红皮梨因颜色鲜艳夺目、富含花青苷等物质深受消费者喜爱,选育优良红梨新品种已成为国内外梨育种重要目标之一[1]。云南省气候条件独特,红色砂梨种质资源丰富,目前发现的红色砂梨地方品种和类型数量居全国第一,是我国主要的红梨栽培地区[2]。2018年红色砂梨种植面积为2.15万hm2,约占梨总种植面积的1/3,主栽红梨品种包括美人酥、满天红等[3]。近年来云南省农业科学院还引进了包括彩云红在内的众多红色砂梨新品种[4]。美人酥、满天红和彩云红均由日本幸水和云南火把梨杂交育成,美人酥和满天红育成时间较早,分别于1997 年和1996年引入中国进行栽培试验,彩云红育成时间较晚,于2007年引进我国云南省等地。
目前,关于美人酥、满天红和彩云红的研究主要集中于品种特性[5-7]、栽培管理技术和果皮着色机理[8]等方面,对这3个红梨品种的内在品质比较研究较少,对彩云红糖酸组分、酚类物质以及香气成分等相关的研究未见报道。已有研究表明,满天红果实着色过程中花青苷、总糖、果糖和蔗糖含量在早期不断积累,在果实成熟后期下降[9];花色苷在美人酥果实成熟过程中呈上升趋势[10];刘婉君等[11]对美人酥和满天红果实香气成分进行了测定,分别检测出6种和5种挥发性成分且主要为醛类物质。笔者以美人酥、满天红和彩云红梨果实为试材,对3个红梨品种果实外观特征、营养特性和挥发性芳香物质进行分析比较,探讨3个红梨品种之间的品质差异,旨在为红梨资源品质研究和生产上红梨新品种选育、引种和推广提供理论依据。
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料
试验所用的美人酥、满天红和彩云红梨于2020年8月采自云南省安宁市云南红梨科技开发有限公司的核心示范园,果园土壤为红壤偏酸性。选取树龄7 a(年)、树势一致、长势良好的梨树进行采样,砧木为棠梨。采样时分别从树冠外围到内膛随机采摘果实,采收后立即装箱空运至中国农业科学院果树研究所(辽宁兴城)进行试验。挑选成熟度相近、大小一致、无磕碰伤及病虫害的果实进行试验,每个品种果实随机分为2组,每组1个重复,每个重复包含20个果实。第1组果实于运达当天进行相关指标测定,第2 组果实在(20±1)℃、相对湿度85%~90%环境条件下贮藏10 d后再进行相关指标测定。在收到样品当天对3个红梨品种在外观、口感、嗅感等方面进行感官评价,结果如表1所示。
表1 不同品种红梨感官评价
Table 1 Sensory evaluation in different red pear cultivar
1.2 基础品质测定
单果质量采用电子天平进行测量,取平均值,单位为g;纵横径值采用游标卡尺进行测定;果实硬度(去皮)采用南非GS-15 水果质地分析仪进行测定,测定部位为果实赤道对称两个点,所用探头直径为11.3 mm,取平均值,单位为kg·cm-2;可溶性固形物含量采用日本PR-101α 折糖仪进行测定,测定部位为果实赤道对称两侧的果肉,挤出果汁进行测定,取平均值,单位为%;可滴定酸含量测定采用瑞士Metrohm808 Titrando 自动电位滴定仪,采用酸碱滴定法,3次重复,单位为%;维生素C含量测定采用瑞士Metrohm808 Titrando 自动电位滴定仪,采用2,6-二氯靛酚滴定法,3次重复,单位为mg·kg-1。
1.3 总黄酮、总多酚和总花色苷含量测定
总黄酮含量测定参考聂继云等[12]的方法,即吸取1 mL 样液或标准溶液于10 mL 容量瓶中,加入5 mL蒸馏水和0.3 mL 5%亚硝酸钠溶液,摇匀,加入0.3 mL 10%铝盐溶液,摇匀,放置5 min,加入2 mL 1 mol·L-1氢氧化钠溶液,摇匀,蒸馏水定容,使用紫外分光光度计(TU-1800SPC)测定500 nm吸光度(A500)。样品总黄酮含量以鲜质量计,单位为mg·kg-1。
总酚含量测定采用Folin-Ciocalteus 法[13],用一水合没食子酸标准溶液绘制标准曲线,总酚含量结果以每100 g鲜果肉中含有的没食子酸质量表示,单位为mg·kg-1。
