青皮红心柚为芸香科(Rutaceae)柑橘属(Citrus)柚[Citrus grandis(L.)Osbeck]的一种,原产地为东南亚的泰国、越南和中国云南南部热区,因成熟后果表绿色,果肉红色而得名青皮红心柚。目前在云南、广西、海南热区均有引种栽培,但青皮红心柚的品种间差异较大,种植效益亦受影响,为解决生产中存在优质种质资源少、优良品种缺乏的问题,有必要开展青皮红心柚种质比较评价和筛选研究。
种质资源是植物改良的基础[1],通过广泛收集种质资源,对材料的性状表现进行观察分析,了解性状的多样性和性状间的相关性,从而了解相应性状的遗传规律,为新品种的培育提供指导[2]。目前,对柚类资源遗传多样性的研究有形态学鉴定[3]、细胞 学 鉴 定[4],以 及 广 泛 采 用 的SNP、GBS、SSR、SRAP 等[5-15]分子标记方法,这些方法需要专用的仪器设备,具有成本高且对人员技术水平要求高的缺点。对柚类种质而言,果实的表型特征对资源的商品属性和价值有重大意义,而相关性分析、聚类分析和主成分分析是种质资源表型多样性研究中应用最为普遍、有效的分析方法,目前已在大豆、芝麻、花生、水稻、高粱、甜高粱等[16-25]作物中广泛应用,在柚类中也有少量运用[26-28],但尚未见到针对青皮红心柚果实进行研究的相关报道。笔者在本研究中以47 份青皮红心柚种质资源为材料,通过对单果质量、挂果数、单株产量、纵径、横径、果形指数、果皮厚度、囊瓣数、种子数等农艺性状进行遗传多样性、相关性、聚类分析和主成分分析,以期为青皮红心柚种质资源评价、品种选育及创新利用提供材料基础和理论依据。
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料
试验在同一地块进行,位于云南省红河热带农业科学研究所内,海拔95 m,缓坡、壤砂土,热带雨林季风气候,极端最高温度40.9 ℃,极端最低温度7.9 ℃,平均温度22.0 ℃,平均降水1 587.3 mm,日照1605 h。以酸柚为砧木,水肥管理一致,树龄4 a(年),树势中庸,于果实二次生理落果结束后,用白色蜡质纸袋套袋处理,果实采摘时成熟度一致。
1.2 仪器设备
电子天平(梅特勒ML6002T/02 精度0.01 g)、电子数显卡尺(苏测0.01 mm)、数码相机尼康D7200。
1.3 方法
每份材料选取果树中部外围、果形端正的柚果3 个,共141 个果实,清洗杀菌后,观察记载单果质量、挂果数、单株产量、纵径、横径、果形指数、果皮厚度、囊瓣数、种子数等12个果实性状,3次重复。
(1)单果质量、挂果数,单株产量、果实横径、纵径、果形指数、果皮厚度、囊瓣数、种子数测定依据NY/T 2435—2013《植物新品种特异性、一致性和稳定性测试指南柑橘》[29],用电子天平测定单果质量,用数显游标卡尺测定果实横纵径和果皮厚度,计算果形指数,计算最宽处;单果质量分级参考GB/T 27633—2011《琯溪蜜柚》[30]。
(2)果肉红色在相同设备条件下拍摄果实横切面,依据红色程度从浅到深,分为粉红、橙红、红色三类,再将每个类型由浅到深分3个等级(即粉红3级,橙红3级,红色3级)共9个等级,参照图1。
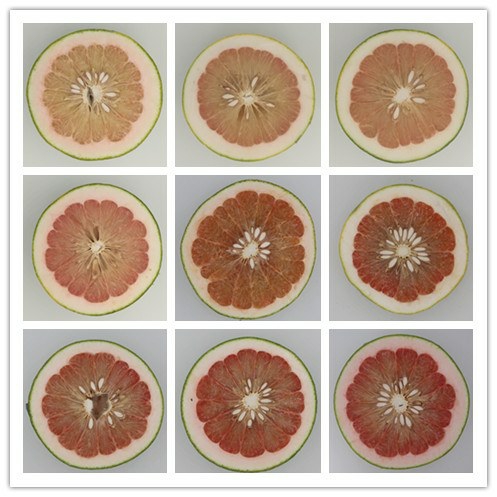

图1 果肉红色分级参照图
Fig.1 Reference picture to grading of red flesh
(3)果表绿色:在相同设备条件下拍摄果表照片,目测绿色在果表所占面积,从20%、30%、40%、50%、60%、70%、80%、90%、100%,依次分为9 个等级,参照图2。
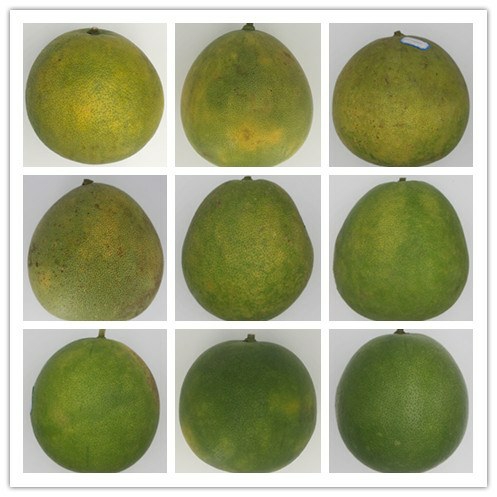

图2 果表绿色分级参照图
Fig.2 Reference picture to grading of fruit surface green
1.4 数据处理与分析方法
数据经Excel 整理并计算出平均值、标准差、变异系数,利用SPSS 19.0 进行相关性分析、主成分分析以及聚类分析,其中聚类分析方法采用组间联接法,遗传距离为平方欧式距离[31],并根据农艺性状综合表现,筛选优异种质。
2 结果与分析
