西瓜(Citrullus lanatus L.)是葫芦科、西瓜属、1年生蔓生藤本植物,原产地为非洲,果肉味甜,能降温去暑,在我国是一种重要的水果型蔬菜作物,在促进农民快速增收和满足人民日益增长的生活需求方面发挥了巨大作用。分子标记辅助选择育种在现代育种过程中发挥重要作用,通过与常规育种相结合,能够准确、快捷地选择具有目标基因或性状的西瓜育种材料,可大大提高育种效率,加快育种进程[1-2]。果皮覆纹是葫芦科作物最为重要的外观品质之一,是育种家、种植者和消费者日益关注的重要性状,具有重要的研究价值。
近年来,多个葫芦科作物的果皮覆纹调控基因得到挖掘,对开展分子标记辅助育种和揭示其调控机制具有重要意义。研究表明,甜瓜果皮有覆纹对无覆纹是显性的,Liu等[3]利用绿皮有条纹材料和白皮无条纹材料构建F2群体,将单显性基因St3 定位在4 号染色体172.8 kb 区间内。Lü 等[4]利用带斑点材料BIM16553 和无斑点材料IM16559 将控制甜瓜果皮斑点的单显性基因CmSp-1 定位在2 号染色体280.872 kb 区间内。在黄瓜果皮覆纹性状的研究中,Song 等[5]利用不规则条纹材料和均匀绿皮自交系材料构建F2群体,将单隐性基因ist 定位在黄瓜1号染色体144 kb 区间内,候选基因Csa1G005490 编码聚半乳糖醛酸酶-1非催化亚基β蛋白(PG1β)。
西瓜作为葫芦科重要作物之一,前人在果皮覆纹方面也开展了一些研究。Gusmini 等[6]利用西瓜果皮表面不连续条纹材料和连续条纹材料为亲本构建六世代群体发现西瓜果皮表面不连续条纹是由隐性基因ins 控制的。Yang 等[7]利用西瓜绿色无条纹材料分别和绿色有条纹、黄色有条纹、深绿色有条纹材料进行杂交,通过构建3个不同的F2群体,发现西瓜果皮条纹性状由单基因S 控制,其中有条纹对无条纹为显性。Zhang 等[8]研究表明西瓜果皮表面宽条纹受显性单基因控制,将控制西瓜果皮宽条纹性状的主效基因RS8.1定位在8号染色体上约2.3 cM。Yue等[9]通过遗传分析表明西瓜齿条对网纹为显性,将西瓜条纹基因CISP 定位在6 号染色体28.17~28.78 Mb约612 kb区间内。
在园艺作物中,不同类型的果皮条纹是由一些功能基因或转录因子调控导致果皮色素积累引起的,苹果和梨的果皮条纹被认为是由Myb10的甲基化调控的[10-11]。Avdeev 等[12]研究表明番茄Karsten ex Farw 果皮上的绿色条纹表型不稳定是受跳跃基因gs调控的。而Liu等[13]发现TAGL1启动子的甲基化差异导致番茄果皮色素沉着不均匀,红色条纹和黄色条纹随机分布在红色成熟果实果皮上。
笔者在本研究中以实验室选育的果皮覆齿条西瓜自交系材料H2和覆网纹西瓜自交系材料H9为亲本,构建F1、BC1P1、BC1P2和F2群体。对西瓜果皮覆纹性状进行遗传分析发现西瓜果皮覆齿条对网纹为显性,通过全基因组混池重测序分析和基因定位,最终将西瓜果皮覆纹调控基因ClRs(Citrullus lanatus rind stripe)定位在6 号染色体305.7 kb 区域内,初步预测了4个候选基因,同时开发了1个可用于辅助育种的分子标记。
1 材料和方法
1.1 试验材料及实验试剂
试验材料:以本实验室选育的高代自交系材料H9 为母本(P1,网纹),高代自交系材料H2 为父本(P2,齿条),利用2 个亲本配制F1、BC1P1、BC1P2和F2群体。用于标记鉴定的自然群体材料由国家园艺种质资源库提供。所有材料均种植在中国农业科学院郑州果树研究所新乡试验基地大棚内,两亲本各定植20 株、F1群体定植50 株,F2群体定植368 株、回交群体各定植100 株。成熟期进行调查,将果皮覆纹类型分为齿条和网纹。
实验试剂:RNAprep Pure多糖多酚植物总RNA提取试剂盒(DP441,TIANGEN)、2×phanta Max Master Mix DNA 聚合酶(P515,GenStar)、StarScriptⅡcDNA 第一链合成预混试剂(含去基因组)(A224-10,GenStar)、StarPrep快速DNA胶回收试剂盒(D205-4,GenStar)、EZ-Blunt 零背景pTOPO 平末端克隆试剂盒(T181-100,GenStar)、DH5α感受态细胞(G6016,昂羽生物)、氯仿、异戊醇、异丙醇、70%乙醇等。
1.2 DNA提取和混池构建
从F2 分离群体中,挑选齿条性状单株15 株,网纹性状单株15 株,用CTAB 方法提取DNA,分别构建2 个DNA 混池(显性池和隐性池),把构建的2 个DNA 混池和2 个亲本DNA 池送至湖南拓唯生物科技有限公司进行建库测序得到全基因组重测序数据。
1.3 分子标记开发与基因定位
分子标记开发:根据全基因组重测序数据,结合西瓜参考基因组数据和初定位结果,查找插入或缺失5个碱基以上的位点设计InDel标记,在位点的前后各截取150~200 bp 作为参考序列,引物的长度一般为15~30 bp,GC 含量适宜,上下游引物退火温度差值小于2 ℃。
基因定位:利用多态性较好的InDel 标记通过聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳对368个F2单株的基因型进行鉴定,利用筛选出的重组单株进一步缩小候选区间。PCR反应体系:西瓜叶片DNA 1 μL,正、反向引物各0.5 μL,2×phanta Max Master Mix DNA 聚合酶5 μL,用3 μL ddH2O将总体积补齐至10 μL。扩增程序为:94 ℃预变性4 min;94 ℃变性30 s,55 ℃退火45 s,72 ℃延伸1 min,35 个循环;72 ℃延伸8 min。对PCR 产物用7%非变性聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳、硝酸银染色后拍照观察记录。
1.4 候选基因的序列分析
