柑橘是世界第一大水果,也是仅次于小麦、大豆、玉米的第四大贸易农产品。我国作为柑橘重要的起源中心之一,柑橘栽培历史长达4000 多年[1]。截止到2018年,中国柑橘栽培面积和产量均居世界首位[2]。柑橘病毒病是阻碍柑橘产业健康持续发展的重要因素之一,我国已发现的柑橘病毒病害有30余种[3],其中柑橘褪绿矮缩病毒(Citrus chlorotic dwarf-associated virus,CCDaV)是近年来柑橘生产上出现的一种新病害,病株叶片畸形、扭曲、花叶,节间变短,植株矮化,果实变小,产量和品质降低[4-5]。目前除甜橙外,未发现其他抗耐病的柑橘类型或品种。CCDaV自20世纪90年代在土耳其被首次报道以来,对其柑橘产业,尤其是葡萄柚产业造成了极其严重的损失[4-6]。中国自2008 年首次在云南瑞丽的尤力克柠檬上发现零星病树以来[7],CCDaV 现已扩散至广西、广东、江西等地的多个柑橘品种上,并呈现出不断扩散的趋势[8],对我国柑橘产业的健康、持续发展造成了一定的风险隐患[9]。
CCDaV 为双生病毒科(Geminiviridae)Citlodavirus成员[10],其基因组序列为约3.64 kb的环状单链DNA 分子,具有双生病毒科保守的TAATATTAC 区域[6],可能含有6个开放阅读框(ORFs)[10]。其中ORF2编码27.9 ku的外壳蛋白(Coat protein,CP)。CCDaV主要通过嫁接进行传播,刀割、杨梅类白粉虱(Parabemisia myricae Kuwana)也是重要的传播方式[11-12]。
种植无病毒苗木是防控CCDaV的重要手段,而快速、高效的病毒检测技术是种苗无毒化的重要保障。早期针对CCDaV 的检测方法主要是指示植物鉴定和电子显微镜观察[3,13],但这2种方法耗时较长,且结果判定较为主观,不适用于病害的快速检测。近年来,以保守的CP 和运动蛋白(Movement protein,MP)为靶标,建立了基于PCR、实时PCR、环介导等温扩增技术(LAMP)[6-7,14]等的高灵敏分子生物学检测方法。但PCR和实时PCR法操作步骤繁琐、耗时耗力,局限于实验室,难以进行大样本规模化、现场检测[15],且LAMP 易污染出现假阳性。血清学检测技术凭借其快速简单、灵敏特异、高通量等优点,一直是植物病毒检测的重要手段。目前尚未获得CCDaV的特异性抗体,严重制约了其血清学检测技术的发展。为此,笔者在本研究中以CCDaV保守的CP 为靶标,构建了重组表达载体pET28a-CCDaV-CP,制备了特异性抗血清,建立、优化了CCDaV的dot-ELISA检测方法,提高了检测效率,为CCDaV的快速检测及脱毒种苗生产提供了支撑。
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料
