促分裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen activated protein kinase, MAPK)级联途径是真核生物中广泛存在的信号转导途径,并在植物应对各种生物和非生物胁迫、激素以及在细胞分裂和发育过程中起关键作用[1-5]。MAPK信号通路通常包括3个功能相互关联的蛋白激酶:促分裂原活化蛋白激酶激酶激酶(MAPKKK/MAP3K/MEKK)、促分裂原活化蛋白激酶激酶(MAPKK/MAP2K/MKK)和促分裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK/MPK)。MAPKKK通过信号分子受体或者自身感知外界刺激而被磷酸化激活,MAPKKK活化后,通过磷酸化下游MAPKK中的保守结构(S/T-X3-5-S/T)来激活MAPKK。MAPKK是一类双重特异性激酶,能磷酸化下游的MAPK的保守氨基酸基序T-X-Y(TDY或TEY)中的苏氨酸(T)和酪氨酸(Y),使MAPK 激活[1]。磷酸化的MAPKs 作用于细胞质或细胞核中不同的蛋白,重新编码基因表达,使植物表现出抗逆性[6]。
植物MAPK 级联在植物抵御病原菌攻击的信号转导中起着重要作用,MAPK 级联参与多种防御反应的信号传导,包括植物胁迫/防御激素的生物合成/信号转导、活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)的产生、防御基因激活以及植物生理功能生物合成[7]。已有研究对拟南芥[1,8]、水稻[9]、杨树[10]、玉米[11]、苹果[12]中MAPK 级联各家族基因组成进行了分析。在紫花苜蓿、烟草中也发现了参与病原菌或病毒胁迫的MAPK级联途径[13-14]。
芪合成酶(stilbene synthase,STS)是葡萄中与抗病相关的白藜芦醇合成过程最后一步的催化酶,研究表明芪类化合物合成需要MAPK级联反应,特异性MAPK 级联抑制剂(PD98059)可以有效抑制STS的激活[15]。王刚[16]对葡萄中的MAPK类激酶家族做了鉴定分析,结果表明葡萄中有45 个MAPKKK激酶、5个MAPKK激酶和12个MAPK激酶。葡萄中MAPKKKs 激酶可以响应生物、非生物胁迫和植物激素的处理;葡萄中VvMKK3 基因可以响应白粉菌的诱导上调表达;葡萄的12个MAPKs中,部分MAPKs参与了葡萄组织的生长发育,在葡萄白粉菌侵染下,VvMPK1、VvMPK9和VvMPK10基因上调表达。毛葡萄丹凤-2中,VqMAPKKK38基因可以响应葡萄白粉菌、盐害和冷害,这是由于VqMAPKKK38基因受到过氧化氢和钙信号刺激而被激活,介导了芪类化合物的生物合成,最终参与了ROS和钙信号的调控途径[17]。燕山葡萄中的2个MAPK基因和Vy-MAPK3基因可以响应水杨酸(salicylic acid,SA)、茉莉酸(Jasmonic acid,JA)和脱落酸(abscisic acid,ABA)等植物生长调节剂而诱导表达,VyMAPK2 基因变化不明显。VyMAPK3基因可以响应干旱、盐害和低温诱导表达,而VyMAPK2 基因仅响应干旱诱导[18]。但目前未见葡萄中MAPK类基因与葡萄炭疽病之间关系的报道。