总花色苷类物质测定方法参照Pertuzatti等[14]略有改动,使用Waters 液相色谱仪。质谱条件:电喷雾(ESI)离子源,MRM(多反应监测)模式,离子源温度为150 ℃,脱溶剂气温度400 ℃,脱溶剂气流量800 L·h-1,锥孔气流速50 L·h-1,碰撞气(高纯氩气)流速0.14 mL·min-1。超高效液相色谱条件:柱温为40 ℃,流速为0.3 mL·min-1,进样量为2.0 μL,流动相A 为乙腈,流动相B 为3%的甲酸溶液,梯度洗脱,A液:5%(0 min)→10%(1 min)→25%(16 min)→40%(18 min)→100%(19 min),20 min回到初始状态,平衡10 min。检测器波长520 nm,单位为mg·kg-1。
1.4 总糖、总酸含量测定
总糖含量采用国标GB 5009.7—2016 食品安全国家标准《食品中还原糖测定》的直接滴定法测定;总酸采用国标GB/T 12456—2008《食品中总酸的测定》的酸碱滴定法测定。
1.5 糖、酸组分含量测定
糖组分测定参考郑丽静等[15]的方法。酸组分测定参考姚改芳等[16]的方法。
1.6 香气成分测定
香气成分测定参考赵欣等[17]的方法略有改动。采用顶空-固相微萃取(HS-SPME)和气相色谱-质谱联用技术(GC-MS-QP 2010 日本岛津),每处理随机取10 个果实,3 次重复,将果肉研磨至匀浆。取5 g匀浆至20 mL顶空萃取瓶,加2 g NaCl,拧紧带硅胶隔垫瓶盖进行上机测定。检测参数:老化温度250 ℃,老化时间(萃取前)1 min,孵化温度100 ℃,孵化时间10 min,萃取时间1 min,进样口温度200 ℃,解吸附时间1 min,老化时间(萃取后)5 min,采集方式为FullScan50-500 amu。未知化合物色谱图经计算机检索同时与NIST14标准谱库相匹配(报道匹配度大于80%的化合物),并结合人工图谱解析定性。按峰面积归一化法计算各挥发性物质的相对含量。
1.7 数据统计
采用Excel 2010 进行数据处理,采用SPSS 21.0 Duncan’s新复极差法进行差异显著性分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 不同红梨品种主要品质分析
由表2 可知,3 个红梨品种中,满天红单果质量最高,美人酥单果质量最低,彩云红单果质量介于二者之间。美人酥果形指数大于1,呈卵圆形;满天红和彩云红果形指数小于1,呈椭圆形。满天红果实硬度和维生素C 含量显著高于彩云红和美人酥;贮藏10 d时,果实硬度下降但顺序不变,满天红维生素C 含量下降,彩云红和美人酥维生素C 含量上升。彩云红果实可溶性固形物含量显著高于满天红和美人酥(p <0.05),可滴定酸含量显著低于满天红和美人酥,彩云红固酸比分别是美人酥和满天红的3.01 倍与2.38 倍(图1);贮藏10 d后,3 个红梨品种可溶性固形物含量上升,可滴定酸含量下降,固酸比上升,甜度增加。
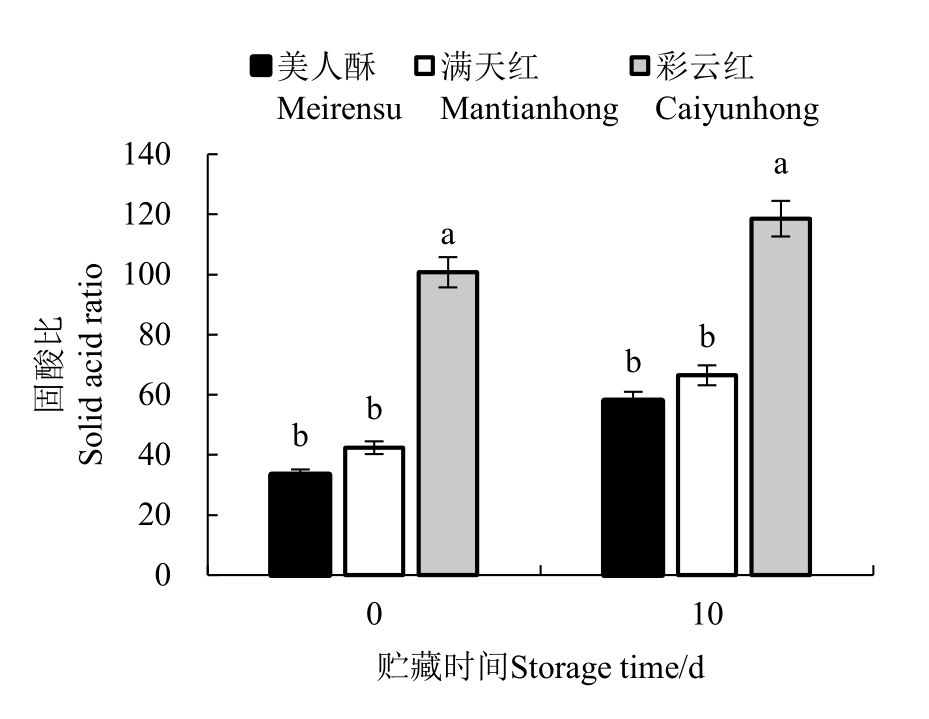
图1 不同品种红梨固酸比
Fig.1 Solid acid ratio in different red pear varieties
表2 不同红梨品种主要品质
Table 2 Main quality in different red pear cultivar
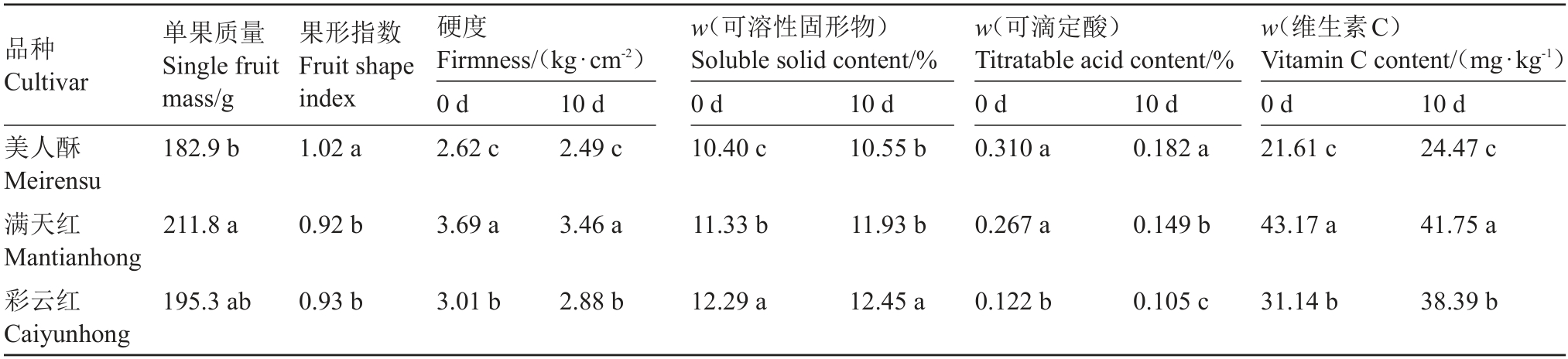
注:同列不同的小写字母代表差异达到显著(p <0.05)水平。0 d 和10 d 代表贮藏时间。下同。
Note:Different large and small letters in the same column represent significant differences level(p <0.05).0 d and 10 d represent storage time.The same below.
