血橙[Citrus sinensis(L.)Osbeck f. sanguinea]是芸香科(Rutaceae)柑橘属(Citrus L.)甜橙品种[1],是柑橘中含花青素最丰富的一类品种,具有非常高的营养价值[2],果实形状呈圆球形或椭圆形,中等大小;果皮橙红色,较难剥离;果肉柔软多汁,酸甜味浓,成熟时有血红色不均匀斑纹,有特殊浓郁香气[3],是近几年来比较受欢迎的柑橘类型。果实品质是决定市场竞争力的重要因素之一,果实品质评价是良种选择和果品选优的重要环节[4-5]。柑橘果实品质分析指标比较多,是外观品质、风味品质、营养品质等多种因素的复合体,主要包括单果质量、果形指数、果皮厚度、可食率、出汁率、可滴定酸含量、可溶性固形物含量、固酸比、维生素C 含量等要素,血橙还包括果汁花青苷含量和果皮色泽2个因素。目前,国内外有很多新的综合评价方法应用于果实品质评价研究[6],主要有主成分分析法、层次分析法、模糊综合评价法、灰色关联度分析法、聚类分析和因子分析法等[7-8],但最后分析结果时,所用的指标都有所删减,笔者在本文中应用的标准化值加权法可以全面分析果实测量的品质指标。血橙果实品质综合评价分析的研究相对较少,需要进一步研究。笔者对湖南农业大学国家柑橘改良中心长沙分中心布置在重庆市万州区进行区域性试验的12 个血橙品种果实品质数据进行7 a(年)的跟踪,量化分析11个品质指标,开发出一套适合血橙果实品质综合评价软件分析系统,并应用专家品鉴法进行验证[9]。该研究为血橙果实品质综合评价提供了一种简便、客观的模式,为血橙新品种的选育、改良以及种植结构的调整提供品质评价科学依据[10]。
1 材料和方法
试验于2014—2021年在湖南农业大学进行。
1.1 材料
2014—2019年连续6 a对12个血橙品种(T.Meli、T.Messina rotondo、T.Tapi nuc.、T.Gallo、T.Nucellare、T. Gabella、T. del Muso、T. Scire、T. Ippolito、T.S.Alfio、T.Rosso 和Moro)在果实成熟期随机采样;利用品质分析数据建立量化公式、开发软件分析系统;2021 年1 月份再次采果验证软件分析系统。期间,每个品种采集30个果实,采摘后装箱,快递运回实验室,4 ℃下贮藏,3日内完成品质分析。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 建立量化公式 1)果实品质指标测定。随机选5 个果实测量,3 次重复。测量指标包括单果质量、果形指数、果皮厚度[11]、可食率[12]、出汁率[12]、可滴定酸含量、可溶性固形物含量、固酸比、维生素C 含量等9个柑橘果实品质常规指标[11]和果汁花青素含量、果皮色泽2个血橙特有指标[13-14],数据测定3次重复。
其中,果形指数=果实纵径/果实横径,可食率/%=(果实总质量-果皮的质量)/果实总质量×100,出汁率/%=果汁总质量/果实总质量×100,可滴定酸含量采用NaOH 中和滴定法[15]测定,可溶性固形物含量采用手持式糖度折光仪[16]测定,固酸比、维生素C 含量采用2,6-二氯靛酚滴定法[15]测定,果汁花青素含量采用光谱法[17-18]测定,果皮色泽用色差值量化,色差值用CR-400/410型色彩色差仪测定[19]。
2)指标趋向性的确定与调整。(1)指标趋向性的确定。综合分析血橙的固有特性,把果实品质指标分为趋大、趋中和趋小指标。趋大指标包括可溶性固形物含量、固酸比、可食率、出汁率、维生素C 含量、果皮色泽和花青素含量;趋中指标包括单果质量、果形指数和果皮厚度;趋小指标包括可滴定酸含量。(2)趋中指标最优值的确定,用平均数代替[20-21]。(3)指标趋向性的调整。为了便于后续的计算,需要将所有指标统一调成趋大[20]。
3)指标观测值的标准化处理。品质指标测定中,不同的指标存在不同的量纲和数量级,需将各指标进行标准化处理使其处于同一数量级,方便后续排序[22]。标准化是用来衡量资料相对位置的指标数据,这种指标数据为标准化值[23-25],具体参考唐帅等[20]和徐国祥等[21]的方法。总之,标准化值的含义是将不同单位的指标均转换为以0 为中心的纯数值,以方便后续处理[26]。
4)果实品质指标权重的分配。通过专家评定法对各项指标进行权重的分配[27]。血橙果实品质指标共100分。外观指标占30分,内质指标占70分,图1为各指标分配的具体权重值。
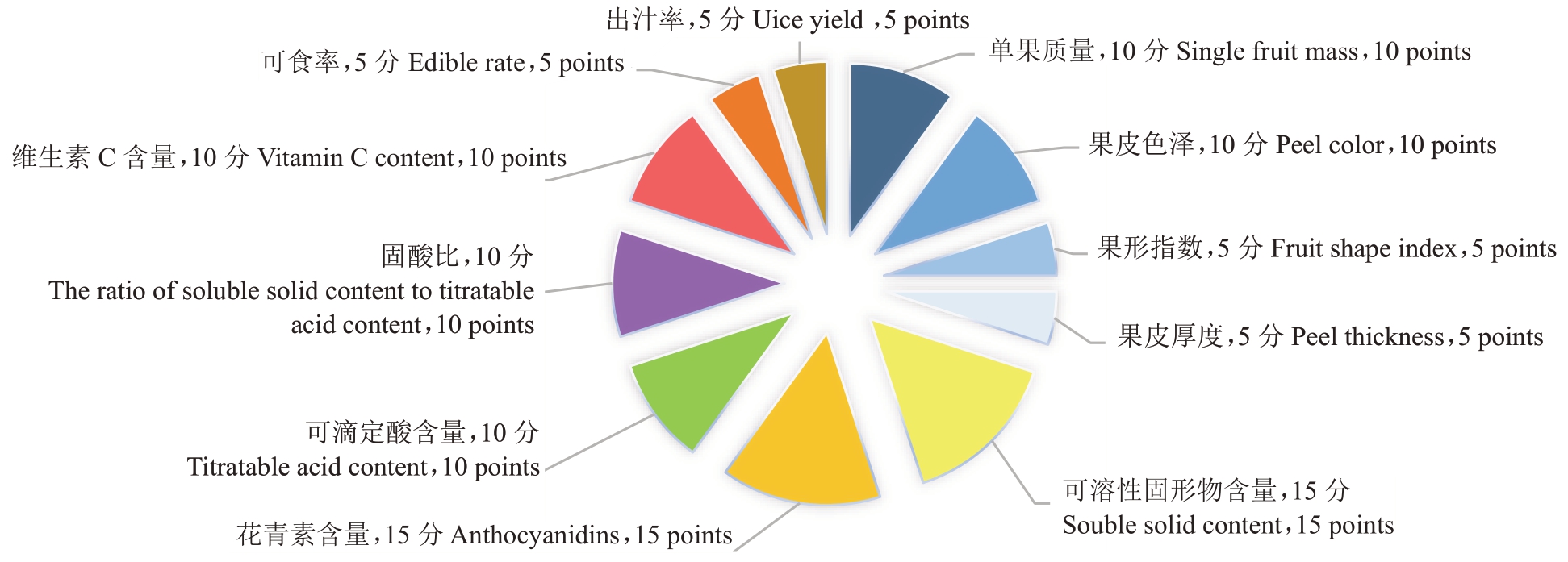
图1 血橙果实品质指标的权重分配
Fig.1 Weight distribution of blood orange fruit quality indicators