2.1 果实性状遗传变异性分析
由表1 可知,47 份青皮红心柚种质的12 个性状的变异系数平均值为27.53%,变异系数在6.49%~74.32%之间。其中单株产量的变异系数最大为74.32%,其次是挂果数的变异系数为73.24%,果肉红色的变异系数为37.49%,果表绿色变异系数为33.43%,种子数的变异系数为27.52%,果皮厚度的变异系数为20.95%,单果质量的变异系数为19.97%,囊瓣数的变异系数为10.74%。因变异系数大于10%表示样本间差异较大[32],本研究中单株产量、挂果数、果肉红色、果表绿色、种子数、果皮厚度、单果质量和囊瓣数这8 个性状的变异系数均大于10%,说明这些参数有利于种质的比较和筛选。
表1 青皮红心柚种质资源的变异性分析
Table 1 Variability analysis of pomelo germplasm with green skin and red pulp
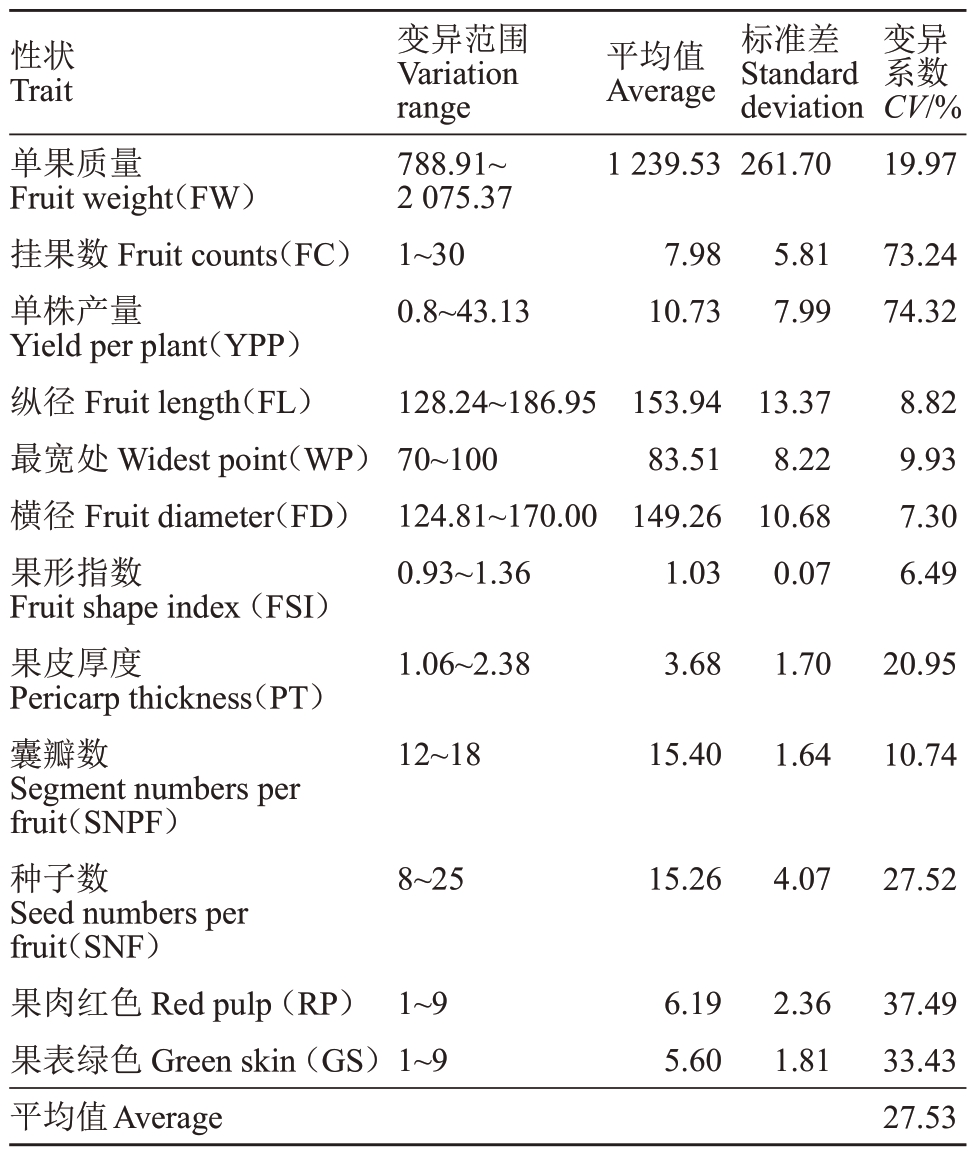
性状Trait平均值Average单果质量Fruit weight(FW)挂果数Fruit counts(FC)单株产量Yield per plant(YPP)纵径Fruit length(FL)最宽处Widest point(WP)横径Fruit diameter(FD)果形指数Fruit shape index(FSI)果皮厚度Pericarp thickness(PT)囊瓣数Segment numbers per fruit(SNPF)种子数Seed numbers per fruit(SNF)果肉红色Red pulp(RP)果表绿色Green skin(GS)平均值Average变异范围Variation range 788.91~2 075.37 1~30 0.8~43.13 1 239.53 7.98 10.73标准差Standard deviation 261.70变异系数CV/%19.97 5.81 7.99 73.24 74.32 128.24~186.95 70~100 124.81~170.00 0.93~1.36 153.94 83.51 149.26 1.03 13.37 8.22 10.68 0.07 8.82 9.93 7.30 6.49 1.06~2.38 12~18 3.68 15.40 1.70 1.64 20.95 10.74 8~25 15.26 4.07 27.52 1~9 1~9 6.19 5.60 2.36 1.81 37.49 33.43 27.53
2.2 47个青皮红心柚果实性状相关性分析
对47 个供试青皮红心柚种质的12 个农艺性状进行相关性分析,结果见表2。从表2中的数据可看出,单果质量与纵径、最宽处和横径呈极显著正相关(p<0.01);单株产量与果皮厚度呈显著负相关(p<0.05);纵径与最宽处、横径和果形指数呈极显著正相关;最宽处与横径、果皮厚度、果表绿色呈极显著正相关;果皮厚度与果表绿色呈极显著正相关;果肉红色与果表绿色呈极显著正相关。以上分析表明,在12个性状中,除囊瓣数和种子数与其他性状均无显著相关性,其余性状间是相互影响的,说明在青皮红心柚品种选育与利用上囊瓣数和种子数不具有代表性,要综合考虑单果质量、挂果数、单株产量、纵径等性状。
表2 47 个青皮红心柚果实性状相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis of characters of 47 pomelo fruits with green skin and red pulp
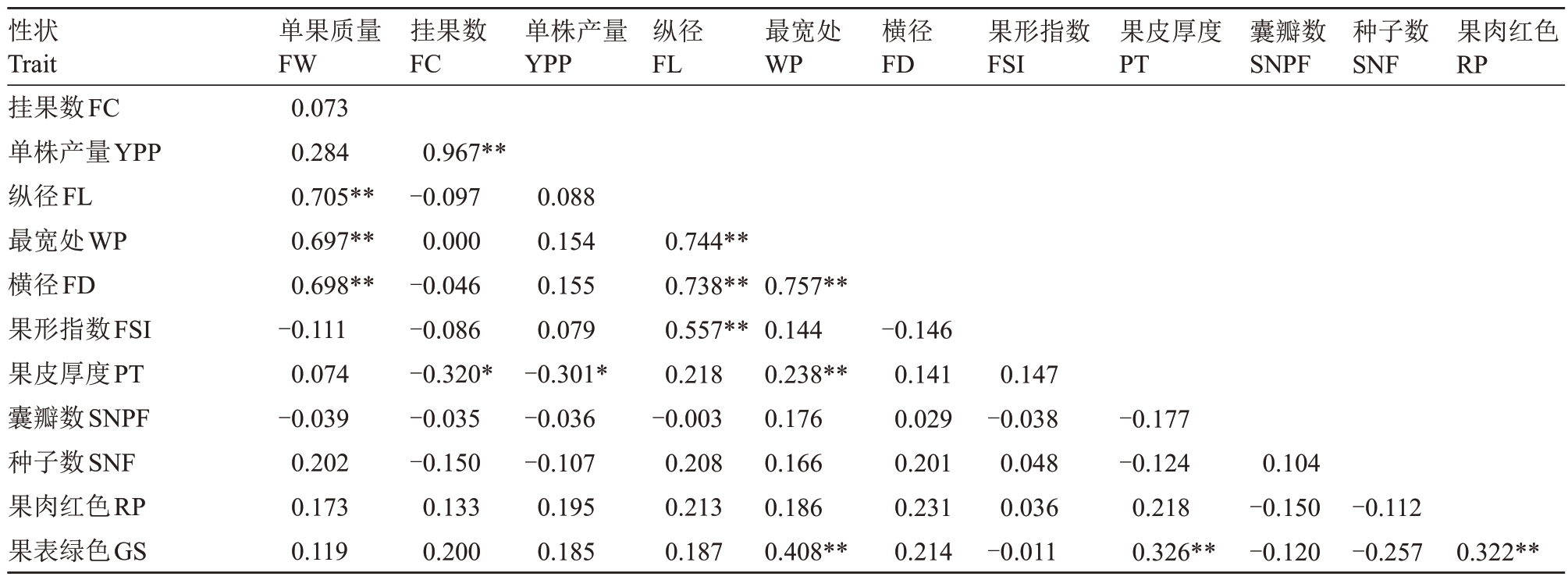
注:*表示显著相关,p<0.05;**表示极显著相关,p<0.01。
Note:*means significant correlation,p<0.05;**indicates very significant correlation,p<0.01.
