瑞雪苹果(Malus domestica Borkh.‘Ruixue’)是由西北农林科技大学以秦富1 号和粉红女士为亲本[1]杂交选育的晚熟、黄色苹果新品种,2015年通过陕西省品种审定,2019 年通过国审[2]。其果面光洁鲜亮,外形好看、肉质脆、口味佳、风味浓郁,独具“清香型”香气,深受消费者喜爱,在外观品质、耐贮性和风味特点上均优于其亲本[3],具有广阔的推广应用前景。且该品种适应性广,抗逆性强,在我国苹果主产区均可栽培。经试验研究发现,瑞雪苹果在陕西、甘肃、山西等黄土高原苹果主产区种植表现尤为突出,2019 年推广面积已超过0.33 万hm2,盛果期666.7 m2产量可超过3000 kg[2],有望成为我国晚熟苹果更新换代品种,特别是黄土高原产区苹果更新换代最具潜力的主栽品种[4]。
随着瑞雪苹果推广面积的逐渐扩大,其相应的育苗特性、栽培管理技术以及采后贮藏保鲜技术也应进行更加深入的研究,而目前关于瑞雪苹果的研究主要集中于适栽区域的探索[5-7]、专用育果袋的筛选[8-10]、套袋对果实品质的影响[11-13]以及与亲本营养成分的比较[14]和香气物质[15-16]的研究等方面,贮藏特性方面的研究很少,其能否适应设置的低温贮藏条件、常规贮藏条件下是否产生冷害、贮藏过程有无生理病害发生、最佳贮藏时间等情况仍不清楚,不利于瑞雪苹果贮藏期间的管理,阻碍了其进一步提高品种的丰产性能。因此,笔者在本研究中以瑞雪苹果为试验材料,探究其在常温和0 ℃贮藏条件下呼吸强度、乙烯释放量、果实质地与品质、病害发生情况等的变化,初步明确瑞雪苹果果实的贮藏特性,从而为其后期贮藏保鲜提供依据及品种推广应用提供有益参考。
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料
瑞雪苹果于2020年10月19日采于陕西省白水苹果试验站(35°2′N,109°6′E),正常成熟时采摘,单果套上塑料发泡网后当日装箱运回学院保鲜加工实验室。挑选大小及成熟度相近、着色无明显差别、无碰压伤和病虫害的苹果在室温下放置过夜,然后按照试验设计进行贮藏。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 试验设计 将果子分为以下2个处理进行试验:
(1)常温贮藏:温度(20±2)℃、相对湿度(85%~90%)的室内。
(2)低温贮藏:低温(0±0.5)℃、相对湿度(85%~90%)的冷库中。
每个处理果实分为3组装于带有透气孔的0.05 mm厚度的双层聚乙烯塑料薄膜内衬的果筐中贮藏,贮藏期间挽住塑料薄膜口以防止水分蒸发散失,定期取样测定相应指标。第1 组60 个果实,每次取样6个,用于测定果实表面色泽、硬度和可溶性固形物(SSC)、可滴定酸(TA)含量,测定完毕后同时留样液氮冷冻研磨后置于-80 ℃超低温冰箱保存,用于测定维生素C(Vc)含量和酶活性;第2 组固定30 个果实,用于测定失重率,观察虎皮病、腐烂情况等;第3 组固定10 个果实,用于测定呼吸强度、乙烯释放量,每次取样从筐内随机选取3 个果实,测定后放回。每个处理3次重复,贮藏当天测定第1次指标,之后常温处理每10 d取1次样,直至60 d;低温处理每隔15 d取1次样,直至120 d。