5)果实品质的综合评判。将各指标的标准化值乘以相应权重,得到该指标的最终评分。即血橙单个样本总分=单果质量×10%+果皮色泽×10%+果形指数×5%+果皮厚度×5%+可溶性固形物含量×15%+花青素含量×15%+可滴定酸含量×10%+固酸比×10%+维生素C 含量×10%+可食率×5%+出汁率×5%。
1.2.2 开发软件分析系统 在1.2.1 建立量化公式的基础上,以C/S为架构,运用Visual Studio 2019对系统计算部分进行相应的代码编写,在.NET平台上采用C#语言构建系统,经过调试与修改,编译生成EXE文件等,逐步完成系统内部设计。系统操作界面采用陈明阳等[28]提出的扁平化设计风格,界面直观、简洁,操作方便,可以直接导入Excel 表进行分析,评价结果直观显示或保存。同时,该评价系统安装后不需要依赖其他工具,可以直接运行,分析结果可直接存储在本地文件,无需通过网络,保存速度快。
1.2.3 验证软件分析系统 组织专家品鉴会进行综合评价血橙果实,为了公平品鉴,另外编一组评审号。评价小组由18 名经过专业培训的专业技术人员组成,参照Obenland 等[29]和何义仲等[30]的方法对果实进行感官评价,目测打分,评分项目和评分标准见表1。最终得分越高,说明专家对果实认可度越高,品质越好。
表1 血橙果实品鉴评分标准
Table 1 Blood orange fruit tasting score criteria

注:果实形状、果皮色泽、一致性、果肉色泽、果肉质地和果实风味6 个项目由专家综合评分;果实大小、果皮厚度、可溶性固形物含量和种子数量4 个项目根据果实品质分析实测平均结果评分。
Note:Six items including fruit shape,peel color,consistency,pulp color,pulp texture and fruit flavor were comprehensively evaluated by experts.The four items of fruit size,pericarp thickness,soluble solids content and seed number were scored according to the measured average results of fruit quality analysis.
评分项目Scoring item外观Appearance果实形状Fruit shape果实大小Fruit size果皮色泽Peel color权重/分Weight/Scores 5评分标准Scoring criteria果形端正,圆球形或椭圆形为满分,其他情况酌情扣分Fruit shape straight,Round or oval for full score,other cases as appropriate points deducted中等大小为满分,过大或过小的酌情扣分Medium is full score,too large or too small as appropriate points deducted果实成熟、着色全面、色泽鲜艳有光泽为满分,其他情况酌情扣分Fruit mature, comprehensive coloring, bright and glossy color is full mark, other cases as appropriate deduction果实个体之间形状、大小和色泽均一致的为满分Full mark for uniform shape,size and color among fruit individuals 0.4 cm为满分,每增加0.1cm,扣1分,扣完为止0.4 cm is the full score,deduct 1 point for every 0.1 cm increase until cleared紫红或近紫红色为满分,部分紫红扣3~4分,黄色扣0~3分Purple or near-purple red is full,some purple buttons 3-4,yellow buttons 0-3可溶性固形物含量≥13%者为满分,每减0.5%减1分,扣完为止Total soluble solids ≥12%is full mark,every 0.5%minus 1 point,until deducted肉质脆嫩、囊壁薄、融化渣的为满分,其他情况适当扣分Meat crisp and tender, capsule wall thin, melting residue for full score, other circumstances appropriate deduction甜酸适度,汁多味浓或有特殊芳香者为满分,其他情况适当扣分Full score for moderate sweet and sour,juicy or special