性状Trait挂果数FC单株产量YPP纵径FL最宽处WP横径FD果形指数FSI果皮厚度PT囊瓣数SNPF种子数SNF果肉红色RP果表绿色GS单果质量FW 0.073 0.284 0.705**0.697**0.698**-0.111 0.074-0.039 0.202 0.173 0.119挂果数FC单株产量YPP纵径FL最宽处WP横径FD果形指数FSI果皮厚度PT囊瓣数SNPF种子数SNF果肉红色RP 0.967**-0.097 0.000-0.046-0.086-0.320*-0.035-0.150 0.133 0.200 0.088 0.154 0.155 0.079-0.301*-0.036-0.107 0.195 0.185 0.744**0.738**0.557**0.218-0.003 0.208 0.213 0.187 0.757**0.144 0.238**0.176 0.166 0.186 0.408**-0.146 0.141 0.029 0.201 0.231 0.214 0.147-0.038 0.048 0.036-0.011-0.177-0.124 0.218 0.326**0.104-0.150-0.120-0.112-0.2570.322**
2.3 主成分分析
由于柚子果实性状间存在一定相关性,故利用主成分分析方法确定各性状指标对青皮红心柚综合性状的影响。通过主成分分析,可为选配亲本和筛选评价指标提供依据。对青皮红心柚12 个果实性状进行主成分分析,以特征向量值大于1为标准,将12个性状归为4个主成分,见表3。从表中数据可看出,第1 主成分的贡献率为30.146%,所有性状的载荷符号都是正向,载荷值较高的性状有单果质量、纵径、最宽处、横径,其特征向量值分别为0.872、0.872、0.888、0.905,主要反映果实大小性状特征,因提取到的4个主成分中第1主成分的贡献率最高,在品种选育中重点考虑这4个性状;第2主成分贡献率18.845%,特征向量中符号为正向且载荷值较高的是挂果数、单株产量,主要反映产量性状特征;第3主成分贡献率为14.327%,特征向量中符号为正向且载荷值较高的是果肉红色、果表绿色、果皮厚度,主要反映果外观性状特征,在青皮红心柚品种选育中要适当把握;第4 主成分贡献率为10.415%,特征向量中符号为正向且载荷值较高的是果形指数、纵径,这主要反映果形性状特征,在品种选育中也有重要意义。
表3 青皮红心柚果实性状的主成分分析
Table 3 Principal component analysis of pomelo fruit characters with green skin and red pulp

性状Trait单果质量FW挂果数FC单株产量YPP纵径FL最宽处WP横径FD果形指数FSI果皮厚度PT囊瓣数SNPF种子数SNF果肉红色RP果表绿色GS贡献率Contribution rate/%累计贡献率Cumulative contribution rate/%成分Component 1 0.872 0.075 0.266 0.872 0.888 0.905 0.158 0.265-0.001 0.184 0.360 0.395 30.146 2 3 4 0.060 0.950 0.922-0.239-0.079-0.049-0.292-0.422-0.067-0.279 0.201 0.230 18.845-0.259-0.034-0.092-0.038-0.051-0.195 0.184 0.637-0.454-0.587 0.483 0.615 14.327 0.217 0.212 0.185 0.380 0.005-0.293 0.922-0.124 0.014 0.095-0.043-0.134 10.415 30.146 48.991 63.319 73.733
在前4 个主成分包括的12 个性状中单果质量、单株产量、果表绿色、果肉红色、果皮厚度、果形(纵径、最宽处、横径)是对青皮红心柚材料评价的重要因素,参考《琯溪蜜柚》GB/T 27633—2011 品质分级标准[30],结合青皮红心柚市场青睐中等果的特点,在青皮红心柚的资源评价时,依次以单果质量(中型果1.1~1.5 kg)>单株产量>果表绿色>果肉红色>果皮厚度>果形(纵径、最宽处、横径)作为主要依据。