1.2.2 指标测定(1)果实硬度和表面色泽。果实硬度采用GS-15 型水果质地分析仪测定,测量头直径10 mm,单位为kg·cm-2;果实表面色泽采用Minolta CR-400型全自动色差仪测定。
(2)可溶性固形物、可滴定酸和维生素C 含量。可溶性固形物和可滴定酸含量采用ATAGO 型糖酸一体机测定;维生素C 含量参照曹建康等[17]的方法采用紫外分光光度计法测定,反应物在波长534 nm处具有最大吸收峰,根据吸光度值,在标准曲线上查出样品提取液中维生素C含量,按公式(1)计算果实组织中维生素C 含量,果实组织中维生素C 含量以100 g样品中含有的维生素C的质量表示,即mg·100 g-1。

式中,V表示样品提取液总体积(mL);m'表示由标准曲线求得的维生素C的质量(μg);Vs表示滴定时所用样品提取液体积(mL);m表示样品质量(g)。
(3)呼吸强度和乙烯释放速率。呼吸强度通过便携式二氧化碳检测仪测量密闭真空干燥器中CO2的释放量来计算。果实质量通过电子天平称量,苹果体积采用排水法测量,将苹果和便携式二氧化碳检测仪放于气密性良好的干燥器中,密闭处涂抹凡士林并用保鲜膜封口,记录CO2 初始浓度,每隔20 min 记数1 次,直至1 h。根据公式(2)计算呼吸强度。
式中,R 表示呼吸强度(mg·kg-1·h-1);Vt 表示干燥器容积(mL);Vs表示苹果果实体积(mL);C表示CO2浓度测定值;M 表示果实质量(kg);T 表示测量时间(h);1.96 表示CO2的摩尔质量/摩尔体积之比(=44/22.4,按标准状况下计算)。
乙烯释放速率通过抽取呼吸强度测定1 h 后干燥器顶部气体1 mL 注入Trace GCUltra 型气相色谱仪中测定,气相色谱仪参数设定:载气为氮气,检测器温度为140 ℃,进样口的温度为90 ℃,氮气流量30 mL·min-1,氢气流量30 mL·min-1,空气流量为300 mL·min-1。
(4)失重率和发病率。失重率用果实贮藏期间质量的下降率表示,果实质量采用电子天平称量。每次取样时称重,利用差重法进行计算,结果用%表示,计算公式(3):
从固定的第2 组筐中,定期观察病害发生情况并记录,通过公式(4)计算发病率。
(5)过氧化氢酶(CAT)、多酚氧化酶(PPO)和过氧化物酶(POD)活性测定。参照曹建康等[17]的方法测定过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性,在240 nm处测定吸光值;采用邻苯二酚法[17]测定多酚氧化酶(PPO)活性,产物最大光吸收峰出现在420 nm处;采用愈创木酚法[17]测定过氧化物酶(POD)活性,产物最大光吸收峰出现在470 nm处。
1.3 统计分析方法
采用Microsoft Excel 2010 进行数据整理、计算和作图。
2 结果与分析
2.1 瑞雪苹果贮藏期间品质变化