aromatics,appropriate discount for other situations无核为满分,1~3粒为4分,3粒以上每增加2粒扣1分,扣完为止Seedless for full score,1-3 for 4points,3 or more for each increase of 2 buttons 1 point,until deducted 10 15一致性Consistency内质Internal fruit quality果皮厚度Pericarp thickness果肉色泽Flesh color可溶性固形物含量Total soluble solids果肉质地Flesh texture 5 5 1 5 15 10果实风味Fruit flavor 15种子数量Seed amount 5
1.3 数据处理
所有数据使用Excel 2010软件进行整理、绘图,运用SPSS 17.0 软件进行数据分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 果实品质数据的量化分析
2014—2019年连续6 a分析12个血橙样品的11个品质指标的平均观测值(表2)。11个品质指标的量化分析。(1)趋中指标最优值的确定。果实品质的平均值作为单果质量(185.15 g)、果形指数(0.99)和果皮厚度(4.57 mm)的最优值;(2)指标趋向性的调整。血橙11 个指标中,趋中指标通过公式yi =-1×|Xi-a|(yi 为第i 个样本调整趋向性后的值,Xi 为第i 个样本指标观测值)调整为趋大;趋小指标通过公式Wi=-1×Xi(Wi为第i个样本调整趋向性后的值,Xi 为第i 个样本指标观测值)调整为趋大,结果见表3;(3)数据标准化的处理,11个指标的标准化值结果见表4;(4)血橙果实品质的综合评分结果见表5。
表2 12 份重庆万州血橙样品果实品质观测值
Table 2 Observation values of fruit quality of 12 blood orange samples from Wanzhou,Chongqing
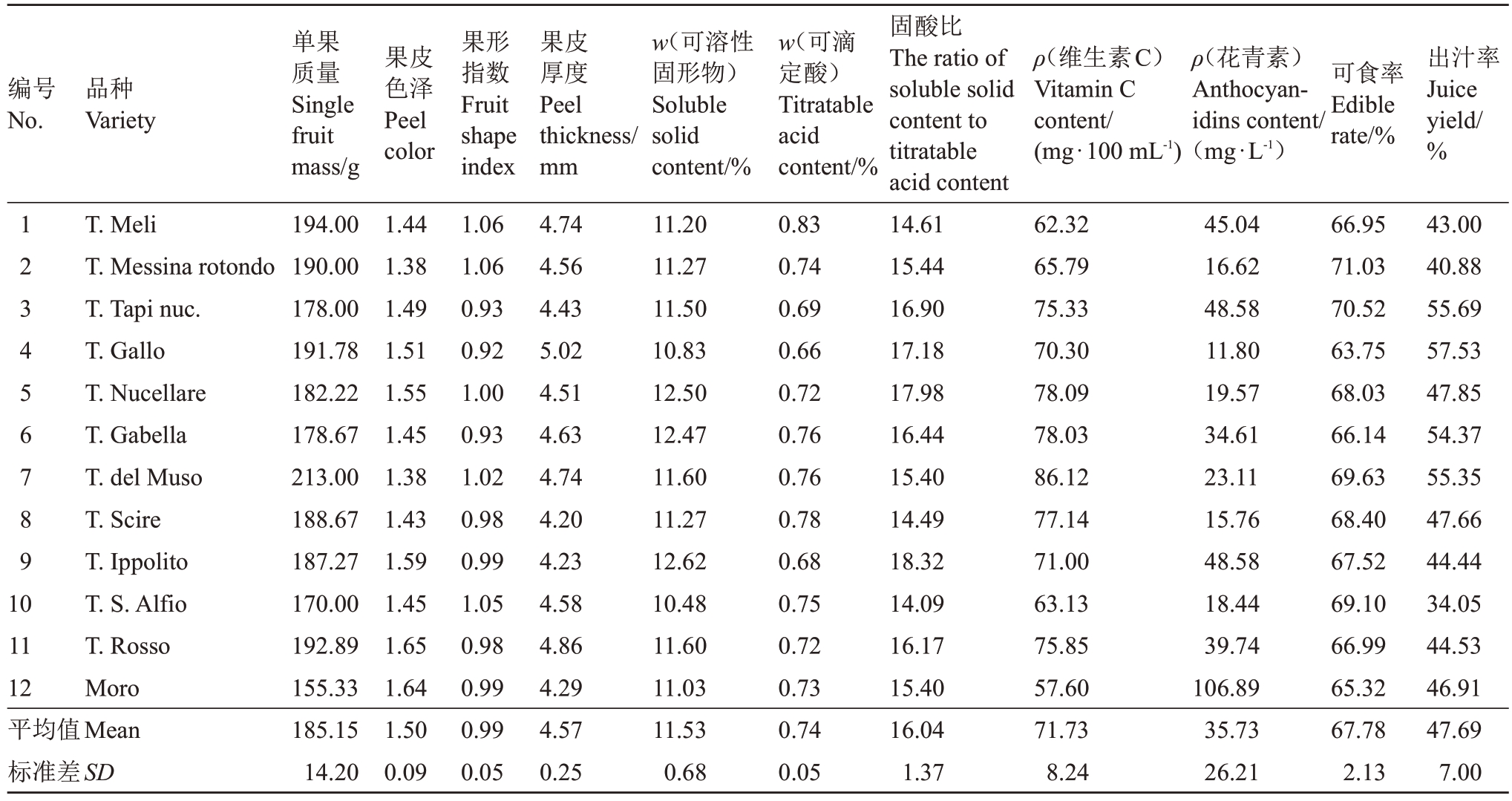
编号No.品种Variety果皮色泽Peel color ρ(维生素C)Vitamin C content/(mg·100 mL-1)ρ(花青素)Anthocyanidins content/(mg·L-1)可食率Edible rate/%出汁率Juice yield/%1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 0 11 12平均值Mean标准差SD T.Meli T.Messina rotondo T.Tapi nuc.T.Gallo T.Nucellare T.Gabella T.del Muso T.Scire T.Ippolito T.S.Alfio T.Rosso Moro单果质量Single fruit mass/g 194.00 190.00 178.00 191.78 182.22 178.67 213.00 188.67 187.27 170.00 192.89 155.33 185.15 14.20 1.44 1.38 1.49 1.51 1.55 1.45 1.38 1.43 1.59 1.45 1.65 1.64 1.50 0.09果形指数Fruit shape index 1.06 1.06 0.93 0.92 1.00 0.93 1.02 0.98 0.99 1.05 0.98 0.99 0.99 0.05果皮厚度Peel thickness/mm 4.74 4.56 4.43 5.02 4.51 4.63 4.74 4.20 4.23 4.58 4.86 4.29 4.57 0.25 w(可溶性固形物)Soluble solid content/%11.20 11.27 11.50 10.83 12.50 12.47 11.60 11.27 12.62 10.48 11.60 11.03 11.53 0.68 w(可滴定酸)Titratable acid content/%0.83 0.74 0.69 0.66 0.72 0.76 0.76 0.78 0.68 0.75 0.72 0.73 0.74 0.05固酸比The ratio of soluble solid content to titratable acid content 14.61 15.44 16.90 17.18 17.98 16.44 15.40 14.49 18.32 14.09 16.17 15.40 16.04 1.37 62.32 65.79 75.33 70.30 78.09 78.03 86.12 77.14 71.00 63.13 75.85 57.60 71.73 8.24 45.04 16.62 48.58 11.80 19.57 34.61 23.11 15.76 48.58 18.44 39.74 106.89 35.73 26.21 66.95 71.03 70.52 63.75 68.03 66.14 69.63 68.40 67.52 69.10 66.99 65.32 67.78 2.13 43.00 40.88 55.69 57.53 47.85 54.37 55.35 47.66 44.44 34.05 44.53 46.91 47.69 7.00