2.2 不同红梨品种果实可溶性糖含量和糖组分分析
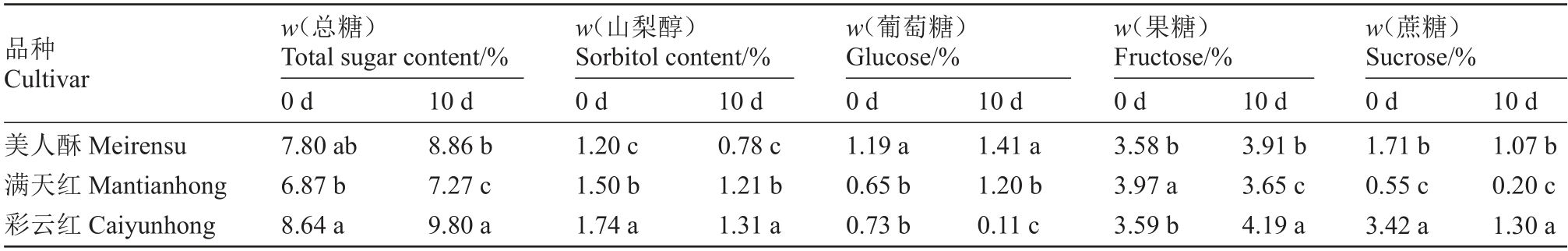
通过对3 个红梨品种的总糖以及山梨醇、葡萄糖、果糖和蔗糖等糖组分含量进行分析,由表3 可知,彩云红梨在贮藏前后总糖、山梨醇、蔗糖含量均显著高于美人酥和满天红,葡萄糖和果糖含量介于二者之间。美人酥果实中葡萄糖含量显著高于满天红和美人酥,山梨醇含量显著低于满天红和美人酥;满天红果实中果糖含量较高,蔗糖含量显著低于美人酥和彩云红。贮藏10 d时,3 个红梨品种总糖和蔗糖含量均升高,山梨醇含量降低。
表3 不同红梨品种可溶性糖和糖组分含量
Table 3 Content of soluble sugar and sugar components in different red pear cultivar
2.3 不同红梨品种果实总酸和组分含量分析
由表4 可知,满天红果实总酸和奎尼酸含量显著高于美人酥和彩云红;美人酥中柠檬酸含量高于其他两个品种,彩云红中奎尼酸、苹果酸和莽草酸含量高于其他两个品种。贮藏10 d时,3 个红梨品种总酸含量均下降。
表4 不同红梨品种总酸和组分含量
Table 4 Contents of total acids and components in different red pear cultivar
2.4 不同红梨品种果实总黄酮、总多酚和总花色苷含量分析
由图2可知,刚采收时彩云红果实的总黄酮、总多酚和总花色苷含量高于美人酥和满天红;贮藏10 d后,彩云红和满天红的总黄酮、总多酚和总花色苷含量下降;美人酥的总黄酮、总多酚和总花色苷含量上升,其中总黄酮和总多酚含量显著高于彩云红和满天红,总花色苷含量显著低于满天红。