2.4 青皮红心柚果实性状聚类分析
采用SPSS 19.0软件对47份青皮红心柚种质的12个果实性状进行系统聚类分析,使用组间联接的树状图进行聚类分析(图3)。结果表明,在欧式距离为7.5 时,可将其大致分为5 类。第Ⅰ类为超大果,包含1份种质,单果质量2.075 kg,果实形状为梨形,果肉浅红(2 级),果表绿色较浅(5 级)。第Ⅱ类有11份种质,这类种质为中小果,单果质量在0.94~1.2 kg,产量中等,果实形状接近圆形(0.94~1.09),果肉红色深(6~8 级),果表绿色深(6~8 级),其中编号为421 和309 的种质单株产量、果形、果肉颜色和果表绿色等综合性状表现较好,在品种选育和筛选工作中可作为优质种质资源。第Ⅲ类有2 份种质,这类种质为小果,单果质量在0.8 kg以下,果实形状接近圆形,果皮薄(1.13、1.35 cm),果肉红色浅(2、4级),果表偏黄色(1、4 级)。第Ⅳ类有21 份种质,这类种质果形为中大果,单果质量在1.2~1.4 kg 之间,单株产量在1.27~43.13 之间,果肉颜色深红(7~9级),果表浓绿(5~8),果皮厚度在1.21~2.36 cm 之间,果形近圆形(0.96~1.09),综合考虑单果质量、单株产量、果表绿色、果肉红色、果表厚度、果形等性状指标,在此类种质中编号为312、420、518、318、314、215、404和414这8个种质的综合性状表现较好,可作为高产、优质种质资源。第Ⅴ类有12 份种质,这类种质为大果,单果质量在1.5~1.7 kg,果形近圆形(0.93~1.06),肉深红(6~9 级),果表绿色较浅(1~5 级)。
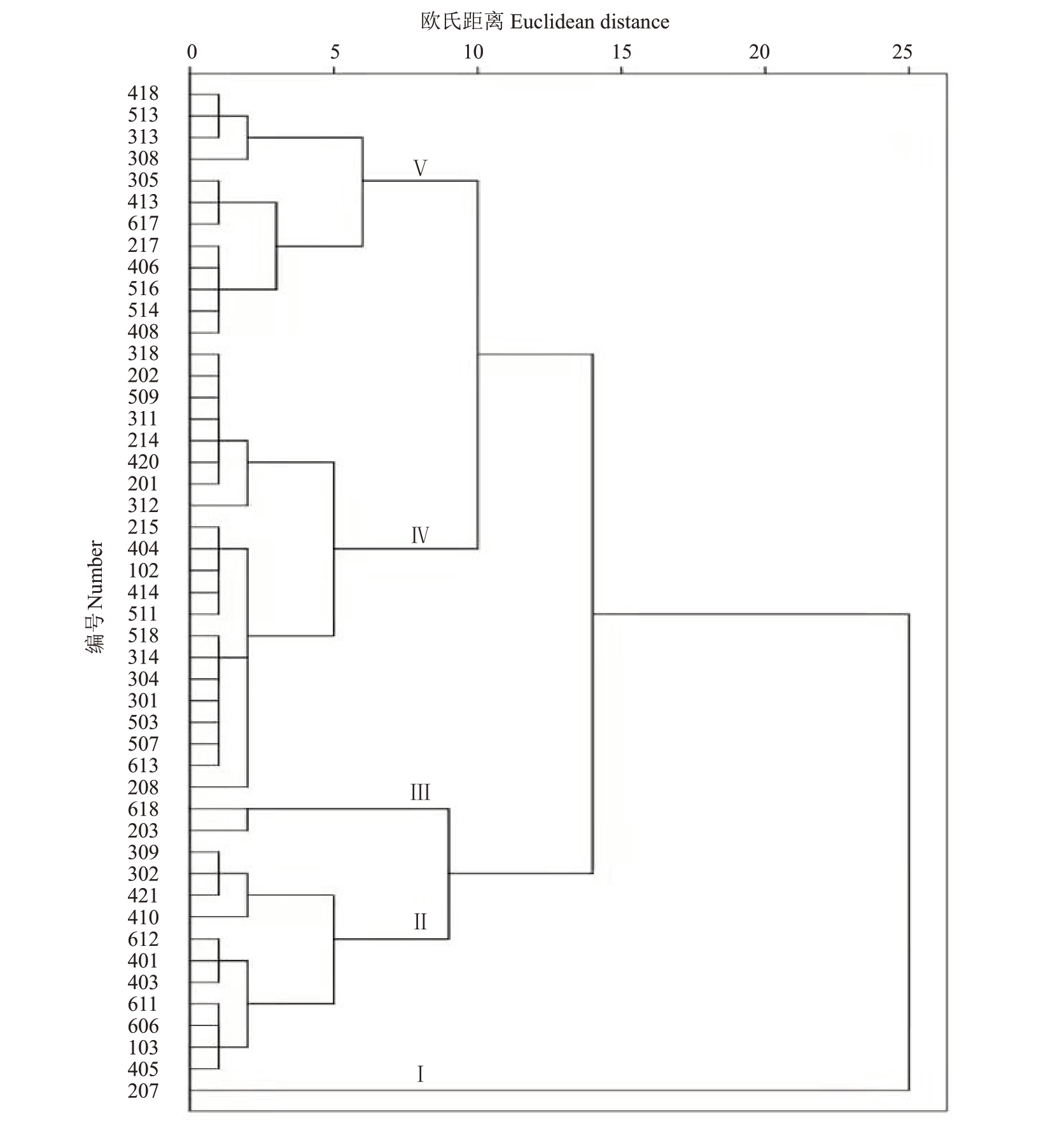
图3 青皮红心柚果实性状的聚类分析
Fig.3 Cluster analysis of fruit characters of pomelo with green skin and red pulp
2.5 优异种质筛选
结合12个农艺性状主成分分析和聚类分析,初步从47 份供试的青皮红心柚种质中筛选出单果质量、单株产量、果表绿色、果肉红色表现较好的14个优异种质(表4),其中单株产量超过40 kg 的种质1个,单株产量20~30 kg 的种质有3 个,单株产量10~20 kg的种质有5个。综合考虑单果质量、产量与果表绿色、果肉红色和果皮厚度,312 综合表现最优,其次是518、420、421。
表4 筛选的青皮红心柚特异种质
Table 4 Specific germplasm of pomelo were selected
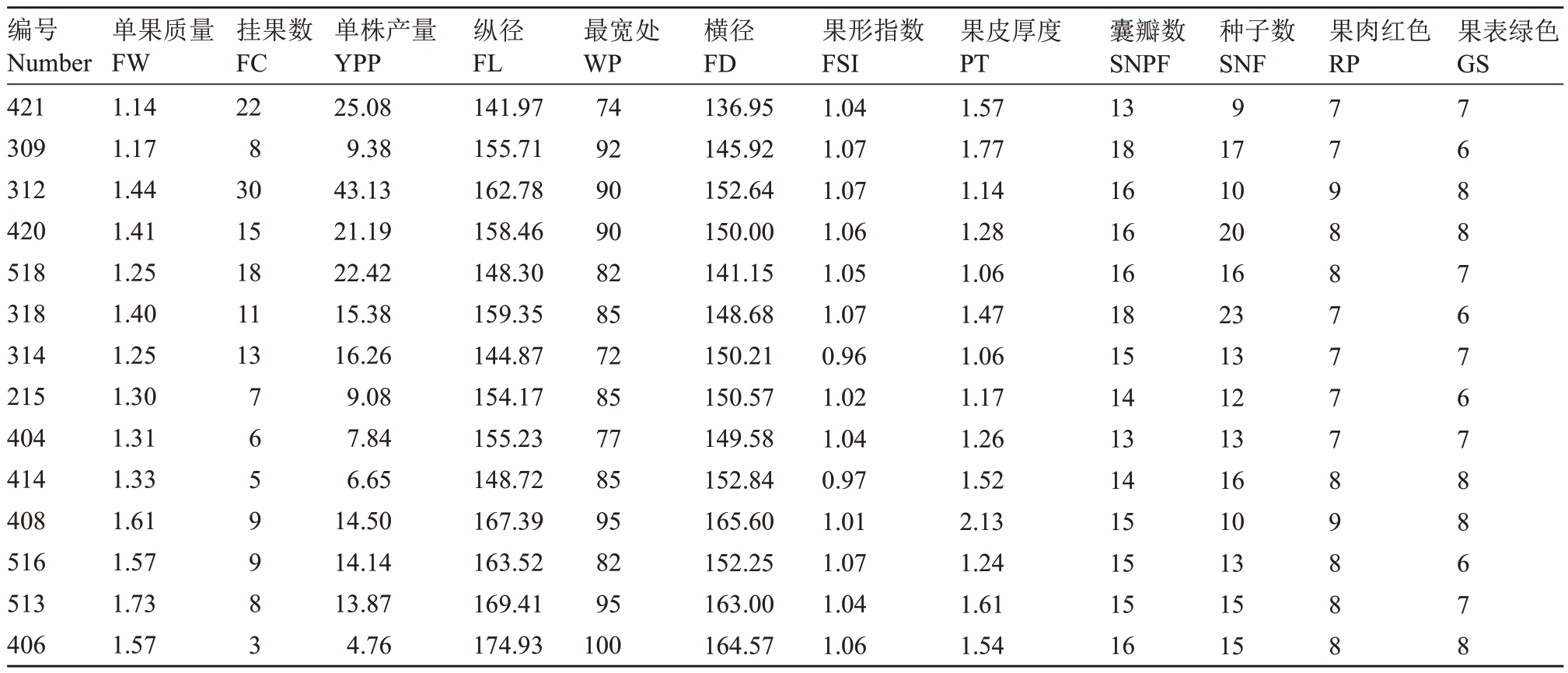
编号Number 421 309 312 420 518 318 314 215 404 414 408 516 513 406单果质量FW 1.14 1.17 1.44 1.41 1.25 1.40 1.25 1.30 1.31 1.33 1.61 1.57 1.73 1.57挂果数FC 22 8 30 15 18 11 13果肉红色RP果表绿色GS 7659983单株产量YPP 25.08 9.38 43.13 21.19 22.42 15.38 16.26 9.08 7.84 6.65 14.50 14.14 13.87 4.76纵径FL 141.97 155.71 162.78 158.46 148.30 159.35 144.87 154.17 155.23 148.72 167.39 163.52 169.41 174.93最宽处WP 74 92 90 90 82 85 72 85 77 85 95 82 95 100横径FD 136.95 145.92 152.64 150.00 141.15 148.68 150.21 150.57 149.58 152.84 165.60 152.25 163.00 164.57果形指数FSI 1.04 1.07 1.07 1.06 1.05 1.07 0.96 1.02 1.04 0.97 1.01 1.07 1.04 1.06果皮厚度PT 1.57 1.77 1.14 1.28 1.06 1.47 1.06 1.17 1.26 1.52 2.13 1.24 1.61 1.54囊瓣数SNPF 13 18 16 16 16 18 15 14 13 14 15 15 15 16种子数SNF 9 17 10 20 16 23 13 12 13 16 10 13 15 15 77988777789888 76887676788678