表3 血橙果实品质指标趋向性调整
Table 3 Trend adjustment of fruit quality indexes of blood orange
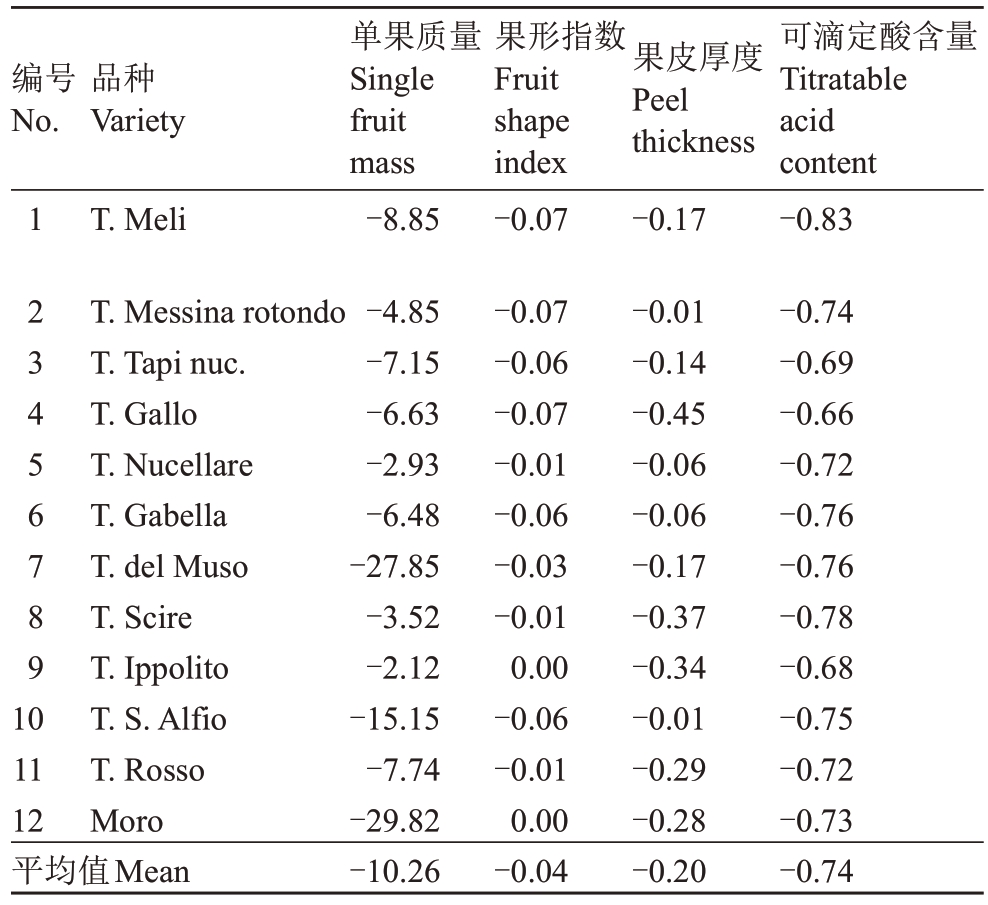
编号No.品种Variety 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 0 T.Meli单果质量Single fruit mass-8.85果形指数Fruit shape index-0.07果皮厚度Peel thickness-0.17可滴定酸含量Titratable acid content-0.83 11 12平均值Mean T.Messina rotondo T.Tapi nuc.T.Gallo T.Nucellare T.Gabella T.del Muso T.Scire T.Ippolito T.S.Alfio T.Rosso Moro-4.85-7.15-6.63-2.93-6.48-27.85-3.52-2.12-15.15-7.74-29.82-10.26-0.07-0.06-0.07-0.01-0.06-0.03-0.01 0.00-0.06-0.01 0.00-0.04-0.01-0.14-0.45-0.06-0.06-0.17-0.37-0.34-0.01-0.29-0.28-0.20-0.74-0.69-0.66-0.72-0.76-0.76-0.78-0.68-0.75-0.72-0.73-0.74
表4 血橙果实品质指标标准化值
Table 4 Standardized values of fruit quality indexes of blood orange
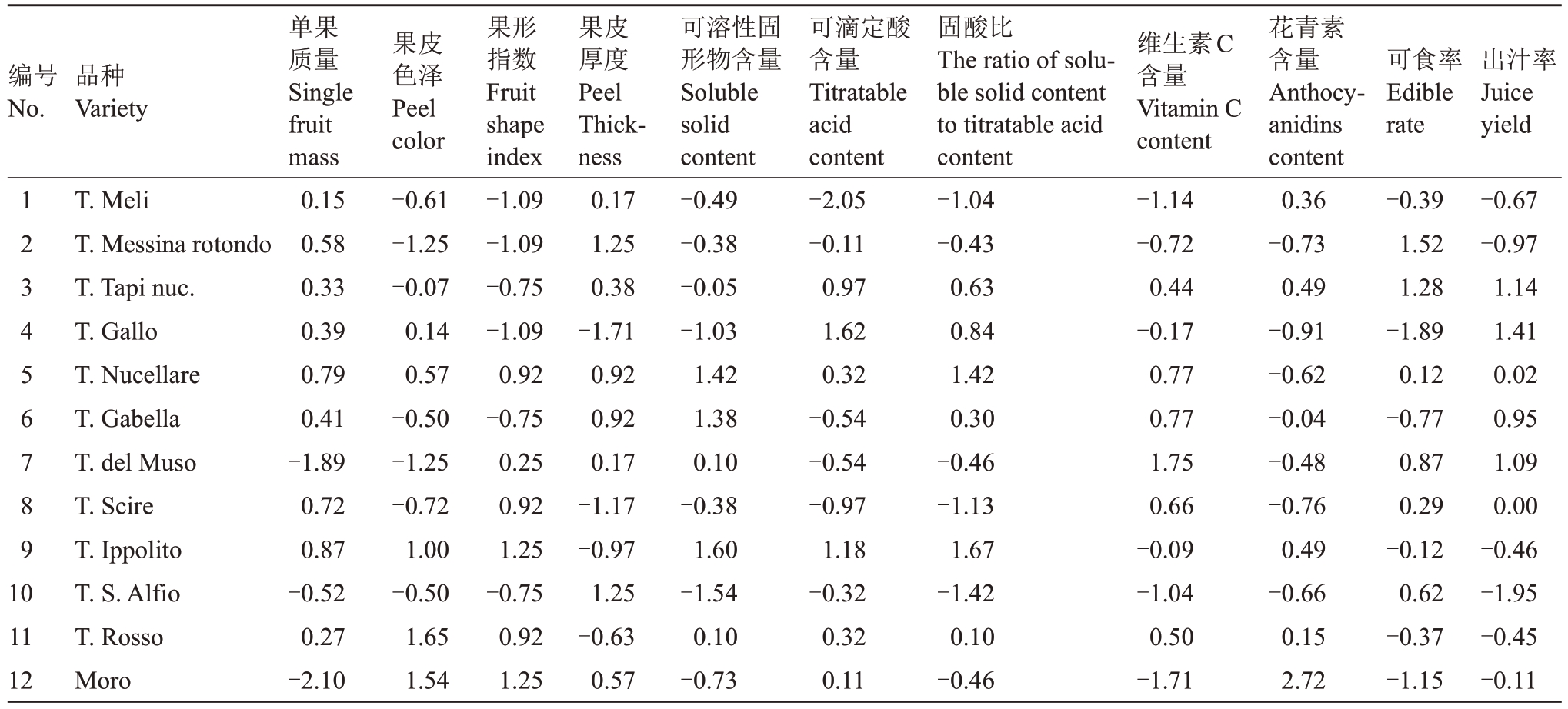
编号No.品种Variety可食率Edible rate出汁率Juice yield 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 0 11 12 T.Meli T.Messina rotondo T.Tapi nuc.T.Gallo T.Nucellare T.Gabella T.del Muso T.Scire T.Ippolito T.S.Alfio T.Rosso Moro单果质量Single fruit mass 0.15 0.58 0.33 0.39 0.79 0.41-1.89 0.72 0.87-0.52 0.27-2.10果皮色泽Peel color-0.61-1.25-0.07 0.14 0.57-0.50-1.25-0.72 1.00-0.50 1.65 1.54果形指数Fruit shape index-1.09-1.09-0.75-1.09 0.92-0.75 0.25 0.92 1.25-0.75 0.92 1.25果皮厚度Peel Thickness 0.17 1.25 0.38-1.71 0.92 0.92 0.17-1.17-0.97 1.25-0.63 0.57可溶性固形物含量Soluble solid content-0.49-0.38-0.05-1.03 1.42 1.38 0.10-0.38 1.60-1.54 0.10-0.73可滴定酸含量Titratable acid content-2.05-0.11 0.97 1.62 0.32-0.54-0.54-0.97 1.18-0.32 0.32 0.11固酸比The ratio of soluble solid content to titratable acid content-1.04-0.43 0.63 0.84 1.42 0.30-0.46-1.13 1.67-1.42 0.10-0.46维生素C含量Vitamin C content-1.14-0.72 0.44-0.17 0.77 0.77 1.75 0.66-0.09-1.04 0.50-1.71花青素含量Anthocyanidins content 0.36-0.73 0.49-0.91-0.62-0.04-0.48-0.76 0.49-0.66 0.15 2.72-0.39 1.52 1.28-1.89 0.12-0.77 0.87 0.29-0.12 0.62-0.37-1.15-0.67-0.97 1.14 1.41 0.02 0.95 1.09 0.00-0.46-1.95-0.45-0.11