将西瓜叶片在液氮中迅速研磨成粉末状后按照RNAprep Pure 多糖多酚植物总RNA 提取试剂盒提供的方法提取总RNA。采用StarScript II cDNA 第一链合成预混试剂(含去基因组)两步法合成cDNA用于后续试验。
基因扩增PCR 体系:西瓜叶片cDNA 1 μL,正、反向引物各0.5 μL,2×phanta Max Master Mix DNA聚合酶12.5 μL,用10.5 μL ddH2O 将总体积补齐至25 μL。扩增程序:94 ℃预变性4 min;94 ℃变性30 s,55 ℃退火45 s,72 ℃延伸90 s,35个循环;72 ℃延伸8 min。
得到的扩增产物,根据其片段大小选择相应浓度的琼脂糖凝胶,电泳10 min 之后,在紫外灯下迅速切出目的片段,采用StarPrep 快速DNA 胶回收试剂盒回收纯化DNA 片段。利用EZ-Blunt 零背景pTOPO 平末端克隆试剂盒连接目的片段,将连接产物加入DH5α 感受态细胞中,冰上静置25 min;42 ℃水浴热激45 s,迅速放回冰上并静置2 min;向离心管中加入700 μL 不含抗生素的LB,混匀后37 ℃、200 r·min-1 复苏60 min;5000 r·min-1 离心1 min 收菌,留取100 μL 左右上清液轻轻吹打重悬菌块并涂布到含氨苄青霉素的LB 培养基上;将平板倒置放于37 ℃培养箱过夜培养;向2 mL 离心管中加入1 mL含氨苄青霉素的LB液体培养基,待培养基表面长出菌斑后,挑取单个菌斑到装有培养基的离心管中,37 ℃、150 r·min-1振荡过夜培养;吸取少量菌液作为模板进行PCR扩增,琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,选取阳性克隆的菌液由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司进行测序,所得序列用DNAMAN软件拼接比对。
2 结果与分析
2.1 西瓜果皮覆纹性状由一对显性基因控制
为研究西瓜果皮覆纹的遗传规律,以本实验室选育的高代自交系材料H9 为母本(P1,网纹),以高代自交系材料H2 为父本(P2,齿条)(图1),利用2个亲本配制得到F1、BC1P1、BC1P2和F2群体。所得F1代的西瓜果皮覆纹均表现为齿条,证明齿条对网纹是显性的。368个F2单株果皮覆纹为齿条与覆网纹的比例为279∶89,经卡方检验符合3∶1 的孟德尔分离比(χ2=0.13<χ20.05=3.841),BC1P1群体中果皮覆纹为齿条与网纹的分离比符合1∶1 的理论比(χ2=0.16<χ20.05=3.841),BC1P2群体中西瓜果皮覆纹全为齿条,结果表明,西瓜果皮齿条由一对显性基因控制(表1)。
表1 西瓜果皮覆纹性状的遗传分析
Table 1 Genetic analysis of watermelon rind stripe
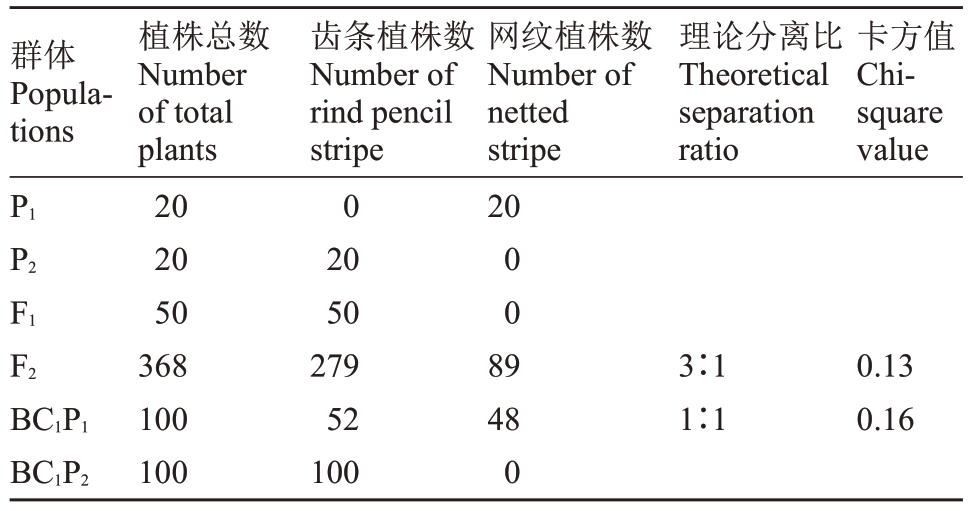
Note:χ20.05=3.841.
群体Populations理论分离比Theoretical separation ratio卡方值Chisquare value P1网纹植株数Number of netted stripe 20 P2 F1 00 F2 BC1P1 BC1P2植株总数Number of total plants 20 20 50 368 100 100齿条植株数Number of rind pencil stripe 0 20 50 279 52 100 89 48 0 3∶1 1∶1 0.13 0.16
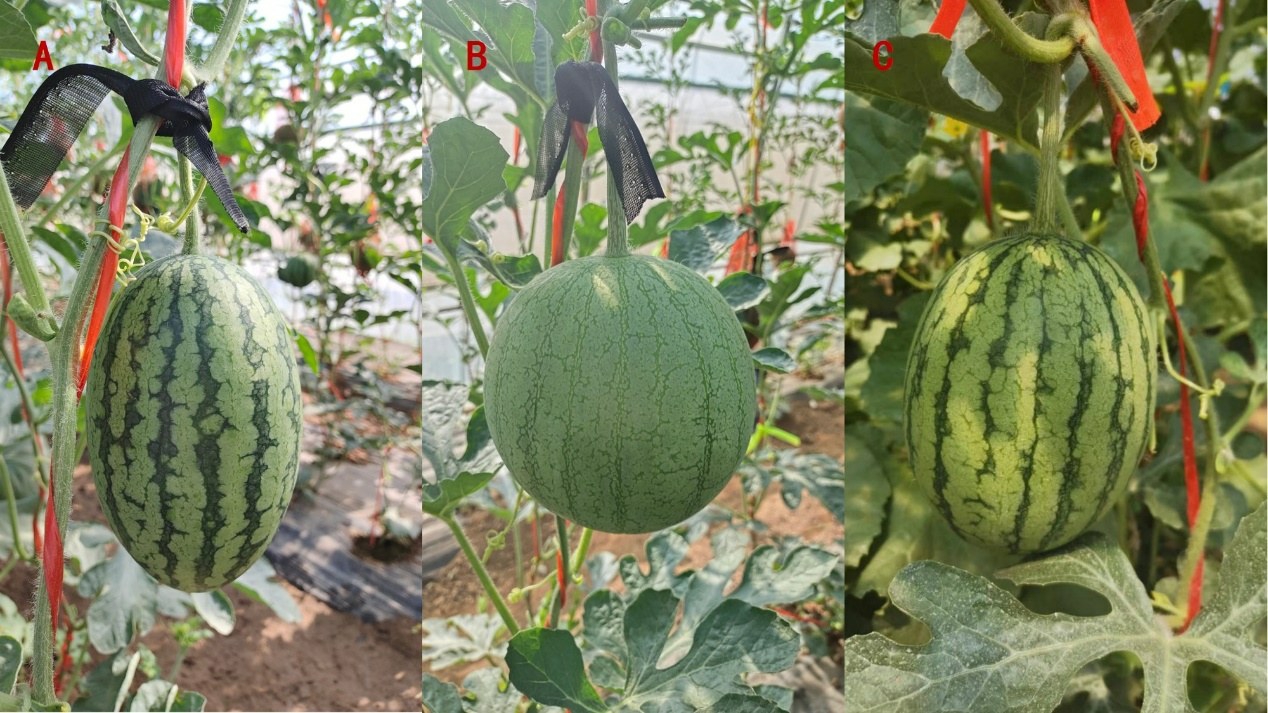

图1 双亲和F1果皮覆纹表型
Fig.1 Parents and F1 rind stripe phenotypic
A.H2;B.H9;C.F1
2.2 果皮覆纹基因ClRs的初步定位
通过对双亲和2 个F2代DNA 混池进行全基因组重测序,产生26.5 Gb的reads数据。利用BWA软件将reads 比对到西瓜参考基因组[Watermelon(97103)v2,http://cucurbitgenomics.org/organism/21]上,通过SAMtools(http://www.htslib.org/)软件寻找全基因组的SNP位点。显性亲本池、隐性亲本池、F2群体显性池、F2群体隐性池的测序深度分别为17×、12×、20×、18×,均覆盖全基因组序列的95%以上。碱基质量值≥30,mapping 质量值≥30,碱基depth 在双亲中≥2且≤80,同时满足碱基depth在2个F2混池中≥2 且≤80,共获得206 033 个差异SNP。以1 Mb为窗口,100 kb为步长画图。
由于与目标性状相关联的SNP 在染色体上与其周围的SNPs 是连锁遗传,因此在隐性池与显性池的SNPindex 差值应在0.5 以上,或接近于1,而在没有性状关联的基因组区域ΔSNPindex 显示在0.0上下随机分布。观察ΔSNPindex值分布,根据2个子代池的SNP-index在基因组上的分布,挑选出1个子代池中SNP-index接近于1,在另一个子代池中SNPindex 接近为0,且两者差异在一定阈值之上的区域,笔者发现6 号染色体上有个候选区间(24.3~29.4 Mb)(图2)。
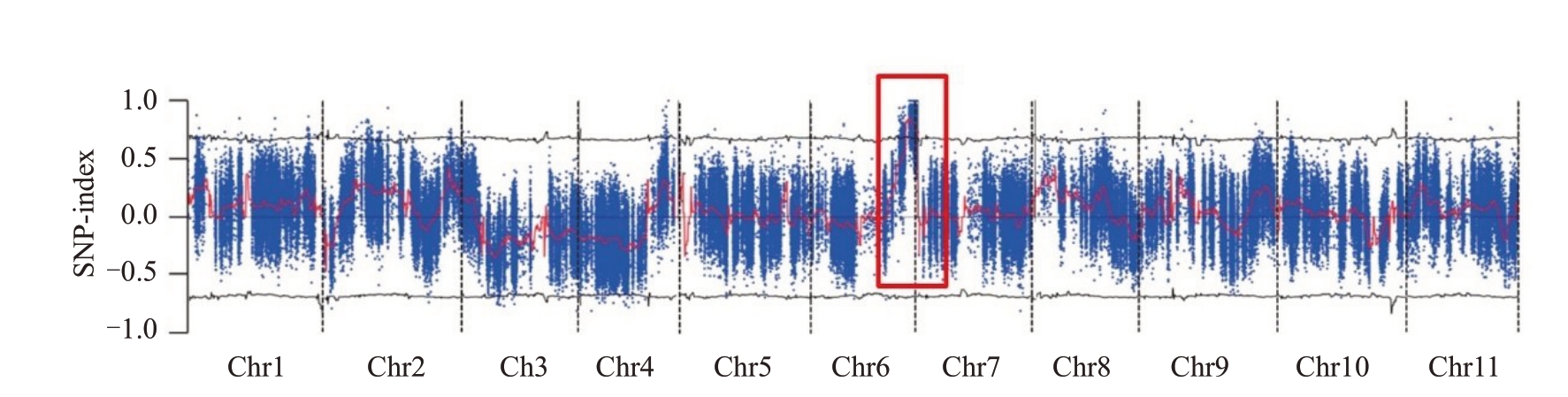
图2 西瓜果皮覆纹基因的初定位
Fig.2 Initial location of watermelon rind stripe gene
横轴表示染色体长度;纵轴表示SNP-index(SNP-index 表示隐性池SNPindex 减去显性池SNPindex);红色方框表示初定位候选区间。