2.1.1 不同贮藏条件对瑞雪苹果硬度、失重率的影响 如图1-A所示,瑞雪苹果刚采摘时,果实硬度较大,达到7.51 kg·cm-2,随着贮藏时间的增加,0 ℃和常温贮藏果实的硬度均下降。常温贮藏前30 d,果实硬度下降较快,贮藏60 d,果实硬度下降到6.38 kg·cm-2。0 ℃条件下果实硬度下降较为平缓,贮藏60 d 时,果实硬度为6.77 kg·cm-2,保持较好;贮藏120 d时,硬度为6.38 kg·cm-2,仍保持较高硬度。
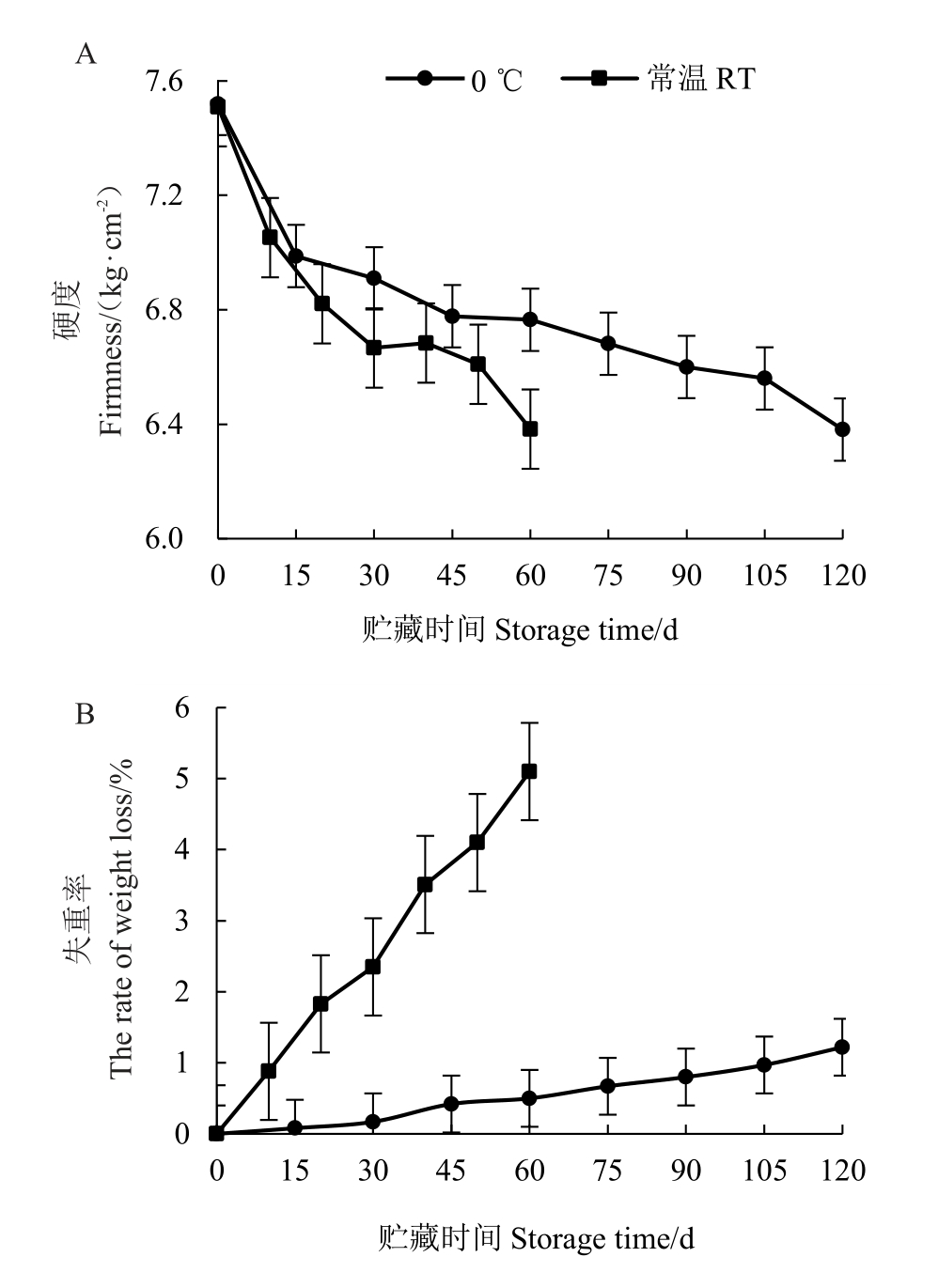
图1 不同贮藏温度下果实硬度、失重率的变化
Fig.1 Changes of fruit hardness and weight loss rate at different storage temperatures
如图1-B 所示,随着贮藏时间的增加,常温贮藏果实的失重率迅速增加,贮藏60 d 时,失重率为5.1%,果实基本失去贮藏价值。而0 ℃冷藏果实在贮藏期间失重率变化很小,贮藏60 d 时为0.50%,贮藏120 d 时,也仅仅下降了1.22%,能较好地降低果实的失重率,改善果实失水状况,保持果实品质。
2.1.2 不同贮藏条件对瑞雪苹果表面色泽的影响果实的表面色泽通常用L*、a*和b*值来表示,其中L*表示光泽明亮度(L*数值越大,果实表面色泽越明亮,反之越暗淡);a*表示红绿值(通常表示果实底色的红绿程度,a*为正,底色偏红,反之偏绿);b*表示蓝黄值(通常表示果实面色的蓝黄程度,b*越大,果实面色越偏黄)。
如图2-A所示,随着贮藏时间的增加,果实的L*值呈现不断上升的趋势,表明贮藏过程中瑞雪苹果果皮的光泽亮度不断增加。0 ℃贮藏90 d 后,果实的L*值下降,果皮色泽开始变暗。如图2-B所示,随着贮藏时间的增加,0 ℃冷藏和常温贮藏果实的a*值呈现不断上升的趋势,且a*为负值,说明瑞雪苹果贮藏过程中果皮绿色逐渐消退,且0 ℃贮藏能明显地减缓苹果表皮a*值的上升,保持果实表面的绿色。如图2-C所示,在贮藏期间,常温贮藏果实b*值呈现上升趋势,表明常温贮藏果实果皮面色逐渐变黄,0 ℃冷藏果实b*值基本无变化,表明果实面色变化不大,变黄缓慢,冷藏条件下能保持果实原有的颜色。

图2 不同贮藏温度下果实表面色泽L*值、a*值和b*值的变化
Fig.2 Changes of L*,a*and b*of fruit surface color at different storage temperatures
2.1.3 不同贮藏条件对瑞雪苹果可溶性固形物、可滴定酸、Vc 含量的影响 如图3 所示,随着贮藏时间的增加,瑞雪苹果的可溶性固形物含量(w,后同)在贮藏期间都呈现先升后降的变化趋势,常温处理在贮藏10 d 时达到最高(16.71%),贮藏10~30 d 含量都保持较高,30 d 之后快速下降,贮藏60 d 时,果实可溶性固形物含量为14.56%。0 ℃贮藏瑞雪果实在贮藏60 d时达到峰值(17.48%),此时苹果的甜度最高,之后逐渐下降,0 ℃贮藏120 d,果实可溶性固形物含量为15.30%,果实品质维持较好(图3-A)。
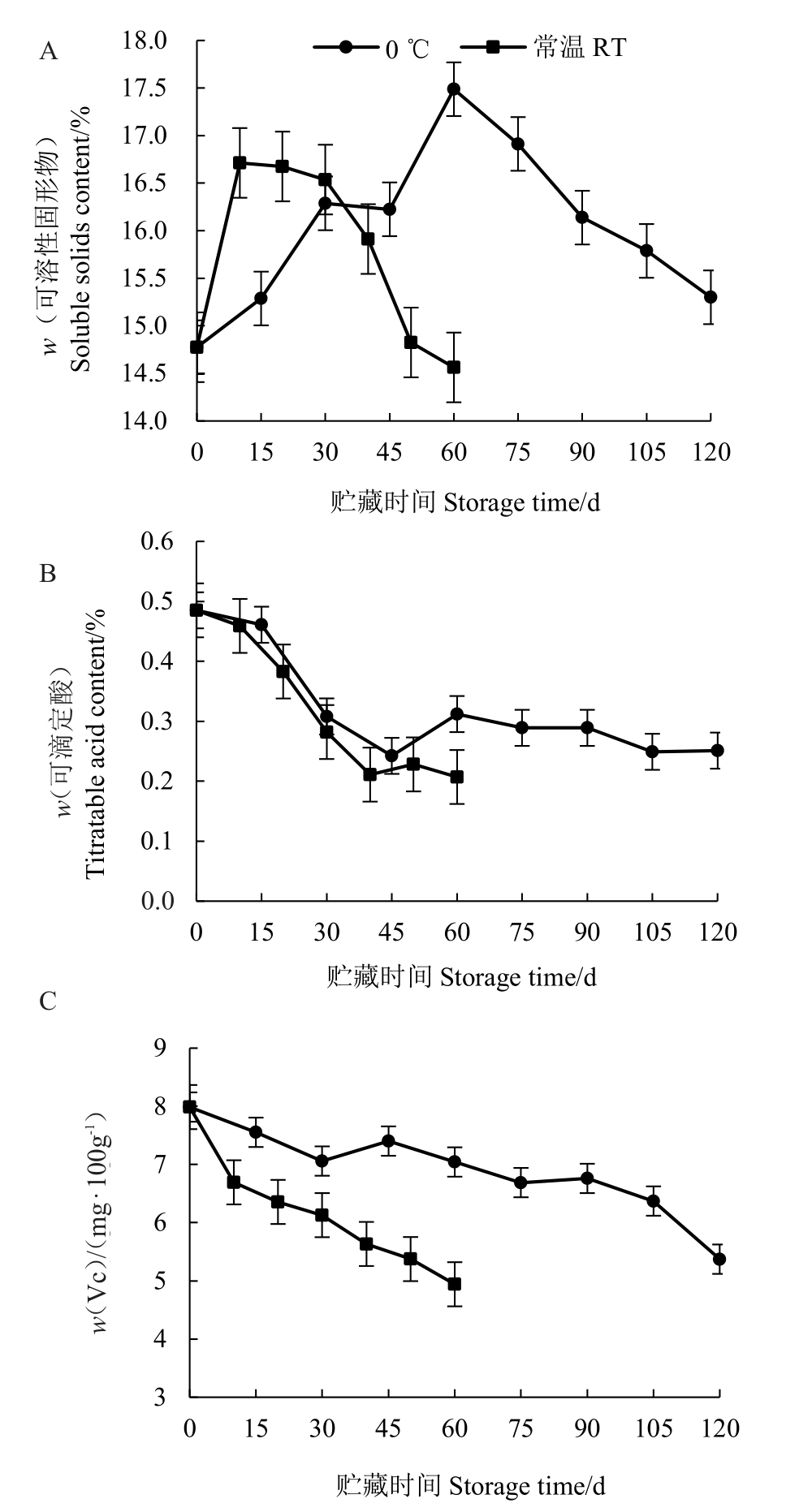
图3 不同贮藏温度下果实可溶性固形物、可滴定酸、Vc 含量的变化