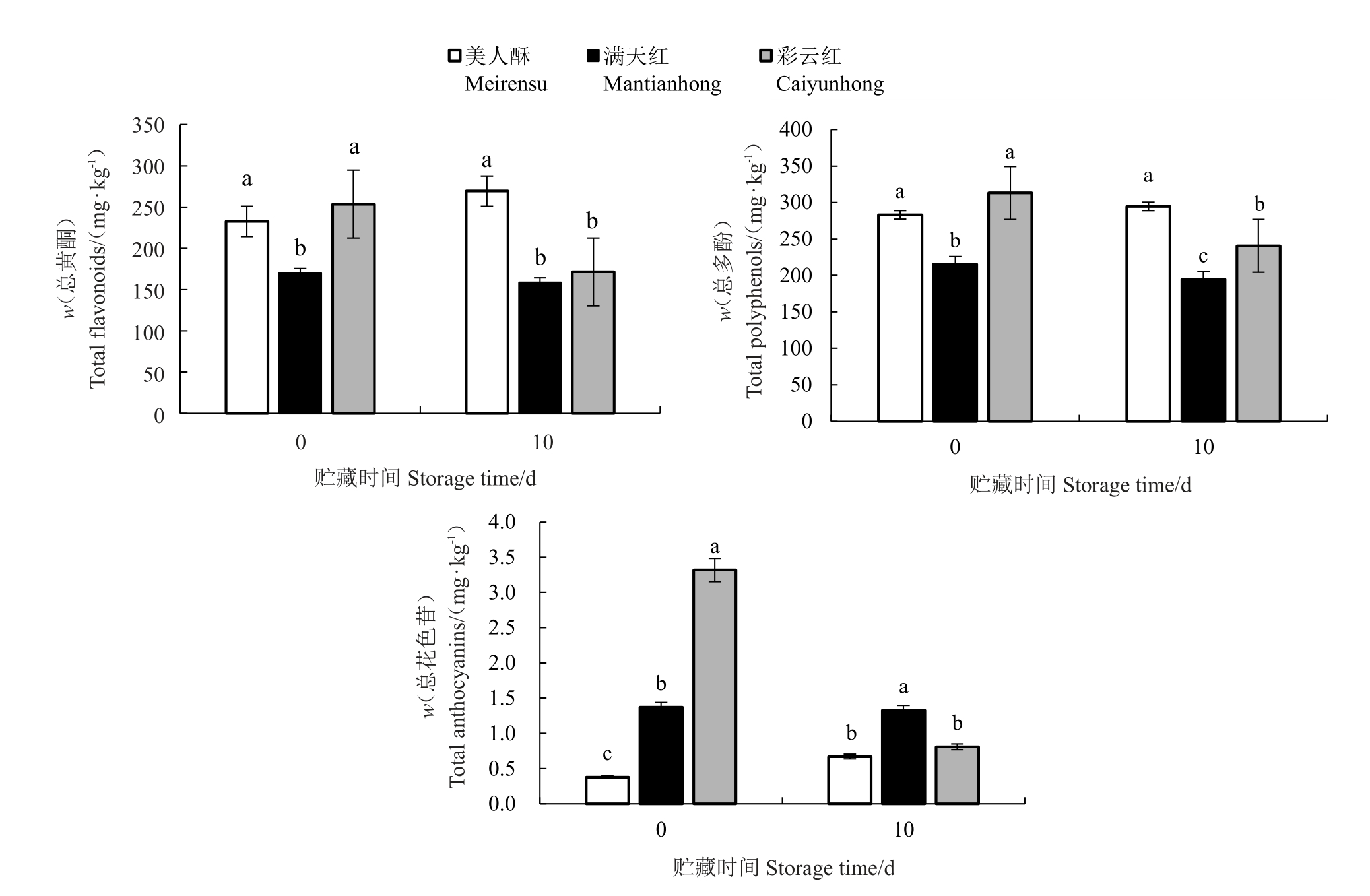
图2 不同红梨品种总黄酮、总多酚和总花色苷含量
Fig.2 Contents of total flavonoids,total polyphenols and total anthocyanins in different red pear cultivar
2.5 香气成分分析
通过对3个品种香气成分种类与相对含量的比较分析,发现不同品种中各香气成分数据差异较大。由表5可知,经GC-MS分析从美人酥中共检测出35种挥发性物质,其中醛类物质7种(相对含量为14.72%),醇类物质13 种(相对含量为36.16%),酯类物质3 种(相对含量为5.67%),酮类物质3 种(相对含量为18.13%),酸类物质6 种(相对含量为20.41%),萜烯类化合物1 种(相对含量为1.48%),其他类化合物2种(相对含量为3.43%)。
表5 不同品种红梨主要挥发性物质成分及相对含量
Table 5 Main volatile components and relative contents in different red pear cultivar %

续表Continued Table
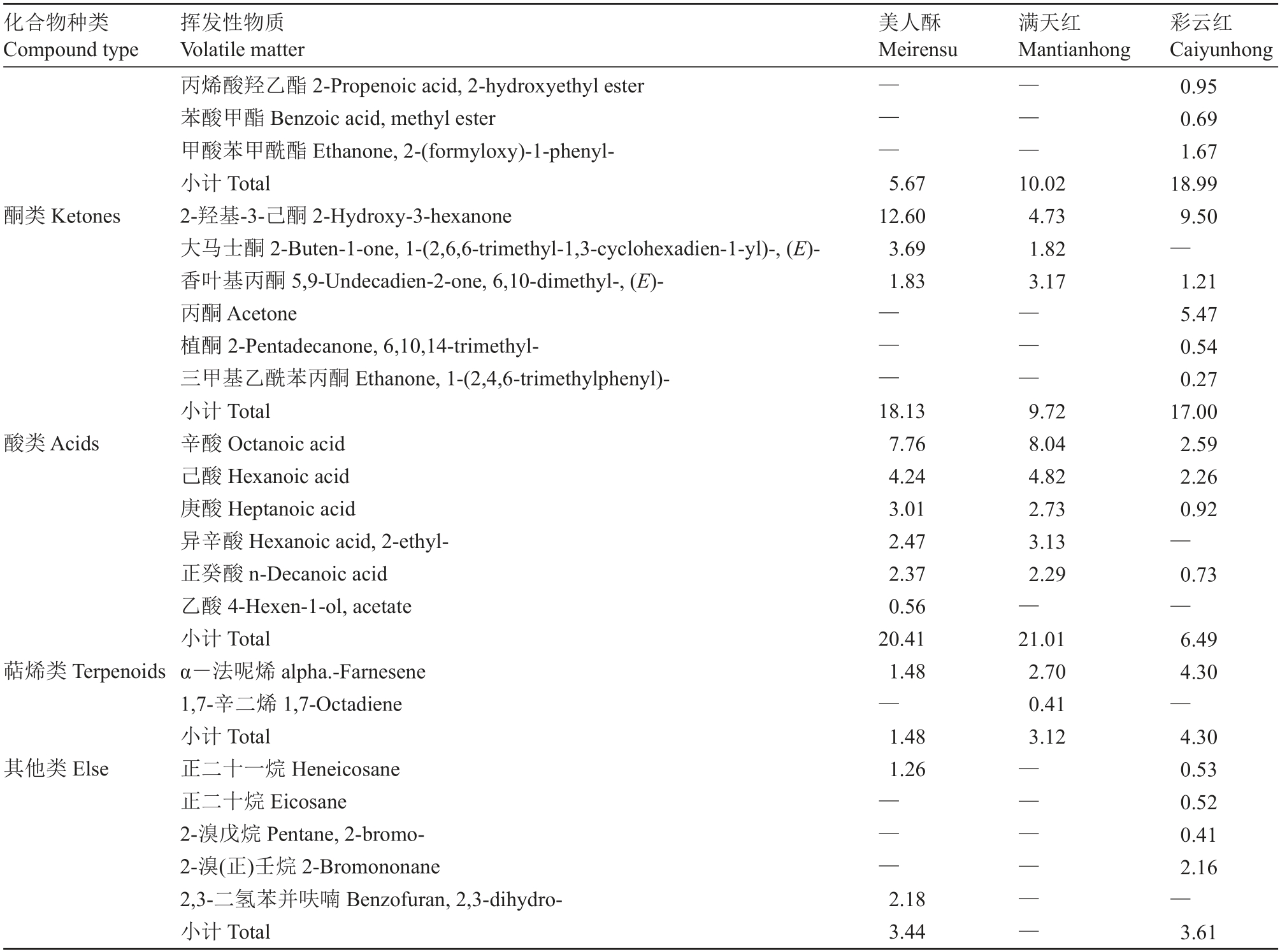
注:—.表示无数据。
Note:—.Indicates no data.