The horizontal axis represents chromosome length and the vertical axis represents SNP-index(SNP-index represents recessive pool SNPindex minus dominant pool SNPindex,The red box represents the initial positioning candidate interval.
2.3 果皮覆纹基因ClRs的进一步定位
为了进一步缩小定位区间,利用两亲本基因组重测序数据设计InDel 标记并验证标记在亲本间的多态性。选用多态性较好的InDel 标记和全部368个F2单株进行基因定位。利用JoinMap软件和21个InDel标记,将ClRs基因定位在标记InDel-128和In-Del-124 之间,遗传距离分别为1.5 cM 和3.0 cM,位于6 号染色体28 252 905~28 558 579 bp 之间(图3,表2)。
表2 基因定位所需引物序列及染色体位置
Table 2 Sequence of primers and chromosome position required for gene localization

标记Marker name InDel-94 InDel-99 InDel-121 InDel-128 InDel-123 InDel-131 InDel-93 InDel-122 InDel-112 InDel-113 InDel-103 InDel-104 InDel-118 InDel-117 InDel-129 InDel-114 InDel-124 InDel-120 InDel-105 InDel-80 InDel-36位置Position/bp 27 722 998~27 723 190 27 731 628~27 731 874 28 107 940~28 108 289 28 252 856~28 253 105 28 539 985~28 540 284 28 541,981~28 542 127 28 521 552~28 521 732 28 286 621~28 286 824 28 340 589~28 340 820 28 387 264~28 387 543 28 485 414~28 485 657 28 511 051~28 511 330 28 536 235~28 536 427 28 336 106~28 336 323 28 272 799~28 273 009 28 404 010~28 404 230 28 558 339~28 558 838 28 589 402~28 589 676 28 596 944~28 597 194 28 965 543~28 965 708 29 061 118~29 061 324上游引物(5’-3’)Forward primer(5’-3’)AGTTGATGTGTCTCCCAACAA TCCCCTGAAGGCTCAACA TGCTCGTAATTCAACTACCACA GGAGTGTGTATAGAAGAGGG ACTACGCTAAGCTCACTTTGA GGTAAGATAAAATTATAGTGTGAGGG TCCACATTAGGGTCCAAACC GGTGTTCCCTTCCACCTTC TTTTGCCGTCCCCTCCAC GAGCACCAAGGGGAAGCT CGTGGGTCGGGTCACTTT CGGAGGCCCTACACTGGA AGGCTGAAGGAAAGGAGGA TGCAAACTTTGGTACGGCT CATACAATACAATGATCTCCATCTTTC AAACATGGTTCCAGAGCTGT GGAGATAGGAGAAATGGTCGG GCTTTTGCTGCATGCGACT AGGTGCTATGAGGGGAGACT TGCCAAACTTTGCACGTAGG TCCTCCTCGTCCTCCTCA下游引物(5’-3’)Reverse primer(5’-3’)CCACAAGCAAACATGGTGGT ACCCCCTCCTTCAACCACA GTGTTAGAGTCCTTGATGTGC GCAAGTGACGAGGAAAATG CATGTTCCTACTTCCTAGGGTC CAACCAAACAAAGTATTTCTTGATTTC TGTCAGCTCAGGGATGTCA GAAAATGCTACCAAACACATATCTAG TCAGGCGGTGCAAGAACA GCTTTTGTTGGCCTCATTCCT GGGCGGCAATAGGACACC GGTCAGTGCCCTTTAGTTCTG TGGATTGGCTTTAGGGTGGT AGGTGCTTTAGGGTCTCCTCT GCATATAAATACACACTTCACCTC TTGAACCTAGGCGCGGTG CAATGATGAGGTCAGCGAGAT GGGAAACAGAATGGGGCCA ACCTAAATCGTCGCAATCCA ACGAAACAATCTACCAGCCA GGCAAGTGTTCACCGGGA
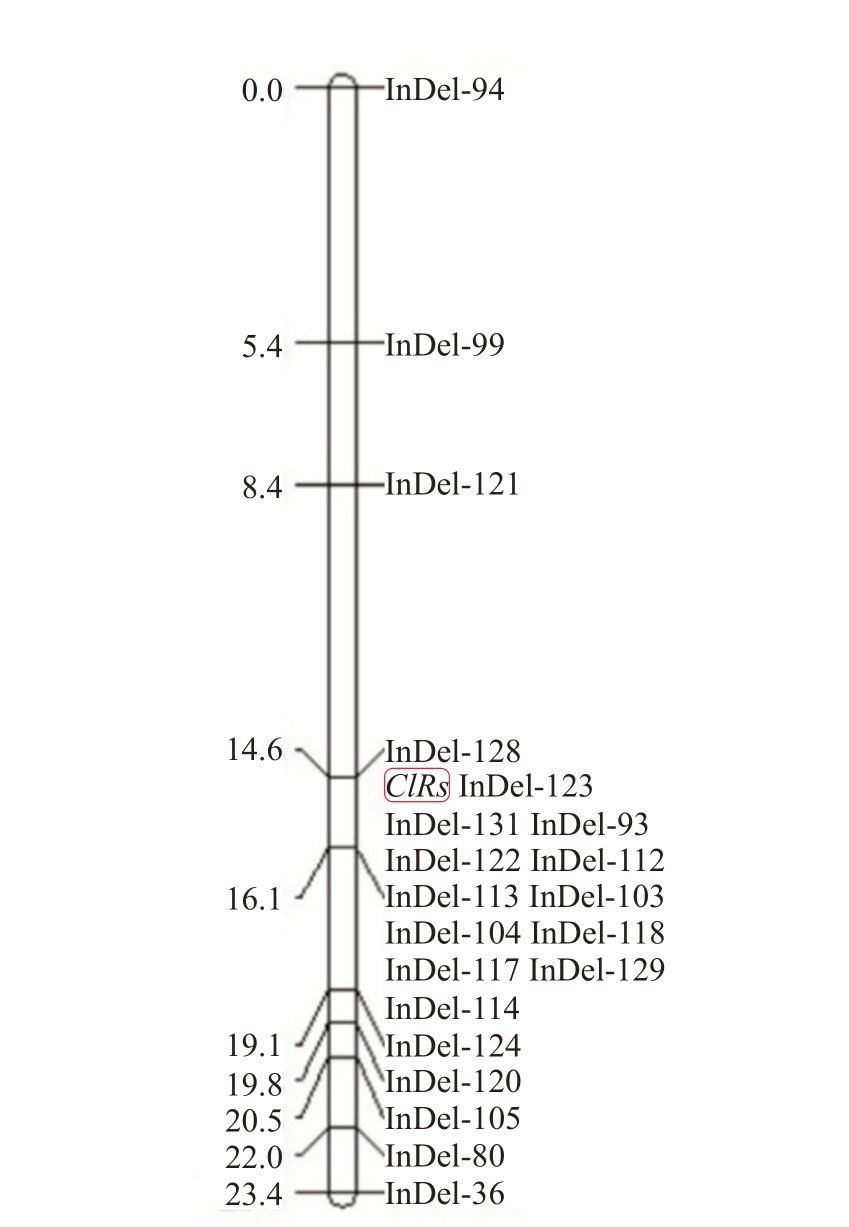
图3 西瓜果皮覆纹基因ClRs 遗传图谱
Fig.3 Genetic map of ClRs controlling watermelon rind stripe type
2.4 候选基因的筛选