炭疽病是影响南方葡萄产业的重要病害,中国葡萄属植物中蕴含丰富的抗炭疽病种质资源,刺葡萄中各株系对炭疽病的抗性极强[19]。笔者在前期炭疽菌侵染下刺葡萄转录组测序的基础上,获得了上调表达的VdMAPK7 基因,并同源克隆了VdMAPK7基因,通过过表达载体构建、番茄遗传转化、表型抗性评价以及亚细胞定位分析,探讨刺葡萄VdMAPK7基因参与炭疽病菌胁迫响应的功能,研究其参与炭疽病胁迫响应的抗病机制,对定向改良葡萄抗病性具有重要意义。
1 材料和方法
1.1 供试材料
以福建省福安市穆云乡溪塔村刺葡萄沟中生长良好的刺葡萄福安(Vitis davidii‘Fu'an’)为材料。从9株葡萄中采集健康成熟、大小一致的葡萄果实,设置3 次生物学重复(每3 株为1 次生物学重复,每株14粒果实)。将果实采回,用70%(φ)乙醇表面消毒1 min,前期研究中的葡萄炭疽菌菌株(Colletotrichum viniferum FJ017)作为病原菌,通过针刺法接种果粒[20]。接种后,收集不同侵染时间点(0、1、3和7 d)的果皮用于进一步分析,受侵染果皮贮存于-80 ℃冰箱备用。番茄尖胞炭疽菌(C.acutatum)由笔者实验室保存,25 ℃培养在马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂培养基(potato dextrose agar medium,PDA)上,每14 d 继代培养1 次。商品化番茄(Micro-Tom)种子由笔者实验室保存。
1.2 RNA提取、反转录和VdMAPK7基因表达模式分析
采用氯化锂沉淀法提取炭疽菌侵染的葡萄果皮RNA[21],RNA样品(2 μg)经无RNase的DNA酶Ⅰ处理去除残余的基因组DNA,然后用带有去除gDNA的Primescript™RT 试剂盒进行cDNA 合成(TaKa-Ra)。反应混合物用蒸馏水稀释1∶40,作为实时荧光定量PCR(quantitative real time PCR,qRT-PCR)模板。在Bio-Rad iQ5 系统(Bio-Rad,USA)中进行定量分析,每个cDNA样本3次重复,并用2-ΔΔCt方法计算相对于葡萄GAPDH(CB973647)的转录水平[22]。所有数据均表示为平均标准差(n=3)。根据VdMAPK7 基因的序列设计定量引物:qPCRMAPK7-F:GGGAACCTCCTTGTGAATGC;qPCRMAPK7-R:AGCGGGTGACAACATACTCA,进行qRT-PCR并对VdMAPK7基因的表达模式进行分析。
1.3 VdMAPK7基因克隆
根据转录组获得VdMAPK7 基因序列,与葡萄基因组网站和GenBank 中的序列进行比对,最终确认VdMAPK7 基因序列。并根据VdMAPK7 基因序列(蛋白质编码区序列,CDS)和pCambia2300 的载体序列选择合适的酶切位点,最终设计扩增引物(p2300-VdMAPK7-BamHⅠ-F:tcggtacccggggatccATGGCCACTCGAGTTGAGCCTCC;p2300- Vd-MAPK7-SalⅠ-R:gctcaccatggtgtcgacGGCATGAGAACAAACAGCTTCAGGA),用高保真酶KOD-Plus-Neo(Toyobo,北京)进行PCR扩增,反应体系和程序均按照说明书步骤进行。参照博迈德公司(Biomed,北京)的无缝克隆试剂盒进行同源重组反应,将上述获得的胶回收产物与线性化载体pCambia2300进行重组反应后转化至大肠杆菌感受态,挑取单克隆测序鉴定,最终获得正确的重组质粒。