单独感染CCDaV、柑橘衰退病(Citrus tristeza virus,CTV)、柑橘黄脉病毒(Citrus yellow vein clearing virus,CYVCV)、柑橘鳞皮病毒(Citrus psorosis virus,CPV)、柑橘碎叶病毒(Citrus tatter leaf virus,CTLV)的病株均保存于西南大学柑桔研究所国家柑桔苗木脱毒中心。
1.2 菌株及试剂
pET28a载体、大肠杆菌Rosetta购自武汉金开瑞生物工程有限公司,pGEM-T vector kit、T4 DNA 连接酶和异丙基硫代半乳糖苷(Isopropyl β-D-Thiogalactoside,IPTG)均购自宝生物工程(大连)有限公司;康为DNA 抽提试剂盒购自葆光生物有限公司;山羊抗兔购自重庆泽物有限公司。引物合成及相关测序均在成都擎科生物科技有限责任公司完成。
1.3 方法
1.3.1 引物设计 利用在线网站Interpro(http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/)对NCBI 中的15 个CCDaV全序列进行分析,发现CP最为保守,但CP的N端有无序性,会影响蛋白表达,因此在本研究中选择CCDaV-CP 的保守区域(29-253 位氨基酸)为靶标,设计引物序列F:5’-GTGGA CAGC AAATGGGTCGCGGATCCCCATGTAAAACACACACGGTGGA -TGTGAT-3’(划线部分为BamH Ⅰ酶切位点);R:-5’CAGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGTTAATTTGA TGTAGAATCATAAAAATACA-3’(划 线部分为Xho Ⅰ酶切位点)。
1.3.2 核酸提取及重组载体构建 取0.1 g CCDaV病株叶片研磨后,采用康为DNA 试剂盒抽提总DNA。将PCR 产物和原核表达载体pET28a 用BamHⅠ和XhoⅠ双酶切后,经T4 DNA 连接酶4 ℃过夜连接。连接产物转化至大肠杆菌DH5α,涂布在含50 mg·L-1 Kana的LB固体培养基过夜培养,经菌落PCR 鉴定结果为阳性后测序。将构建好的重组质粒转化到表达菌株Rosetta。PCR 检测为阳性的菌落扩大培养后提取质粒,并进行酶切验证。
1.3.3 融合蛋白的诱导表达、纯化与抗血清制备参照Zhu 等[16]稍作修改进行融合蛋白的诱导表达。筛选含有重组质粒的表达菌株,用不同终浓度(0.1、0.3、0.5、0.7、0.9 mol·L-1)的IPTG 于18 ℃诱导蛋白表达,诱导时间12 h。表达产物经SDS-PAGE 验证后,纯化、回收,并参照张静等[17]的方法用于抗血清制备。