表5 血橙样品的综合评分
Table 5 Comprehensive score of blood orange samples

编号No.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 0排名Rank 11 10 3 7 2 5 8 9 1 1 11 12品种Variety T.Meli T.Messina rotondo T.Tapi nuc.T.Gallo T.Nucellare T.Gabella T.del Muso T.Scire T.Ippolito T.S.Alfio T.Rosso Moro综合得分Comprehensive score-58.69-32.48 39.93-17.43 60.72 26.02-17.74-31.36 76.24-75.31 29.55 0.55 2 4 6
2.2 综合评价系统的分析结果
2014—2019 年连续6 a 分析12 个血橙品种的11个品质指标的平均观测值,通过点击【数据导入】按键一键导入观测值,然后点击【品质分析】按键,即可得到果实品质排名情况,操作简便,从表6 可以看出,“品质值”得分与量化公式计算的结果完全一致。
表6 血橙果实分析系统排名
Table 6 Ranking of Blood Orange fruit evaluation system
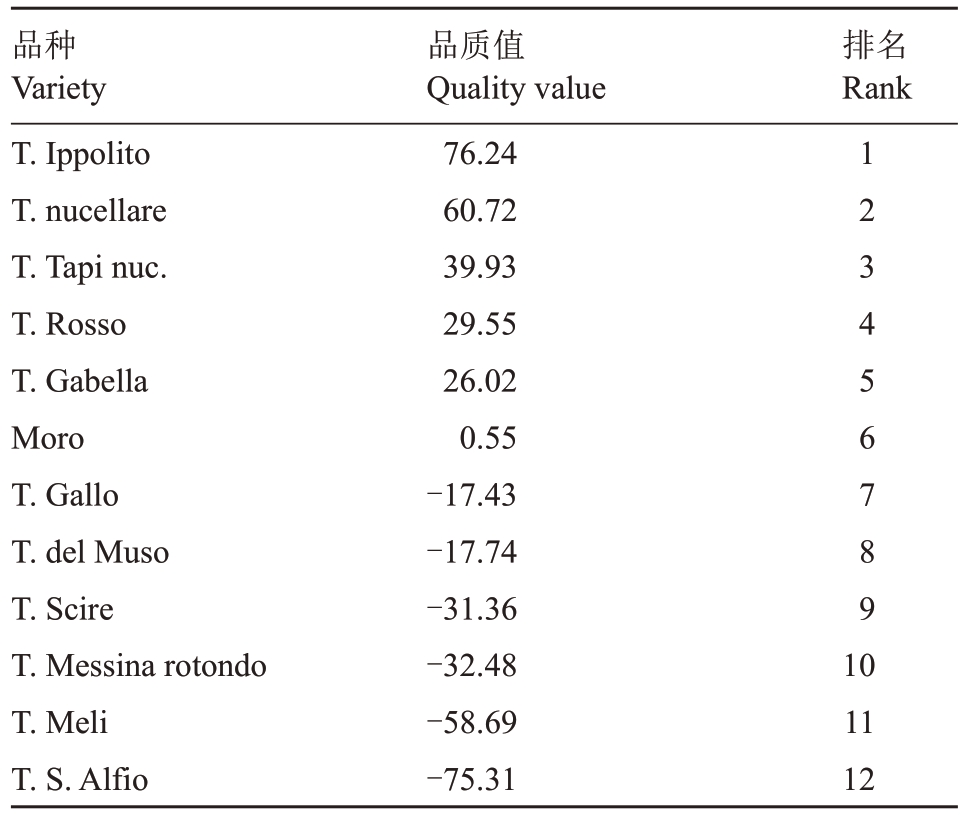
品种Variety T.Ippolito T.nucellare T.Tapi nuc.T.Rosso T.Gabella Moro T.Gallo T.del Muso T.Scire T.Messina rotondo T.Meli T.S.Alfio品质值Quality value 76.24 60.72 39.93 29.55 26.02 0.55-17.43-17.74-31.36-32.48-58.69-75.31排名Rank 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 0 11 12
2.3 组织专家品鉴会验证综合评价系统
2021年再次对这12个血橙品种采样进行品质分析,并组织专家品鉴会对软件分析系统的结果进行验证。
2.3.1 软件分析系统评价结果 应用软件分析系统分析的排名结果见表7。在参评样品中,综合排名前5 的样品为T. Tapi nuc.、T. Ippolito、T. Nucellare、T. Gallo 和T. Rosso,都是市场上受欢迎的品种。并且,排名靠前的品种可溶性固形物含量、固酸比和维生素C含量等相对较高,由此看出,果实内在风味是果实选育的基础,只有内在品质优良,才能引导消费者再次回购。
表7 血橙果实评价系统排名
Table 7 Ranking of Blood Orange fruit evaluation system
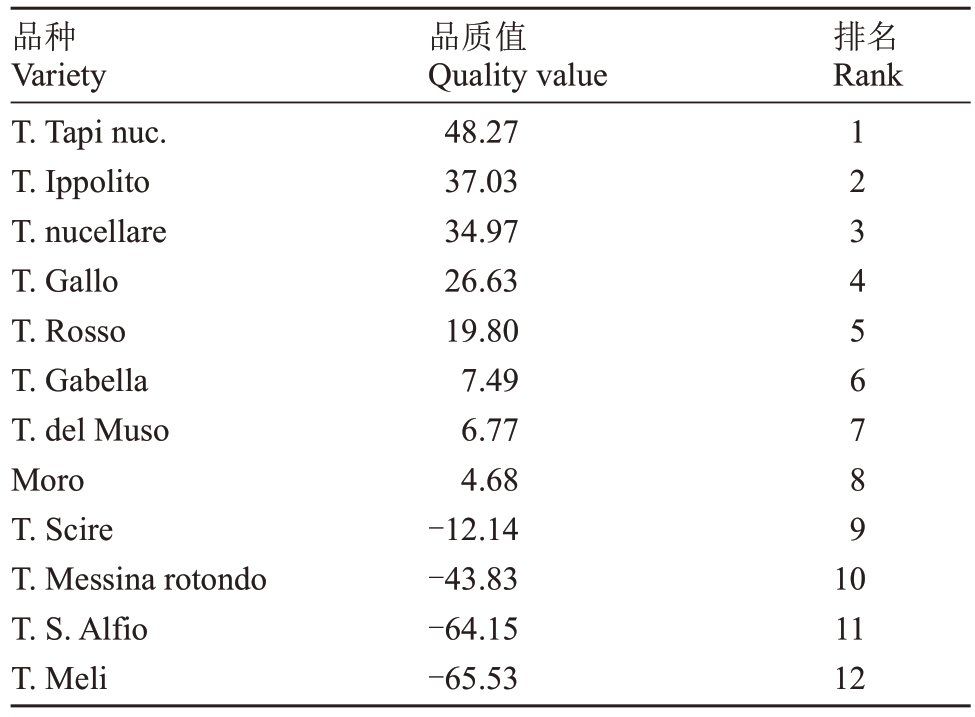
品种Variety T.Tapi nuc.T.Ippolito T.nucellare T.Gallo T.Rosso T.Gabella T.del Muso Moro T.Scire T.Messina rotondo T.S.Alfio T.Meli品质值Quality value 48.27 37.03 34.97 26.63 19.80 7.49 6.77 4.68-12.14-43.83-64.15-65.53排名Rank 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 0 11 12
2.3.2 专家品鉴会评价结果 由表8 可知,参与专家品鉴的12 个血橙品种排名情况。排名前5 的品种为T. Tapi nuc.、T. Ippolito、T. Nucellare、T. Rosso和Moro,与系统排名相似度高达80%。至于系统排名中Moro排名第8,而专家品鉴会排名第5,是因为系统排名中Moro 的可滴定酸含量高、固酸比低;品鉴时Moro 的果肉色泽指标得分高明显高于其他品种,接近满分15分。这说明在血橙果实品质相似的情况下,消费者更喜欢花青素含量高的品种,花青素含量对血橙的外观和品质的影响非常大[31]。
表8 血橙果实专家品鉴会排名
Table 8 Ranking of expert tasting of blood orange fruit

