H J,WU G L.Comparative transcriptome analysis of genes involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis in red and green walnut(Juglans regia L.)[J].Molecules,2017,23(1):25.
[77]ZHAO W,LIU Y H,LI L,MENG H J,YANG Y,DONG Z B,WANG L,WU G L. Genome-wide identification and characterization of bHLH transcription factors related to anthocyanin biosynthesis in red walnut(Juglans regia L.)[J].Frontiers in Genetics,2021,12:145.
[78]吴国良,刘群龙,郑先波,宋宇琴,简在海,彭功波.核桃种质资源研究进展[J].果树学报,2009,26(4):539-545.WU Guoliang,LIU Qunlong,ZHENG Xianbo,SONG Yuqin,JIAN Zaihai,PENG Gongbo. Advances in research on the worldwide walnut germplasm[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2009,26(4):539-545.
[79]温家康,马荣,王大芬,张萍.新疆野核桃种质资源对核桃腐烂病的抗性评价[J].果树学报,2022,39(8):1469-1478.WEN Jiakang,MA Rong,WANG Dafen,ZHANG Ping.Evaluation of resistance of Xinjiang wild walnuts to walnut canker[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2022,39(8):1469-1478.
[80]谢蕾,李贤忠,宁德鲁,马婷,吴涛.深纹核桃种质资源评价与挖掘研究进展[J].林业科技通讯,2021(11):26-31.XIE Lei,LI Xianzhong,NING Delu,MA Ting,WU Tao. Advances in germplasm resources evaluation and exploratory research progress of Juglans sigillata[J]. Forest Science and Technology,2021(11):26-31.
[81]赵廷松,范志远,邹伟烈,潘莉,刘娇,杜春花,杨建华,李淑芳,曾清贤,饶绍松,王斌,张顺芬.核桃抗寒避晚霜新品种‘云林1 号’的选育[J].中国果树,2016(3):66-68.ZHAO Tingsong,FAN Zhiyuan,ZOU Weilie,PAN Li,LIU Jiao,DU Chunhua,YANG Jianhua,LI Shufang,ZENG Qingxian,RAO Shaosong,WANG Bin,ZHANG Shunfen. Breeding of a new walnut variety‘Yunlin No.1’resistant to cold and avoiding late frost[J].China Fruits,2016(3):66-68.
[82]赵廷松,范志远,邹伟烈,刘娇,潘莉,杜春花,杨建华,李淑芳,曾清贤,饶绍松,王斌,张顺芬. 避晚霜核桃新品种‘云林2号’的选育[J].中国南方果树,2016,45(5):150-151.ZHAO Tingsong,FAN Zhiyuan,ZOU Weilie,LIU Jiao,PAN Li,DU Chunhua,YANG Jianhua,LI Shufang,ZENG Qingxian,RAO Shaosong,WANG Bin,ZHANG Shunfen. Breeding of a new walnut variety‘Yunlin No.2’for avoiding late frost[J].South China Fruits,2016,45(5):150-151.
[83]赵梓岑,徐士忠,季梅,赵宁,杨斌.云南主栽核桃品种对炭疽病的抗性评价[J].贵州农业科学,2018,46(5):41-45.ZHAO Zicen,XU Shizhong,JI Mei,ZHAO Ning,YANG Bin.Resistance of main walnut varieties against anthracnose in Yunnan[J].Guizhou Agricultural Sciences,2018,46(5):41-45.
[84]贺占雪,泽桑梓,杨斌,赵宁.云南主栽核桃品种对Phyllosticta juglandis 叶斑病的抗性评价[J]. 浙江农业科学,2019,60(11):1989-1992.HE Zhanxue,ZE Sangxin,YANG Bin,ZHAO Ning. Evaluation of resistance to leaf spot caused by Phyllosticta juglandis of walnut cultivars in Yunnan Province[J].Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences,2019,60(11):1989-1992.
[85]国家市场监督管理总局,国家标准化管理委员会.核桃坚果质量等级:GB/T 20398—2021[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2021:10.State Market Regulatory Administration,Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China.Grade of walnut:GB/T 20398—2021[S].Beijing:Standards Press of China,2021:10.