1.3.4 抗血清效价检测 将获得的抗血清按1∶500的浓度稀释后作为一抗,将山羊抗兔作为二抗,用纯化的目的多肽作为抗原检测抗血清特异性。同时,将抗血清以1∶500、1∶1000、1∶2000、1∶3000、1∶4000的浓度稀释,测定抗血清效价。
1.3.5 dot-ELISA检测方法的建立,及其特异性、灵敏度分析 dot-ELISA 检测参考尚海丽等[18]的方法并稍作修改,即0.1 g柑橘叶加0.01 mol·L-1 PBS研磨匀浆,5500 r·min-1离心5 min。取2 μL上清液点于硝酸纤维素膜上,室温晾干。1%(w)BSA 100 r·min-1封闭90 min;PBS 稀释一抗100 r·min-1孵育90 min,后加入AP 标记的山羊抗兔IgG 100 r·min-1 孵育1 h。以上每一步结束后,使用PBST 洗脱液洗膜3次,每次5 min。随后用BCIP/NBT 避光显色5 min。利用方阵实验明确一抗和二抗的最适稀释倍数。用优化后的dot-ELISA 法检测分别感染了CCDaV、CTV、CYVCV、CTLV、CPV 的病株,以及健康植株叶片的提取液,验证其特异性。此外,将CCDaV 病株和健康柑橘叶片的粗提液进行倍比(1∶20、1∶40、1∶80、1∶160、1∶320、1∶640、1∶1280)稀释后进行检测,确定灵敏度。
1.3.6 田间样品检测 随机采集田间42 份疑似感染CCDaV 的柑橘样品,运用优化后的dot-ELISA 以及常规PCR法[6]比较检测结果,采用夏婷等[19]的方法比较2种检测方法的符合度。
2 结果与分析
2.1 CCDaV-CP的扩增和目的蛋白的诱导表达
用引入酶切位点的引物扩增出CCDaV-CP 片段(图1-A)。将重组质粒双切酶后分别得到5000 bp 和690 bp 的条带,其大小与预期相符(图1-B)。同时序列测定结果正确,表明已成功构建了含有CCDaV-CP 基因的原核表达载体,标记为pET28a-CCDaV-CP。
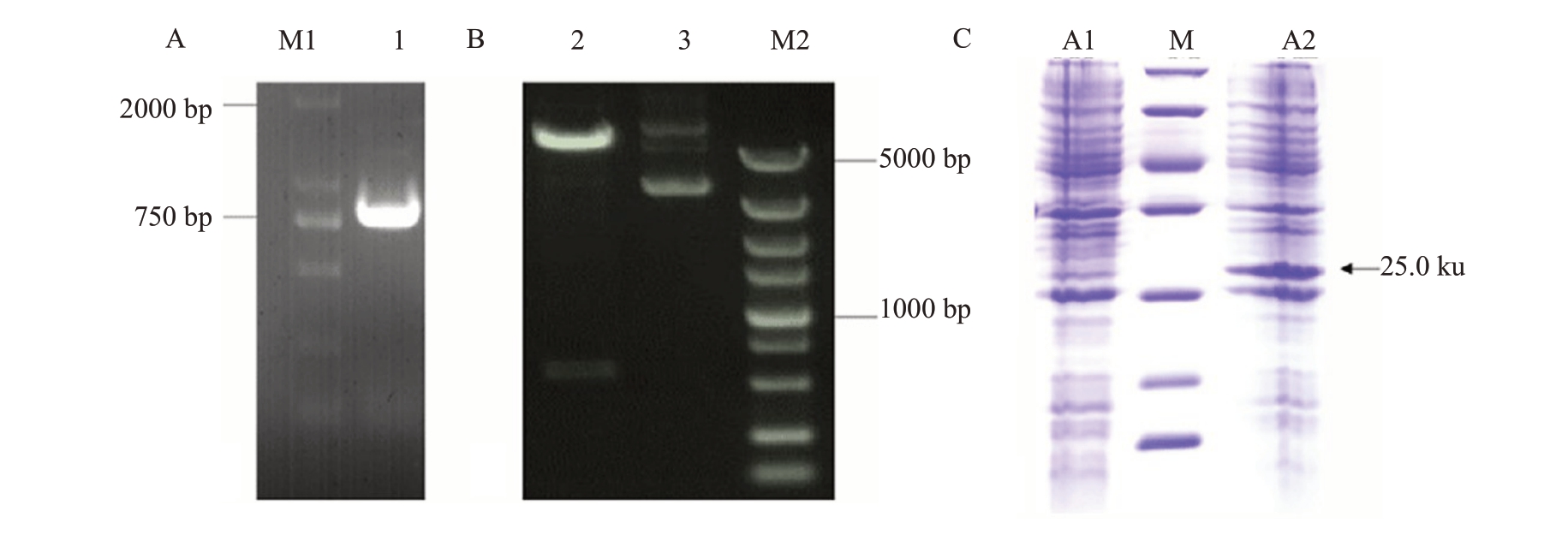
图1 CCDaV-CP 的PCR 扩增、重组质粒双酶切验证和重组菌在IPTG 诱导下的蛋白表达
Fig.1 PCR amplification of CCDaV-CP,verification of recombinant plasmid by restriction enzymes and protein expression of recombinant bacteria induced by IPTG