1.4 VdMAPK7生物信息学分析
将VdMAPK7 氨基酸序列放到BLAST 网站上进行序列比对,并将不同物种的同源序列下载,用于构建系统进化树。使用DNAMAN(v6.0)进行多重比较以确定VdMAPK7的氨基酸序列相似性。使用GenDoc(v2.7.0)软件输出序列多重比较分析结果。VdMAPK7 基因在染色体上位置预测在葡萄基因组网站Genoscope Genome Browser中分析。系统进化树的构建在Phylogeny.fr platform(http://www.phylogeny.fr)上,采用最大似然法(Maximum likelihood)进行。
1.5 烟草表皮亚细胞定位与转基因番茄鉴定
将测序正确的重组质粒使用电激法转入农杆菌GV3101 中,参照Xie 等[23]的方法,配制农杆菌重悬液,用无针头的1 mL注射器在健康的本氏烟草叶背面注射入重悬菌液,在光照培养箱中培养72 h,激光共聚焦显微镜下(莱卡TCS SP8)观察烟草叶片中GFP融合蛋白的分布,并保存图片。
采用农杆菌介导的叶盘法[23]转化番茄(Micro-Tom),将0.5 cm×0.5 cm 的番茄无菌叶片放入重悬好的农杆菌菌液(OD600=0.5)中悬浮5 min,吸去多余菌液后暗培养2 d,利用卡那霉素进行抗性筛选,42 d后,将获得的抗性芽切下进行生根培养,将生根良好的番茄植株移栽至营养钵中,放入人工气候室中培养,最终获得T0代转基因番茄植株。
参照Xie 等[23]的方法提取番茄叶片DNA 进行PCR 反 应,使 用 引 物(p2300- F:TCCTTCGCAAGACCCTTCCTCTAT;p2300- R:CAGGGTCAGCTTGCCGTAG)检测VdMAPK7 基因是否整合到番茄基因组中,同时以野生型植株DNA作为阴性对照进行PCR 反应,以p2300-VdMAPK7 质粒DNA作为阳性对照进行PCR 反应。取PCR 反应产物进行1%(w)琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测。
为检测VdMAPK7 基因在转基因番茄中是否表达,选取PCR 检测阳性植株的幼嫩叶片,提取总RNA,经过反转录后得到cDNA,利用SlActin(SlActinF:ATTCCCTGACTGTTTGCTAGT;SlActinR:TCCAACACAATACCGGTGGT)内参引物和1.2 中的VdMAPK7 基因定量引物进行28 个循环的PCR反应,将产物进行1%(w)琼脂糖凝胶电泳半定量检测。
1.6 转基因番茄抗炭疽病鉴定
选取成熟、无病斑的T0代转基因番茄果实,使用70%(φ)乙醇溶液表面消毒15 s,用无菌水清洗3 遍,解剖针在果实顶部造伤,使用6 mm 番茄尖胞炭疽病菌PDA 菌块(预培养7 d)接种到造伤部位。在28 ℃培养箱进行保湿暗培养,48 h 后移出菌块,于接种后的0、6、12、24、48、72 h 采集果实果皮,液氮速冻,-80 ℃冰箱保存备用。参照1.2 提取上述样品RNA 并反转录为cDNA(100 ng·μL-1),以1.5 中番茄SlActin 为内参基因,采用qRT-PCR 的方法,比较番茄在接种炭疽菌后,番茄SlPR1(EU589238,SlPR1-F:ATAAAGTGATCGATTGTCGAGGA;SlPR1- R:TAAGCTGCAACATACACACATCC)和SlPR2(EU589238,SlPR2-F:TCTGTAGACATGACGTTGATTGG;SlPR2-R:AGAGCATACGGAAGTGAAATCTG)在不同时间段的表达量。