从满天红中共检测出34种挥发性物质,其中醛类物质8 种(相对含量为18.10%),醇类物质13 种(相对含量为38.04%),酯类物质3 种(相对含量为10.02%),酮类物质3 种(相对含量为9.72%),酸类物质5 种(相对含量为21.01%),萜烯类化合物2 种(相对含量为3.12%)。
从彩云红中共检测出47种挥发性物质,其中醛类物质10 种(相对含量为13.28%),醇类物质14 种(相对含量为36.34%),酯类物质9 种(相对含量为18.99%),酮类物质5 种(相对含量为17.00%),酸类物质4 种(相对含量为6.49%),萜烯类化合物1 种(相对含量为4.30%),其他类化合物4 种(相对含量为3.61%)。
3个梨品种果实共有的香气成分为23种。美人酥和满天红果实中醇类和醛类相对含量较高,彩云红果实中醇类和酯类相对含量较高。
3 讨论
果实品质是直接影响果农经济利益和果实市场竞争力的重要因素,主要包括外观品质和内在品质[18]。在外观品质方面,满天红和美人酥果实红色着色面积可达50%,而彩云红果实红色着色可达到80%,说明彩云红果实在色泽上比其他两个品种更具优势。彩云红梨果实单果质量和果实硬度介于满天红和美人酥之间,固酸比显著高于满天红和美人酥,与孙平平等[19]的研究结果一致。梨果实中可溶性糖主要由果糖、葡萄糖、蔗糖和山梨醇组成,有机酸主要由苹果酸、柠檬酸、莽草酸和奎尼酸组成[20]。研究结果表明,3个红梨品种中果糖为主要糖组分,苹果酸与柠檬酸为主要酸组分,与前人对砂梨糖酸组分测定结果一致[21],但不同品种中各项糖酸组分含量存在差异,因此形成了不同果实的风味差别。与满天红和美人酥相比,彩云红果实中果糖含量相对较低,但蔗糖、山梨醇和总糖含量较高,说明蔗糖和山梨醇对总糖含量影响较大。彩云红中苹果酸含量高于满天红和美人酥,而柠檬酸和总酸含量相对较低,这可能是由于苹果酸酸味强度虽略大于柠檬酸,但其酸味更柔和、刺激性更缓慢、保留时间更长[22]。综合来看,彩云红梨甜度较高,酸度较低,其果实甜度占主导。
酚类物质作为植物体内的次生代谢产物,不仅赋予果实特殊色泽和风味,而且具有较强的抗氧化能力[23-24]。结果表明,彩云红果实的总黄酮、总多酚和总花色苷含量高于美人酥和满天红,说明彩云红果实具有较强的抗氧化能力,营养价值更高。但在贮藏10 d后,彩云红梨果实酚类物质含量下降且介于满天红和美人酥之间,花色苷含量较不稳定,该现象在苹果[25]和红皮洋梨[26]等果实中也有相关报道。这可能是由于果实贮藏后花青苷合成酶活性下降、降解酶活性升高及转运受阻等因素造成花青苷降解,而果皮细胞膜脂化程度升高造成酚类物质被多酚氧化酶等氧化也会加速花青苷的降解[27]。已有研究表明,使用4%食用盐酸处理可将荔枝果皮花色素苷含量维持在较高水平[28]。1-甲基环丙烯处理[29]、低温贮藏[30]等技术能够延缓果实衰老,抑制酚类物质降解及PPO活性,也可作为解决果实褪色问题的技术途径。
香气是果实品质的重要组成部分,主要决定梨果实的嗅感,主要包括醛类、酯类、醇类、酸类和萜类等[31-32]。笔者对彩云红、美人酥和满天红3个红色砂梨品种香气成分进行分析,共检出香气物质61种,其中醇类最多为20种,酯类和醛类次之均为11种,酮类和酸类物质均为6 种。醇类物质在3 个品种的梨中相对含量最高,与田长平等[33]对砂梨香气的研究结果一致。(E)呋喃氧化芳樟醇是主要的醇类化合物之一,具有木香味[34];正己醇属于C6醇类,具有青草味;正辛醇具有脂肪、蘑菇香气;芳樟醇和香叶醇也是重要的香气成分[35]。醛类物质相对含量较高(13.28%~18.10%)。2-己烯醛是主要检出的醛类物质,属于C6 醛类,是青香型化合物的代表,另一种C6醛为正己醛,仅在彩云红中检测出。酮类物质共检出6种,2-羟基-3-己酮和香叶基丙酮为3种梨果中共有,其中香叶基丙酮广泛存在于烟草和茶叶中,具有清香型香气特征[36-37]。另外,3种梨果中均检测到的萜类物质为α-法呢烯,具有花香气味[38]。
彩云红、美人酥和满天红3 个红色砂梨品种之间挥发性芳香物质的组成差别较大。其中,彩云红果实中共检测到47 种香气物质,明显高于美人酥(35 种)和满天红(34 种)。果品中香气物质的种类和含量受其品种(基因)影响较大,前人研究表明梨品种之间酯类物质种类和含量存在较大差异[39]。彩云红梨中酯类物质检出数量明显较高,为9种,相对含量最高的为烟酸乙酯(6.35%),表明彩云红梨具有较强的酯香[40]。有文献[41-42]报道,C10以下的酯类具有水果风味,尤其是乙酯类物质水果风味浓郁,阈值较低,在香气构成中发挥主要作用。彩云红梨检测到的9 类酯类物质中,有6 种酯类物质的碳数在10 以下。另外,彩云红样品中检出3 种乙酯类香气物质,相对含量为0.95%~6.35%,表明彩云红梨果香味更浓郁,与感官鉴评(嗅感)结果一致。
4 结论
彩云红梨固酸比显著高于美人酥和满天红,甜度最高。不同品种红梨果实中果糖为主要糖组分,苹果酸与柠檬酸为主要酸组分。彩云红梨的总黄酮、总多酚和总花色苷含量高于美人酥和满天红,营养价值较高。彩云红果实中检测到的香气物质种类最多,主要为醇类、醛类和酯类,香气更浓郁。因此,基于感官品鉴、营养物质以及风味物质等综合评价结果,彩云红梨品质更佳,可作为红皮砂梨品种选育的参考品种,也可作为红皮砂梨品种中的优良品种进行规模化发展。
[1] 薛华柏,王芳芳,杨健,王龙,王苏珂,苏艳丽,乔玉山,李秀根.红皮梨研究进展[J].果树学报,2016,33(S1):24-33.XUE Huabai,WANG Fangfang,YANG Jian,WANG Long,WANG Suke,SU Yanli,QIAO Yushan,LI Xiugen.A review of research advances in red skin pear[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2016,33(S1):24-33.