A.CCDaV-CP 基因序列的扩增;M1 为DNA 分子质量标准;1 为CCDaV-CP;B.重组质粒的双酶切验证;M2 为DNA 分子质量标准;2 为重组质粒;3 为重组质粒双酶切验证;C.重组菌在IPTG 诱导下的蛋白表达;M 为蛋白质分子质量标准(条带分别为14.4、18.4、25.0、35.0、45.0、66.2、116.0 ku);A1 为未被诱导的菌株pET28a;A2 为0.5 mmol·L-1 IPTG 诱导的菌株pET28a。
A.Amplification of CCDaV- CP gene sequence; M1.DNA Marker;1 is CCDaV- CP; B.Verification of recombinant plasmid by restriction enzymes;M2 is DNA Marker;2-3 are Verification of recombinant plasmid by double digestion;C.Protein expression of recombinant bacteria induced by IPTG; M is Protein molecular weight marker (14.4,18.4,25.0,35.0,45.0,66.2,116.0 ku);A1 is Uninduced pET28a;A2 is pET28a induced by 0.5 mmol·L-1 IPTG.
用终浓度0.5 mmol·L-1的IPTG于18 ℃诱导12 h时成功表达了目的蛋白,且表达量高,其分子质量在25 ku左右,与预期大小相符(图1-C)。
2.2 抗血清检测和抗血清效价测定
将获得的抗血清以1∶500 的浓度稀释,将纯化目的多肽进行Western blot检测,结果表明抗血清与纯化的目的蛋白有特异性免疫反应,条带单一(图2-A)。而与空载体蛋白、Rosetta菌株蛋白均无特异性反应。将抗血清按1∶500、1∶1000、1∶2000、1∶3000、1∶4000 的浓度稀释后与纯化的目的蛋白进行Western blot检测抗血清效价,发现抗血清的效价达到了1∶3000(图2-B)。
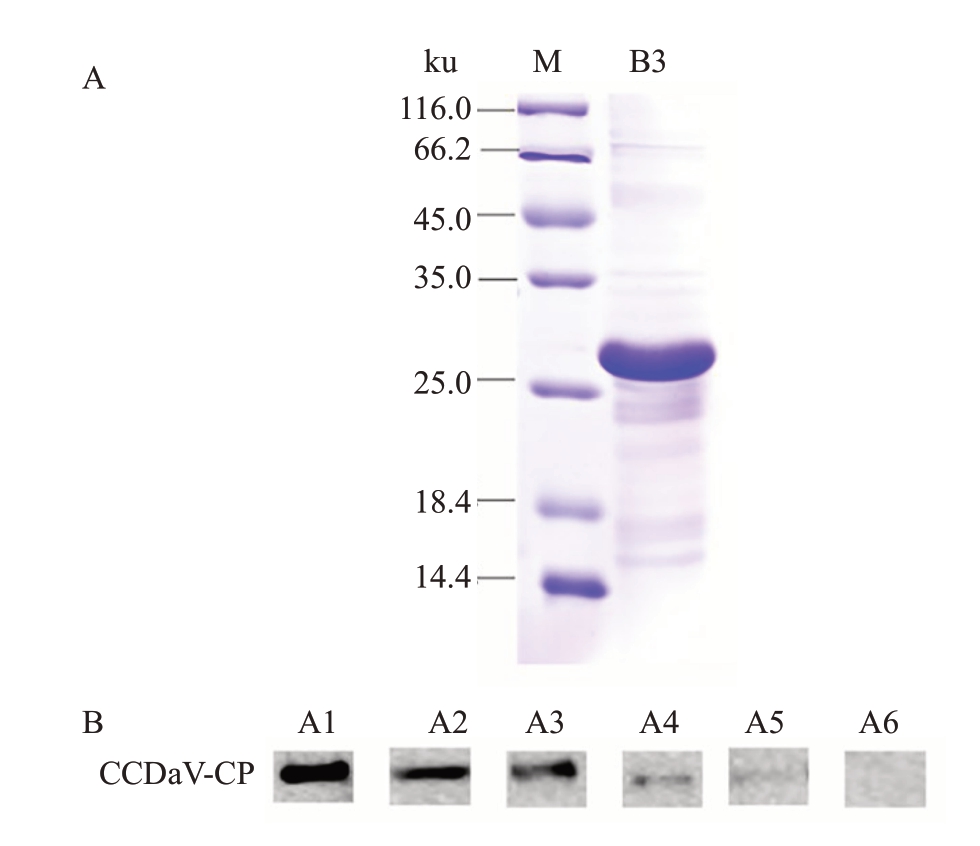
图2 抗血清检测和抗血清效价检测
Fig.2 Detection of specificity and titer of pET28a-CCDaVCP antiserum by Western blot
A.抗血清的特异性检测;M 为蛋白质分子质量标准;B3 为抗血清特异性检测;B.抗血清的效价检测;A1~A5 表示制备的抗血清稀释成不同的倍数:500、1000、2000、3000、4000;A6 为阴性对照。