1.7 数据统计与分析
使用SPSS 22.0软件分析数据,利用单因素方差分析和独立样本T 检验法进行显著性分析(*p<0.05),并用Sigmaplot 12.5作图。
2 结果与分析
2.1 VdMAPK7基因的表达模式分析
对刺葡萄福安果实接种葡萄炭疽病菌,接种0、1、3、7 d 后果皮中VdMAPK7 基因表达情况见图1。VdMAPK7 基因的表达量随着侵染时间延长持续升高,第7 天达到高峰。结果表明,VdMAPK7 基因可以响应葡萄炭疽病而诱导表达。

图1 刺葡萄福安VdMAPK7 基因响应葡萄炭疽病诱导表达
Fig.1 The qRT-PCR expression analysis of VdMAPK7 in Vitis davidii Föex under C.viniferum inoculation
误差线代表SE,3 次生物学重复(*p<0.05)。
Each value represents the means±SE of three different experiments(*p<0.05).
2.2 VdMAPK7基因克隆及其蛋白结构分析
将VdMAPK7 基因克隆测序的结果在NCBI 网站上进行Blastn 分析,并将克隆出的VdMAPK7(序列号:VIT_04s0023g02420)基因放入葡萄基因组Grape Genome Browser(http://www.genoscope.cns.fr/externe/Genome Browser/Vitis/)中进行比对。应用该网站的Blat-Search 选项,对获得的VdMAPK7基因进行染色体定位。结果如图2-A所示,VdMAPK7基因可以映射(mapping)至欧洲葡萄参考基因组的4号染色体上,分布于18 972 351~18 978 329 bp 的区域。
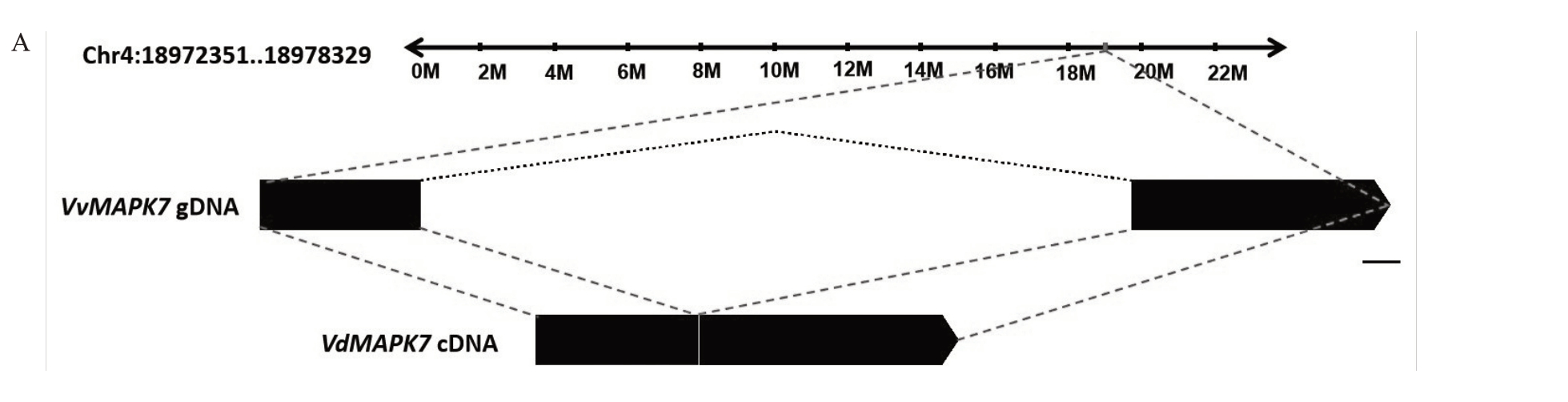
图2 刺葡萄VdMAPK7 基因克隆及其蛋白结构域分析
Fig.2 Analysis of cloning VdMAPK7 and protein domain of VdMAPK7 from Vitis davidii Föex
A.刺葡萄VdMAPK7 基因染色体定位,Chr4.4 号染色体;标尺.100 bp;gDNA.基因组DNA;cDNA.互补DNA。B.刺葡萄VdMAPK7蛋白结构域分析,刺葡萄(Vitis davidii Föex)VdMAPK7 与欧洲葡萄(Vitis vinifera)、拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)、栽培稻(Oryza sativa)、烟草(Nicotiana tabacum)和番茄(Solanum lycopersicum)中的同源蛋白结构域分析。红色横线代表S_TKc 结构域。