根据基因定位结果,区间内有35 个基因,结合西瓜基因组注释信息以及前人有关果皮覆纹调控基因的报道,初步筛选到4 个可能与西瓜果皮覆纹相关的基因(表3)。Cla97C06G126560 编码多聚半乳糖醛酸酶-1 非催 化 亚 基β 蛋 白(PG1 β);Cla97C06G126680 为Myb 家族转录因子Cla97C06G126710 编码WD40 蛋 白;Cla97C06G126770 编 码MORC 家 族cw 型锌指蛋白。通过克隆基因的编码区序列 发 现Cla97C06G126560、Cla97C06G126710 和Cla97C06G126770 3 个基因的编码区序列在两亲本中存在差异:Cla97C06G126560 基因编码区序列存在2 个由单碱基替换造成的非同义突变位点;Cla97C06G126710 基因编码区序列存在3 个由单碱基替换造成的非同义突变位点;Cla97C06G126770 基因编码区序列存在8 个由单碱基替换造成的非同义突变位点和1 个三碱基插入缺失(表4)。利用3 个基因的非同义突变位点设计dCAPS 标记或InDel 标记(表5),并 利 用F2 群 体 与 由7 个 齿 条 材 料 和13 个网纹材料构成的自然群体材料进行基因型鉴定。发 现Cla97C06G126560、Cla97C06G126710和Cla97C06G126770 三个基因位于西瓜6 号染色体28 280 025、28 452 256 和28 500 594 bp 的突变位点基因型与F2群体和自然群体材料的表型完全一致,说明Cla97C06G126560、Cla97C06G126710和Cla97C06G126770 三个基因所处的染色体区段与目标基因是共分离的。
表3 定位区间内基因功能注释
Table 3 Annotation of gene function within localization interval

基因Gene ID Cla97C06G126530 Cla97C06G126540 Cla97C06G126550 Cla97C06G126560 Cla97C06G126570 Cla97C06G126580 Cla97C06G126590 Cla97C06G126600 Cla97C06G126610 Cla97C06G126620 Cla97C06G126630 Cla97C06G126640 Cla97C06G126650 Cla97C06G126660 Cla97C06G126670 Cla97C06G126680 Cla97C06G126690 Cla97C06G126700 Cla97C06G126710 Cla97C06G126720 Cla97C06G126730 Cla97C06G126740 Cla97C06G126750 Cla97C06G126760 Cla97C06G126770 Cla97C06G126780 Cla97C06G126790 Cla97C06G126800 Cla97C06G126810 Cla97C06G126820 Cla97C06G126830 Cla97C06G126840 Cla97C06G126850 Cla97C06G126860 Cla97C06G126870基因注释Gene annotation Cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 16 Aldehyde dehydrogenase,putative Protein kinase Polygalacturonase-1 non-catalytic subunit beta RING-finger ubiquitin ligase protein EXECUTER 2,chloroplastic CASP-like protein Unknown protein Tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR)-like superfamily protein Exosome complex exonuclease RRP40 Peroxisomal membrane protein PEX14 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase DUF1645 family protein prohibitin-3,mitochondrial serine/threonine-protein kinase ATM-like Myb family transcription factor Phox domain-containing family protein Unknown protein WD40 repeat transcription factor MYB98-like Homeobox transcription factor KN4 Homeobox transcription factor KN4 Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A 55 kDa regulatory subunit B Unknown protein MORC family CW-type zinc finger protein Unknown protein tRNA-processing ribonuclease BN Embryo defective 2759 protein,putative Protein MODIFIER OF SNC1 1-like protein Unknown protein Sec14p-like phosphatidylinositol transfer family protein Unknown protein Protein of Unknown Function(DUF239)JmjC domain cell division cycle protein 48 homolog
表4 候选基因编码区非同义突变位点
Table 4 Candidate gene coding region non-synonymous mutation sites
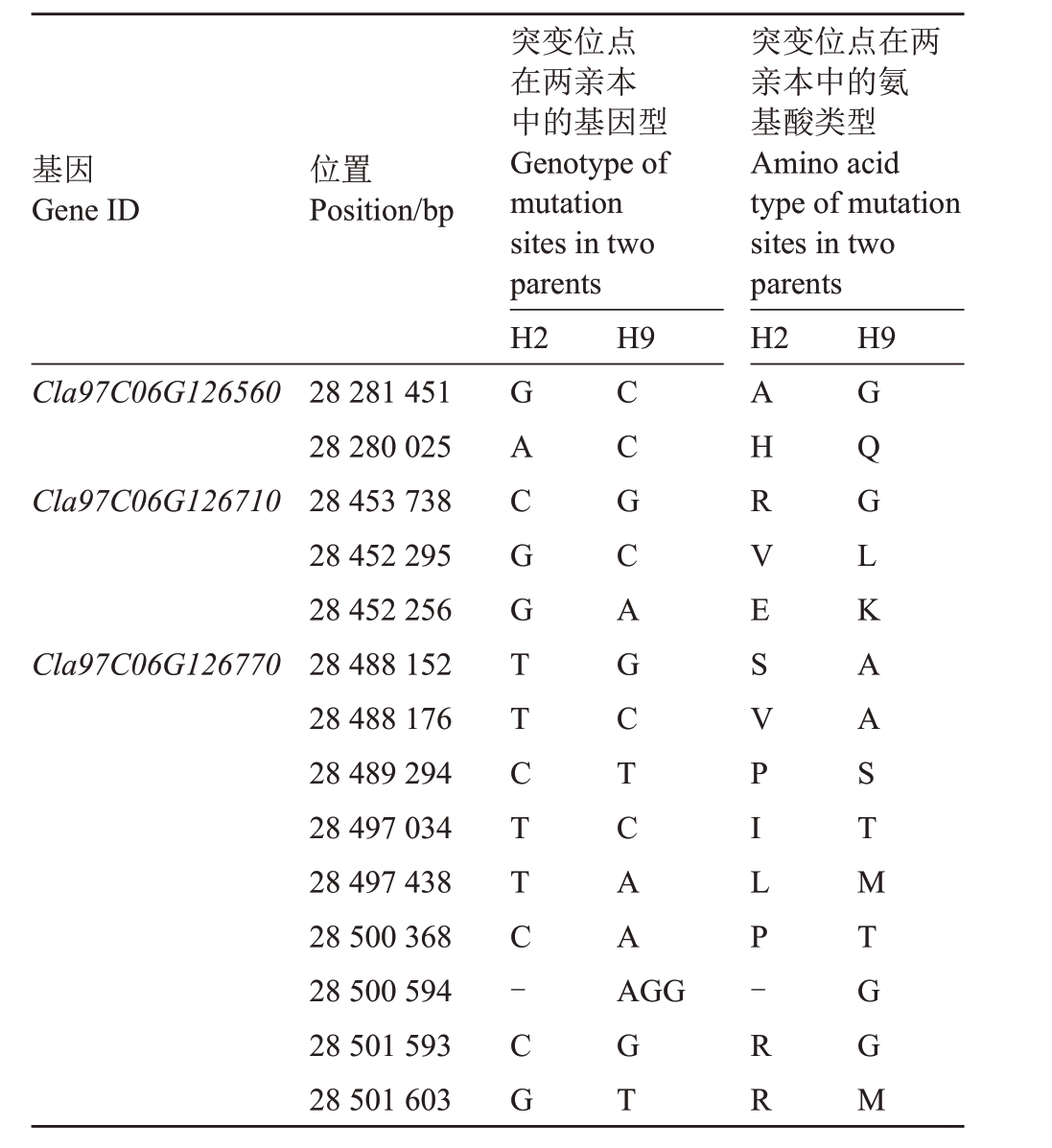
注:-表示碱基缺失。
Note:-indicates the deletion of the bases.