编号No.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 0排名Rank 12 10 1 8 3 6 7 9 2 1 11 12品种Variety T.Meli T.Messina rotondo T.Tapi nuc.T.Gallo T.Nucellare T.Gabella T.del Muso T.Scire T.Ippolito T.S.Alfio T.Rosso Moro综合得分Comprehensive score 80.68 82.92 91.84 84.67 86.80 85.25 85.17 83.00 89.50 82.83 86.66 85.74 1 4 5
2.3.3 系统排名与专家品鉴会排名相关性比较 对本次参与评价的血橙样品进行相关性分析,结果显示,系统排名与专家品鉴会排名呈极显著正相关(r=0.909,p <0.01),这说明软件分析系统符合实际。
3 讨 论
目前,评价果实品质主要采用主成分分析法,但它不能保证排名结果的一致性[32]。因此,应深入研究其他方法。笔者在本研究中运用标准化值加权法对果实品质指标进行趋向性确定(血橙属于“高糖高酸”型品种,适当的酸含量可以使血橙果实的风味更浓),将全部观测指标的数据进行趋向性调整,用专家打分法[33]分配指标权重,避免指标信息丢失,使果实品质评价更客观全面;对各项指标进行标准化值处理,使数据简洁化、消除单位、变成纯数值,降低数据处理难度。该方法能够客观准确地对12 个血橙品质进行分析,非模糊判断,但此方法引出大量计算问题;为了简化计算,基于上述数学原理开发了软件分析系统。
组织专家品鉴会对开发的软件分析系统进行验证。结果显示,软件排名前三的分别为T.Tapi nuc.、T.Ippolito和T.Nucellare,都是市场上较受欢迎的品种;T.Messina rotondo、T.Meli、T.S.Alfio排名靠后,也与市场实际情况相似。根据曾维友等[34]评价血橙品种发现T.Tapi nuc.总酸含量较低,T.Meli 的总酸含量较高;T.Ippolit可溶性固形物含量较高,T.S.Alfio可溶性固形物含量较低;而本文T.Tapi nuc.和T.Ippolito 在系统排名和品鉴排名中均靠前,T.Meli 和T.S.Alfio系统排名和品鉴排名中均靠后,与前人评价结果一致。系统排名中Moro排名靠后,而专家品鉴时排名中靠前,主要是由于文中的11个品质检测指标和专家组的鉴评指标略有微小差异,现场品鉴时Moro的果肉色泽指标得分明显高于其他品种,但综合来看,2 种评价结果差异不大。只能说明在品质相似的情况下,消费者更青睐花青素含量高的品种。将本次参与评价的血橙品种按照排名分成3个等级,第1~4 名为品质优秀,第5~8 名为品质良好,第9~12名为品质一般,则系统排名和品鉴排名均为“品质优秀”的品种有3个,占比75%;系统排名和品鉴排名均为“品质良好”的品种有2个,占比50%;系统排名和品鉴排名均为“品质一般”的品种有4 个,占比100%。系统排名与品鉴排名呈极显著正相关(r=0.909,p <0.01),说明该软件分析系统的结果符合实际情况,且更科学客观,更快速,为血橙品种的优劣选育提供科学依据。
品种选育过程中会涉及大量的品质分析数据,且需要反复确认评价是否准确,工作量巨大[35]。建立的软件分析系统能够对血橙果实品质数据进行客观分析,解决了柑橘果实品质分析指标多、育种材料数量大、评价标准不一等问题;且在品种选育过程中,根据育种目标修改指标的趋向性和权重就能选出目标特性最优的材料,但系统的缺点是,必须测全11个品种指标,缺一不可,否则无法评判。另外,举办专家品鉴会选优需要专业人员,花费大量的人力、财力和时间。该分析系统同样适用于非专业人员,操作简单、方便快速,排除人为的主观性评价,使结果更加科学合理。将本评价系统微调后可用于其他柑橘品种的综合评价,也给其他果树的果实评价提供参考。
4 结 论
利用血橙果实品质分析数据建立量化公式,开发出软件分析系统,然后组织专家品鉴会验证软件分析系统,结果表明该分析系统是合理可行的,能应用于实际。因此,此系统能客观、科学地评价血橙果实品质优劣,提高了血橙新品种选育工作效率,不足之处在于,通过大量试验发现,该评价系统更适用于对样品数量(>10)与指标数量(>5)较多的果实品质进行评价,样品数量较少时,可直观判断,无需用软件系统评价。
[1]陈杰忠.果树栽培学各论南方本[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2005.CHEN Jiezhong. Fruit tree cultivation in Southern China[M].Beijing:China Agriculture Press,2005.