A.Chromosomal location schematic diagrams of VdMAPK7 from Vitis davidii Föex, Chr4.No.4 chromosome; Scale bar.100 bp; gDNA.Genomic DNA; cDNA.Complementary DNA.B.Protein domain analysis of VdMAPK7 from Vitis davidii Föex, VdMAPK7 from Vitis davidii Föex compared with its homologous proteins from Vitis vinifera, Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa, Nicotiana tabacum and Solanum lycopersicum.Red line represents S_TKc domain.

续图Continued Figure
将本研究克隆到的刺葡萄VdMAPK7氨基酸序列与欧洲葡萄MAPK7 氨基酸序列进行比对,发现二者氨基酸同源率为99.18%。将VdMAPK7氨基酸序列应用Clustw程序与欧洲葡萄、拟南芥、栽培稻、烟草和番茄进行了比对,结果显示VdMAPK7蛋白与其他物种均含有S_TKc结构域(32~319 aa)(图2-B)。
2.3 VdMAPK7蛋白进化树分析
将刺葡萄中的VdMAPK7 氨基酸序列与Gen-Bank 中下载的其他植物MAPK 氨基酸序列进行同源性比对,应用Phylogeny.fr platform 中的最大似然法构建进化树,如图3 所示。所有进行比对的序列可以分为3大类,刺葡萄中的VdMAPK7基因与欧洲葡萄、番茄、马铃薯、茶树、珙桐、烟草同源基因聚为一大类,且与欧洲葡萄关系最近。
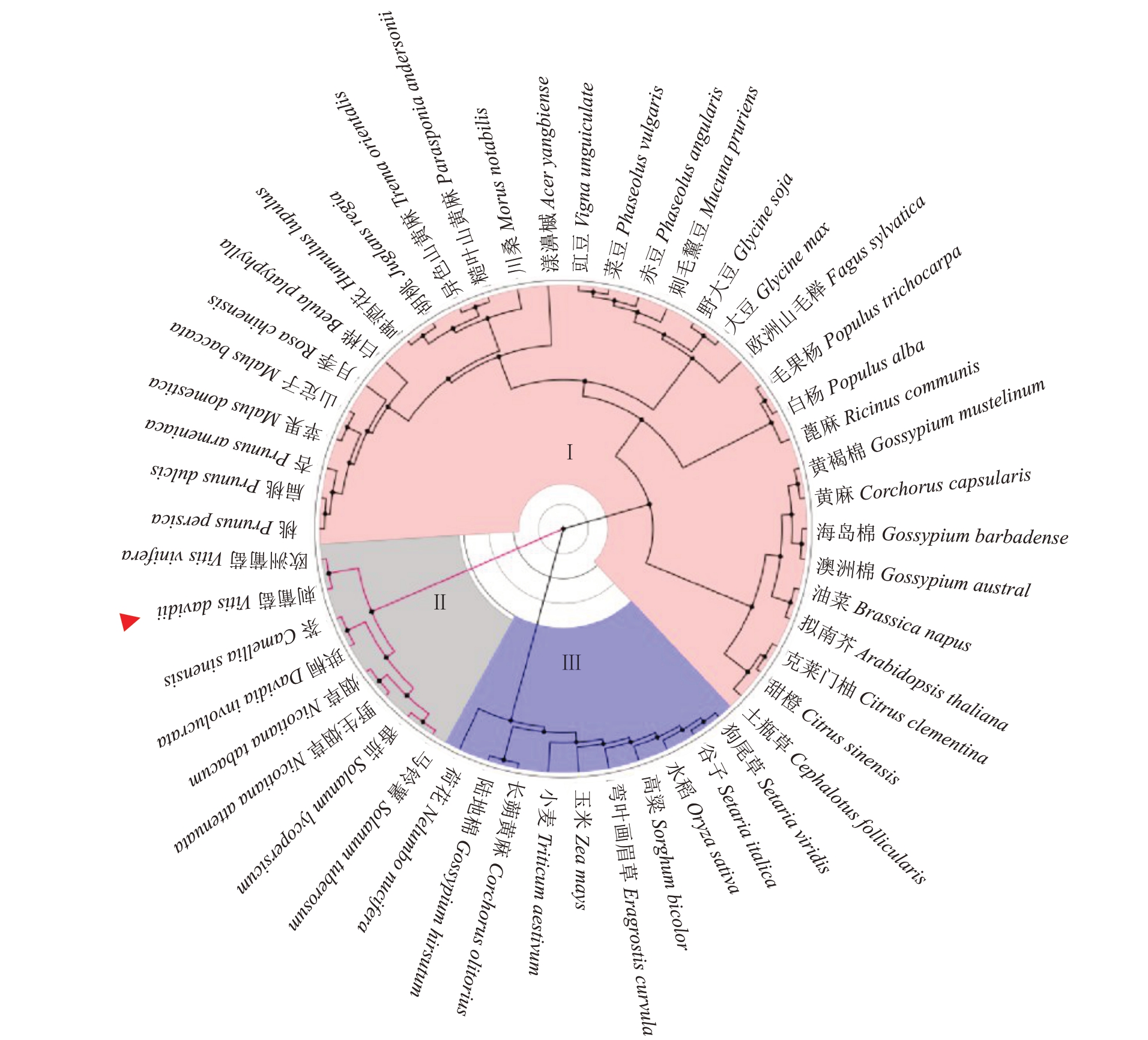
图3 刺葡萄VdMAPK7 蛋白与其他植物MAPK 同源蛋白序列聚类分析
Fig.3 Phylogenetic tree of VdMAPK7 from Vitis davidii Föex and other homologous protein sequences
红色箭头代表刺葡萄VdMAPK7,Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ代表不同类别。
Red arrow represents VdMAPK7 from Vitis davidii Föex,Ⅰ,Ⅱand Ⅲrepresent different classes.
2.4 VdMAPK7蛋白亚细胞定位分析
以本氏烟草叶片为材料,将活化后含有Vd-MAPK7 蛋白的农杆菌菌液注射到本氏烟草叶片中,培养3 d后,在激光共聚焦显微镜下观察荧光分布情况。以细胞核染料DAPI 作为核定位对照,以35s-GFP 作为空载体对照。结果如图4 所示,35s-GFP 定位于细胞质和细胞核上,VdMAPK7-GFP 定位情况与对照一致,同样定位在细胞核与细胞质上。

图4 VdMAPK7 亚细胞定位分析
Fig.4 Subcellular localization of VdMAPK7-GFP
激光通道分别为GFP 激发荧光下、DAPI 染色荧光、明场图和合并图。35s-GFP,VdMAPK7-GFP 的标尺为20 μm。
From left to right:GFP;Fluorescent dyes of DAPI;bright field and merged.Scale bars=20µm.