基因Gene ID位置Position/bp突变位点在两亲本中的基因型Genotype of mutation sites in two parents H2 H9突变位点在两亲本中的氨基酸类型Amino acid type of mutation sites in two parents H2 H9 Cla97C06G126560 Cla97C06G126710 Cla97C06G126770 28 281 451 28 280 025 28 453 738 28 452 295 28 452 256 28 488 152 28 488 176 28 489 294 28 497 034 28 497 438 28 500 368 28 500 594 28 501 593 28 501 603 GACGGTTCTTC-CG CCGCAGCTCAA AGG GT AHRVESVPILP-RR GQGLKAASTMTGGM
表5 利用候选基因编码区非同义突变位点设计分子标记
Table 5 The non-synonymous mutation sites in the coding region of candidate genes were used to design molecular markers
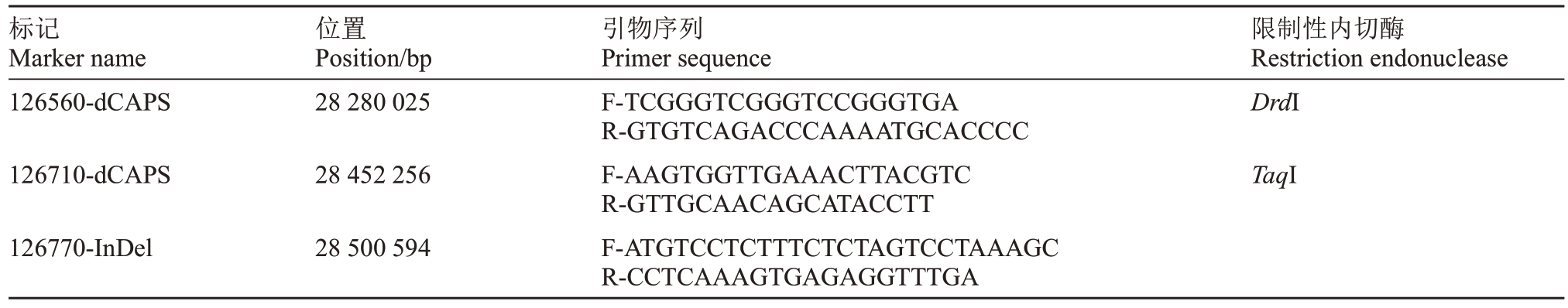
标记Marker name 126560-dCAPS位置Position/bp 28 280 025限制性内切酶Restriction endonuclease DrdI 126710-dCAPS 28 452 256 TaqI 126770-InDel 28 500 594引物序列Primer sequence F-TCGGGTCGGGTCCGGGTGA R-GTGTCAGACCCAAAATGCACCCC F-AAGTGGTTGAAACTTACGTC R-GTTGCAACAGCATACCTT F-ATGTCCTCTTTCTCTAGTCCTAAAGC R-CCTCAAAGTGAGAGGTTTGA
2.5 标记的开发及验证
通过进一步定位,在共分离区间内筛选到了12 个与目的基因紧密连锁的InDel 标记,其中In-Del-93 标记的可辨识度高、差异明显,便于利用聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳进行区分鉴定。标记InDel-93的基因型与F2群体单株表型完全一致,表明该标记与条纹基因ClRs 共分离。利用此标记对7 个果皮覆齿条西瓜材料和13 个果皮覆网纹西瓜材料构成的自然群体进行验证,标记基因型与20 份西瓜材料的表型完全吻合(图4,表6),证明该标记可用于分子标记辅助育种。
表6 20 个西瓜自然群体材料的果皮覆纹类型
Table 6 Phenotype of rind stripe in 20 watermelon natural population materials
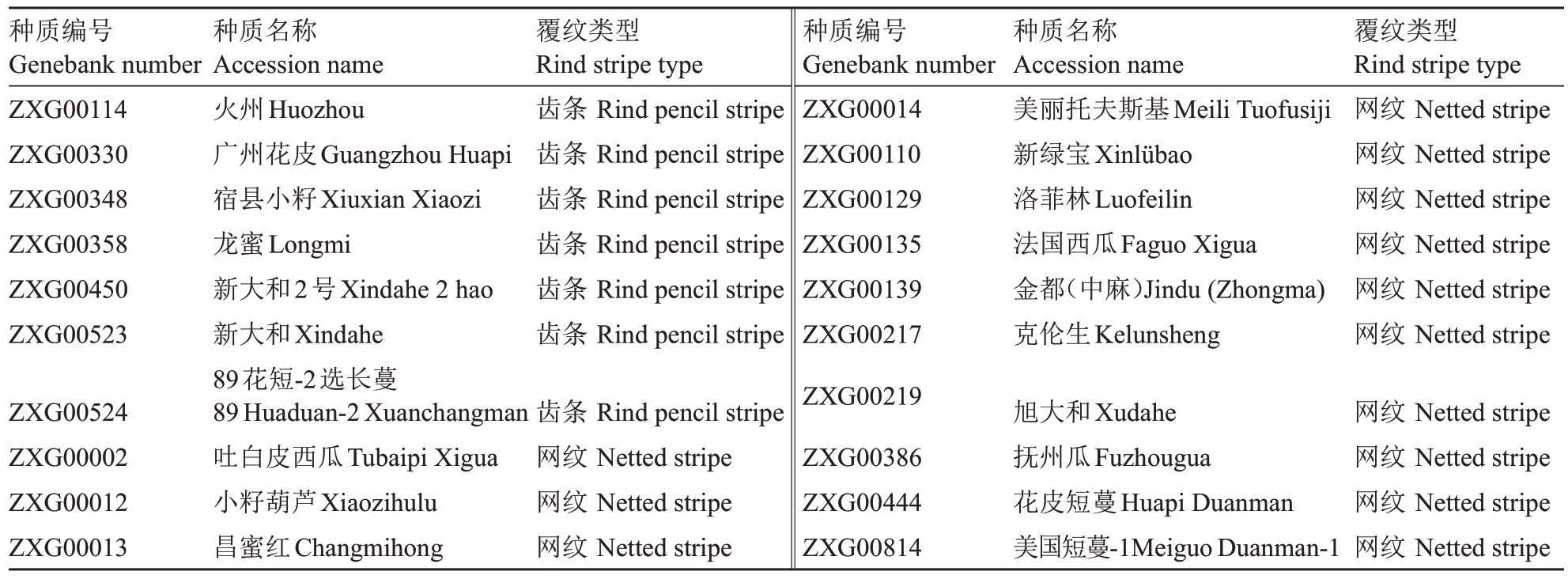