Fig.3 The content of soluble solid,acid and Vc at different storage temperatures
如图3-B所示,瑞雪苹果刚采摘时,果实可滴定酸含量较高,为0.49%。随着贮藏时间的增加,果实的可滴定酸含量逐渐下降。常温贮藏前40 d,果实可滴定酸含量下降幅度较大,40 d 时为0.21%,40 d后趋于平稳,60 d时为0.20%。0 ℃贮藏前45 d可滴定酸含量下降幅度较大,45 d 时为0.24%,45 d 之后可滴定酸含量略有升高并趋于平稳,后期下降缓慢,120 d时为0.23%,相比45 d时仅下降了0.01%,表明0 ℃贮藏后期可以较好地保持瑞雪的可滴定酸含量。
如图3-C 所示,瑞雪苹果在贮藏过程中果实的Vc 含量逐渐下降,且常温贮藏果实下降速率更快。常温贮藏前15 d,Vc含量下降最快,贮藏60 d时,Vc含量由7.99 mg·100 g-1下降到4.94 mg·100 g-1。0 ℃冷藏条件下,贮藏30 d 时,Vc 含量略有上升之后下降较快,贮藏105 d之后也下降较快,105 d时含量为6.37 mg·100 g-1,120 d时下降到5.37 mg·100 g-1。
2.2 瑞雪苹果贮藏期间生理变化
2.2.1 不同贮藏条件对瑞雪苹果呼吸强度的影响如图4所示,随着贮藏时间的增加,瑞雪苹果的呼吸强度和乙烯释放量都呈现先升后降的规律。常温贮藏果实在开始贮藏后呼吸速率迅速增加,20 d 时达到呼吸高峰,高峰值为20.47 mg·kg-1·h-1,贮藏30 d至60 d,呼吸强度一直保持在较高水平,呼吸代谢旺盛;乙烯在贮藏40 d后释放量急速增加,50 d达到最大释放量后快速下降,峰值区间短,高峰值为285.76 μL·kg-1·h-1。0 ℃冷藏果实在贮藏期间呼吸强度较低,呼吸高峰出现在贮藏45 d 时,高峰值为3.85 mg·kg-1·h-1,达到峰值后逐渐下降,之后一直在较低水平;在贮藏期间乙烯释放量相对较少,且变化不是很大,乙烯高峰出现在贮藏后60 d,高峰值为80.51 μL·kg-1·h-1,贮藏105 d,出现第2次小高峰,高峰值为70.78 μL·kg-1·h-1。
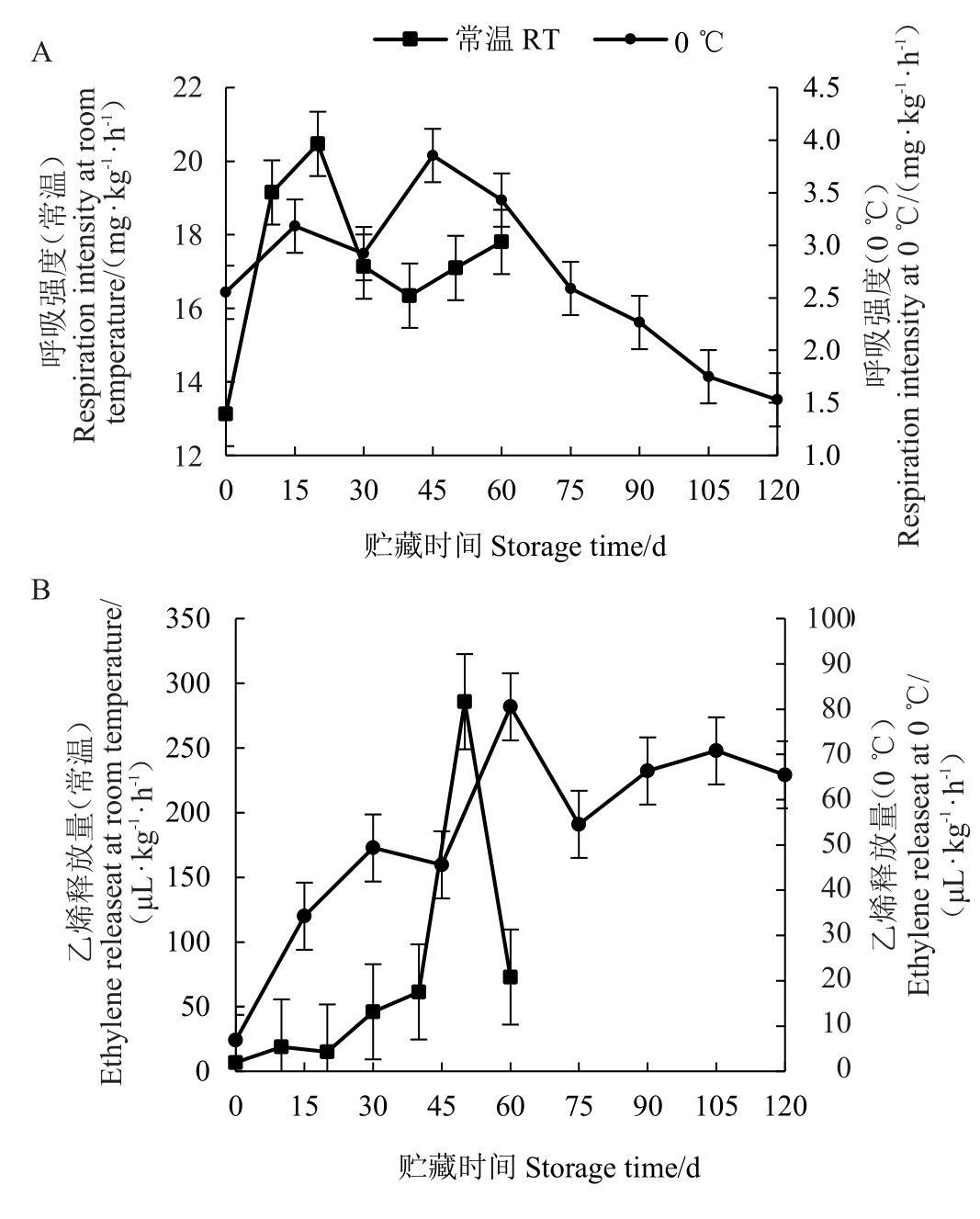
图4 不同贮藏温度果实呼吸强度、乙烯释放量的变化
Fig.4 Respiratory intensity and ethylene release of fruits at different storage temperatures
2.2.2 不同贮藏条件对瑞雪苹果过氧化氢酶(CAT)、多酚氧化酶(PPO)和过氧化物酶(POD)活性的影响 如图5所示,随着贮藏时间的增加,瑞雪苹果的过氧化氢酶、多酚氧化酶和过氧化物酶活性都呈现先上升后下降的变化趋势。常温贮藏前30 d时,CAT活性一直保持在较低水平,30 d之后过氧化氢酶活性出现显著变化并在40 d 时达到活性高峰,之后迅速下降到较低水平。0 ℃冷藏果实过氧化氢酶活性在贮藏后75 d 出现较大变化,高峰出现在贮藏90 d。常温贮藏前20 d,PPO 活性保持在较低水平,20 d 后多酚氧化酶活性迅速增加并在30 d 时达到活性高峰,0 ℃冷藏苹果,PPO活性在贮藏75 d时达到活性峰值。常温贮藏果实POD活性在贮藏30 d时达到活性高峰,0 ℃低温冷藏果实活性峰出现在75 d时。
