毛花猕猴桃(Actinidia eriantha)是隶属于猕猴桃科(Actinidiaceae)猕猴桃属(Actinidia)的多年生落叶藤本果树,是我国特有的野生种质资源[1],果实中抗坏血酸(AsA)含量极高,AsA 是研究植物中代谢与调控的宝贵材料。AsA 是一种多功能代谢物,在植物中广泛调控光合作用、环境诱导的氧化胁迫、机械损伤响应等生理生化过程[2]。氧化胁迫是对植物造成伤害的主要非生物胁迫,在长期的演化过程中植物体内形成了多种应对氧化胁迫清除氧自由基的酶,如超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、抗坏血酸过氧化物酶(APX,EC1.11.1.11)、谷胱甘肽还原酶(GR)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)和过氧化物酶(POD)等。同时SOD、APX 和GR 也参与了AsA-谷胱甘肽循环[3]。其中,APX是以AsA为电子供体的一种清除H2O2的关键酶[4],可以催化H2O2转化为H2O和O2,将AsA氧化为单脱氢抗坏血酸(MDHA),也是AsA代谢的主要酶类[5]。前人的研究发现,APX 基因的表达受到光照、干旱、盐胁迫等多种逆境胁迫诱导[6-7],作为AsA 氧化分解途径的关键酶,APX 基因的表达情况与AsA含量密切相关。
植物中APX 可分为4 种类型:细胞质型、叶绿体型、线粒体型和过氧化物酶体型[8]。目前为止,APX 基因已经在多个物种中进行了成员鉴定,如拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)、水稻(Oryza sativa)、玉米(Zea mays)、番茄(Solanum lycopersicum)、巴西橡胶树(Hevea brasiliensis)、棉花(Gossypium hirsutum)等[9-14],研究表明拟南芥APXs 家族含有8 个基因,其中有3个(APX1、APX2和APX6)位于细胞质,2个(sAPX、tAPX)位于叶绿体,3 个(APX3、APX4、APX5)位于过氧化物酶体[15];水稻APXs基因家族含有8 个成员,2 个在细胞质、2 个在过氧化物酶体、3个在叶绿体、1个在线粒体[16]。但在毛花猕猴桃上未见APX基因家族成员鉴定的报道。据此,笔者在本研究中利用生物信息学的方法鉴定毛花猕猴桃APX基因家族成员,对其基因家族成员基因结构及系统进化等进行分析,同时对基因家族成员在果实不同发育时期和套袋处理之后的表达情况进行检测,以期为毛花猕猴桃AsA代谢调控机制研究奠定理论基础。
1 材料和方法
1.1 试验材料和处理
选取江西省奉新县农业农村局猕猴桃种质资源圃内生长健壮、无病虫害感染的毛花猕猴桃赣绿1号为试验材料。选取6株树体大小、生长势相似,均匀接受阳光的成熟植株随机分成3 组(重复),每组两株。在盛花30 d 后,每株树选取来自不同方位的大约120个果实使用外黄内黑单层纸袋进行套袋处理,不套袋作为对照。套袋处理参考Liao 等[17]的方法。采集幼果期(盛花后25 d)、转色期(盛花后125 d)、采摘期(盛花后165 d)果实,取中果皮并将中果皮切碎后用液氮处理,储存于-80 ℃超低温条件下备用。
1.2 APX基因家族成员的鉴定
从Pfam数据库(http://pfam.xfam.org)下载过氧化物酶蛋白的隐马尔可夫模型文件,利用TBtools软件[18]在毛花猕猴桃品种华特猕猴桃基因组蛋白序列中进行搜索,获取毛花猕猴桃APX基因家族成员的候选序列。同时以拟南芥APX 基因家族成员蛋白序列为探针,在猕猴桃基因组数据库中进行blastp,获取同源性较高的序列,并作为毛花猕猴桃APX基因家族成员的候选序列。上述两种方法共同鉴定出的序列进行下一步分析。以是否含有APX 基因家族特有保守域(PF00141)为标准,进一步在Pfam 数据库进行验证。确定毛花猕猴桃APX 基因家族成员后,在ProtProm(http://web.expasy.org/protparam/)网站中测定毛花猕猴桃APX蛋白的分子质量、等电点等理化性质[19]。此外,从NCBI(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)上分别下载拟南芥、棉花APXs 蛋白的氨基酸序列用于后续的序列比对。
1.3 进化分析
利用Clustal X 将拟南芥、棉花、毛花猕猴桃APXs 基因家族的氨基酸序列进行多序列比对,然后用MEGA X软件中的比邻接法(neighbor-joining)构建系统发育树,参数使用默认值,Bootstrap 值设置为1000 次。利用TBtools 软件[18]进行染色体共线性分析。
1.4 基因结构、保守域及motif分析
利用MEME 在线网站(http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme)对毛花猕猴桃APXs 蛋白的motifs 进行识别,motifs 的最大设置值为10[20]。使用GSDS 2.0(http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/)在线软件分析毛花猕猴桃APXs 基因家族的基因结构[21]。通过WoLF PSORT(http://wolf psort.org)网站来进行亚细胞定位预测。
1.5 顺式作用元件分析
用TBtools软件[18]提取AeAPXs基因转录起始位点上游2000 bp的序列,然后利用PlantCARE(http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/)在线网站进行顺式作用元件分析[22]。
1.6 跨膜分析及蛋白二级结构预测
使用TMHMM Server v.2.0(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/)在线软件预测AeAPXs 基因家族成员的跨膜结构。利用NPSA(https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi- bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=npsa_sopma.html)来进行AeAPXs基因家族成员的蛋白质二级结构分析[23]。
1.7 实时荧光定量PCR分析
用北京擎科生物科技有限公司的多糖多酚植物总RNA 提取试剂盒提取RNA。用北京聚合美生物科技有限公司M5 Super plus qPCR RT kit with gDNA remover 进行cDNA 第一链的合成。通过Primer Premier 5 软件设计荧光定量引物,引物由北京擎科生物科技有限公司进行引物合成(表1)。选择Actin作为内参基因。反应体系为2×Realtime Super mix 10 μL,正、反引物浓度为10 nmol·L-1,cDNA 1.0 μL,ddH2O 8 μL。设置3个生物学重复。PCR仪型号为CFX96TM Real-Time System。qRT-PCR 反应程序为:95 ℃1 min,95 ℃10 s,60 ℃5 s,72 ℃12 s,40个循环。基因的相对表达量采用2-ΔΔCT计算[24]。
表1 qRT-PCR 定量引物设计
Table 1 Primers for qRT-PCR

基因名称Gene name AeAPX3 AeAPX6 AeAPX8 AeAPX13 AeAPX14 AeAPX21 AeAPX22 AeAPX24 AeAPX25 AeAPX27 Actin上游引物(5’-3’)Forward primer(5’-3’)ACCGTCAGGGTCTTTTCACTTC GGGAGGCATCTGAGTTTGACA CCCTATGGGAAGTGAAGTTGG GGCTATGCTCTTGCCGACCTA CCACTTCCACGACTGCTTTG CGTGCGACGGGTGAAAGTT CGCCTTCCAGATGCCAAAC ACTGCTTTGTTGAGGGATGTGA GTCCAGGGATGTGATTCTTCG ACTCTACTCTTGGACGAAGGGAC GTGCTCAGTGGTGGTTCAA下游引物(5’-3’)Reverse primer(5’-3’)CGCTCAACTGGCTCATCTTTAT CAAAGGAACTGGGAGTGAACC CGGAAGACGATTGAGAAGCA AAGTTCACGCAGCGACCCA CCAACTCGGTCCTCCAAGAAT CGCACCAGAATCGGATGACA CCTCCTCCGACTCCTTATTCA CGGCTTCTACTGCTTGTTTTGC GGGTCGCTATGGCAAGAATGT AGATGAGATTGCTGAGGTCGG GACGCTGTATTTCCTCTCAG