因果皮厚度影响柚果的贮运保鲜和商品性,对品种选育具有特殊意义,筛选出的种质中314、518果皮超薄,可作为优异种质材料;试验结果显示果肉红色由浅到深呈现粉红色、橙红色、红色3 种类型,各类红色之间亦有深浅差异,在选育“红肉”品种的同时,果肉粉红的215和橙红的420两个特异种质材料具有开发应用价值,以充分满足市场对“红肉”柚的多样性需求。
3 讨 论
对于果树生产来说,品种是发展的关键因素,科学、合理地评价果实农艺性状是全面评价果树品种的基础和前提,而表型性状是结构基因的功能表现,是长期自然与人工选择的结果,表型性状观察结果直观、经济实用,表型性状的遗传多样性分析已经在多种作物中得到应用[31-35]。笔者在本研究中选取的47 份青皮红心柚在栽培环境和管理措施上基本一致,因此,农艺性状取决于其遗传特性。通过农艺性状统计可知,供试品种各种质农艺性状差异较大,12个农艺性状变异系数为6.49%~74.32%,其中单株产量、挂果数、果皮厚度、果肉红色、果表绿色、种子数、单果质量和囊瓣数这8 个性状的变异系数均大于10%,说明这些参数有利于种质的比较和筛选。
相关性分析结果表明,单果质量与果实大小(纵径、最宽处和横径)、果形指数和纵径呈极显著相关(p<0.01),这与卢华琼等[26]和孙珍珠等[27]的研究结果一致。另外,试验还发现纵径与最宽处、横径、果形指数,最宽处与横径、果皮厚度、果表绿色呈极显著正相关(p<0.01)。
本试验通过主成分分析,青皮红心柚12项指标可转化为4 个综合指标,累计贡献率达73.733%,反映果实农艺性状的大部分信息,符合分析要求。按主成分方差贡献率从大到小依次为青皮红心柚的果实大小性状特征、产量性状特征、果实外观性状特征和果形性状特征,在这12 个性状中单果质量、单株产量、果表绿色、果肉红色、果皮厚度等性状是评价青皮红心柚种质资源优异的主要指标,可作为品种选育中的主要依据。
在欧式距离为7.5 时,聚类分析将47 个种质分为5个类群,各类群之间在各性状上有明显差异,但每一类群内均有综合性状表现优异的种质和较差的种质,因此在进行种质综合评价时为保证结果的准确性应尽量采取多种分析方法进行分析[35]。
4 结 论
果实大小、丰产性、果肉红色程度、果表绿色程度、果皮厚度和果形是影响青皮红心柚品种选育的主要因素,应作为品种评价的关键指标,可作为青皮红心柚优质品种选育的重要依据。结合主成分分析和聚类分析共选出14份优异种质,其中农艺性状综合表现较好的种质为312>518>420>421。同时,青皮红心柚红肉性状特征呈现粉红、橙红和红色3种类型,具有丰富的多样性,为红肉柚的新品种选育拓展方向。
[1] 周丽艳,郭振清,马玉玲,东方阳,林小虎.春小麦品种农艺性状的主成分分析与聚类分析[J].麦类作物学报,2011,31(6):1057-1062.ZHOU Liyan,GUO Zhenqing,MA Yuling,DONGFANG Yang,LIN Xiaohu.Principal component and cluster analysis of different spring wheat cultivars based on agronomic traits[J].Journal of Triticeae Crops,2011,31(6):1057-1062.
[2] 张炯,严斌,高营,薛晨晨,陈新,袁星星.蚕豆种质资源主要农艺性状遗传多样性分析[J].浙江农业科学,2020,61(6):1109-1114.ZHANG Jiong,YAN Bin,GAO Ying,XUE Chenchen,CHEN Xin,YUAN Xingxing.Analysis of genetic diversity of main agronomic traits in Vicia faba germplasm resources[J].Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences,2020,61(6):1109-1114.