2.5 VdMAPK7基因过表达番茄植株获得与表型
采用叶盘转化法获得了VdMAPK7 基因过表达番茄植株,将移栽成活的番茄炼苗后,取幼嫩叶片提取DNA 进行PCR 检测。以pCambia2300-Vd-MAPK7-GFP 质粒为阳性对照,以野生型番茄植株叶片DNA 为阴性对照,进行PCR 电泳,结果如图5-A所示。候选植株(#2、#3、#9、#14、#21)与阳性对照有一致条带,野生型植株中检测不到电泳条带,说明候选植株可能为转基因植株。为进一步验证Vd-MAPK7基因在上述候选植株中是否表达,提取候选植株幼嫩叶片RNA 并进行反转录,根据VdMAPK7基因序列设计特异引物,并以番茄SlActin为内参基因进行PCR 半定量检测,经过28 个循环的PCR 检测,#2 和#9 植株中检测到目的条带,而野生型植株中没有条带,可以断定#2 和#9 植株为阳性植株(图5-B),VdMAPK7 基因在阳性植株(#2、#9)中表达。相较于野生型番茄,VdMAPK7 基因过表达植株矮小,叶片卷曲,果实变小(图5-C~F)。

图5 VdMAPK7 过表达的转基因番茄鉴定与表型
Fig.5 Verification and phenotypes of wild type tomato and VdMAPK7 overexpression tomato plants
A.PCR 检测转基因番茄;B.qRT-PCR 检测转基因番茄。C.番茄植株(左为野生型,右为转基因型);D.单果质量比较;E.番茄果实(左为野生型,右为转基因型);F.果实横、纵径比较。M.Marker;Po.阳性对照;WT.野生型。#2、#3、#9、#14、#21.转基因候选植株;OE.过表达。误差线代表SD,3 次生物学重复(*p<0.05)。
A.PCR analysis of VdMAPK7 from transgenic tomato plants; B.qRT-PCR analysis of VdMAPK7 from transgenic tomato plants.C.Wild type plant(left)and transgenic plant(right);D.Comparison single fruit weight between wild type tomato and VdMAPK7 overexpression tomato;E.Wild type fruit(left)and transgenic fruit(right).F.Comparison transverse and vertical diameter between wild type tomato and VdMAPK7 overexpression tomato.M.Marker;Po.Positive control;WT.Wild type.#2,#3,#9,#14,#21.Transgenic candidate plants;OE.Overexpression.Data are means±SD based on three independent replicates(*p<0.05).
2.6 VdMAPK7基因过表达番茄果实接种炭疽菌试验
为研究VdMAPK7 基因与抗炭疽病之间的关系,对VdMAPK7 转基因番茄果实和野生型番茄果实接种尖胞炭疽菌(C.acutatum),72 h后,相对于野生型番茄果实中的病斑,VdMAPK7转基因番茄果实病斑较小,发病症状较轻(图6-A)。为更好阐释Vd-MAPK7 转基因番茄果实接种炭疽菌后病斑较小现象,将野生型和VdMAPK7 转基因番茄果实接种炭疽菌,接种后0、6、12、24、48 和72 h 采集番茄果皮,提取RNA 反转录后,以SlActin 为内参基因,分析VdMAPK7接种炭疽菌后不同时间段SlPR1和SlPR2的表达量变化。结果表明,相对于野生型番茄果实,VdMAPK7 转基因番茄果实中SlPR1 基因的表达量在接种炭疽菌后各时间段均显著升高(图6-B);转基因番茄果实SlPR2 基因表达量在接种6、12、48 和72 h 后显著升高(图6-C)。这些结果说明过表达VdMAPK7基因的番茄果实对炭疽菌的抗性增强。

图6 过表达VdMAPK7 转基因番茄果实对炭疽菌抗性的比较
Fig.6 Assessment of resistance to C.acutatum in VdMAPK7-overexpressing tomato fruits
3 讨 论
MAPK是一类丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,广泛存在于植物之中,位于MAPK 级联途径中最下游,参与生物胁迫[24]。植物受到生物胁迫时,MAPK 信号通路被激活形成免疫应答,是植物产生抗病反应的早期信号[25]。
本研究中,葡萄炭疽病菌接种刺葡萄福安,Vd-MAPK7 基因在接种后第7 天表达量最高,说明Vd-MAPK7基因可以响应葡萄炭疽菌而诱导表达。抗、感炭疽病的茶树品种转录组测序结果表明MAPK被R基因激活并介导了下游的抗病反应[26]。欧洲葡萄中共有12 个MAPK 基因,其中VvMPK1 与VvMPK10 基因受到活体寄生菌白粉菌诱导后表达[16],葡萄中MAPK 基因与死体营养型的葡萄炭疽病菌之间的关系未见报道。本研究中,VdMAPK7转基因番茄植株表现为植株矮小,果实变小。这可能是由于基因过表达之后,影响转基因植株的正常代谢,从而影响转基因植株的生长发育,表现为矮化、弱小,这在别的研究中已有报道[27]。SA作为植物激素,同时也是信号分子,在植物抗病反应过程中发挥重要功能,SA信号通路多参与活体营养型的病原菌应答,而JA 途径则参与死体营养型的抗病反应[7]。本研究中,通过对转基因果实接种番茄炭疽病菌,病斑的面积相较于野生型番茄变小。这可能是由于过表达VdMAPK7 基因后,番茄的抗病基因表达量升高,对炭疽病菌抗性增强。为了进一步验证转基因番茄果实中的抗病基因的表达量,研究中进行了qRT-PCR分析,转基因番茄果实中SlPR1和SlPR2基因表达量均显著高于野生型。有研究发现,PR基因在植物抗病过程中,不仅参与了对活体寄生菌的抗性反应,还参与了对死体营养型病原菌的抗性反应。例如,Ma 等[28]证实,葡萄中PR10.1 通过结合VpVDAC 激活ROS 通路,来抑制葡萄霜霉菌的侵染;Xie等[23]对过表达VqDUF642的转基因番茄接种灰霉病后发现,SlPR1、SlPR2、SlPR3 和SlPR4基因均诱导表达。综合VdMAPK7 基因可以响应葡萄炭疽菌的表达,以及过表达VdMAPK7 的转基因番茄果实接种炭疽菌的表型和抗病基因的定量分析结果,说明VdMAPK7 基因可以增强番茄对炭疽菌的抗性,并推测VdMAPK7 基因参与葡萄对炭疽菌的抗病过程。