A.Detection of specificity of pET28a-CCDaV-CP antiserum by Western blot; M is Protein marker; B3 is Antiserum specificity detection;B.Detection of titer of pET28a-CCDaV-CP antiserum by Western blot:A1-A5 indicates that the prepared antiserum is diluted into different multiples:500,1000,2000,3000,4000;A6 is negative control.
2.3 dot-ELISA 检测方法的优化、特异性和灵敏度分析
方阵实验表明,dot-ELISA 中抗血清和AP 标记二抗的最适稀释倍数分别为1∶4000和1∶10 000。基于此,将优化后的dot-ELISA 分别检测CCDaV、CTV、CYVCV、CTLV、CPV病株叶片,以及健康植株叶片提取物,检测结果显示,仅CCDaV 病株样品呈现紫色的阳性斑点,其余样品的检测结果均为阴性(图3-A)。在不同稀释倍数下,健康植株的叶片提取液均不能出现紫色的阳性斑点。表明该检测方法特异性强。此外,当CCDaV 病叶提取液被稀释到1∶640 倍时,仍能观察紫色的阳性斑点(图3-B),表明该检测方法的灵敏度较高。
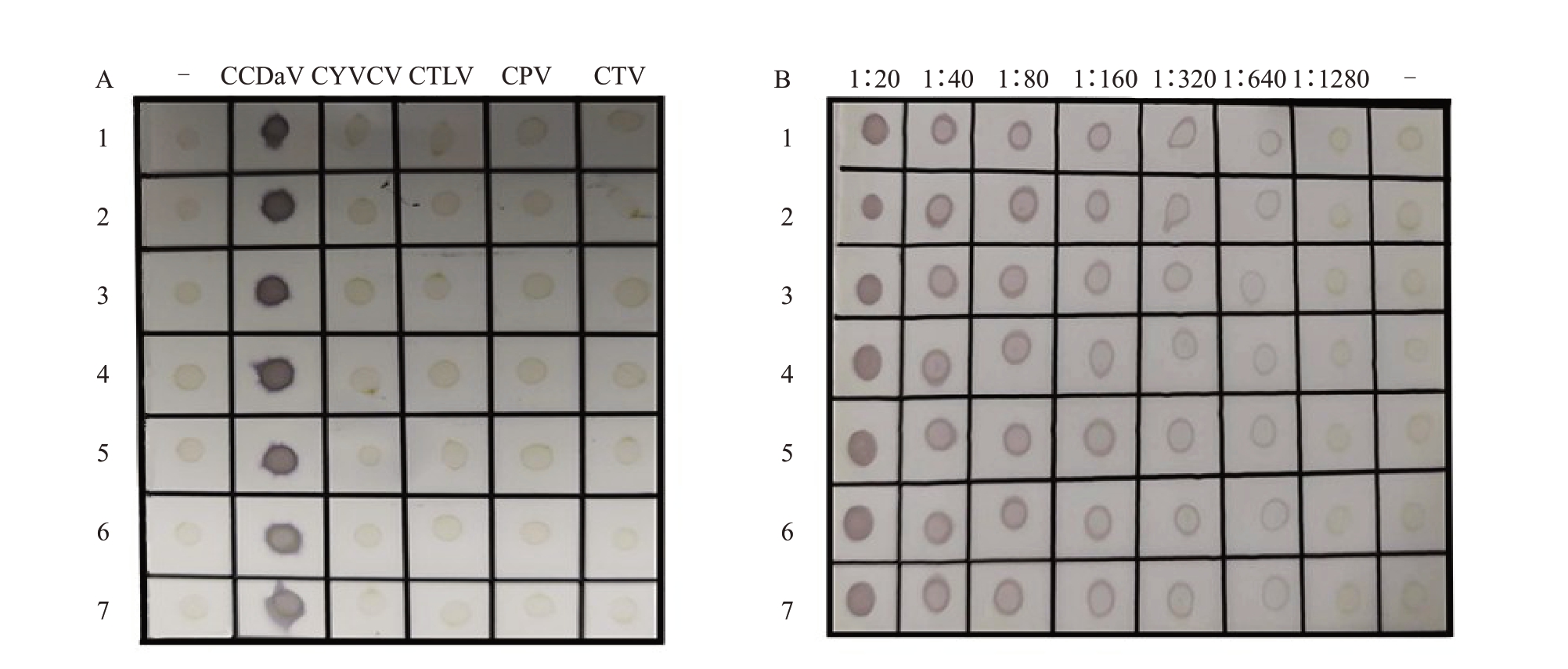
图3 dot-ELISA 特异性和灵敏度分析
Fig.3 dot-ELISA specificity and sensitivity analysis for CCDaV detection
A.dot-ELISA 特异性分析:-为健康柑橘;CCDaV 为柑橘褪绿矮缩病(CCDaV)病株;CYVCV 为柑橘黄脉病毒(CYVCV)病株;CTLV 为柑橘碎叶病毒(CTLV)病株;CPV 为柑橘鳞皮病毒(CPV)病株;CTV 为柑橘衰退病(CTV)病株;B.dot-ELISA 检测方法的灵敏度分析;1~7 为CCDaV 病株;-为健康柑橘。
A.dot-ELISA specificity analysis;- is Healthy citrus sample; CCDaV is CCDaV infected sample; CYVCV is CYVCV infected sample; CTLV is CTLV infected sample;CPV is CPV infected sample;CTV is CTV infected sample;B.dot-ELISA sensitivity analysis;1-7 are CCDaV-infected citrus sample;-is healthy citrus sample.