[2] 冉昆,张雪飞,魏树伟,王宏伟,董冉,张勇,王少敏.我国红皮梨种质资源及育种现状[J].中国南方果树,2018,47(S1):27-31.RAN Kun,ZHANG Xuefei,WEI Shuwei,WANG Hongwei,DONG Ran,ZHANG Yong,WANG Shaomin.Germplasm resources and breeding status of Yed-skinned pear in China[J].South China Fruits,2018,47(S1):27-31.
[3] 苏俊,黄兴龙,陈霞,何英云,李自生,舒群.3 个红色砂梨新品种的果实氨基酸组分与含量分析[J].果树学报,2018,35(S1):114-117.SU Jun,HUANG Xinglong,CHEN Xia,HE Yingyun,LI Zisheng,SHU Qun.Analysis of amino acid composition and content in three new varieties of red sand pear[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2018,35(S1):114-117.
[4] 陈霞,苏俊,何英云,李自生,舒群.红色沙梨新品种‘彩云红’关键栽培管理技术[J].中国南方果树,2018,47(1):155-157.CHEN Xia,SU Jun,HE Yingyun,LI Zisheng,SHU Qun.Key cultivation and management techniques of a new red pear variety‘Caiyunhong’[J].South China Fruits,2018,47(1):155-157.
[5] 魏闻东,田鹏,苏艳丽.红梨新品种‘满天红’[J].园艺学报,2009,36(2):303.WEI Wendong,TIAN Peng,SU Yanli.A new red pear cultivar‘Mantianhong’[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2009,36(2):303.
[6] 魏闻东,李桂荣,田鹏,张传来,苏艳丽.红梨新品种‘美人酥’[J].园艺学报.2010,37(7):1187-1188.WEI Wendong,LI Guirong,TIAN Peng,ZHANG Chuanlai,SU Yanli.A new red pear cultivar‘Meirensu’[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2010,37(7):1187-1188.
[7] 苏俊,陈霞,李林,范建成,李自生,舒群.红色砂梨新品种‘彩云红’[J].园艺学报,2016,43(S20):2687-2688.SU Jun,CHEN Xia,LI Lin,FAN Jiancheng,LI Zisheng,SHU Qun.A new red sand pear cultivar‘Caiyunhong’[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2016,43(S20):2687-2688.
[8] 黄春辉,俞波,苏军,舒群,滕元文.‘美人酥’和‘云红梨1 号’红皮砂梨果实的着色生理[J].中国农业科学,2010,43(7):1433-1440.HUANG Chunhui,YU Bo,SU Jun,SHU Qun,TENG Yuanwen.A study on coloration physiology of fruit in two red chinese sand pear cultivars‘Meirensu’and‘Yunhongli No.1’[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2010,43(7):1433-1440.
[9] 张健.满天红梨果实品质发育及硼、钾对其影响的研究[D].保定:河北农业大学,2013.ZHANG Jian.Study on quality formation and effect of Potassium and Boron on Mantianhong pear[D].Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University,2013.
[10] 高晓宇,邓浪,付开强,王大玮,秦秀兰,李德龙,罗万德,周军.‘巍山红雪梨’和‘美人酥’叶绿素、花色苷和类黄酮的动态变化分析[J].果树学报,2016,33(S1):83-89.GAO Xiaoyu,DENG Lang,FU Kaiqiang,WANG Dawei,QIN Xiulan,LI Delong,LUO Wande,ZHOU Jun.Dynamic changes in chlorophylls,anthocyanins and flavonoids in‘Weishanhongxueli’and‘Meirensu’(Pyrus pyrifolia) fruits[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2016,33(S1):83-89.
[11] 刘婉君,张莹,张玉星,杜国强.18 个品种授粉‘鸭梨’果实品质和香气成分分析与评价[J].食品科学,2022,43(2):294-302.LIU Wanjun,ZHANG Ying,ZHANG Yuxing,DU Guoqiang.Analysis and evaluation of fruit quality and aroma components of‘Yali’pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.) pollinated by eighteen pollinizers[J].Food Science,2022,43(2):294-302.