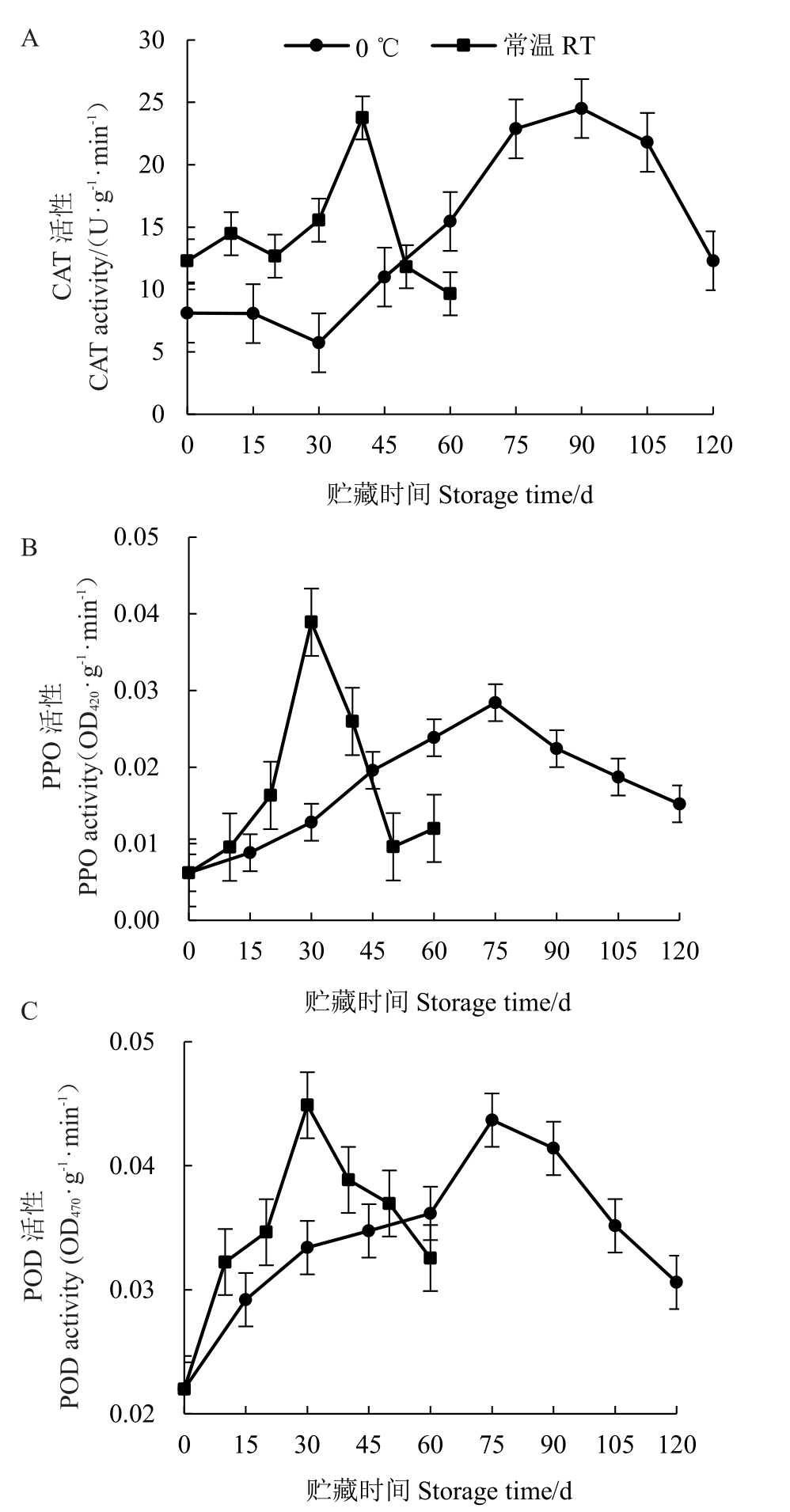
图5 不同贮藏温度果实CAT、PPO 和POD 活性的变化
Fig.5 Changes of CAT,PPO and POD activities in fruits at different storage temperatures
2.3 瑞雪苹果贮藏期间发病情况
如图6及表1所示,常温贮藏10 d开始出现苦痘病,20 d出现梗洼处果面褐变,30 d开始出现虎皮病症状和果皮油腻化(图7),40 d果实出现灰霉病,贮藏60 d发病率达20%,此时贮藏果实油腻化严重,主要病害虎皮病发病率10%。0 ℃贮藏果实前105 d,没有病害发生,贮藏105 d时出现轻微果柄处果面褐变,120 d时出现虎皮病,发病率为6.67%。
表1 不同贮藏温度下瑞雪苹果发病情况统计
Table 1 Statistics on the occurrence of Ruixue apple diseases at different storage temperatures
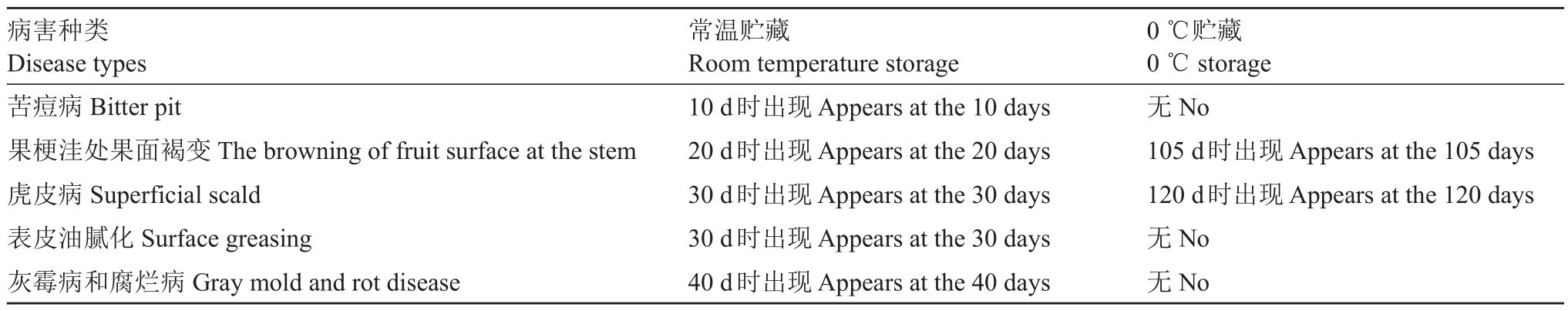
病害种类Disease types苦痘病Bitter pit果梗洼处果面褐变The browning of fruit surface at the stem虎皮病Superficial scald表皮油腻化Surface greasing灰霉病和腐烂病Gray mold and rot disease常温贮藏Room temperature storage 10 d时出现Appears at the 10 days 20 d时出现Appears at the 20 days 30 d时出现Appears at the 30 days 30 d时出现Appears at the 30 days 40 d时出现Appears at the 40 days 0 ℃贮藏0 ℃storage无No 105 d时出现Appears at the 105 days 120 d时出现Appears at the 120 days无No无No
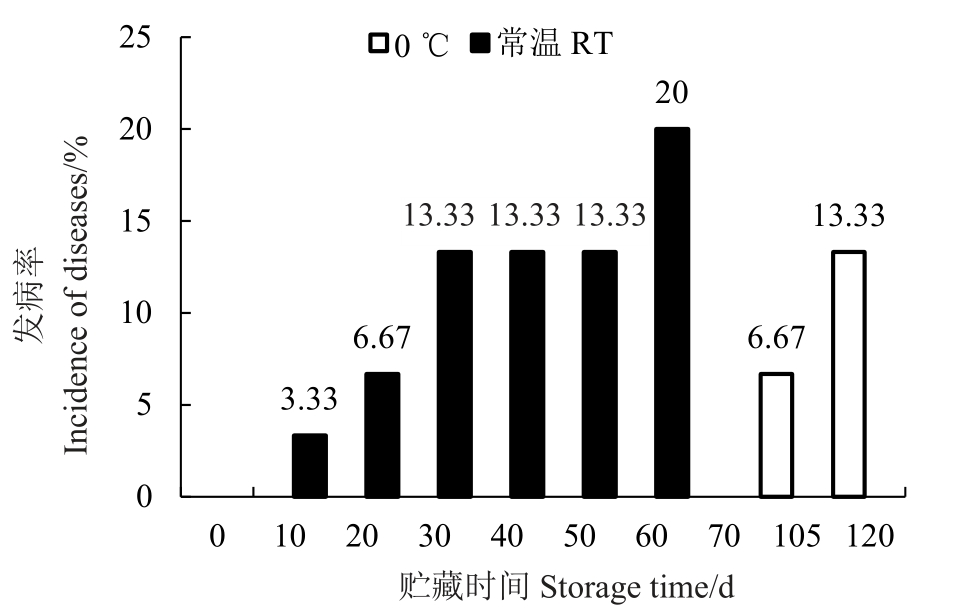
图6 不同贮藏温度果实发病情况
Fig.6 Disease status of fruits at different storage temperatures
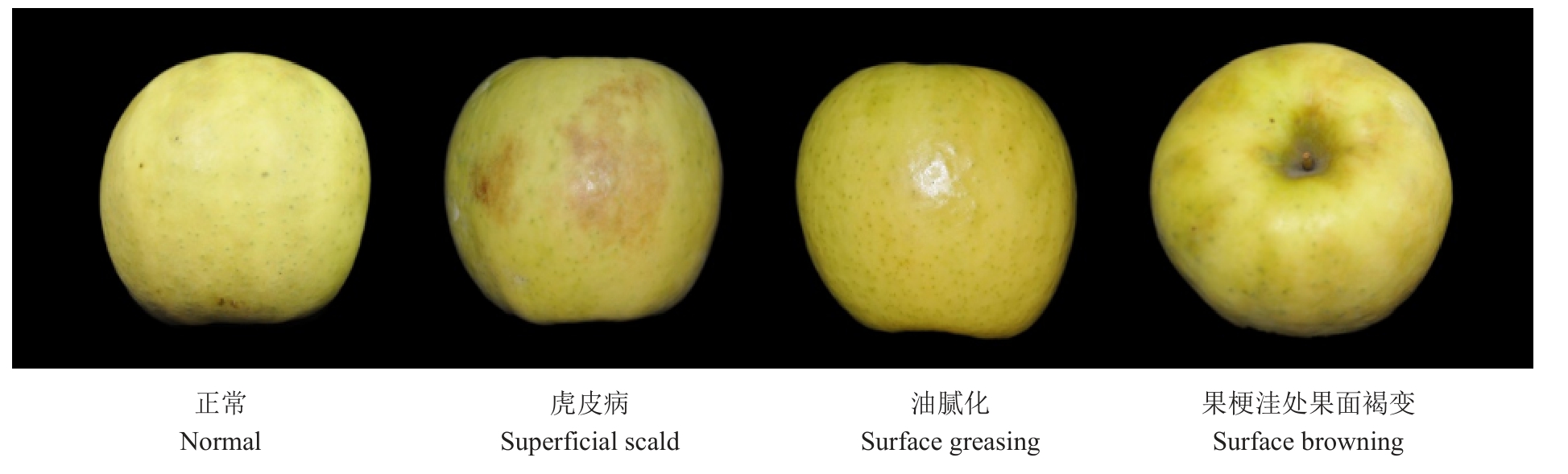
图7 瑞雪苹果发病情况
Fig.7 The occurrence of Ruixue apple diseases
3 讨 论