2.4 dot-ELISA田间样品检测
利用优化后的dot-ELISA 方法,对42 份疑似感染CCDaV的田间柑橘样品进行检测。结果显示,有18 份柑橘样品检出CCDaV,24 份样品未检出CCDaV(图4)。除dot-ELISA检测为阳性的样品外,PCR 法还从1 份dot-ELISA 检测为阴性的样品中检测出病毒。dot-ELISA法与PCR法的检测符合率为94.73%,表明建立的dot-ELISA法灵敏度较高,适用于田间样品检测(图5)。
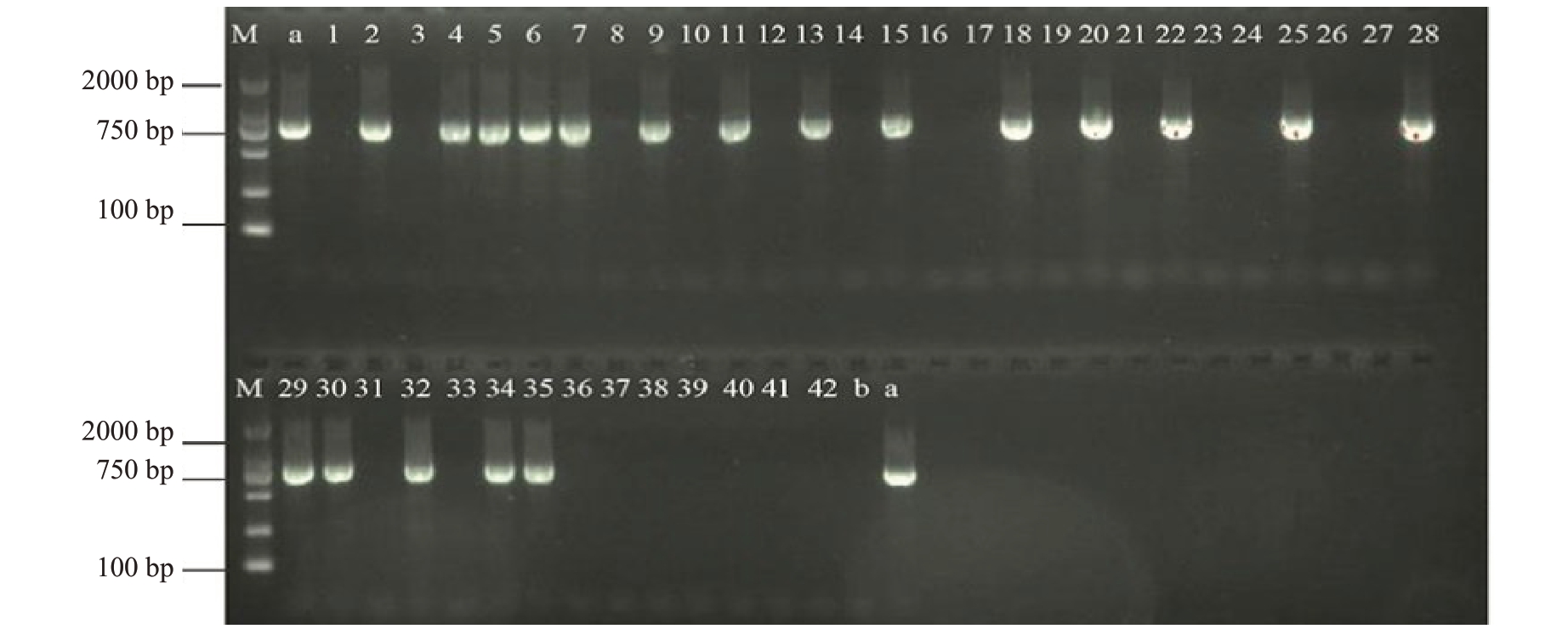
图4 田间病样PCR 检测结果
Fig.4 PCR amplification of CCDaV-suspected citrus sample in the field
M 为DNA 分子质量标准;1~42 为田间疑似样品;a 为阳性对照;b 为阴性对照。
M is DNA marker;1-42 are CCDaV-suspected citrus sample in the field;a is positive control;b is negative control

图5 dot-ELISA 方法田间柑橘样品的检测
Fig.5 Detection of field citrus samples by dot-ELISA method
3 讨 论
CCDaV作为一种新发生的柑橘病毒病,自2015年在我国首次被发现以来,长期零星分布于云南瑞丽的尤力克柠檬园。近年来随着我国柑橘产业的快速发展,柑橘苗木、接穗交流频繁,CCDaV也随苗木扩散至广西、广东、江西等地,并开始危害柚类、莱檬等柑橘类型。由于目前除甜橙外,尚未发现抗/耐柑橘褪绿矮缩病的柑橘品种,因此柑橘褪绿矮缩病对我国柑橘产业的风险加剧。目前使用无病毒苗木是防治柑橘褪绿矮缩病最有效的途径,因此快速、高效、灵敏的检测技术是防治该病的重要保障。
目前植物病毒的检测主要利用血清学和分子生物学方法,其中利用单克隆抗体或抗血清建立的血清学检测方法,具有高通量、易操作的优点。植物病毒单克隆抗体或抗血清制备,一般以提纯病毒作为免疫原,但是因果树病毒含量低、分布不均,且果树中多酚多糖类含量高,导致病毒提纯的难度大。近年来,利用分子生物学方法体外表达病毒蛋白为免疫原制备抗血清,可以有效解决上述难题。笔者在本研究中通过比对15个不同来源的CCDaV毒株发现,其CP的29~253位氨基酸最为保守,因此将其进行原核表达后作为抗原。重组菌在IPTG 诱导后表达产物所得量的高低以及其存在形式是蛋白成功表达的重要因素。在本研究中,当IPTG 终浓度为0.5 mmol·L-1时,诱导的蛋白表达量与0.7 和0.9 mmol·L-1 IPTG 诱导时差异不大,因此考虑到IPTG 对细菌的毒性,同时兼顾经济成本,本研究中pET28a-CCDaV-CP重组质粒表达时选择的IPTG终浓度为0.5 mmol·L-1。此外,笔者在本研究中还发现在16 ℃时诱导12 h ,pET28a-CCDaV-CP 的表达量较低(数据未显示)。沈继朵等[20]发现,适当提升诱导温度可以提高蛋白的表达水平。为此,笔者在IPTG 终浓度0.5 mmol·L-1 时,将诱导温度提高到18 ℃,诱导12 h,成功获得了表达目的蛋白,且表达量高。由此制备的抗血清可特异性检测CCDaV,且效价为1∶3000,表明其效果较好。以此建立、优化的dot-ELISA 方法最低可检测到1∶640 倍稀释液中的CCDaV,且与常规PCR 的检测符合度高,可以满足田间CCDaV检测的需要。笔者在田间样品检测时还发现,PCR法的阳性检出率略高于dot-ELISA法,这可能是由于PCR法灵敏度更高所造成的[21]。
4 结 论
笔者首次制备出特异性检测CCDaV-CP多肽的高效价抗血清,建立了CCDaV的dot-ELISA检测方法,将为我国今后检测和防治CCDaV提供技术支撑。
[1] 莫星煜,毛玲莉,王梓,徐梦茜.国内外柑橘产业发展现状综述[J].农村实用技术,2021(2):9-10.MO Xingyu,MAO Lingli,WANG Zi,XU Mengqian.Development status of citrus industry at home and abroad[J].Practical Rural Technology,2021(2):9-10.