1.8 抗坏血酸含量的测定和数据分析
根据Liao 等[25]的方法,通过2,6-二氯靛酚滴定法测定AsA 含量。使用Excel 2019 整理试验数据并采用IBM SPSS Statistics 22 进行差异显著性分析;用TBtools制图软件绘制基因表达热图。
2 结果与分析
2.1 毛花猕猴桃APX基因家族成员鉴定
利用生物信息学方法,对猕猴桃全基因组数据库进行筛选,通过对候选基因保守结构域分析,共鉴定出29 个AeAPXs 基因家族成员,根据它们在染色体上的分布,依次命名为AeAPX1~AeAPX29。从表2可见,AeAPXs 的编码区在840(AeAPX7)~1515 bp(AeAPX13)之间。基因全长在1362(AeAPX9)~10 391 bp(AeAPX21)之间,编码氨基酸数在279~504 aa 之间。AeAPXs基因家族成员分别有16个APX基因定位在叶绿体,5 个定位在细胞外基质,4 个定位在细胞质,2个定位在液泡,2个定位在细胞核。
表2 毛花猕猴桃APX 基因家族成员信息
Table 2 APX gene family members information of A.eriantha
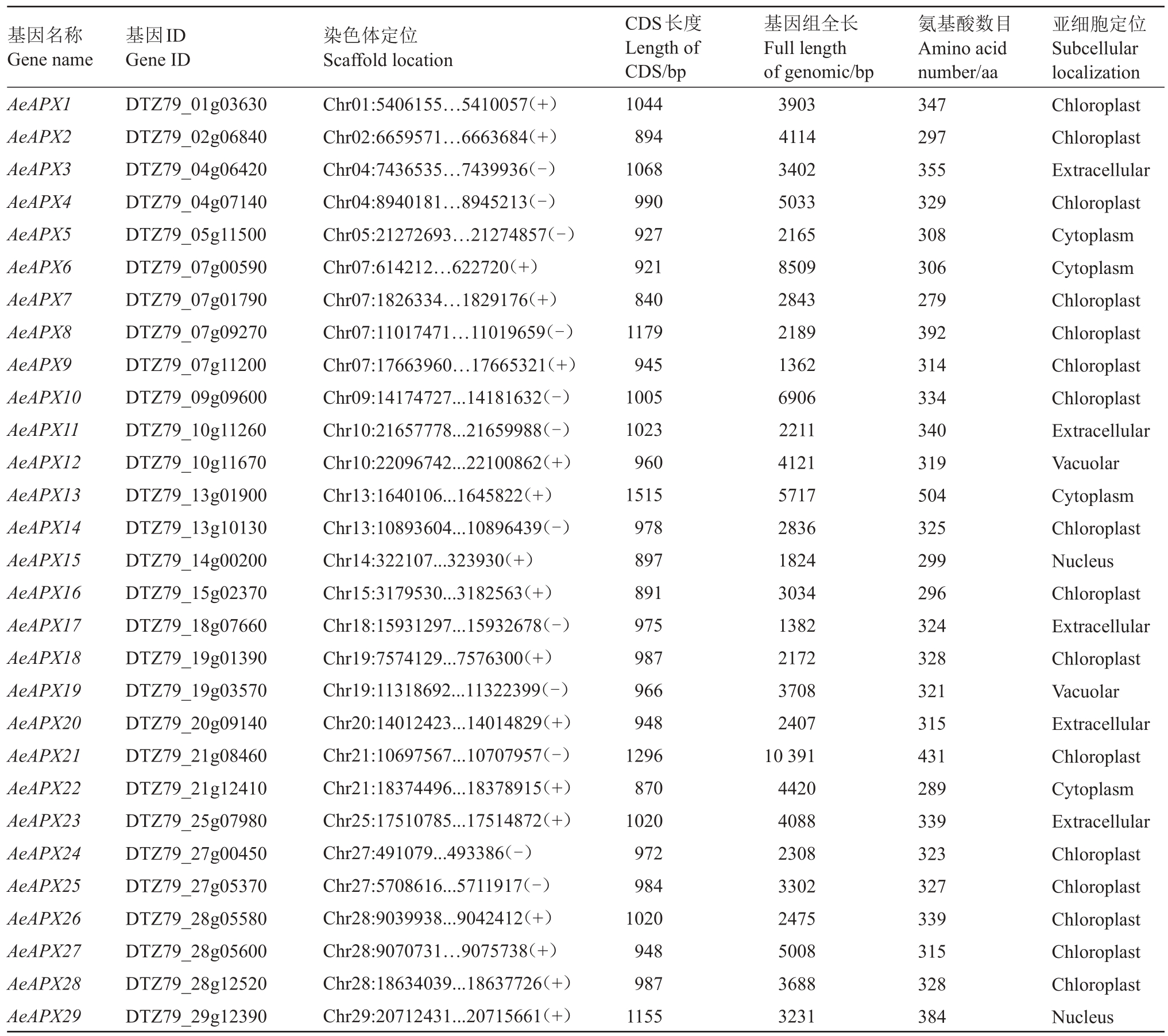
基因名称Gene name AeAPX1 AeAPX2 AeAPX3 AeAPX4 AeAPX5 AeAPX6 AeAPX7 AeAPX8 AeAPX9 AeAPX10 AeAPX11 AeAPX12 AeAPX13 AeAPX14 AeAPX15 AeAPX16 AeAPX17 AeAPX18 AeAPX19 AeAPX20 AeAPX21 AeAPX22 AeAPX23 AeAPX24 AeAPX25 AeAPX26 AeAPX27 AeAPX28 AeAPX29基因ID Gene ID DTZ79_01g03630 DTZ79_02g06840 DTZ79_04g06420 DTZ79_04g07140 DTZ79_05g11500 DTZ79_07g00590 DTZ79_07g01790 DTZ79_07g09270 DTZ79_07g11200 DTZ79_09g09600 DTZ79_10g11260 DTZ79_10g11670 DTZ79_13g01900 DTZ79_13g10130 DTZ79_14g00200 DTZ79_15g02370 DTZ79_18g07660 DTZ79_19g01390 DTZ79_19g03570 DTZ79_20g09140 DTZ79_21g08460 DTZ79_21g12410 DTZ79_25g07980 DTZ79_27g00450 DTZ79_27g05370 DTZ79_28g05580 DTZ79_28g05600 DTZ79_28g12520 DTZ79_29g12390染色体定位Scaffold location Chr01:5406155…5410057(+)Chr02:6659571…6663684(+)Chr04:7436535…7439936(-)Chr04:8940181…8945213(-)Chr05:21272693…21274857(-)Chr07:614212…622720(+)Chr07:1826334…1829176(+)Chr07:11017471…11019659(-)Chr07:17663960…17665321(+)Chr09:14174727...14181632(-)Chr10:21657778...21659988(-)Chr10:22096742...22100862(+)Chr13:1640106...1645822(+)Chr13:10893604...10896439(-)Chr14:322107...323930(+)Chr15:3179530...3182563(+)Chr18:15931297...15932678(-)Chr19:7574129...7576300(+)Chr19:11318692...11322399(-)Chr20:14012423...14014829(+)Chr21:10697567...10707957(-)Chr21:18374496...18378915(+)Chr25:17510785...17514872(+)Chr27:491079...493386(-)Chr27:5708616...5711917(-)Chr28:9039938...9042412(+)Chr28:9070731…9075738(+)Chr28:18634039...18637726(+)Chr29:20712431...20715661(+)CDS长度Length of CDS/bp 1044 894 1068 990 927 921 840 1179 945 1005 1023 960 1515 978 897 891 975 987 966 948 1296 870 1020 972 984 1020 948 987 1155基因组全长Full length of genomic/bp 3903 4114 3402 5033 2165 8509 2843 2189 1362 6906 2211 4121 5717 2836 1824 3034 1382 2172 3708 2407 10 391 4420 4088 2308 3302 2475 5008 3688 3231氨基酸数目Amino acid number/aa 347 297 355 329 308 306 279 392 314 334 340 319 504 325 299 296 324 328 321 315 431 289 339 323 327 339 315 328 384亚细胞定位Subcellular localization Chloroplast Chloroplast Extracellular Chloroplast Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Chloroplast Chloroplast Chloroplast Chloroplast Extracellular Vacuolar Cytoplasm Chloroplast Nucleus Chloroplast Extracellular Chloroplast Vacuolar Extracellular Chloroplast Cytoplasm Extracellular Chloroplast Chloroplast Chloroplast Chloroplast Chloroplast Nucleus
2.2 AeAPXs家族成员蛋白理化性质分析
蛋白质理化性质分析结果(表3)表明,其理论等电点在4.73~9.12 之间,且AeAPX24 最小,AeAPX1 和AeAPX27 最大。相对分子质量为30 019.12~55 354.20 ku。除了AeAPX3、AeAPX5、AeAPX6、AeAPX9、AeAPX12、AeAPX13、AeAPX17、AeAPX21、AeAPX22、AeAPX23、AeAPX24、AeAPX29蛋白为不稳定蛋白外,其他AeAPXs 均属于稳定蛋白。AeAPX10、AeAPX19、AeAPX24、AeAPX26、AeAPX28 蛋白为亲水性蛋白;除了AeAPX23 蛋白外,其他AeAPXs蛋白均属于脂溶蛋白。
表3 AeAPXs 蛋白理化性质分析
Table 3 Physical and chemical properties of AeAPXs

注:总平均亲水性为负值表示亲水性,正值表示疏水性;不稳定指数大于40 为不稳定蛋白;脂溶指数小于100 为脂溶蛋白。
Note: Value of grand average of hydropathicity being negative means hydropathicity, while positive means hydropathicity; instability index more than 40 means unstable;aliphatic index less than 100 means lipid soluble protein.