苹果采后耐贮性与果实呼吸强度和相关酶活性密切相关,通常苹果采后呼吸强度越高,则营养物质消耗越快,果实耐贮性越差、保鲜期越短[18]。笔者发现,0 ℃贮藏呼吸峰和乙烯峰分别比低温贮藏提前了20 d和10 d,且峰值更小,这是因为低温可以抑制苹果的呼吸强度,减缓呼吸跃变高峰的到来。对于果实而言,适宜的低温能有效抑制果实的衰老,但温度过低则会造成果实的生理伤害[19]。魏树伟[20]的研究得出,0 ℃贮藏条件下,新红星、嘎拉和红富士的呼吸高峰和乙烯高峰均低于对照,李学进等[21]研究得出,20 ℃贮藏40 d,糖心苹果TSS、TA、SS 含量及硬度明显下降,糖心部位出现褐变现象,0 ℃贮藏80 d,糖心部位无褐变现象,糖心苹果仍具有商品价值。本研究中,0 ℃贮藏过程中没有出现冷害或其他较严重问题,瑞雪苹果适宜在0 ℃条件下冷藏。
瑞雪苹果在低温条件下的耐贮性较好也可以从保护酶活性上看出来,CAT、PPO 和POD 是与果实成熟衰老相关的酶,常温贮藏果实酶活性在贮藏30~40 d 出现较大变化,且活性值高于低温,说明此时果实可能已经受到伤害,物质分解较快,激活果实体内的抗性系统产生大量的酶来帮助机体抵抗不良逆境,抵御细胞的衰老,PPO活性在30 d左右出现较大变化,并达到峰值,也可能与30 d出现虎皮病和果面褐变有关,这与刘丹丹等[22]的研究结果一致。虎皮病通常表现为果面出现褐色微凹陷且不规则的烫伤状病斑,随贮藏时间的延长,褐变加重且病斑的面积不断扩大,严重影响果实的商品价值[23]。多数研究认为虎皮病的发生与α-法尼烯及其氧化产物的积累有关[24],不同品种对虎皮病的抗病能力有所不同,一般而言,虎皮病易在浅色品种上发病,如瑞雪、澳洲青苹,且发病部位多在非着色面。其他采前因素和采后因素也是影响虎皮病发病的重要因素。
齐秀东等[25]研究得出富士苹果在0 ℃贮藏时呼吸峰出现在42 d,推测瑞雪苹果可能比富士苹果耐贮。0 ℃低温贮藏虽然能较大程度的延缓瑞雪苹果鲜品质变劣,但随着贮藏时间的延长,贮藏后期也开始发病和营养物质流失,所以0 ℃低温冷藏苹果在贮藏90 d内出库销售可以保持其最好的品质。贮藏120 d 时,其各项指标基本都保持的较好,贮藏后期也可结合其他处理延长其贮藏期,实现果品市场的连续供应。
4 结 论
瑞雪苹果在0 ℃条件下贮藏,能够较好地维持果实硬度、SSC、TA、Vc 含量等指标,显著降低失重率,120 d之内,各项指标保持较好,120 d以后,开始出现虎皮病。常温贮藏30 d 之内,果实品质维持较好,30 d 之后,营养物质流失严重,虎皮病、苦痘病、腐烂病发病严重,果柄褐变增多。因此,瑞雪苹果在0 ℃条件下耐贮性较好,120 d之内各项品质保持最佳,常温放置30 d后品质明显下降,应尽快销售。
[1]高华,赵政阳,王雷存,刘振中,武月妮,杨亚州,张伯虎.苹果新品种瑞雪的选育[J].果树学报,2016,33(3):374-377.GAO Hua,ZHAO Zhengyang,WANG Leicun,LIU Zhenzhong,WU Yueni,YANG Yazhou,ZHANG Bohu.Breeding of a new apple variety Ruixue[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2016,33(3):374-377.