4 结 论
探究了刺葡萄VdMAPK7 基因在葡萄抗炭疽菌中的作用。刺葡萄VdMAPK7 基因可以响应炭疽菌诱导后表达量逐渐升高,在接种的第7天达到高峰;VdMAPK7 基因在番茄中过量表达均可增强对尖孢炭疽菌的抗性,推测VdMAPK7 基因参与了葡萄对炭疽菌的胁迫响应,对定向改良葡萄抗病性提供了一定的参考依据。
[1] ICHIMURA K,SHINOZAKI K,TENA G,SHEEN J,HENRY Y,CHAMPION A,KREIS M,ZHANG S,HIRT H,WILSON C,HEBERLE-BORS E,ELLIS B E,MORRIS P,INNES R,ECKER J R,SCHEEL D K,KLESSIG D,MACHIDA Y,MUNDY J,OHASHI Y,WALKER J C.Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plants:A new nomenclature[J].Trends in Plant Science,2002,7(7):301-308.
[2] SHI Y,HAN G H,WU H L,YE K,TIAN Z,WANG J,SHI H,YE M,ZOU H,HUO K.Casein kinase 2 interacts with human mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase MSK1 and phosphorylates it at multiple sites[J].BMB Reports,2009,42(12):840-845.
[3] JONAK C,KIEGERL S,LIGTERINK W,BARKER P J,HUSKISSON N S,HIRT H.Stress signaling in plants:A mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway is activated by cold and drought[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,1996,93(20):11274-11279.
[4] BECKERS G J M,JASKIEWICZ M,LIU Y D,UNDERWOOD W R,HE S Y,ZHANG S,CONRATH U.Mitogen-activated protein kinases 3 and 6 are required for full priming of stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana[J].The Plant Cell,2009,21(3):944-953.
[5] ZIPFEL C,ROBATZEK S,NAVARRO L,OAKELEY E J,JONES J D G,FELIX G,BOLLER T.Bacterial disease resistance in Arabidopsis through flagellin perception[J].Nature,2004,428(6984):764-767.
[6] ANDREASSON E,ELLIS B.Convergence and specificity in the Arabidopsis MAPK nexus[J].Trends in Plant Science,2010,15(2):106-113.
[7] LÓPEZ M A,BANNENBERG G,CASTRESANA C.Controlling hormone signaling is a plant and pathogen challenge for growth and survival[J].Current Opinion in Plant Biology,2008,11(4):420-427.
[8] HAMEL L P,NICOLE M C,SRITUBTIM S,MORENCY M J,ELLIS M,EHLTING J,BEAUDOIN N,BARBAZUK B,KLESSIG D,LEE J,MARTIN G,MUNDY J,OHASHI Y,SCHEEL D,SHEEN J,XING T,ZHANG S,SEGUIN A,ELLIS B E.Ancient signals:Comparative genomics of plant MAPK and MAPKK gene families[J].Trends in Plant Science,2006,11(4):192-198.
[9] REYNA N S,YANG Y N.Molecular analysis of the rice MAP kinase gene family in relation to Magnaporthe grisea infection[J].Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions,2006,19(5):530-540.
[10] NICOLE M C,HAMEL L P,MORENCY M J,BEAUDOIN N,ELLIS B E,SÉGUIN A.MAP-Ping genomic organization and organ-specific expression profiles of poplar MAP kinases and MAP kinase kinases[J/OL].BMC Genomics,2006,7:223.DOI:10.1186/1471-2164-7-223.
[11] KONG X P,PAN J W,ZHANG D,JIANG S,CAI G,WANG L,LI D.Identification of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase gene family and MKK-MAPK interaction network in maize[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2013,441(4):964-969.