总平均亲水性Grand average of hydropathicity-0.195-0.143-0.026-0.153-0.207-0.274-0.119-0.165-0.110 0.021-0.093-0.113-0.066-0.018-0.321-0.098-0.122-0.057 0.082-0.048-0.403-0.255-0.125 0.012-0.065 0.041-0.342 0.073-0.219基因名称Gene name AeAPX1 AeAPX2 AeAPX3 AeAPX4 AeAPX5 AeAPX6 AeAPX7 AeAPX8 AeAPX9 AeAPX10 AeAPX11 AeAPX12 AeAPX13 AeAPX14 AeAPX15 AeAPX16 AeAPX17 AeAPX18 AeAPX19 AeAPX20 AeAPX21 AeAPX22 AeAPX23 AeAPX24 AeAPX25 AeAPX26 AeAPX27 AeAPX28 AeAPX29基因ID Gene ID DTZ79_01g03630 DTZ79_02g06840 DTZ79_04g06420 DTZ79_04g07140 DTZ79_05g11500 DTZ79_07g00590 DTZ79_07g01790 DTZ79_07g09270 DTZ79_07g11200 DTZ79_09g09600 DTZ79_10g11260 DTZ79_10g11670 DTZ79_13g01900 DTZ79_13g10130 DTZ79_14g00200 DTZ79_15g02370 DTZ79_18g07660 DTZ79_19g01390 DTZ79_19g03570 DTZ79_20g09140 DTZ79_21g08460 DTZ79_21g12410 DTZ79_25g07980 DTZ79_27g00450 DTZ79_27g05370 DTZ79_28g05580 DTZ79_28g05600 DTZ79_28g12520 DTZ79_29g12390理论等电点pI 9.12 8.63 6.23 5.90 5.85 8.72 5.97 6.95 8.62 7.96 8.35 8.28 5.21 8.92 7.68 5.93 5.66 6.52 4.89 8.58 8.18 6.47 5.93 4.73 8.79 5.53 9.12 6.43 5.19相对分子质量Molecular weight/ku 38 786.68 31 052.76 38 817.38 35 680.53 33 923.62 34 475.55 30 019.12 43 518.84 33 794.13 36 961.25 36 834.16 34 531.53 55 354.20 34 748.59 33 601.33 31 432.32 35 365.11 36 065.19 34 308.89 34 282.34 46 968.27 31 836.35 38 095.48 34 674.20 35 545.46 36 338.00 34 349.71 35 294.30 42 018.15不稳定指数Instability index 30.15 34.35 41.67 33.68 41.45 40.91 32.99 34.55 40.21 37.25 38.42 51.59 45.80 35.05 39.88 29.00 40.59 33.74 37.24 32.26 46.20 43.17 50.49 41.00 28.10 26.63 30.02 37.73 44.07脂溶指数Aliphatic index 87.38 76.26 92.34 90.09 74.12 91.50 84.59 88.04 85.83 87.28 85.21 86.30 93.79 85.51 82.11 82.80 84.66 82.07 91.68 86.38 79.81 88.10 100.09 78.27 80.58 85.75 72.73 87.74 78.54
2.3 AeAPXs基因家族成员的跨膜分析以及蛋白结构预测
对29 个APX 基因家族成员的氨基酸序列进行跨膜区预测,结果(表4,图1)表明,只有AeAPX1、AeAPX3、AeAPX5、AeAPX6、AeAPX8、AeAPX11、AeAPX14、AeAPX18、AeAPX21、AeAPX22、AeAPX23、AeAPX26、AeAPX28这13个基因编码的蛋白质各含有1个跨膜区,均属于跨膜蛋白。

图1 AeAPXs 基因家族膜蛋白跨膜区预测
Fig.1 Predicted transmembrane domains of APXs protein in A.eriantha
表4 毛花猕猴桃13 种APX 膜蛋白跨膜区
Table 4 Transmembrane region of 13 APX membrane proteins in A.eriantha