[2]李娅楠,王雷存.八个苹果新优品种在陕西渭北的栽培表现[J].西北园艺(果树),2020(6):38-40.LI Yanan,WANG Leicun.Cultivation performance of eight new superior apple varieties in Weibei,Shaanxi[J].Northwest Horticulture(Fruits),2020(6):38-40.
[3]郭梦月.苹果新品种‘瑞阳’、‘瑞雪’主要果实特性研究[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2017.GUO Mengyue.Study on the main fruit characteristics of new apple varieties‘Ruiyang’and‘Ruixue’[D].Yangling:Northwest A&F University,2017.
[4]陕西苹果新品种‘瑞阳’‘瑞雪’通过国家审定[J].农村百事通,2019(17):21.ShaanxiApple‘Ruiyang’‘RuiXue’passedthenationalapprove[J].Nongcun Baishitong,2019(17):21.
[5]石游,陈淑英,刁永强,吴松梅.引入伊犁河谷的8 个苹果品种抗寒性评价[J].经济林研究,2020,38(2):147-153.SHI You,CHEN Shuying,DIAO Yongqiang,WU Songmei.Evaluation of cold resistance of eight apple varieties introduced into Yili Valley[J].Non-Wood Forest Research,2020,38(2):147-153.
[6]赵桂琴.部分苹果新品种矮化幼树在陇东地区的生长表现[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2015.ZHAO Guiqing.Growth performance of some new apple varieties dwarf saplings in Longdong region[D].Yangling:Northwest A&F University,2015.
[7]徐华.‘瑞阳’‘瑞雪’苹果在不同产区主要品质的差异分析[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2019.XU Hua.Analysis on the difference of main quality of‘Ruiyang’and‘Ruixue’apples in different production areas[D].Yangling:Northwest A&F University,2019.
[8]王世明.不同果袋对苹果果实品质的影响[J].中国果业信息,2020(10):64.WANG Shiming.Effects of different fruit bags on apple fruit quality[J].China Fruit News,2020(10):64.