[3] 曾勉.对柑橘分类的认识体会和整理的意见[J].中国果树,1960(2):31-37.ZENG Mian.The understanding and opinion of the citrus classification[J].China Fruits,1960(2):31-37.
[4] 粱国鲁.柑橘类的细胞分类学研究:Ⅰ.柑橘属30 个分类群的核型及进化[J].武汉植物学研究,1990,8(1):1-7.LIANG Guolu.Studies on the cytotaxonomy of Citrus:Ⅰ.Karyotype and evolution of 30 taxa of the genus Citrus[J].Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research,1990,8(1):1-7.
[5] LI Y Z,CHENG Y J,YI H L,DENG X X.Genetic diversity in mandarin landraces and wild mandarins from China based on nuclear and chloroplast simple sequence repeat markers[J].Journal of Horticutural Science&Biotechnology,2006,81(3):371-378.
[6] KACAR Y,UZUN A,POLAT I,YESILOGLU T,YILMAZ B,GULSEN O,TUZCU O,KAMILOGLU M,KURT S,SEDAY U.Molecular characterization and genetic diversity analysis of mandarin genotypes by SSR and SRAP markers[J].Journal of Food Agriculture&Environment,2013,11(11):516-521.
[7] ZHOU L,TRACIE M,TAN H W,LYNDEL W M,SUE M,BOYI W,DAPENG Z.Developing single nucleotide polymorphism markers for the identification of pineapple(Ananas comosus)germplasm[J].Horticulture Research,2015,2:15056.
[8] 王小柯,郑乾明,罗悸,李文云,柏自琴,李金强.贵州武陵山地区19 份柚资源的遗传多样性[J].贵州农业科学,2019,47(2):75-80.WANG Xiaoke,ZHENG Qianming,LUO Ji,LI Wenyun,BAI Ziqin,LI Jinqiang.Genetic diversity of 19 resources of Citrus maxima in Wulingshan region [J].Guizhou Agricultural Sciences,2019,47(2):75-80.
[9] 刘召亮,万水林,闫承璞,胡钟东,何新华,曾平章,黄其高.金沙柚及其近缘种质基于SSR 分子标记的遗传多样性分析[J].中国南方果树,2017,46(3):1-4.LIU Zhaoliang,WAN Shuilin,YAN Chengpu,HU Zhongdong,HE Xinhua,ZENG Pingzhang,HUANG Qigao.Genetic diversity analysis of Jinsha pomelo and its related germplasm based on SSR molecular markers[J].South China Fruits,2017,46(3):1-4.