种质编号Genebank number ZXG00114 ZXG00330 ZXG00348 ZXG00358 ZXG00450 ZXG00523覆纹类型Rind stripe type齿条Rind pencil stripe齿条Rind pencil stripe齿条Rind pencil stripe齿条Rind pencil stripe齿条Rind pencil stripe齿条Rind pencil stripe种质名称Accession name美丽托夫斯基Meili Tuofusiji新绿宝Xinlübao洛菲林Luofeilin法国西瓜Faguo Xigua金都(中麻)Jindu(Zhongma)克伦生Kelunsheng覆纹类型Rind stripe type网纹Netted stripe网纹Netted stripe网纹Netted stripe网纹Netted stripe网纹Netted stripe网纹Netted stripe ZXG00524 ZXG00002 ZXG00012 ZXG00013种质名称Accession name火州Huozhou广州花皮Guangzhou Huapi宿县小籽Xiuxian Xiaozi龙蜜Longmi新大和2号Xindahe 2 hao新大和Xindahe 89花短-2选长蔓89 Huaduan-2 Xuanchangman吐白皮西瓜Tubaipi Xigua小籽葫芦Xiaozihulu昌蜜红Changmihong齿条Rind pencil stripe网纹Netted stripe网纹Netted stripe网纹Netted stripe种质编号Genebank number ZXG00014 ZXG00110 ZXG00129 ZXG00135 ZXG00139 ZXG00217 ZXG00219 ZXG00386 ZXG00444 ZXG00814旭大和Xudahe抚州瓜Fuzhougua花皮短蔓Huapi Duanman美国短蔓-1Meiguo Duanman-1网纹Netted stripe网纹Netted stripe网纹Netted stripe网纹Netted stripe
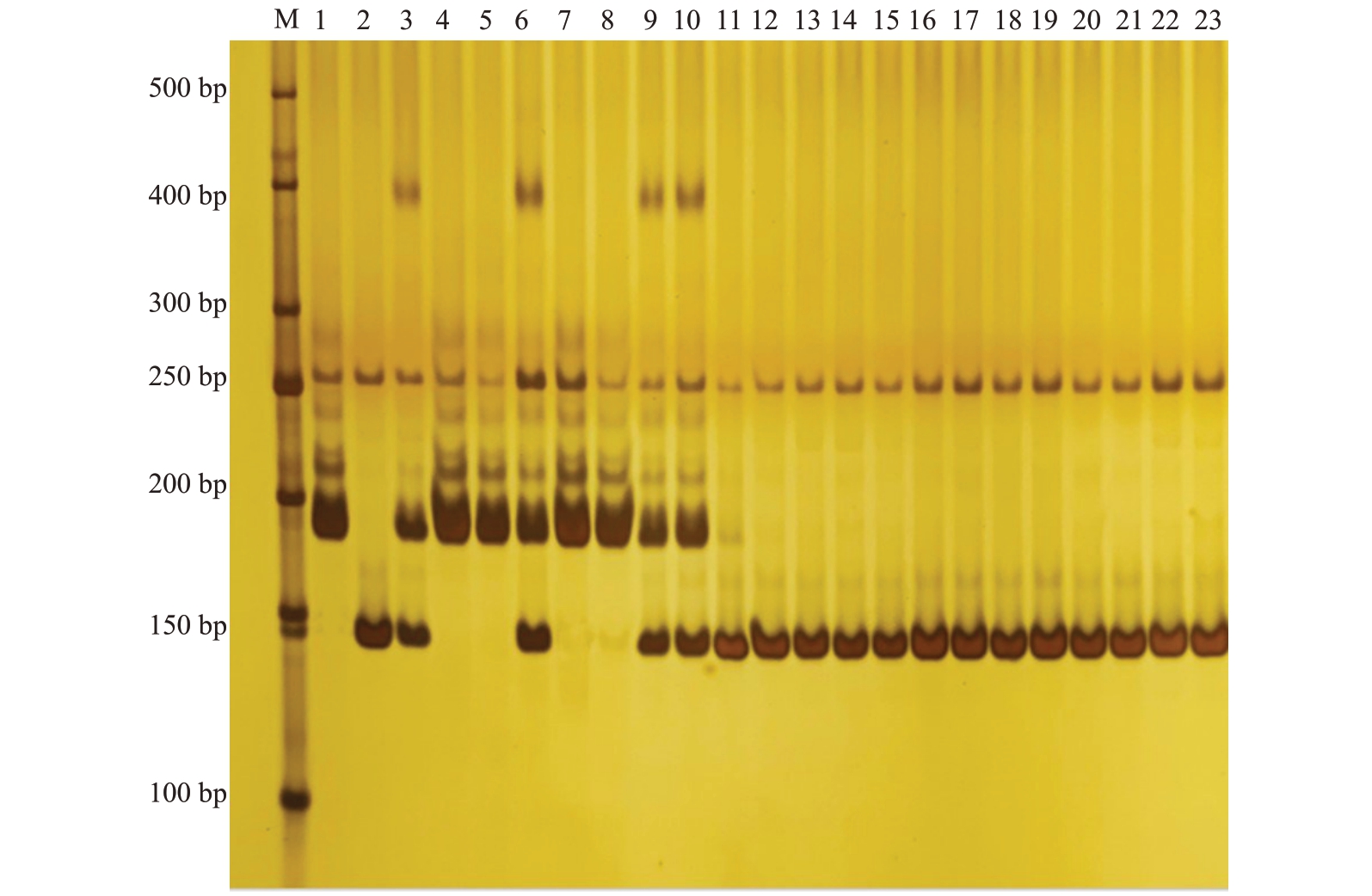
图4 InDel-93 标记在双亲、F1、自然群体材料中的基因型
Fig.4 Genotypes of InDel-93 in parental,F1,natural population materials
M.500 bp Marker;1.齿条亲本H2 基因型;2.网纹亲本H9 基因型;3.F1 基因型;4~23.20 个西瓜材料构成的自然群体材料(其中4~10 是齿条材料,11~23 是网纹材料)。
M.500 bp Marker;1.Rind pencil stripe parent H2 genotype;2.Netted parent H9 genotype;3.F1 genotype;4-23.Natural population materials composed of watermelon material(of which 4-10 are rind pencil stripe materials and 11-23 are netted materials).