[12] 聂继云,吕德国,李静,李萍,刘凤之.分光光度法测定苹果果实总黄酮含量的条件优化[J].果树学报,2010,27(3):466-470.NIE Jiyun,LÜ Deguo,LI Jing,LI Ping,LIU Fengzhi.Condition optimization for spectrophotometric method of total flavonoids in apple fruit[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2010,27(3):466-470.
[13] 李静,聂继云,李海飞,徐国峰,王孝娣,毋永龙,王贞旭.Folin-酚法测定水果及其制品中总多酚含量的条件[J].果树学报,2008,25(1):126-131.LI Jing,NIE Jiyun,LI Haifei,XU Guofeng,WANG Xiaodi,WU Yonglong,WANG Zhenxu.On determination conditions for total polyphenols in fruits and its derived products by Folin-phenol methods[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2008,25(1):126-131.
[14] PERTUZATTI P B,BARCIA M T,PORTUGAL L,REBELLO G,HERMOSÍN-GUTIÉRREZ I.Antimicrobial activity and differentiation of anthocyanin profiles of rabbiteye and highbush blueberries using HPLC–DAD–ESI-MS n and multivariate analysis[J].Journal of Functional Foods,2016,26:506-516.
[15] 郑丽静,聂继云,闫震,徐国锋,王昆,高源,叶孟亮.苹果可溶性糖组分及其含量特性的研究[J].园艺学报,2015,42(5):950-960.ZHENG Lijing,NIE Jiyun,YAN Zhen,XU Guofeng,WANG Kun,GAO Yuan,YE Mengliang.Studies on the characteristics of the composition and content of soluble sugars in apple fruit[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2015,42(5):950-960.
[16] 姚改芳,张绍铃,吴俊,曹玉芬,刘军,韩凯,杨志军.10 个不同系统梨品种的可溶性糖与有机酸组分含量分析[J].南京农业大学学报,2011,34(5):25-31.YAO Gaifang,ZHANG Shaoling,WU Jun,CAO Yufen,LIU Jun,HAN Kai,YANG Zhijun.Analysis of components and contents of soluble sugars and organic acids in ten cultivars of pear by high performance liquid chromatography[J].Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University,2011,34(5):25-31.
[17] 赵欣,梁克红,朱宏,刘莉,王靖.不同品种梨营养品质及风味物质比较研究[J].食品安全质量检测学报,2020,11(21):7797-7805.ZHAO Xin,LIANG Kehong,ZHU Hong,LIU Li,WANG Jing.Comparative research on nutritional quality and flavor compounds of different pear varieties[J].Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2020,11(21):7797-7805.
[18] 刘美迎,李小龙,梁茁,张振文.基于模糊数学和聚类分析的鲜食葡萄品种综合品质评价[J].食品科学,2015,36(13):57-64.LIU Meiying,LI Xiaolong,LIANG Zhuo,ZHANG Zhenwen.Comprehensive quality assessment of table grapes varieties using fuzzy mathematics and cluster analysis[J].Food Science,2015,36(13):57-64.
[19] 孙平平,陈霞,贾晓辉,舒群,王文辉.美人酥、满天红与彩云红梨的贮藏品质比较[J].中国南方果树,2017,46(4):107-111.SUN Pingping,CHEN Xia,JIA Xiaohui,SHU Qun,WANG Wenhui.Comparison of storage quality of Meirensu,Mantianhong and Caiyunhong pears[J].South China Fruits,2017,46(4):107-111.
[20] 姚改芳.不同栽培种梨果实糖酸含量特征及形成规律研究[D].南京:南京农业大学,2011.YAO Gaifang.Conformation and characteristics of sugar and acid in pear fruits of cultivated species[D].Nanjing:Nanjing Agricultural University,2011.
[21] 蒋爽,岳晓燕,滕元文,王晓庆,施春晖,徐芳杰,张学英,白松龄,骆军.不同砂梨果实中糖酸含量及代谢相关基因表达分析[J].果树学报,2016,33(S1):65-70.JIANG Shuang,YUE Xiaoyan,TENG Yuanwen,WANG Xiaoqing,SHI Chunhui,XU Fangjie,ZHANG Xueying,BAI Songling,LUO Jun.The contents of sugars and acids,and the expression analysis of metabolism associated genes in fruit of Pyrus pyrifolia[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2016,33(S1):65-70.
[22] 段敏杰,伊洪伟,杨丽,武峥,王进.不同砂梨品种果实糖酸组分及含量分析[J].南方农业学报,2020,51(9):2236-2244.DUAN Minjie,YI Hongwei,YANG Li,WU Zheng,WANG Jin.Sugar and acid compositions and their contents in different Pyrus pyrifolia varieties[J].Journal of Southern Agriculture,2020,51(9):2236-2244.
[23] BLOKHINA O.Antioxidants,oxidative damage and oxygen deprivation stress: A review[J].Annals of Botany,2003,91(2):179-194.
[24] 刘旭,杨丽,张芳芳,张振文.酿酒葡萄成熟期间果实质地特性和花色苷含量变化[J].食品科学,2015,36(2):105-109.LIU Xu,YANG Li,ZHANG Fangfang,ZHANG Zhenwen.Changes in textural properties and anthocyanins content of wine grape during maturation[J].Food Science,2015,36(2):105-109.
[25] 陈磊,郭玉蓉,白鸽,袁莉.‘红富士’苹果气调贮藏期间果皮色泽变化及花青苷合成相关基因相对表达量的差异比较[J].食品科学,2015,36(24):326-331.CHEN Lei,GUO Yurong,BAI Ge,YUAN Li.Changes in pericarp color and the expression of anthocyanin biosynthesis-related genes of two kinds of colored‘Red Fuji’apples during controlled atmosphere storage[J].Food Science,2015,36(24):326-331.