[10] 林绍生,刘冬峰,郭秀珠,黄品湖,徐文荣,陈巍.浙江柚类地方资源SRAP 标记的遗传多样性分析[J].分子植物育种,2015,13(3):562-566.LIN Shaosheng,LIU Dongfeng,GUO Xiuzhu,HUANG Pinhu,XU Wenrong,CHEN Wei.Analyses of genetic diversity of pummelo (Citrus grandis Osbeck) in Zhejiang gerplasms by SRAP markers[J].Molecular Plant Breeding,2015,13(3):562-566.
[11] 李先信,陈婕平,邹学校,邓子牛.湖南柚类资源及近缘种的SRAP 遗传多样性分析[J].湖南农业科学,2013(15):1-5.LI Xianxin,CHEN Jieping,ZOU Xuexiao,DENG Ziniu.Analysis of genetic diversity for pummelo resources and its related species in Hunan Province by SRAP[J].Hunan Agricultural Sciences,2013(15):1-5.
[12] 刘通,邓崇岭,程玉芳,李秋景,陈传武,刘冰浩,伊华林.利用SSR 和SRAP 技术分析广西柑橘种质遗传多样性[J].华中农业大学学报,2016,35(2):23-29.LIU Tong,DENG Chongling,CHENG Yufang,LI Qiujing,CHEN Chuanwu,LIU Binghao,YI Hualin.Analyzing genetic diversity of citrus germplasm in Guangxi Province with SSR and SRAP markers[J].Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University,2016,35(2):23-29.
[13] 陈巍,郭秀珠,黄品湖,徐文荣,林绍生.浙南柚类地方资源遗传多样性分析和鉴定[J].植物遗传资源学报,2012,13(4):643-646.CHEN Wei,GUO Xiuzhu,HUANG Pinhu,XU Wenrong,LIN Shaosheng.Genetic diversity analysis and identification of pummelo germplasms in southern Zhejiang Province[J].Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,2012,13(4):643-646.
[14] 刘冬峰,陈巍,林绍生,徐文荣,郭秀珠,黄品湖.基于SSR 标记的浙江地方柚类种质资源遗传关系分析[J].果树学报,2017,34(2):166-174.LIU Dongfeng,CHEN Wei,LIN Shaosheng,XU Wenrong,GUO Xiuzhu,HUANG Pinhu.Analysis of genetic relationship of pummelo germplasms by SSR markers in Zhejiang Province[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2017,34(2):166-174.
[15] 刘慧宇.云南柚类种质资源的遗传多样性分析[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2017.LIU Huiyu.Genetic diversity analysis of germplasm resources in Yunnan[D].Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University,2017.
[16] 张加强,陈常理,骆霞虹,金关荣.26 份黄麻种质资源产量性状的主成分聚类分析及其评价[J].植物遗传资源学报,2016,17(3):475-482.ZHANG Jiaqiang,CHEN Changli,LUO Xiahong,JIN Guanrong.Comprehensive evaluation and cluster analysis on yield characters of 26 jute germplasm resources based on principal components[J].Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,2016,17(3):475-482.
[17] 王燕平,宗春美,孙晓环,齐玉鑫,白艳风,李文,任海祥,王晓梅,侯国强,徐德海,张帅,师红财.东北春大豆种质资源表型分析及综合评价[J].植物遗传资源学报,2017,18(5):837-845.WANG Yanping,ZONG Chunmei,SUN Xiaohuan,QI Yuxin,BAI Yanfeng,LI Wen,REN Haixiang,WANG Xiaomei,HOU Guoqiang,XU Dehai,ZHANG Shuai,SHI Hongcai.Phenotype analysis and comprehensive evaluation on northeast Spring soybean resources in Mudanjiang[J].Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,2017,18(5):837-845.
[18] 吕伟,韩俊梅,文飞,任果香,王若鹏,刘文萍.不同来源芝麻种质资源的表型多样性分析[J].植物遗传资源学报,2020,21(1):234-242.LÜ Wei,HAN Junmei,WEN Fei,REN Guoxiang,WANG Ruopeng,LIU Wenping.Phenotypic diversity analysis of sesame germplasm resources[J].Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,2020,21(1):234-242.
[19] 孙东雷,卞能飞,陈志德,邢兴华,徐泽俊,齐玉军,王幸,王晓军,王伟.花生种质资源表型性状的综合评价及指标筛选[J].植物遗传资源学报,2018,19(5):865-874.SUN Donglei,BIAN Nengfei,CHEN Zhide,XING Xinghua,XU Zejun,QI Yujun,WANG Xing,WANG Xiaojun,WANG Wei.Comprehensive evaluation and index screening of phenotypic traits in peanut germplasm resources[J].Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,2018,19(5):865-874.
[20] 汤翠凤,张恩来,董超,阿新祥,张斐斐,申时全,韩龙植.云南新收集水稻地方品种的表型多样性分析[J].植物遗传资源学报,2018,19(6):1106-1116.TANG Cuifeng,ZHANG Enlai,DONG Chao,A Xinxiang,ZHANG Feifei,SHEN Shiquan,HAN Longzhi.Analysis on phenotypic diversity of rice landraces newly collected in Yunnan Province[J].Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,2018,19(6):1106-1116.
[21] 相吉山,徐峰,索良喜,程凯,王艳超,孟海龙,张佳乐,贾斌,王冬雪,刁现民.东北地区谷子地方品种和育成品种表型比较分析[J].植物遗传资源学报,2018,19(4):642-656.XIANG Jishan,XU Feng,SUO Liangxi,CHENG Kai,WANG Yanchao,MENG Hailong,ZHANG Jiale,JIA Bin,WANG Dongxue,DIAO Xianmin.Comparison on the phenotypic traits between landraces and cultivars of foxtail millet [Setaria italica(L.) P.Beauv.] in Northeast China[J].Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,2018,19(4):642-656.