膜蛋白Membrane protein AeAPX1 AeAPX3 AeAPX5 AeAPX6 AeAPX8 AeAPX11 AeAPX14 AeAPX18 AeAPX21 AeAPX22 AeAPX23 AeAPX26 AeAPX28 N端位置Position of N terminal 12 7 12 265 32 7 15 13 416 265 10 15 12跨膜区Transmembrane domain GLGLLFLPLLAVFALGSWWFVVV ALLSLFCLTSLLLVISLLLLSSY LGAILVMEIIVMSGTRFGAV AILAQSAFGVAVAAAVVVLTYLY LSLFLLLLSLSDIAAVSAVLPPF AFLKVLSSLMVVVFLFPTLSLAF SMLAFVLFLLVLLVGSSSAQLSA YLTIFIFSLVIFLYPFAN YFLNIIIVIAVLAILTYLLG TILAQSAVGVAVATAVVLLSYFY PILLIVLILIFHGLGSYSGPLVL FCFSVVFLFVFLGISSAQLSSNY FNGFYFFIALLMSCMAVRAQLSA C端位置Position of C terminal 34 29 31 287 54 29 37 30 435 287 32 37 34长度Length/aa 23 23 20 23 23 23 23 18 20 23 23 23 23
AeAPXs 基因家族编码蛋白质的二级结构(表5),主要有α-螺旋(Alpha helix)占34.74%~43.14%、β-转角(Beta turn)占4.36%~8.55%、不规则卷曲(Random coil)占37.14%~41.52%、延伸链(Extended strand)占9.28%~20.24%,α-螺旋与不规则卷曲所占比相差不大,但是远高于β-转角和延伸链所占比。
表5 毛花猕猴桃APX 蛋白二级结构分析
Table 5 The secondary structure analysis of APX protein sequence in A.eriantha
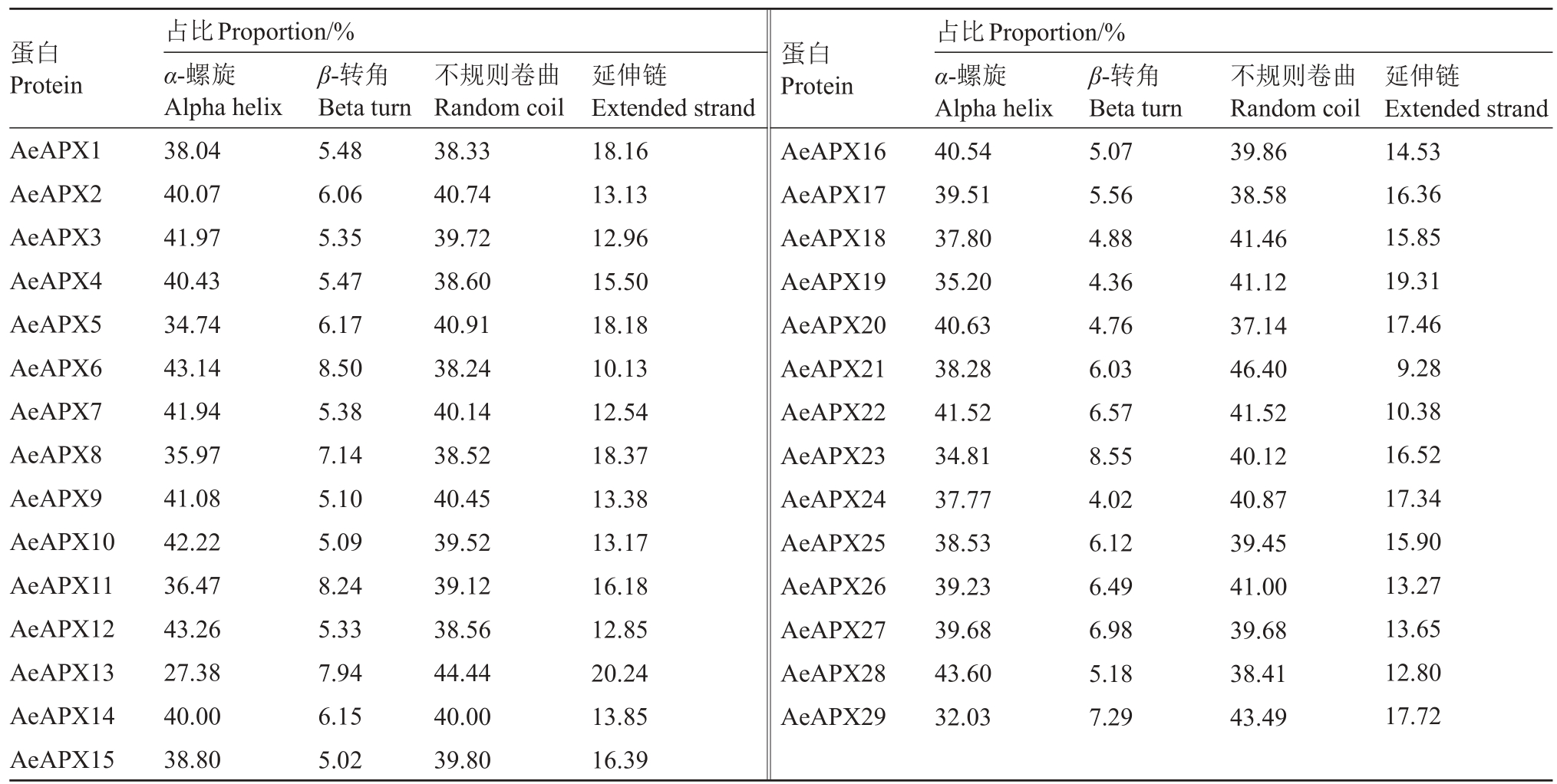
蛋白Protein蛋白Protein AeAPX1 AeAPX2 AeAPX3 AeAPX4 AeAPX5 AeAPX6 AeAPX7 AeAPX8 AeAPX9 AeAPX10 AeAPX11 AeAPX12 AeAPX13 AeAPX14 AeAPX15占比Proportion/%α-螺旋Alpha helix 38.04 40.07 41.97 40.43 34.74 43.14 41.94 35.97 41.08 42.22 36.47 43.26 27.38 40.00 38.80 β-转角Beta turn 5.48 6.06 5.35 5.47 6.17 8.50 5.38 7.14 5.10 5.09 8.24 5.33 7.94 6.15 5.02不规则卷曲Random coil 38.33 40.74 39.72 38.60 40.91 38.24 40.14 38.52 40.45 39.52 39.12 38.56 44.44 40.00 39.80延伸链Extended strand 18.16 13.13 12.96 15.50 18.18 10.13 12.54 18.37 13.38 13.17 16.18 12.85 20.24 13.85 16.39 AeAPX16 AeAPX17 AeAPX18 AeAPX19 AeAPX20 AeAPX21 AeAPX22 AeAPX23 AeAPX24 AeAPX25 AeAPX26 AeAPX27 AeAPX28 AeAPX29占比Proportion/%α-螺旋Alpha helix 40.54 39.51 37.80 35.20 40.63 38.28 41.52 34.81 37.77 38.53 39.23 39.68 43.60 32.03 β-转角Beta turn 5.07 5.56 4.88 4.36 4.76 6.03 6.57 8.55 4.02 6.12 6.49 6.98 5.18 7.29不规则卷曲Random coil 39.86 38.58 41.46 41.12 37.14 46.40 41.52 40.12 40.87 39.45 41.00 39.68 38.41 43.49延伸链Extended strand 14.53 16.36 15.85 19.31 17.46 9.28 10.38 16.52 17.34 15.90 13.27 13.65 12.80 17.72
2.4 基因结构和保守域分析
采用GSDS 2.0 在线工具对AeAPXs 的内含子/外显子结构进行分析,结果(图2)表明,AeAPXs具有相似的基因结构,外显子数分布为2~12 个。除了AeAPX6、AeAPX21、AeAPX22 分别含有10、12、9 个外显子数外,其余AeAPXs 家族成员的外显子数为2~5个,但大多数含有4个外显子。
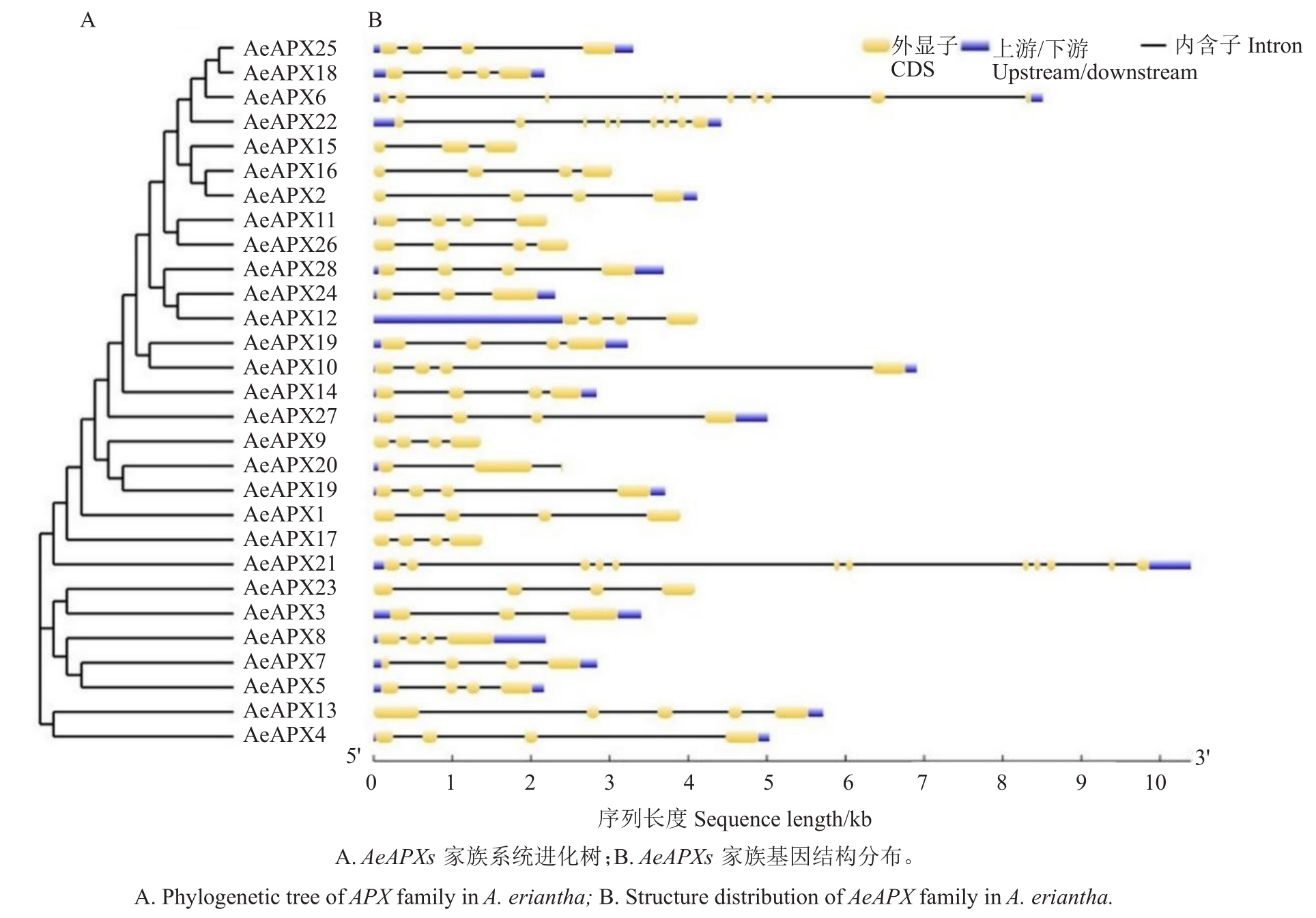
图2 AeAPXs 基因家族结构
Fig.2 Structure of APX gene family in A.eriantha
通过MEME 软件构建AeAPXs 保守区域基序分析图(图3),结果表明,毛花猕猴桃AeAPXs 序列中含有10 个基序,分别为Motif 1~Motif 10。其中Motif 3和Motif 9存在于所有AeAPXs蛋白中,除Motif 3和Motif 9 之外,AeAPX21、AeAPX22 蛋白还含有Motif 1、Motif 5、Motif 7 这3 个基序;其余26 个AeAPXs 家族成员含有7 个相似的Motif 基序,整体上看这26 个基因编码的氨基酸序列保守性较强。以上结果显示,保守域中各基因家族成员的基序位置不同,数量不同,很可能导致基因功能分化。

图3 AeAPXs 基因家族基序分析
Fig.3 Motif analysis of APX gene family in A.eriantha
2.5 进化分析