[2] 沈兆敏.二十年来我国柑橘产业的十大变化[J].果农之友,2021(6):1-3.SHEN Zhaomin.Ten changes of Citrus industry in China in the past twenty years[J].Fruit Growers’Friend,2021(6):1-3.
[3] 陆英,漆艳香,喻群芳,杨毅.柑橘病害名录[J].热带生物学报,2017,8(4):474-481.LU Ying,QI Yanxiang,YU Qunfang,YANG Yi.A list of diseases on citrus in mainland China[J].Journal of Tropical Biology,2017,8(4):474-481.
[4] GARNSEY S.M. Citrus chlorotic dwarf,a new whitefly-transmitted disease in the eastern Mediterranean region of Turkey[C]//International Organization of Citrus Virologists Conference Proceedings (1957—2010).California,USA:IOCV,Riverside,1997:220-225.
[5] LOCONSOLE G,OHELGE N,POTERE O,GIAMPETRUZZIA,BOZAN O,SATAR S,DE STRADIS A,SAVINO V,YOKOMI R K,SAPONARI M.Identification and characterization of Citrus yellow vein clearing virus,a putative new member of the genus Mandarivirus[J].Phytopathology,2012,102(102):1168-1175.
[6] LOCONSOLE G,SALDARELLI P,DODDAPANENI H,SAVINO V,MARTELLI G P,SAPONARI M.Identification of a single-stranded DNA virus associated with Citrus chlorotic dwarf disease,a new member in the family Geminiviridae[J].Virology,2012,432(1):162-172.
[7] GUO J,LAI X P,LI J X,YUE J Q,ZHANG S Y,LI Y Y,GAO J Y,WANG Z R,DYAN H F,YANG J D.First report on Citrus chlorotic dwarf associated virus on lemon in Dehong prefecture,Yunnan,China[J].Plant Disease,2015,9(9):1287.
[8] YANG Z,ZHANG L,ZHAO J F,ZHANG X K,WANG Y,L I T S,ZHANG W,ZHOU Y.New geographic distribution and molecular diversity of Citrus chlorotic dwarf-associated virus in China[J].Journal of IntegrativeAgriculture,2022,21(1):293-298.
[9] KARANFIL A,KORKMAZ S.Geographic distribution and molecular characterization of Turkish isolates of the Citrus chlorotic dwarf[J].Journal of Plant Pathology,2019,101(3):621-628.