[2]周艳蕊.鲜榨橙汁加工新工艺及副产物高值开发[D].合肥:合肥工业大学,2020.ZHOU Yanrui. New processing technology of fresh orange juice and high value development of by-products[D]. Hefei:Hefei University of Technology,2020.
[3]鲍江峰,夏仁学,邓秀新,彭抒昂,刘永忠,马湘涛,张红艳.湖北省纽荷尔脐橙果实品质状况的研究[J].武汉植物学研究,2005,23(6):583-587.BAO Jiangfeng,XIA Renxue,DENG Xiuxin,PENG Shu’ang,LIU Yongzhong,MA Xiangtao,ZHANG Hongyan. Study on fruit quality of Newhall Navel orange in Hubei province[J].Wuhan Botanical Research,2005,23(6):583-587.
[4]ZHOU Y,HE W Z,ZHENG W L,TAN Q L,XIE Z Z,ZHENG C S,HU C X.Fruit sugar and organic acid were significantly related to fruit Mg of six citrus cultivars[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,259(1):278-285.
[5]朱丽莎,董超,赵静,江东,王成秋,焦必宁.重庆主栽甜橙品种果实品质比较分析[J].中国南方果树,2018,47(5):128-135.JU Lisha,DONG Chao,ZHAO Jing,JIANG Dong,WANG Chengqiu,JIAO Bining.Comparative analysis of fruit quality of main Sweet Orange varieties in Chongqing[J]. South China Fruits,2018,47(5):128-135.
[6]WU Z B,CHEN Y H. The maximizing deviation method for group multiple attribute decision making under linguistic environment[J].Fuzzy Sets and Systems,2007,158(14):1608-1617.
[7]ZOU Z H,YUN Y,SUN J N.Entropy method for determination of weight of evaluating indicators in fuzzy synthetic evaluation for water quality assessment[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences,2006,18(5):1020-1023.
[8]冯娟,任小林,田建文,樊丽,王晓飞.不同产地富士苹果品质分析与比较[J].食品工业科技,2013,34(14):108-112.FENG Juan,REN Xiaolin,TIAN Jianwen,FAN li,WANG Xiaofei. Quality analysis and comparison of Fuji apples from different origins[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2013,34(14):108-112.
[9]肖婷,朱昌明,翟东宇,邓莹.聚类分析法与专家评价法在企业绩效评价中的应用与结果比较[J].科技创业,2016,29(7):32-33.XIAO Ting,ZHU Changming,ZHAI Dongyu,DENG Ying.Application and results comparison of cluster analysis method and expert evaluation method in enterprise performance evaluation[J].Pioneering with Science&Technology,2016,29(7):32-33.
[10]李勋兰,洪林,王武,杨蕾,谭平.晚熟杂柑新品种果实品质综合评价[J].果树学报,2018,35(2):195-203.LI Xunlan,HONG Lin,WANG Wu,YANG Lei,TAN Ping.Comprehensive evaluation of fruit quality of new late maturing hybrid citrus varieties[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2018,35(2):195-203.
[11]周开隆,叶荫民.中国果树志柑橘卷[M].北京:中国林业出版社,2009.ZHOU Kailong,YE Yinmin. China fruit tree journal Citrus volume[M].Beijing:China Forestry Press,2009.
[12]国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 柑橘鲜果检验方法GB/T8210—2011[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2011.State Adminstration for Market Regulation. Citrus fruit inspection method:GB/T8210—2011[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China,2011.
[13]王鲲娇,韩旭,张志成,朱宗瑛,谭启玲,胡承孝.推荐施肥对‘温州蜜柑’和‘南丰蜜橘’品质与化渣性的影响[J].果树学报,2018,35(10):1190-1196.WANG Kunjiao,HAN Xu,ZHANG Zhicheng,ZHU Zongying,TAN Qiling,HU Chengxiao. Effects of recommended fertilization on quality and slagging of‘Wenzhou mandarin’and‘Nan feng mandarin’[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2018,35(10):1190-1196.
[14]曹少谦,刘亮,潘思轶.血橙果汁贮藏过程中品质变化研究[J].食品科学,2011,32(2):297-301.CAO Shaoqian,LIU Liang,PAN Siyi.Quality changes of Blood Orange juice during storage[J]. Food Science,2011,32(2):297-301.
[15]李大志,周嘉,刘曙东,蒋青岚,胡双双,邓子牛.湖南产区甜橙果实品质分析[J].中国南方果树,2019,48(4):10-13.LI Dazhi,ZHOU Jia,LIU Shudong,JIANG Qinglan,HU Shuangshuang,DENG Ziniu.Fruit quality analysis of Sweet Orange in Hunan producing area[J]. South China Fruits,2019,48(4):10-13.
[16]罗艺,唐帅,郑艳婷,周敏,邓子牛,李大志.融安滑皮金橘在浏阳引种报告[J].湖南农业科学,2017(4):83-85.LUO Yi,TANG Shuai,ZHENG Yanting,ZHOU Min,DENG Ziniu,LI Dazhi. Report on the introduction of Rongan Hua Pi Jinju in Liuyang[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences,2017(4):83-85.
[17]曹少谦,潘思轶.血橙花色苷研究进展[J].食品科学,2006,27(9):278-281.CAO Shaoqian,PAN Siyi. Research progress of blood orange anthocyanins[J].Food Science,2006,27(9):278-281.