[9]樊淼淼,陶茹,张天皓,王辉,王爽,孙鲁龙,高华.不同果袋对瑞雪苹果果实品质的影响[J].果树学报,2020,37(9):1326-1335.FAN Miaomiao,TAO Ru,ZHANG Tianhao,WANG Hui,WANG Shuang,SUN Lulong,GAO Hua.Effects of different fruit bags on fruit quality of‘Ruixue’apple[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2020,37(9):1326-1335.
[10]李静.苹果新品种瑞雪专用育果袋的筛选[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2019.LI Jing.Screening of special breeding bags for new apple variety Ruixue[D].Yangling:Northwest A&F University,2019.
[11]邓瑞,袁仲玉,夏雪,刘振中,史涛,高华,赵政阳.套袋对‘瑞雪’苹果果实品质的影响[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2018,46(7):117-123.DENG Rui,YUAN Zhongyu,XIA Xue,LIU Zhenzhong,SHI Tao,GAO Hua,ZHAO Zhengyang.Effects of bagging on fruit quality of‘Ruixue’apple[J].Journal of Northwest A& F University(Natural Science Edition),2018,46(7):117-123.
[12]邓瑞.套袋对‘瑞阳’‘瑞雪’苹果果实品质的影响[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2017.DENG Rui.Effects of bagging on fruit quality of‘Ruiyang’and‘Ruixue’apple[D].Yangling:Northwest A&F University,2017.
[13]王爽,孙鲁龙,王辉,樊淼淼,郝妮妮,孟智鹏,赵政阳.套袋瑞雪苹果果皮褐变发生规律及其与温度的关系[J].果树学报,2021,38(5):692-701.WANG Shuang,SUN Lulong,WANG Hui,FAN Miaomiao,HAO Nini,MENG Zhipeng,ZHAO Zhengyang.The occurrence of browning in bagged apples and its relationship with temperature[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2021,38(5):692-701.
[14]党美乐,张旭,朱珍珍,刘俊灵,郭延平,赵政阳.‘瑞阳’和‘瑞雪’苹果及其亲本果实中主要营养成分的比较分析[J].果树学报,2020,37(1):50-58.DANG Meile,ZHANG Xu,ZHU Zhenzhen,LIU Junling,GUO Yanping,ZHAO Zhengyang.Comparative analysis of main nutrients in‘Ruiyang’and‘Ruixue’apples and their parents [J].Journal of Fruit Science,2020,37(1):50-58.
[15]冯帅帅.瑞雪苹果香气物质测定及相关基因表达分析[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2020.FENG Shuaishuai.Determination of aroma compounds and expression analysis of related genes in Ruixue apple[D].Yangling:Northwest A&F University,2020.
[16]刘俊灵.苹果新品种瑞雪果实挥发性香气物质分析及其遗传特性初探[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2019.LIU Junling.Analysis of volatile aroma compounds in the fruit of a new apple variety Ruixue and its genetic characteristics[D].Yangling:Northwest A&F University,2019.
[17]曹建康,姜微波,赵玉梅.果蔬采后生理生化实验指导[M].北京:中国轻工业出版社,2013.CAO Jiankang,JIANG Weibo,ZHAO Yumei.Experiment guidance of postharvest physiology and biochemistry of fruits and vegetables[M].Beijing:China Light Industry Press,2013.
[18]LIN Y Z,LI N,LIN H T.Effects of chitosan treatment on the storability and quality properties of longan fruit during storage[J].Food Chemistry,2020,30(6):125-127.
[19]李超,王亮,赵猛,焦旋,王春生.不同冰温温度对山楂果实生理及品质的影响[J].中国农学通报,2017,33(15):150-155.LI Chao,WANG Liang,ZHAO Meng,JIAO Xuan,WANG Chunsheng.Effects of different ice temperature and temperature on physiology and quality of hawthorn fruit[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2017,33(15):150-155.
[20]魏树伟.套袋苹果贮藏生理及香气变化研究[D].泰安:山东农业大学,2008.WEI Shuwei.Study on physiological and aroma changes of bagged apple during storage[D].Tai’an:Shandong Agricultural University,2008.
[21]李学进,刘紫韫,李喜宏,郑艳丽,范江明,贾红霞.不同贮藏温度对套袋糖心富士苹果采后品质的影响[J].保鲜与加工,2021,21(5):8-13.LI Xuejin,LIU Ziyun,LI Xihong,ZHEN Yanli,FAN Jiangming,JIA Hongxia.Effects of different storage temperatures on postharvest quality of baggage-sugared Fuji apple[J].Storage and Process,2021,21(5):8-13.
[22]刘丹丹,南学平,曹格妮,郑爱英,景姗.苹果虎皮病的研究现状探析:基于CNKI 40 年间学术论文的内容分析[J].河南农业,2021,10(35):43-45.LIU Dandan,NAN Xueping,CAO Geni,ZHENG Aiying,JING Shan.Research status of apple tiger skin disease based on CNKI research contents analysis[J].Agriculture of Henan,2021,10(35):43-45.
[23]刘少华.AVG 和CTM 处理对红星苹果虎皮病的影响[D].泰安:山东农业大学,2020.LIU Shaohua.Effects of AVG and CTM treatment on tiger skin disease of red star apple[D].Tai’an:Shandong Agricultural University,2020.
[24]蒋帅,周会玲,刘焕,贺军花,马利菁.苹果冷藏期间虎皮病发病原因及防治方法[J].北方园艺,2017(19):179-183.JIANG Shuai,ZHOU Huiling,LIU Huan,HE Junhua,MA Lijing.Causes and prevention of tiger skin disease during apple refrigeration[J].Northern Horticulture,2017(19):179-183.
[25]齐秀东,魏建梅.冷藏和乙烯处理对采后苹果果实糖代谢及关键基因表达的调控[J].现代食品科技,2015,31(7):137-145.QI Xiudong,WEI Jianmei.Effects of cold storage and ethylene treatment on sugar metabolism and key gene expression in postharvest apple[J].Modern Food Science and Technology,2015,31(7):137-145.