3 讨 论
果皮条纹是一种重要的外观和品质性状,尤其对于以果实为食用器官的园艺作物来说,果实表面覆纹类型对其商品性影响很大。西瓜果皮表面多数都有覆纹,果皮覆纹形状可分级描述为:网条、齿条、条带、放射条、斑条[14-15]。本试验在表型鉴定过程中,将F2群体中覆盖连续齿条和不连续齿条的单株均归为齿条类型;细网条归为网纹类型。将调控西瓜果皮覆纹基因定位在6 号染色体305.7 kb区间内,侧翼标记为InDel-128 和InDel-124,遗传距离分别为1.5 cM 和3.0 cM。在后续的精细定位过程中,利用12 个共分离标记进一步鉴定了568个F2单株后,仍然没有发现该区段内的染色体交换,笔者推测该区段存在重组抑制现象。染色体的重组抑制现象在番茄抗根结线虫Mi 基因所处染色体区域同样存在,产生原因是抗感病栽培番茄材料在该区段存在染色体区段的倒置现象[16-19]。笔者在本研究中发现的重组抑制现象将通过进一步实验进行验证。
有研究表明,果皮色泽发育的色素包括叶绿素、花青素、胡萝卜素和黄酮素等[20]。在定位区间内存在35 个基因,结合西瓜基因组注释信息以及前人有关果皮覆纹调控基因的报道,初步筛选到3个可能与西瓜果皮覆纹相关的基因,通过序列比对发 现 Cla97C06G126560、Cla97C06G126710 和Cla97C06G126770 三个基因的编码区序列在两亲本中存在差异,且差异位点与目标基因共分离。Cla97C06G126560 编码多聚半乳糖醛酸酶-1 非催化亚基β 蛋白(PG1β),与调控黄瓜表皮不规则条纹的候选基因Csa1G005490高度同源[7]。研究表明PG1β 蛋白在番茄果实成熟过程中引起果实的逐渐软化并伴随着果皮由绿色转为红色[21-24]。Sitrit等[25]认为PG 基因的转录受乙烯调控,PG 基因对乙烯十分敏感,低水平的乙烯即可诱导PG 基因的大量表达,Yue 等[9]通过转录组分析发现多个乙烯响应因子(ERFs)在网纹部位的表达量显著高于在齿条部位的表达量,推测乙烯可能与西瓜果皮条纹的发育有关,而PG 基因对乙烯的高敏感性也导致其可能与西瓜果皮条纹的形成有关。Cla97C06G126710 编码WD40 蛋白,是一类高度保守的蛋白,一般含有4~16 个串联重复的WD 基元序列,每个WD 基元由44~60 个氨基酸残基组成,WD40 主要功能是促进蛋白相互作用,酵母双杂交实验发现与其互作的蛋白主要是MYB 和bHLH 转录因子[26]。在拟南芥、玉米、矮牵牛等植物 中,WD40 蛋 白 与MYB 以 及bHLH 转 录 因 子 相互作用,以MYB/bHLH/WD40 复合物的调控模式调控花青素的生物合成[27-29]。拟南芥中TTG1 突变导致DFR 基因的表达量下调,影响花青素的下调,矮牵牛中an11 的突变导致DFR 基因的表达量下调,影响花色素的下调,在拟南芥中过表达PFWD可以增加花青素的含量[26,30-31]。Guo 等[32]通过全基因重测序分析也筛选出编码WD40 蛋白的Cla97C06G126710 基因可能与西瓜果皮条纹有关。Cla97C06G126770 编码MORC 家族cw 型锌指蛋白,Brabbs 等[33]发现MORC 家族的成员morc6参与DNA 甲基化导致的基因沉默。Liu 等[13]发现在番茄中由于启动子的高度甲基化导致TAGL1基因表达受抑制,使得未成熟果实产生深绿色条纹,而低水平甲基化使得未成熟果实出现浅绿色条纹,在果实成熟后呈现红色和黄色条纹的随机分布。而Cla97C06G126770 是否通过DNA 甲基化调控西瓜果皮条纹的发育还需进一步试验验证。Cla97C06G126680 为Myb 家族转录因子,虽然其编码区序列在两亲本中没有差异,但有研究表明苹果和梨果皮条纹的形成是由MYB10 的甲基化导致的,MYB10 甲基化/去甲基化可以抑制/激活MYB10 的转录,进而抑制/诱导花青素生物合成关键结构基因的表达[10-11],因此Cla97C06G126680 也有可能是调控西瓜果皮条纹的基因,后续将通过分析其表达调控模式和功能加以验证。
4 结 论
本研究利用果皮覆齿条材料H2和覆网纹材料H9 2个高代自交系为亲本将西瓜果皮覆纹基因ClRs定位在6号染色体305.7 kb区间内,推测该区间内可能存在重组抑制现象,结合基因组注释在该区间内筛选到4个候选基因(Cla97C06G126560、Cla97C06G126680、Cla97C06G126710、Cla97C06G126770)。还开发了1个可辨识度高、差异明显的InDel-93标记,经鉴定可用于分子辅助育种。后续工作中笔者将对候选基因的功能和调控机制进行研究。
[1] 张金鹏,金鑫,赵艳菲,陈莹,惠长敏.西瓜分子标记辅助育种研究与应用进展[J].中国瓜菜,2022,35(4):1-7.ZHANG Jinpeng,JIN Xin,ZHAO Yanfei,CHEN Ying,HUI Changmin.Research and application progress of watermelon molecular marker assisted breeding[J].China Cucurbits and Vegetables,2022,35(4):1-7.
[2] 李兵兵,刘文革.西瓜遗传图谱构建和基因定位研究进展[J].中国瓜菜,2019,32(2):1-6.LI Bingbing,LIU Wenge.Research progress on genetic map construction and gene mapping for watermelon[J].China Cucurbits and Vegetables,2019,32(2):1-6.
[3] LIU L,SUN T T,LIU X Y,GUO Y,HUANG X,GAO P,WANG X Z.Genetic analysis and mapping of a striped rind gene(st3)in melon(Cucumis melo L.)[J].Euphytica,2019,215(2):1-12.
[4] LÜ J C,FU Q S,LAI Y,ZHOU M D,WANG H S.Inheritance and gene mapping of spotted to non-spotted trait gene CmSp-1 in melon (Cucumis melo L.var. chinensis Pangalo)[J].Molecular Breeding,2018,38(8):1-9.
[5] SONG M F,ZHANG M R,CHENG F,WEI Q Z,WANG J,DAVOUDI M,LOU Q F.An irregularly striped rind mutant reveals new insight into the function of PG1β in cucumber(Cucumis sativus L.)[J].Theoretical and Applied Genetics,2020,133(2):371-382.
[6] GUSMINI G,WEHNER T C.Qualitative inheritance of rind pattern and flesh color in watermelon[J].Journal of Heredity,2006,97(2):177-185.
[7] YANG H B,PARK S W,PARK Y,LEE G P,KANG S C,KIM Y K.Linkage analysis of the three loci determining rind color and stripe pattern in watermelon[J].Horticultural Science &Technology,2015,33(4):559-565.
[8] ZHANG Z P,ZHANG Y N,SUN L,QIU G,SUN Y J,ZHU Z C,LUAN F S,WANG X Z.Construction of a genetic map for Citrullus lanatus based on CAPS markers and mapping of three qualitative traits[J].Scientia Horticulturae,2017,233:532-538.
[9] YUE Z,MA R X,CHENG D H,YAN X,HE Y P,WANG C X,PAN X N,YIN L J,ZHANG X,WEI C H.Candidate gene analysis of watermelon stripe pattern locus ClSP ongoing recombination suppression[J].Theoretical and Applied Genetics,2021,134(10):3263-3277.
[10] TELIAS A,LIN-WANG K,STEVENSON D E,COONEY J M,HELLENS R P,ALLAN A C,BRADEEN J M.Apple skin patterning is associated with differential expression of MYB10[J].BMC Plant Biology,2011,11(1):1-15.
[11] QIAN M J,SUN Y W,ALLAN A C,TENG Y W,ZHANG D.The red sport of‘Zaosu’pear and its red-striped pigmentation pattern are associated with demethylation of the PyMYB10 promoter[J].Phytochemistry,2014,107:16-23.