[12] ZHANG S Z,XU R R,LUO X C,JIANG Z,SHU H.Genomewide identification and expression analysis of MAPK and MAPKK gene family in Malus domestica[J].Gene,2013,531(2):377-387.
[13] ZHANG S,KLESSIG D F.Salicylic acid activates a 48-kD MAP kinase in tobacco[J].The Plant Cell,1997,9(5):809-824.
[14] ZHANG X T,CHENG T C,WANG G H,YAN Y,XIA Q.Cloning and evolutionary analysis of tobacco MAPK gene family[J].Molecular Biology Reports,2013,40(2):1407-1415.
[15] CHANG X L,NICK P.Defence signalling triggered by Flg22 and Harpin is integrated into a different stilbene output in Vitis cells[J/OL].PLoS ONE,2012,7(7):e40446.DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0040446.
[16] 王刚.葡萄MAPK 类基因家族的鉴定、表达分析及部分基因的功能验证[D].南京:南京农业大学,2014.WANG Gang.Identification,expression analysis of mapk-like gene families in grapevine and functional characteration of some members[D].Nanjing:Nanjing Agricultural University,2014.
[17] JIAO Y T,WANG D,WANG L,JIANG C,WANG Y.VqMAPKKK38 is essential for stilbene accumulation in grapevine[J].Horticulture Research,2017,4(1):95-103.
[18] 朱自果,张庆田,李秀杰,韩真,李桂荣,李勃.燕山葡萄MAPK 基因的克隆、亚细胞定位及表达分析[J].农业生物技术学报,2020,28(3):429-440.ZHU Ziguo,ZHANG Qingtian,LI Xiujie,HAN Zhen,LI Guirong,LI BO.Cloning,subcellular localization and expression analysis of MAPK genes from Vitis yeshanesis[J].Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology,2020,28(3):429-440.
[19] 贺普超,任治邦.我国葡萄属野生种对炭疽病抗性的研究[J].果树科学,1990,7(1):7-12.HE Puchao,REN Zhibang.Study on the resistances of wild Vitis species native to China to grape ripe rot[J].Journal of Fruit Science,1990,7(1):7-12.
[20] 雷龑,林雄杰,陈婷,蔡盛华,范国成.福建葡萄炭疽病病原鉴定及致病性分析[J].果树学报,2014,31(6):1123-1127.LEI Yan,LIN Xiongjie,CHEN Ting,CAI Shenghua,FAN Guocheng.Pathogen identification and pathogenicity analysis of grape ripe rot in Fujian[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2014,31(6):1123-1127.
[21] REID K E,OLSSON N,SCHLOSSER J,PENG F,LUND S T.An optimized grapevine RNA isolation procedure and statistical determination of reference genes for real-time RT-PCR during berry development[J/OL].BMC Plant Biology,2006,6:27.DOI:10.1186/1471-2229-6-27.
[22] RAO X Y,HUANG X L,ZHOU Z C,LIN X.An improvement of the 2ˆ(-delta delta CT)method for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis[J].Biostatistics,Bioinformatics and Biomathematics,2013,3(3):71-85.
[23] XIE X Q,WANG Y J.VqDUF642,a gene isolated from the Chinese grape Vitis quinquangularis,is involved in berry development and pathogen resistance[J].Planta,2016,244(5):1075-1094.
[24] ZHANG S Q,KLESSIG D F.MAPK cascades in plant defense signaling[J].Trends in Plant Science,2001,6(11):520-527.
[25] MELKSHAM K J,WECKERT M A,STEEL C C.An unusnal bunch rot of grapes in sub-tropical regions of Anstralia caused by Colletotrichum acutatum[J].Australasian Plant Pathology,2002,31(2):193-194.
[26] WANG Y,HAO X,LU Q,WANG L,QIAN W,LI N,DING C,WANG X,YANG Y.Transcriptional analysis and histochemistry reveal that hypersensitive cell death and H2O2 have crucial roles in the resistance of tea plant (Camellia sinensis (L.) O.Kuntze)to anthracnose[J/OL].Horticulture Research,2018,5:18.DOI:10.1038/s41438-018-0025-2.
[27] THALHAMMER A,BRYANT G,SULPICE R,HINCHA D K.Disordered cold Regulated15 proteins protect chloroplast membranes during freezing through binding and folding,but do not stabilize chloroplast enzymes in vivo[J].Plant Physiology,2014,166(1):190-201.
[28] MA H,XIANG G Q,LI Z Q,WANG Y,DOU M,SU L,YIN X,LIU R,WANG Y,XU Y.Grapevine VpPR10.1 functions in resistance to Plasmopara viticola through triggering a cell deathlike defence response by interacting with VpVDAC3[J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2018,16(8):1488-1501.