[10] ROUMAGNAC P,LETT J M,FIALLO-OLIVé E,NAVAS-CASTILLO J,ZERBINI F M,MARTIN D P,VARSANI A.Establishment of five new genera in the family geminiviridae:Citlodavirus,maldovirus,mulcrilevirus,opunvirus,and topilevirus[J].Archives of Virology,2022,167(2):695-710.
[11] KORKMAZ S. Citrus chlorotic dwarf-associated virus:A new whitefly-transmitted virus like disease of citrus in Turkey[J].Plant Disease,1995,79(10):1074.
[12] KARANFIL A,KORKMAZ S.Genetic diversity of Turkish Citrus chlorotic dwarf-associated virus isolates based on coat protein gene[J].Fresenius Environmental Bulletin,2018,27(9):6403-6407.
[13] CAO M J,LI P,ZHANG S,YANG F Y,ZHOU Y,WANG X F,LI R H,LI R H,LI Z A.Correction to:Molecular characterization of a novel citrivirus from citrus using next-generation sequencing[J].Archives of Virology,2018,163:3479-3482.
[14] 刘科宏,陈洪明,周彦,宋震,李中安.柑橘褪绿矮化相关病毒LAMP 检测体系的建立[J].园艺学报,2017,44(5):999-1004.LIU Kehong,CHEN Hongming,ZHOU Yan,SONG Zhen,LI Zhong’an.Establishment of LAMP assay for detection of Citrus chlorotic dwarf- associated virus(CCDAV) [J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2017,44(5):999-1004.
[15] 宾羽,宋震,李中安,周常勇.柑橘黄化脉明病毒DTBIA 检测方法的建立[J].园艺学报,2015,42(9):1843-1850.BIN Yu,SONG Zhen,LI Zhong’an,ZHOU Changyong.Direct tissue blot immunoassay for detection of Citrus yellow vein clearing virus[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2015,42(9):1830-1850.
[16] ZHU F,XU M Y,WANG S D,JIA S D,ZHANG P,LIN H H,XI D H.Prokaryotic expression of pathogenesis related protein 1 gene from Nicotiana benthamiana:Antifungal activity and preparation of its polyclonal antibody[J].Biotechnology Letters,2012,34(5):919-924.
[17] 张静,朱峰,陈应娟,邓星光,刘健,林宏辉,席德慧.芜菁皱缩病毒P38 蛋白的原核表达及抗血清的制备[J].四川大学学报(自然科学版),2015,52(2):441-445.ZHANG Jing,ZHU Feng,CHEN Yingjuan,DENG Xingguang,LIU Jian,LIN Honghui,XI Dehui.Prokaryotic expression of P38 from Turnip crinkle virus and preparation of its polyclonal antibody[J].Journal of Sichuan University(Natural Science Edition),2015,52(2):441-445.
[18] 尚海丽,周雪平,吴建祥.免疫斑点法和免疫捕获RT-PCR 检测黄瓜绿斑驳花叶病毒[J].浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2010,36(5):485-490.SAHNG Haili,ZHOU Xueping,WU Jianxiang.Polyclonal antibody-based dot-ELISA and immunocapture-RT-PCR for Cucumber green mottle mosaic virus detection[J].Journal of Zhejiang University(Agriculture and Life Sciences),2010,36(5):485-490.
[19] 夏婷,郭娇娇,廖晨星,阮文科.变异型PEDV 北京分离株ELISA 检测法的建立[J].北京农学院学报,2021,36(4):81-86.XIA Ting,GUO Jiaojiao,LIAO Chenxing,RUAN Wenke.Establishment of ELISA detection method for Beijing strains of variant PEDV[J].Journal of Beijing University of Agriculture,2021,36(4):81-86.
[20] 沈继朵,王聪,张莉,栗俞程.重组猪α 干扰素工程菌的诱导表达及产物纯化[J].江苏农业科学,2019,47(9):214-218.SHEN Jiduo,WANG Cong,ZHNAG Li,LI Yucheng,Induction expression and product purification of recombinant porcine interferon α engineering bacteria[J].Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2019,47(9):214-218.
[21] 刘永清,曹孟籍,王雪峰,李中安,唐科志,周常勇.植物组织和单头蚜虫中柑橘衰退病毒的快速分子检测技术[J].中国农业科学,2010,43(7):1397-1403.LIU Yongqing,CAO Mengji,WANG Xuefeng,LI Zhong’an,TANG Kezhi,ZHOU Changyong.Rapid molecular detection technologies of Citrus tristeza virus in plant tissues and single aphid[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2010,43(7):1397-1403.