为了探究APX 基因家族的进化关系,利用毛花猕猴桃、拟南芥、棉花APXs基因家族的蛋白序列构建了系统进化树。结果(图4)表明,该基因家族可分为3个亚类。A亚类由7个AeAPXs基因家族成员组成;其中AeAPX6 与拟南芥AtAPX3 和棉花GhAPX4 的同源性为100%,AeAPX22 与AtAPX5 的同源性为98%。B 亚类由10 个AeAPXs 基因家族成员组成。C 亚类由12 个AeAPXs 基因家族成员组成;其中AeAPX15 和棉花GhAPX6 的同源性为96%。以上分析表明,APX 基因家族的不同成员间在进化上有一定差异,是一个具有功能多样性的大家族,进化树中的不同分支也预示着该家族蛋白具有多种功能。
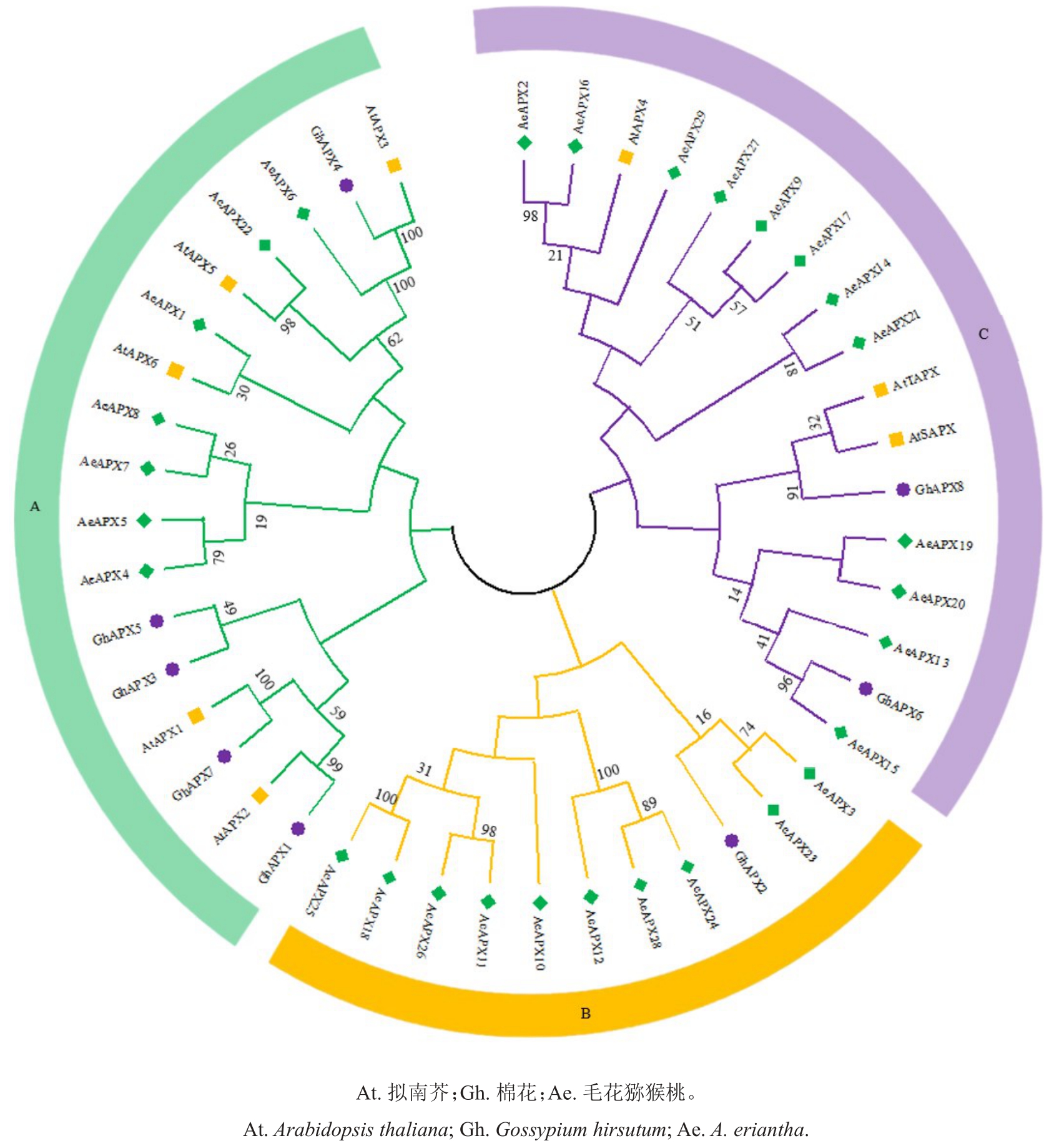
图4 毛花猕猴桃与其他植物APX 蛋白的系统进化关系
Fig.4 Phylogenetic relationship of APX protein between A.eriantha and other plants
2.6 顺式作用元件、染色体共线性分析
从PlantCARE 在线网站中预测AeAPXs 基因家族成员上游2000 bp序列,这些序列除了具有典型的核心启动子TATA-Box外,还具有光响应、激素响应及逆境响应等元件。如图5 所示,与光响应相关的顺式响应元件主要有Box4、G-Box、GT1-motif、GATA-motif、MRE、TCT-motif、TCCC-motif;其中Box4和G-Box在基因家族中分布较多。一共有5种激素相关的顺式响应元件,包括ABA(ABRE)、GA3(TATC-box)、MeJA(TGACG-motif、CGTCA-motif)、SA(TCA-element)、Auxin(TGA-element)。除此之外,基因家族中还有与逆境响应相关的元件,主要是与干旱诱导(MBS)、厌氧反应(ARE)、低温条件(LTR)、抵御逆境胁迫(TC-rich repeats)相关的顺式作用元件。
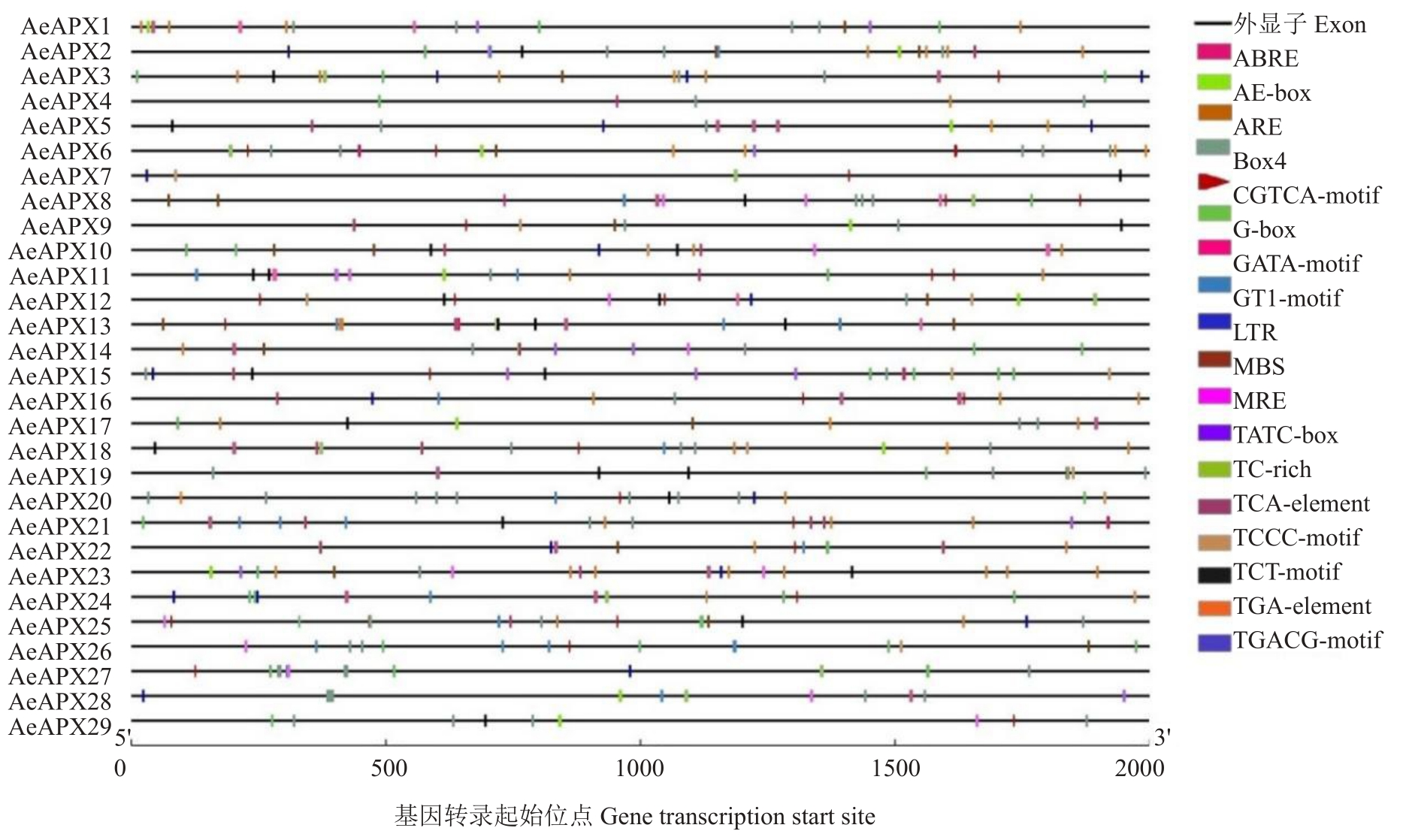
图5 AeAPXs 基因家族上游启动子系列中的响应元件数
Fig.5 Number of cis-acting elements in promoter regions of AeAPXs
为了进一步解析毛花猕猴桃APX 家族基因的进化关系,基于猕猴桃基因组注释信息,对APX 家族基因进行了染色体定位分析和物种内共线性分析。染色体定位分析结果(图6)表明,AeAPXs 基因家族成员不均匀分布在18条染色体上,分别定位于1 号和2 号染色体(AeAPX1、AeAPX2)、4 号染色体(AeAPX3和AeAPX4)、5号和7号染色体(AeAPX5和AeAPX6、AeAPX7、AeAPX8、AeAPX9)、9号和10号染色体(AeAPX10和AeAPX11、AeAPX12)、13号染色体(AeAPX13、AeAPX14)、14 号和15 号染色体(AeAPX15 和AeAPX16)、18 号和20 号染色体(AeAPX17 和AeAPX20)、19 号染色体(AeAPX18、AeAPX19)、21 号染色体(AeAPX21 和AeAPX22)、25号和29 号染色体(AeAPX23、AeAPX29)、27 号染色体(AeAPX24、AeAPX25)、28 号染色体(AeAPX26、AeAPX27、AeAPX28)。同时,物种内共线性分析观察到29 个基因中含有AeAPX2 和AeAPX16、AeAPX2 和AeAPX26、AeAPX6 和AeAPX22、AeAPX7和AeAPX18、AeAPX14 和AeAPX26、AeAPX16 和AeAPX26 这6 个片段重复事件,说明在该基因进化的过程中存在基因复制。29个AeAPXs基因家族成员中一共存在6 对共线性基因对。共线性结果表明,这些基因在进化上高度同源,且在进化过程中非常保守。
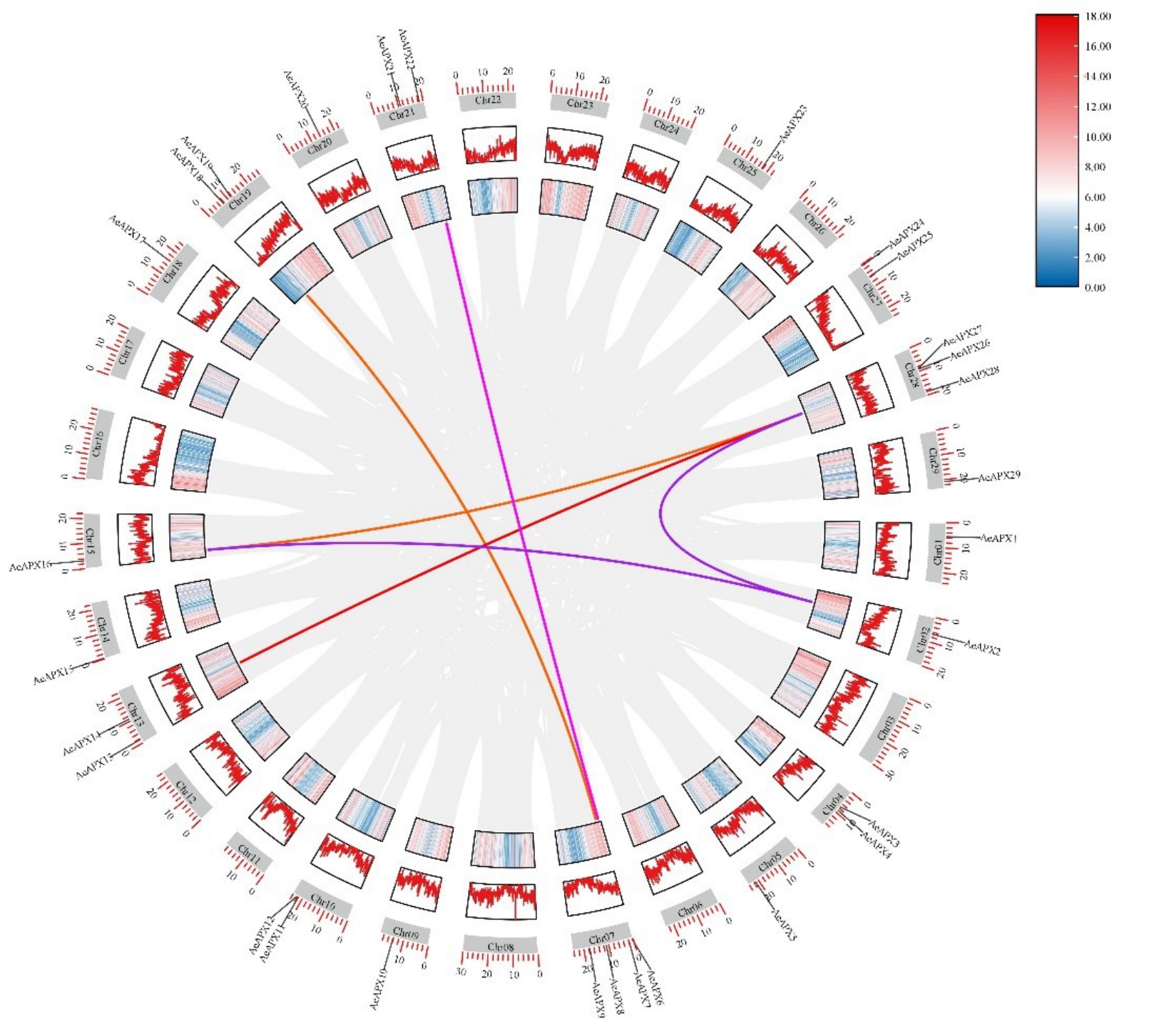
图6 染色体共线性分析
Fig.6 Chromosome collinearity analysis
2.7 果实不同发育阶段和套袋处理的基因表达分析
基于课题组现有的转录组数据分析,发现仅有AeAPX3、AeAPX6、AeAPX8、AeAPX13、AeAPX14、AeAPX21、AeAPX22、AeAPX24、AeAPX25、AeAPX27这10 个基因家族成员在毛花猕猴桃果实发育过程中能检测到表达量,因此选取这些基因进行qRTPCR 分析。结果(图7)表明,这10 个基因可分为3类,其中AeAPX3、AeAPX27单独聚为一类,AeAPX27在果实的幼果期、转色期、成熟期都具有高表达水平,而抗坏血酸含量随着果实的成熟逐渐下降[26],这表明AeAPX27 基因的表达与果实抗坏血酸含量极显著相关,是毛花猕猴桃果实抗坏血酸正调控的关键基因。而AeAPX3基因的表达量刚好与AeAPX27的表达量呈相反趋势。 AeAPX8、AeAPX13、AeAPX14、AeAPX22、AeAPX25 聚为一类,它们的基因表达水平为逐渐降低,与AsA 含量一致。AeAPX6、AeAPX21、AeAPX24 这3 个基因在果实的3个发育时期表达水平上调,与AsA 含量呈相反趋势。因此,笔者推测AeAPX27这一个基因可能参与调控果实生长发育期间AsA的代谢。
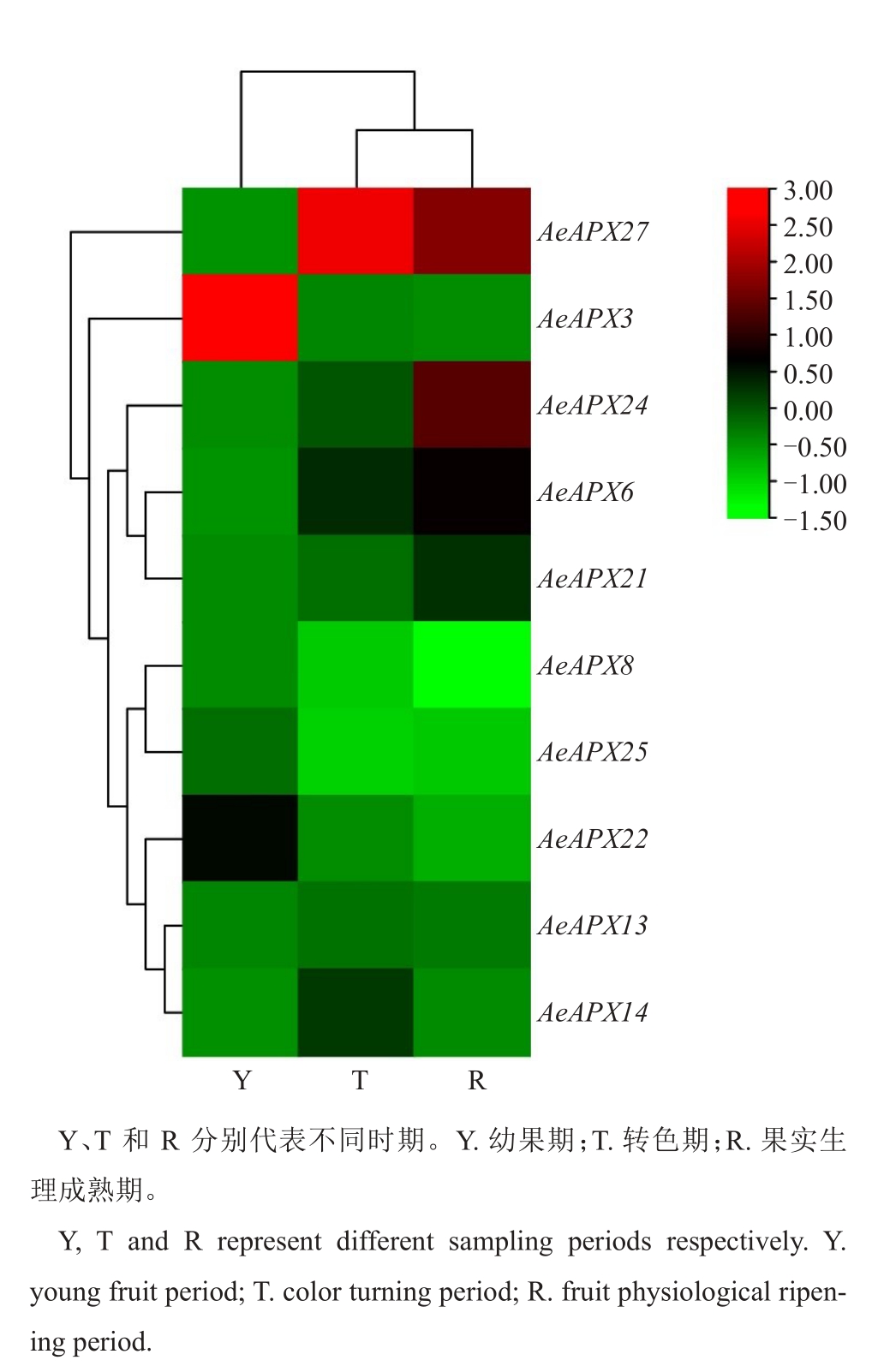
图7 AeAPXs 基因在果实不同发育阶段的表达谱分析
Fig.7 Expression profiling of AeAPX genes in different development of fruit