[22] 王黎明,焦少杰,严洪冬,江燕喜,苏德峰,孙广全.甜高粱主要农艺性状的遗传性及其在杂交育种中的应用[J].山西农业大学学报(自然科学版),2020,40(3):9-14.WANG Liming,JIAO Shaojie,YAN Hongdong,JIANG Yanxi,SU Defeng,SUN Guangquan.Heredity of main agronomical traits and its utilization in sweet sorghum hybrid breeding[J].Journal of Shanxi Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition),2020,40(3):9-14.
[23] 刘思辰,曹晓宁,温琪汾,王海岗,田翔,王君杰,陈凌,秦慧彬,王纶,乔治军.山西谷子地方品种农艺性状和品质性状的综合评价[J].中国农业科学,2020,53(11):2137-2148.LIU Sichen,CAO Xiaoning ,WEN Qifen,WANG Haigang,TIAN Xiang,WANG Junjie,CHEN Ling,QIN Huibin,WANG Lun,QIAO Zhijun.Comprehensive evaluation of agronomic traits and quality traits of foxtail millet landrace in Shanxi[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2020,53(11):2137-2148.
[24] 张静,百瑞,贾莹,温仕达,郎小平,徐小勇.番茄种质资源的多样性和聚类分析[J].中国瓜菜,2018,31(2):11-14.ZHANG Jing,BAI Rui,JIA Ying,WEN Shida,LANG Xiaoping,XU Xiaoyong.Diversity and cluster analysis of tomato germplasm resources[J].China Cucurbits and Vegetables,2018,31(2):11-14.
[25] 李清,郭禄芹,方晓霞,胡倩梅,杨世超,刘东明,杨路明,马长生.100 份西瓜种质果实品质相关性状的遗传多样性分析[J].中国瓜菜,2019,32(1):12-17.LI Qing,GUO Luqin,FANG Xiaoxia,HU Qianmei,YANG Shichao,LIU Dongming,YANG Luming,MA Changsheng.Genetic diversity analysis of fruit related traits of 100 watermelon germplasms[J].China Cucurbits and Vegetables,2019,32(1):12-17.
[26] 卢华琼,苏智先.部分柚类品种主要果实性状变异及相关性研究[J].中国农学通报,2006,22(12):220-222.LU Huaqiong,SU Zhixian.Variation and correlation research of main fruit characters of pumelo cultivars[J].Chinese Agriculture Science Bulletin,2006,22(12):220-222.
[27] 孙珍珠,李秋月,王小柯,赵婉彤,薛杨,冯锦英,刘小丰,刘梦雨,江东.宽皮柑橘种质资源表型多样性分析及综合评价[J].中国农业科学,2017,50(22):4362-4383.SUN Zhenzhu,LI Qiuyue,WANG Xiaoke,ZHAO Wantong,XUE Yang,FENG Jinying,LIU Xiaofeng,LIU Mengyu,JIANG Dong.Comprehensive evaluation and phenotypic diversity analysis of germplasm resources in Mandarin[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2017,50(22):4362-4383.
[28] 胡安华,窦万福,祁静静,雷天刚,陈善春,邹修平,彭爱红,许兰真,姚丽晓,何永睿,李强.柚类种质资源表型多样性分析及综合评价[J].分子植物育种,2020,18(2):650-664.HU Anhua,DOU Wanfu,QI Jingjing,LEI Tiangang,CHEN Shanchun,ZOU Xiuping,PENG Aihong,XU Lanzhen,YAO Lixiao,HE Yongrui,LI Qiang.Phenotypic diversity analysis and comprehensive evaluation of pomelo germplasms[J].Molecular Plant Breeding,2020,18(2):650-664.
[29] 中华人民共和国农业部.植物新品种特异性、一致性和稳定性测试指南柑橘:NY/T 2435—2013[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2013.Chinese Ministry of Agriculture.Guidelines for the conduct of tests for distinctness,uniformity and stability,Citrus:NY/T 2435—2013[S].Beijing:China Standards Press,2013.
[30] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局,中国国家标准化管理委员会.琯溪蜜柚:GB/T 27633—2011[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2011.General Administration of Quality Supervision,Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China.Guanxi honey pomolo:GB/T 27633—2011[S].Beijing:China Standards Press,2011.
[31] 龚雪臣.试验统计方法及SPSS 应用[M].北京:科学出版社,2014:215-216.GONG Xuechen.Experimental statistical methods and application of SPSS[M].Beijing:Science Press,2014:215-216.
[32] 孙铭,付开欣,范彦,张新全,张成林,郭志慧,汪霞,马啸.15份多花黑麦草优良引进种质的表型变异分析[J].植物遗传资源学报,2016,17(4):655-622.SUN Ming,FU Kaixin,FAN Yan,ZHANG Xinquan,ZHANG Chenglin,GUO Zhihui,WANG Xia,MA Xiao.Analysis of phenotypic variations in 15 introduced elite germplasm of Lolium multiflorum Lam.[J].Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,2016,17(4):655-622.
[33] 余斌,杨宏羽,王丽.引进马铃薯种质资源在干旱半干旱区的表型性状遗传多样性分析及综合评价[J].作物学报,2018,44(1):63-74.YU Bin,YANG Hongyu,WANG Li.Genetic diversity analysis and comprehensive assessment of phenotypic traits introduced potato germplasm resources in arid and semi-arid area[J].Acta Agronomica Sinica,2018,44(1):63-74.
[34] 董承光,王娟,周小凤,马晓梅,李生秀,余渝,李保成.基于表型性状的陆地棉种质资源遗传多样性分析[J].植物遗传资源学报,2016,17(3):438-446.DONG Chengguang,WANG Juan,ZHOU Xiaofeng,MA Xiaomei,LI Shengxiu,YU Yu,LI Baocheng.Evalution on genetic diversity of cotton germplas resources (Gossypium hirsutum L.)on morphological characters[J].Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,2016,17(3):438-446.
[35] 白弈雄,郑雪晴,姚有华,姚晓华,吴昆仑.青稞种质资源表型性状的遗传多样性分析及综合评价[J].中国农业科学,2019,52(23):4201-4214.BAI Yixiong,ZHENG Xueqing,YAO Youhua,YAO Xiaohua,WU Kunlun.genetic diversity analysis and comprehensive evaluation of phenotypic traits in hulless barley germplasm resources[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2019,52(23):4201-4214.