[26] 杜红.红皮西洋梨果皮红色消退候选基因的筛选分析[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2017.DU Hong.Screening analyses of coloration-fading candidate genes in red-skinned european pear[D].Yangling:Northeast Agricultural and Forestry University,2017.
[27] 陈磊,郭玉蓉,白鸽,袁莉.低温和气调对不同色泽‘红富士’苹果贮藏期间果皮褪色现象的影响[J].食品科学,2015,36(22):210-215.CHEN Lei,GUO Yurong,BAI Ge,YUAN Li.Effects of low temperature storage and controlled atmosphere(CA) storage on skin burning in two different kinds of colored‘Red Fuji’apples[J].Food Science,2015,36(22):210-215.
[28] 胡位荣,张昭其,季作梁,刘顺枝.酸处理对采后荔枝果皮色泽与生理活性的影响[J].食品科学,2004(7):176-180.HU Weirong,ZHANG Zhaoqi,JI Zuoliang,LIU Shunzhi.Study on acid treatment effects on pericarp color and physiological characteristics of litchi fruit[J].Food Science,2004(7):176-180.
[29] CHENG Y,LIU L,FENG Y,DONG Y,GUAN J.Effects of 1-MCP on fruit quality and core browning in‘Yali’pear during cold storage[J].Scientia Horticulturae,2019,243:350-356.
[30] LI D,CHENG Y,DONG Y,SHANG Z,GUAN J.Effects of low temperature conditioning on fruit quality and peel browning spot in‘Huangguan’pears during cold storage[J].Postharvest Biology and Technology,2017,131:68-73.
[31] 王建华,王汉忠.果蔬芳香物质的研究方法[J].山东农业大学学报,1996,27(2):219-226.WANG Jianhua,WANG Hanzhong.Methods for studies on aroma compounds in fruits and vegetables[J].Journal of Shandong Agricultural University,1996,27(2):219-226.
[32] EL HADI M,ZHANG F,WU F,ZHOU C,TAO J.Advances in fruit aroma volatile research[J].Molecules,2013,18(7):8200-8229.
[33] 田长平,魏景利,刘晓静,王娜,王海波,孙家正,李登涛,陈学森.梨不同品种果实香气成分的GC-MS 分析[J].果树学报,2009,26(3):294-299.TIAN Changping,WEI Jingli,LIU Xiaojing,WANG Na,WANG Haibo,SUN Jiazheng,LI Dengtao,CHEN Xuesen.GCMS analysis of fruit aromatic components of pear cultivars originat ed from different species of Pyrus[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2009,26(3):294-299.
[34] 杨始刚,秦婷,苏美允,苏佳怡,汤习霞,许杨,孙越.一种呋喃型氧化芳樟醇的制备方法:201710287134[P].2019-05-31.YANG Shigang,QIN Ting,SU Meiyun,SU Jiayi,TANG Xixia,XU Yang,SUN Yue.A preparation method of furan type linalool oxide:201710287134[P].2019-05-31.
[35] 王小柯,罗怿,郑乾明,林乾,韩秀梅,李金强,蔡永强,李文云.5 个柠檬品种果皮挥发性物质差异分析[J].中国南方果树,2021,50(1):25-30.WANG Xiaoke,LUO Yi,ZHENG Qianming,LIN Qian,HAN Xiumei,LI Jinqiang,CAI Yongqiang,LI Wenyun.Analysis of volatile compounds in peel of five lemon varieties[J].South China Fruits,2021,50(1):25-30.
[36] 史宏志,刘国顺,谢子发,李超,魏跃伟,王芳,凌爱芬.不同产地白肋烟中性香气成分及生物碱组成和含量分析[J].中国烟草学报,2008(4):23-27.SHI Hongzhi,LIU Guoshun,XIE Zifa,LI Chao,WEI Yuewei,WANG Fang,LING Aifen.Comparison of composition and contents of neutral aroma components and alkaloids between burley tobaccos from different producing areas[J].Acta Tabacaria Sinica,2008(4):23-27.
[37] KANG Suyoung,朱荫,郑新强,梁月荣,林智.不同季节绿茶香气成分的判别与聚类分析[J].食品科学,2018,39(14):268-275.KANG Suyoung,ZHU Yin,ZHENG Xinqiang,LIANG Yuerong,LIN Zhi.Multivariate statistical analysis of volatiles compounds in green teas from different harvesting seasons[J].Food Science,2018,39(14):268-275.
[38] 敖常伟,吕姗,吴香菊,赵智慧,刘孟军.枣花及枣花蜜香气成分分析[J].食品科学,2018,39(20):182-189.AO Changwei,LÜ Shan,WU Xiangju,ZHAO Zhihui,LIU Mengjun.Analysis of aroma components from jujube flowers and honey[J].Food Science,2018,39(20):182-189.
[39] YI X,LIU G,RANA M M.Volatile profiling of two pear genotypes with different potential for white pear aroma improvement[J].Scientia Horticulturae,2016,209:221-228.
[40] QIN G,TAO S,CAO Y.Evaluation of the volatile profile of 33 Pyrus ussuriensis cultivars by HS-SPME with GC–MS[J].Food Chemistry,2012,134(4):2367-2382.
[41] SUN W,ZHAO Q,ZHAO H,ZHAO M,YANG B.Volatile compounds of Cantonese sausage released at different stages of processing and storage[J].Food Chemistry,2010,121(2):319-325.
[42] 索化夷,赵欣,骞宇,陈娟,李键,张玉,阚建全.永川豆豉发酵过程中香气的变化[J].食品科学,2015,36(20):95-100.SUO Huayi,ZHAO Xin,QIAN Yu,CHEN Juan,LI Jian,ZHANG Yu,KAN Jianquan.Changes in aroma components of yongchuan douchi during the fermentation process[J].Food Science,2015,36(20):95-100.