以未套袋(Control)处理作为对照,利用实时荧光定量PCR 对APX 基因在套袋(Treatment)处理下的表达量进行检测。采用独立样本T 检验方法在p≤0.05 和p≤0.01 水平检测套袋与未套袋处理之间基因表达量的差异。如图8 所示,套袋处理后AeAPX3、AeAPX13 的表达量相对于对照略微升高,但都与未套袋处理没有显著性差异。AeAPX6、AeAPX8、AeAPX14、AeAPX21、AeAPX27 的表达量下降,分别约为未套袋处理组的0.92、0.58、0.87、0.93、0.72 倍,但均与未套袋处理没有显著性差异。而AeAPX22、AeAPX24、AeAPX25基因表达量与对照组相比有显著性下降,分别约为未套袋处理组的0.05、0.25、0.05 倍,均与未套袋处理存在极显著性差异。抗坏血酸含量测定结果表明,套袋后抗坏血酸含量与对照组相比显著下降[26],套袋后除了AeAPX3、AeAPX13这两个基因,其余基因的表达量下降,这与AsA 的含量呈相同趋势。但APX 作为AsA 氧化分解途径的关键酶,APX 基因的表达量与AsA 含量密切相关。也就是说当AsA 含量下降的时候APX 基因的表达量应该上升才符合AsA 氧化分解途径的规律。而课题组现有的转录组学数据[27]揭示毛花猕猴桃果实套袋遮光处理之后获得调控AsA 的差异基因为DTZ79_21g12410,对应本文的AeAPX22 基因。通过qRT-PCR 验证转录组数据结果显示出一致性(图8),均为套袋之后基因表达量下降。因此,根据套袋后AsA 含量和APX 基因表达分析的关联性并结合转录组数据,得出AeAPX22基因可能受到光的调控。

图8 AeAPXs 基因在套袋处理后的表达谱分析
Fig.8 Expression profiling of AeAPX genes after bagging treatment
3 讨 论
APX是重要的氧化酶类之一,对于维持植物体内活性氧代谢平衡有着重要的作用[28-29]。笔者在本研究中利用生物信息学分析方法从猕猴桃基因组数据库中共获得79个AeAPX基因,剔除其中结构域缺失或不完整的基因,最终获得29个具有完整且只有1 个过氧化物酶功能元件的APX 基因,分别命名为AeAPX1~AeAPX29。在前期研究中,从拟南芥、水稻、玉米、番茄、巴西橡胶树等中分别鉴定出8、8、8、7、8个APX基因家族成员[9-13]。这些基因家族成员个数相似,而毛花猕猴桃却含有29个APX基因家族成员,可能是由于猕猴桃AsA 代谢途径分子机制复杂,存在更为丰富的APX基因调控机制。系统进化分析结果与基因结构及保守域分析结果一致,具有相似数量的内含子和保守基序的基因家族成员优先聚为一类,这与前人在葡萄上的研究结果一致[30],且聚为同一类的APX 基因家族成员均含有相同的保守结构域(PF00141)。结合前期转录组数据发现A、B、C亚类均由在果实发育期拥有高表达水平和低表达水平的基因组成。此外,各个亚类基因家族成员的蛋白质理化性质存在差异,在毛竹中也发现类似的情况[31]。亚细胞定位分析发现具有相同定位的基因家族成员在系统进化树上的近缘关系并非最近,如AeAPX1、AeAPX4、AeAPX7、AeAPX8属于A亚类,而AeAPX10、AeAPX18、AeAPX24、AeAPX25 属于B亚类,表明在长期进化过程中APXs 的功能出现分化,在巴西橡胶树中研究发现也有此类现象[32]。葡萄、陆地棉、中华猕猴桃红阳APXs 基因家族成员中蛋白质二级结构所占比例最高的是α-螺旋和不规则卷曲,并推测不规则卷曲主要参与构建APX的酶活性中心,构成酶的活性部位和其他蛋白质特异的功能部位[26,30,33]。本研究得到的29个APX基因中比例最高的也是α-螺旋和不规则卷曲,这与前人的研究结果一致。
跨膜分析显示,AeAPX基因家族成员中有13个基因属于跨膜蛋白,其中7个基因定位于叶绿体上,其余6 个基因定位于细胞外基质、细胞质。而中华猕猴桃红阳、陆地棉APXs基因家族成员中分别也有4、5个基因属于跨膜蛋白,都分别定位于叶绿素、细胞质、细胞核中[26, 33]。由于跨膜蛋白都定位于不同的细胞器,以此推测这些跨膜蛋白的功能具有多样性,不仅能够维持植物生长发育所需要的营养物质,而且通过多细胞器的配合,能够起到保护植物免受活性氧的伤害,具有抗氧化作用。
植物在受到多种逆境胁迫后,会启动自我保护模式,主要表现在应激基因的表达,而基因的表达受到启动子或转录因子的调控,因此启动子顺式作用元件的分析对某个特定基因功能的研究有重要意义[34]。通过对AeAPXs各家族成员ATG上游2000 bp的序列分析,发现各个基因家族成员含有多个光照、激素、干旱胁迫相关的调控元件,如Box4、G-box、CGTCA-motif、ABRE、ARE 等。推测由于这些顺式作用元件的存在,该基因家族多个成员均有可能参与了干旱、低温等逆境胁迫响应。在马铃薯、甜樱桃中的各基因家族启动子上游2000 bp 处也发现了与光照、激素、干旱胁迫等相关的响应元件[35-36]。