[12] AVDEEV Y I,KIGASHPAEVA O P.Jumping gene gs of Lycopersicon lycopersicum (L.) Karsten ex Farw[J].Russian Journal of Genetics,2002,38(5):496-500.
[13] LIU G Z,LI C X,YU H Y,TAO P W,YUAN L,YE J,CHEN W F,WANG Y,GE P F,ZHANG J H,ZHOU G L,ZHENG W,YE Z B,ZHANG Y Y.GREEN STRIPE,encoding methylated TOMATO AGAMOUS-LIKE 1,regulates chloroplast development and Chl synthesis in fruit[J].New Phytologist,2020,228(1):302-317.
[14] 尚建立,王吉明,马双武.西瓜种质资源若干性状描述与数据采集[J].中国瓜菜,2010,23(6):39-41.SHANG Jianli,Wang Jiming,MA Shuangwu.Characterization and data collection of watermelon germplasm resources[J].China Cucurbits and Vegetables,2010,23(6):39-41.
[15] 王铭,刘江,王长彪,郝科星,侯富恩,张涛,杨晋明.109 份西瓜育种材料果实性状的遗传多样性分析[J].中国瓜菜,2020,33(10):23-28.WANG Ming,LIU Jiang,WANG Changbiao,HAO Kexing,HOU Fuen,ZHANG Tao,YANG Jinming.Genetic diversity analysis of fruit characters in 109 watermelon breeding materials[J].China Cucurbits and Vegetables,2020,33(10):23-28.
[16] 唐为江.精细定位控制抽穗期、株高和每穗颖花数的QTL 与图位克隆汕优63 中控制胶稠度、糊化温度的基因[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2008.TANG Weijiang.Fine mapping of QTLS controlling heading date,plant height and spikelet number per panicle and mapping of genes controlling gel consistency and gelatinization temperature in Shanyou 63[D].Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University,2008.
[17] 赵统敏,王银磊,杨玛丽,赵丽萍,余文贵.番茄根结线虫病抗性基因的研究进展[J].江苏农业学报,2012,28(6):1492-1497.ZHAO Tongmin,WANG Yinlei,YANG Mali,ZHAO Liping,YU Wengui.Research progress on resistance genes of root knot nematode in tomato[J].Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2012,28(6):1492-1497.
[18] GANAL M W,TANKSLEY S D.Recombination around the Tm2a and Mi resistance genes in different crosses of Lycopersicon peruvianum[J].Theoretical and Applied Genetics,1996,92(1):101-108.
[19] HO J Y,WEIDE R,MA H M,VAN WORDRAGEN M F,LAMBERT K N,KOORNNEEF M,WILLIAMSON V M.The rootknot nematode resistance gene(Mi)in tomato:Construction of a molecular linkage map and identification of dominant cDNA markers in resistant genotypes[J].The Plant Journal,1992,2(6):971-982.
[20] 赵海娟,刘宁,张玉萍,刘威生,张玉君,徐铭,马小雪,刘家成,刘硕.李果皮颜色遗传多样性及其成色因子研究进展[J].果树学报,2022,39(8):1479-1489.ZHAO Haijuan,LIU Ning,ZHANG Yuping,LIU Weisheng,ZHANG Yujun,XU Ming,MA Xiaoxue,LIU Jiacheng,LIU Shuo.Advances in genetic diversity of plum skin color and its color forming factors[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2022,39(8):1479-1489.
[21] 肖鑫丽.西瓜Rab18、BURP domain-containing protein 17 基因的克隆、序列分析及表达研究[D].昆明:云南农业大学,2015.XIAO Xinli.Cloning,sequence analysis and expression study of Rab18 and BURP domain-containing protein 17 genes in watermelon[D].Kunming:Yunnan Agricultural University,2015.
[22] ZHENG L S,HEUPEL R C,DELLAPENNA D.The beta subunit of tomato fruit polygalacturonase isoenzyme 1:Isolation,characterization,and identification of unique structural features[J].The Plant Cell,1992,4(9):1147-1156.
[23] WATSON C F,ZHENG L S,DELLAPENNA D.Reduction of tomato polygalacturonase beta subunit expression affects pectin solubilization and degradation during fruit ripening[J].The Plant Cell,1994,6(11):1623-1634.
[24] 饶俊,郑新欣,胡英考.BURP 蛋白家族研究进展[J].生物技术通报,2009,25(7):8-11.RAO Jun,ZHENG Xinxin,HU Yingkao.Research progress of BURP protein family[J].Biotechnology Bulletin,2009,25(7):8-11.
[25] SITRIT Y,BENNETT A B.Regulation of tomato fruit polygalacturonase mRNA accumulation by ethylene:A re-examination[J].Plant Physiology,1998,116(3):1145-1150.
[26] 郭凤丹,王效忠,刘学英,夏晗,王兴军.植物花青素生物代谢调控[J].生命科学,2011,23(10):938-944.GUO Danfeng,WANG Xiaozhong,LIU Xueying,XIA Han,WANG Xingjun.Regulation of anthocyanin metabolism in plants[J].Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences,2011,23(10):938-944.
[27] WALKER A R,DAVISON P A,BOLOGNESI-WINFIELD A C,JAMES C M,SRINIVASAN N,BIUNDELL T L,ESCH J J,MARKS M D,GRAY J C.The TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA1 locus,which regulates trichome differentiation and anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis,encodes a WD40 repeat protein[J].The Plant Cell,1999,11(7):1337-1349.
[28] QUATTROCCHIO F,WING J F,VAN DER WOUDE K,JOSEPH N M,KOES R.Analysis of bHLH and MYB domain proteins:species-specific regulatory differences are caused by divergent evolution of target anthocyanin genes[J].The Plant Journal:For Cell and Molecular Biology,1998,13(4):475-488.
[29] MORITA Y,SAITOH M,HOSHINO A,NITASAKA E,IIDA S.Isolation of cDNAs for R2R3-MYB,bHLH and WDR transcriptional regulators and identification of c and ca mutations conferring white flowers in the Japanese morning glory[J].Plant and Cell Physiology,2006,47(4):457-470.
[30] DE VETTEN N,QUATTROCCHIO F,MOL J,KOES R.The an11 locus controlling flower pigmentation in petunia encodes a novel WD-repeat protein conserved in yeast,plants,and animals[J].Genes&development,1997,11(11):1422-1434.
[31] 闵远琴,闫海芳,李玉花.花青素合成中的WD40 蛋白[J].植物生理学通讯,2010,46(9):863-870.MIN Yuanqin,YAN Haifang,LI Yuhua.WD40 protein in anthocyanin synthesis[J].Plant Physiology Communications,2010,46(9):863-870.
[32] GUO S G,ZHAO S J,SUN H H,WAN X,WU S,LIN T,REN Y,GAO L,DENG Y,ZHANG J,LU X Q,ZHANG H Y,SHANG J L,GONG G Y,WEN C L,HE N,TIAN S W,LI M Y,LIU J P,WANG Y P,ZHU Y C,JARRET R,LEVI A,ZHANG X P,HUANG S W,FEI Z J,LIU W G,XU Y.Resequencing of 414 cultivated and wild watermelon accessions identifies selection for fruit quality traits[J].Nature Genetics,2019,51(11):1616-1623.
[33] BRABBS T R,HE Z S,HOGG K,KAMENSKI A,LI Y,PASZKIEWICZ K H,MOORE K,O'TOOLE P,GRAHAM I,JONES L.The stochastic silencing phenotype of Arabidopsis morc6 mutants reveals a role in efficient RNA-directed DNA methylation[J].The Plant Journal:for Cell and Molecular Biology,2013,75(5):836-846.