[18]王梦,李娜,李恩情,张春苗,张凤,邹巧玲,柴爽,邓子牛,龙桂友.紫外光照射对通风贮藏塔罗科血橙花青苷含量的影响[J].中国南方果树,2020,49(5):31-35.WANG Meng,LI Na,LI Enqing,ZHANG Chunmiao,ZHANG Feng,ZOU Qiaoling,CHAI Shuang,DENG Ziniu,LONG Guiyou. Effects of UV irradiation on anthocyanin content in Taroko blood during ventilation storage[J].South China Fruits,2020,49(5):31-35.
[19]陈婷,王日葵,周炼,陆智明,刘涛.柑橘贮藏期间色差指数变化规律的研究[J].农产品加工(学刊),2010(3):4-7.CHEN Ting,WANG Rikui,ZHOU Lian,LU Zhiming,LIU Tao.Study on the change rule of color difference index during citrus storage[J]. Academic Periodical of Farm Products Processing,2010(3):4-7.
[20]唐帅,易自力,李娜,谢一顾,邓子牛,李大志.冰糖橙果实品质综合评价量化模型的建立及应用[J]. 果树学报,2018,35(7):889-897.TANG Shuai,YI Zili,LI Na,XIE Yigu,DENG Ziniu,LI Dazhi.Establishment and application of quantitative model for comprehensive evaluation of fruit quality of sugar orange[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2018,35(7):889-897.
[21]徐国祥,刘汉良,孙允午.统计学[M].上海:上海财经大学出版社,2001.XU Guoxiang,LIU Hanliang,SUN Yunwu. Statistics[M].Shanghai:Shanghai University of Finance and Economics Press,2001.
[22]张梦雪,江冬冬,刘星媛,郝晋伟,王全.基于主成分分析的武汉市公立医院综合评价研究[J].中国社会医学杂志,2021,38(1):84-87.ZHANG Mengxue,JIANG Dongdong,LIU Xingyuan,HAO Jinwei,WANG Quan. Comprehensive evaluation of public hospitals in Wuhan based on principal component analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Social Medicine,2021,38(1):84-87.
[23]赖国毅,陈超.SPSS 17.0 中文版常用功能与应用实例精讲[M].北京:电子工业出版社,2010.LAI Guoyi,CHEN Chao. Chinese Version of SPSS 17.0 common functions and application examples[M]. Beijing:Publishing House of Electronics Industry,2010.
[24]CAI Q H,LIU J K,KING L.A comprehensive model for assessing lake eutrophication[J].Journal of Applied Ecology,2002,13(12):1674-1678.
[25]吴冬友,杨玉坤.统计学[M].北京:中国税务出版社,2005.WU Dongyou,YANG Yukun.Statistics[M].Beijing:China Taxation Publishing House,2005.
[26]俞立平,潘云涛,武夷山.学术期刊综合评价数据标准化方法研究[J].图书情报工作,2009,53(12):136-139.YU Liping,PAN Yuntao,WU Yishan. Research on data normalization methods in multi-attribute evaluation[J]. Library and Information Service,2009,53(12):136-139.
[27]何超,李萌,李婷婷,彭雪,李婕,赵锦慧.多目标综合评价中四种确定权重方法的比较与分析[J].湖北大学学报(自然科学版),2016,38(2):172-178.HE Chao,LI Meng,LI Tingting,PENG Xue,LI Jie,ZHAO Jinhui. Comparison and analysis of four weight determination methods in multi-objective comprehensive evaluation[J]. Journal of Hubei University (Natural Science),2016,38(2):172-178.
[28]陈明阳,李晢.“less is more”在UI 界面中的应用与研究[J].科技视界,2017(5):197.CHEN Mingyang,LI Xi. The application and research of‘less is more’in UI interface[J].Science&Technology Vision,2017(5):197.
[29]OBENLAND D,COLLIN S,MACKEY B,SIEVERT J,ARPAIA L M. Storage temperature and time influences sensory quality of mandarins by altering soluble solids,acidity and aroma volatile composition[J].Postharvest Biology and Technology,2011,59(2):187-193.
[30]何义仲,陈兆星,刘润生,方贻文,古祖亮,严翔,陈红,张洪铭,唐焕庆,程运江.不同贮藏方式对赣南纽荷尔脐橙果实品质的影响[J].中国农业科学,2014,47(4):736-748.HE Yizhong,CHEN Zhaoxing,LIU Runsheng,FANG Yiwen,GU Zuliang,YAN Xiang,CHEN Hong,ZHANG Hongming,TANG Huanqing,CHENG Yunjiang.Effects of different storage methods on fruit quality of Newhall navel orange in southern Jiangxi[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2014,47(4):736-748.
[31]FATTAHI J,FOTOUHI R,BAKHSHI D,AGHAJANZADEH S.Fruit quality,anthocyanin,and Cyanidin 3-Glucoside concentrations of several Blood Orange cultivars grown in different areas of Iran[J]. Horticulture Environment & Biotechnology,2009(8):290-294.
[32]叶明确,杨亚娟.主成分综合评价法的误区识别及其改进[J].数量经济技术经济研究,2016,33(10):142-153.YE Mingque,YANG Yajuan. Identification and improvement of the misunderstanding of the principal component comprehensive evaluation method[J].The Journal of Quantitative&Technical Economics,2016,33(10):142-153.
[33]金志农,李端妹,金莹,熊妮.地方科研机构绩效考核指标及其权重计算:基于专家分析法和层次分析法的对比研究[J].科技管理研究,2009,29(12):103-106.JIN Zhinong,LI Duanmei,JIN Ying,XIONG Ni. Performance evaluation indexes of local research institutions and their weight calculation-a comparative study based on expert analysis method and hierarchical analysis method[J]. Science and Technology Management Research,2009,29(12):103-106.
[34]曾维友,张才健,夏仁斌,周心智,杨海健,刘芳,弓亚林,张云贵.十个意大利血橙品种在重庆市江津区的品质表现[J].南方农业,2013,7(5):47-48.ZENG Weiyou,ZHANG Caijian,XIA Renbin,ZHOU Xinzhi,YANG Haijian,LIU Fang,GONG Yalin,ZHANG Yungui.Quality performance of ten Italian Blood Orange cultivars in Jiangjin district,Chongqing[J]. South China Agriculture,2013,7(5):47-48.
[35]李娜,李大志,何建明,龙紫薇,黄婷,龙立长,邓子牛,文跃伟,龙桂友. 柑橘新品种‘黔阳冰糖脐橙’的选育[J]. 果树学报,2020,37(1):140-143.LI Na,LI Dazhi,HE Jianming,LONG Ziwei,HUANG Ting,LONG Lichang,DENG Ziniu,WEN Yuewei,LONG Guiyou.Breeding of a new citrus variety‘Qianyang Bing Tang Navel Orange’[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2020,37(1):140-143.