果实的不同发育时期APX 的作用机制也是研究的重点之一。研究表明,植物APX基因的表达是由胁迫诱导的。研究结果表明,AeAPX27在幼果期、转色期、成熟期都高表达,可能是受到温度变化的影响,因此高表达APX 是为了保护植物抵抗高温、低温胁迫[37-39]。APX 也是AsA 代谢途径中的关键基因[40],AeAPX8、AeAPX13、AeAPX14、AeAPX22、AeAPX25 的基因表达量与AsA 含量的变化一致,表明这些基因可能参与AsA的循环,但AeAPX27是调控果实AsA 代谢最关键的一个基因。AeAPX6、AeAPX21、AeAPX24 的基因表达水平与AsA 含量的变化趋势相反。Liao等[26]研究套袋对果实AsA含量积累的影响相对于对照组下降,与抗坏血酸合成途径相关基因DHAR、GalUR、GalLDH 表达量均显著低于对照,因此,推测DHAR、GalUR、GalLDH 基因的差异表达是造成套袋和对照组间AsA 含量积累差异的关键。套袋之后AeAPX22、AeAPX24、AeAPX25基因表达量极显著下降,AsA含量也下降;这说明AeAPX22 基因可能受到光的调控而表达量下降,而AsA含量同时下降的原因可能是其他合成代谢通路的基因在套袋之后受到影响,从而影响AsA 的合成。目前为止,毛花猕猴桃APX 基因家族成员的信息还没有相关报道,本研究结果可为毛花猕猴桃AsA代谢调控机制奠定理论基础。
4 结 论
从猕猴桃基因组中鉴定AeAPX 基因家族并进行生物信息学分析。同时,对AeAPX基因家族在果实不同发育阶段和套袋处理之后的表达量进行了分析,筛选出候选基因DTZ79_21g12410 和DTZ79_28g05600,为进一步展开基因功能研究提供依据。
[1]LIAO G L,XU X B,HUANG C H,ZHONG M,JIA D F. Resource evaluation and novel germplasm mining of Actinidia eriantha[J].Scientia Horticulturae,2021,282:110037.
[2]LORENCE A,CHEVONE B I,MENDES P,NESSLER C L.Myo-inositol oxygenase offers a possible entry point into plant ascorbate biosynthesis[J].Plant Physiology,2004,134(3):1200-1205.
[3]李娜,陆海.植物抗坏血酸过氧化物酶基因家族研究进展[J].成都大学学报(自然科学版),2011,30(2):97-101.LI Na,LU Hai. Research progress in ascorbate peroxidase gene family in plants[J]. Journal of Chengdu University (Natural Science Edition),2011,30(2):97-101.
[4]陈花,吴俊林,李晓军.叶绿体中活性氧的产生和清除机制[J].现代生物医学进展,2008,8(10):1979-1981.CHEN Hua,WU Junlin,LI Xiaojun. Generation and scavenging of reactive oxygen species in chloroplasts[J]. Progress in Modern Biomedicine,2008,8(10):1979-1981.
[5]孙卫红,王伟青,孟庆伟.植物抗坏血酸过氧化物酶的作用机制、酶学及分子特性[J].植物生理学通讯,2005,41(2):143-147.SUN Weihong,WANG Weiqing,MENG Qingwei. Functional mechanism and enzymatic and molecular characteristic of ascorbate peroxidase in plants[J].Plant Physiology Communications,2005,41(2):143-147.
[6]YOSHIMURA K,YABUTA Y,ISHIKAWA T,SHIGEOKA S.Expression of spinach ascorbate peroxidase isoenzymes in response to oxidative stresses[J]. Plant Physiology,2000,123(1):223-234.
[7]YABUTA Y,MARUTA T,YOSHIMURA K,ISHIKAWA T,SHIGEOKA S. Two distinct redox signaling pathways for cytosolic APX induction under photooxidative stress[J]. Plant Cell Physiology,2004,45(11):1586-1594.
[8]SHIGEOKA S,ISHIKAWA T,TAMOI M,MIYAGAWA Y,TAKEDA T,YABUTA Y,YOSHIMURA K. Regulation and function of ascorbate peroxidase isoenzymes[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany,2002,53(372):1305-1319.
[9]李泽琴,李锦涛,邴杰,张根发.拟南芥APX 家族基因在植物生长发育与非生物逆境胁迫响应中的作用分析[J]. 遗传,2019,41(6):534-547.LI Zeqin,LI Jintao,BING Jie,ZHANG Genfa.The role analysis of APX gene family in the growth and developmental processes and in response to abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana[J].Hereditas,2019,41(6):534-547.
[10]TEIXEIRA F K,MENEZES-BENAVENTE L,MARGIS R,MARGIS-PINHEIRO M. Analysis of the molecular evolutionary history of the ascorbate peroxidase gene family:Inferences from the rice genome[J]. Journal of Molecular Evolution,2004,59(6):761-770.
[11]LIU Y J,YUAN Y,LIU Y Y,LIU Y,FU J J,ZHENG J,WANG G Y. Gene families of maize glutathione-ascorbate redox cycle respond differently to abiotic stresses[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology,2012,169(2):183-192.
[12]NAJAMI N,JANDA T,BARRIAH W,KAYAM G,TAL M,GUY M,VOLOKITA M. Ascorbate peroxidase gene family in tomato:its identification and characterization[J]. Molecular Genetics&Genomics,2008,279(2):171-182.
[13]CHAO J Q,ZHANG S X,CHEN Y Y,TIAN W M.Cloning,heterologous expression and characterization of ascorbate peroxidase(APX)gene in laticifer cells of rubber tree(Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.)[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2015,97:331-338.
[14]TAO C C,JIN X,ZHU L P,XIE Q L,WANG X C,LI H B.Genome-wide investigation and expression profiling of APX gene familyinGossypiumhirsutumprovidenewinsightsinredoxhomeostasis maintenance during different fiber development stages[J].Molecular Genetic and Genomics,2018,293(3):685-697.
[15]PANCHUK I I,VOLKOV R A,SCHÖFFL F. Heat stress and heat shock transcription factor-dependent expression and activity of ascorbate peroxidase in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Physiology,2002,129(2):838-853.
[16]TEIXEIRA F K,MENEZES-BENAVENTE L,GALVÃO V C,MARGIS R,MARGIS-PINHEIRO M. Rice ascorbate peroxidase gene family encodes functionally diverse isoforms localized in different subcellular compartments[J]. Planta,2006,224(2):300-314.
[17]LIAO G L,LI Z Y,HUANG C H,ZHONG M,TAO J J,QU X Y,CHEN L,XU X B. Genetic diversity of inner quality and SSR association analysis of wild kiwifruit(Actinidia eriantha)[J].Scientia Horticulturae,2019b,248:241-247.
[18]CHEN C J,CHEN H,ZHANG Y,THOMAS H R,FRANK M H,HE Y H,XIA R. TBtools:An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data[J]. Molecular Plant,2020,13(8):1194-1202.
[19]WILKINS M R,GASTEIGER E,BAIROCH A,SANCHEZ J C,WILLIAMS K L,APPEL R D,HOCHSTRASSER D F. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology,1999,112:531-552.
[20]BAILEY T L,WILLIAMS N,MISLEH C,LI W W. MEME:Discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs[J].Nucleic Acids Research,2006,34:W369-W373.
[21]HU B,JIN J P,GUO A Y,ZHANG H,LUO J C,GAO G.GSDS 2.0:An upgraded gene feature visualization server[J]. Bioinformatics,2015,31(8):1296-1297.
[22]ROMBAUTS S,DÉHAIS P,VAN MONTAGU M,ROUZÉ P.PlantCARE,a plant cis-acting regulatory element database[J].Nucleic Acids Research,1999,27(1):295-296.
[23]COMBET C,BLANCHET C,GEOURJON C,DELÉAGE G.NPS@:Network protein sequence analysis[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences,2000,25(3):147-150.
[24]VANDESOMPELE J,DE PRETER K,PATTYN F,POPPE B,VAN ROY N,DE PAEPE A,SPELEMAN F.Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes[J]. Genome Biology,2002,3(7):research0034. http://genomebiology.com/2002/3/7/research/0034
[25]LIAO G L,HE Y Q,LI X S,ZHONG M,HUANG C H,YI S Y,LIU Q,XU X B. Effects of bagging on fruit flavor quality and related gene expression of AsA synthesis in Actinidia eriantha[J].Scientia Horticulturae,2019,256:108511.
[26]LIAO G L,LIU Q,LI Y Q,ZHONG M,HUANG C H,JIA D F,XU X B. Identification and expression profiling analysis of ascorbate peroxidase gene family in Actinidia chinensis (Hongyang)[J].Journal of Plant Research,2020,133(5):715-726.
[27]LIU Q,LI Y Q,LIAO G L,XU X B,JIA D F,ZHONG M,WANG H L,YE B. Transcriptome and metabolome reveal AsA regulatory network between metabolites and genes after fruit shading by bagging in kiwifruit (Actinidia eriantha)[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2022,302:111184.
[28]PANDEY S,FARTYAL D,AGARWAL A,SHUKLA T,JAMES D,KAUL T,NEGI Y K,ARORA S,REDDY M K.Abiotic stress tolerance in plants:Myriad roles of ascorbate peroxidase[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2017,8:581.
[29]王亦学,杜建中,郝曜山,张欢欢,王晓清,孙毅. 过量表达GhAPX 基因提高中林美荷杨耐盐性[J].分子植物育种,2017,15(7):2579-2583.WANG Yixue,DU Jianzhong,HAO Yaoshan,ZHANG Huanhuan,WANG Xiaoqing,SUN Yi. Overexpression of GhAPX gene in the improvement of salt tolerance in Populus sp.[J].Molecular Plant Breeding,2017,15(7):2579-2583.
[30]王晗,刘涛,何红红,梁国平,马宗桓,毛娟,陈佰鸿.葡萄APX 基因家族的鉴定与表达分析[J].果树学报,2020,37(4):472-484.WANG Han,LIU Tao,HE Honghong,LIANG Guoping,MA Zonghuan,MAO Juan,CHEN Baihong. Identification and expression analysis of APX gene family in grape[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2020,37(4):472-484.
[31]宋笑龙,孔波,高志民,牟少华,李雪平.毛竹APX 家族基因鉴定和表达分析[J].热带亚热带植物学报,2020,28(3):255-264.SONG Xiaolong,KONG Bo,GAO Zhimin,MU Shaohua,LI Xueping. Identification and expression analysis of the APX gene family in Phyllostachys edulis[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany,2020,28(3):255-264.
[32]晁金泉,杨署光,陈月异,田维敏.巴西橡胶树APX 基因家族成员的鉴定及表达分析[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2018,37(11):4769-4774.CHAO Jinquan,YANG Shuguang,CHEN Yueyi,TIAN Weimin. Identification and expression of APX gene family members in Hevea brasiliensis[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology,2018,37(11):4769-4774.
[33]刘娜,吴金华,安亚茹,杨君,张艳,王省芬,马峙英.陆地棉抗坏血酸过氧化物酶基因家族全基因组生物信息学分析[J].棉花学报,2017,29(1):17-28.LIU Na,WU Jinhua,AN Yaru,YANG Jun,ZHANG Yan,WANG Xingfen,MA Zhiying. Bioinformatics analysis of the ascorbate peroxidase gene family in the Gossypium hirsutum L.genome[J].Cotton Science,2017,29(1):17-28.
[34]HADIARTO T,TRAN L S. Progress studies of drought-responsive genes in rice[J].Plant Cell Reports,2011,30(3):297-310.
[35]赵希胜,张冉冉,曾鼎宸,吕承承,李立芹,鲁黎明. 马铃薯APX 基因家族的生物信息学分析[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2020,39(12):5669-5677.ZHAO Xisheng,ZHANG Ranran,ZENG Dingchen,LÜ Chengcheng,LI Liqin,LU Liming. Bioinformatics analysis of APX gene family in potato[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology,2020,39(12):5669-5677.
[36]侯黔东,沈天娇,余欢欢,仇志浪,文壮,张惠敏,吴亚维,文晓鹏.甜樱桃GH3 基因家族全基因组鉴定与表达分析[J].园艺学报,2021,48(12):2360-2374.HOU Qiandong,SHEN Tianjiao,YU Huanhuan,QIU Zhilang,WEN Zhuang,ZHANG Huimin,WU Yawei,WEN Xiaopeng.Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of Prunus avium Gretchen Hagen 3 (GH3) gene family[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2021,48(12):2360-2374.
[37]ALMESELMANI M,DESHMUKH P S,SAIRAM R K,KUSHWAHA S R,SINGH T P. Protective role of antioxidant enzymes under high temperature stress[J]. Plant Science,2006,171(3):382-388.
[38]KIM M D,KIM Y H,KWON S Y,YUN D J,KWAK S S,LEE H S. Enhanced tolerance to methyl viologen-induced oxidative stress and high temperature in transgenic potato plants overexpressing the CuZnSOD,APX and NDPK2 genes[J]. Physiologia Plantarum,2010,140(2):153-162.
[39]YUNGYUEN W,MA G,ZHANG L C,YAMAWAKI K,YAHATA M,OHTA S,YOSHIOKA T,KATO M.Regulation of ascorbic acid metabolism in response to different temperatures in citrus juice sacs in vitro[J].Scientia Horticulturae,2017,217:1-7.
[40]ZHANG Y Y,LI H X,SHU W B,ZHANG C J,YE Z B. RNA interference of a mitochondrial APX gene improves vitamin C accumulation in tomato fruit[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2011,129(2):220-226.