菠萝[Ananas comosus(L.)Merr.]属于凤梨科凤梨属多年生单子叶常绿草本植物,原产于南美洲,是全球三大热带水果之一。我国是菠萝生产和消费大国,但不是菠萝贸易强国[1],据统计,全国菠萝种植面积的80%是皇后类品种巴厘[2],该品种已种植80多年,在品质和外观等方面缺乏竞争力[3]。品种单一严重制约了我国菠萝产业的发展,需要选育新的优良的品种满足市场需求。因此,需要研究菠萝种质资源的各性状变异情况,发掘优异种质,为育种亲本的选择提供科学数据。果实作为重要的商品器官,果实性状的鉴定评价犹为重要。近年来,我国生产企业和科研机构等从境外引进菠萝种质进行试种应用,市场上不断出现新的品种,市场的管理和规范也需要对进入流通和市场领域中的果实仅通过果实外观实现品种的快速识别和鉴定。
菠萝果实性状包括外观性状和内在品质性状两个方面。内在品质主要包括果实的糖、酸含量以及糖酸比、香气、果肉纤维素含量、矿质成分和维生素含量等;外观性状包括果实大小、形状、果实颜色、果眼大小、果眼深度等,这些性状也是消费者购买鲜果的重要依据。贺军虎等[4]对10份菠萝种质资源的株高、叶长、叶刺的多少、果实的大小、口感、风味等果实品质进行描述和评价,结果表明上海2 号是较好的鲜食和加工皆宜品种,品种ST 口感较好,是一个优良的鲜食品种;张阳梅等[5]利用主成分分析的方法对11 份菠萝种质资源果实的单果质量、可食率、可滴定酸和可溶性固形物含量等9个性状进行评价和比较,结果显示,Pattawia、冬蜜、无刺卡因、甜蜜蜜4 个品种综合表现优良;严程明等[6]对5 个菠萝品种的果眼深度和可溶性糖、可滴定酸和可溶性固形物含量进行比较分析,结果表明黄金菠萝的果实品质最优。还有不少研究者对不同品种菠萝果实的某些单一品质进行研究和评价,如陆新华等[7-8]采用高效液相色谱法分别对50 份菠萝种质果实中可溶性糖组分和含量及40 份菠萝种质果实中的有机酸组分和含量进行测定分析,以比较不同类群及种质间的差异和特点。魏长宾等[9]对6 个菠萝品种香气成分及特征进行分析,李苗苗等[10]对不同品种菠萝的维生素组分及含量进行了评价和比较,杨祥燕等[11]对菠萝果实的颜色及色素组分进行了研究。这些对菠萝果实性状的评价多集中在内在品质性状方面,而对菠萝小果大小及果眼深度等外观性状的研究却少见报道,也缺乏通过果实外观性状进行种质鉴定的方法。
笔者在本研究中以18份菠萝种质为材料,通过测量单果质量、果实横径、果实纵径、果眼深、小果宽、小果高、果心直径、小果数、果形指数等9个果实外观性状,对这18 份菠萝种质进行比较和分析,在筛选外观品质优良的种质同时分析这些性状在种质内和种质间的变异情况,并对这些性状进行相关性分析,探究各性状之间的关联,为选育品种和通过果实外观性状进行种质识别鉴定提供科学依据。
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料
18份菠萝种质分别是上海2号、开英1号、广西引观赏类红果、Puket、Phetchaburi#2、观赏类红果、Giant Kew、印度5M、无刺卡因、黑菠萝、马来西亚沙捞越、Josapine、New Puket、越南无刺卡因、C180、Maroochy、N36、印度5Q。这些材料均来源于中国热带农业科学院南亚热带作物研究所内的农业农村部湛江菠萝种质资源圃。各种质生长期间管理水平一致,所有菠萝均于成熟期(果实基部1~2层小果的果皮呈黄色)采摘,每份种质5个果实作为1个重复,每份种质2个重复。
1.2 方法
参照《热带、南亚热带果树种质资源数据质量控制规范》[12],测量每个菠萝果实的单果质量、果实横径、果实纵径、小果数、果心直径,并对菠萝的小果大小(以小果高、小果宽来表示)、果眼深度、果心直径等性状的测定方法略作修改。具体操作如下:
单果质量(g):用电子天平称量果实质量(不包括冠芽部分);果实纵径(mm):用游标卡尺测量果实果基至果顶部分的距离;果实横径(mm):用游标卡尺测量果实横向最长部分直径;小果高(mm):使用游标卡尺分别测定菠萝果实纵向长度1/4、1/2 以及3/4 处各3 个小果的纵向长度,计算平均值;小果宽(mm):使用游标卡尺分别测定菠萝果实纵向长度1/4、1/2 以及3/4 处各3 个小果的横向长度,计算平均值;小果数:人工数每个果实的小果数;果眼深度(mm):分别选择菠萝果实纵向长度1/4、1/2 以及3/4处的各2个果眼,使用游标卡尺测量果实果眼从顶部至果眼底部的距离,计算平均值;果心直径(mm):使用游标卡尺分别测量菠萝果实纵向长度1/4、1/2 以及3/4 处菠萝果实的果心直径,计算平均值。
果形指数:果形指数=果实纵径/果实横径。
1.3 数据处理
利用Excel 2013 计算各外观性状的平均值、标准差及变异系数。利用SPSS 16.0 对数据进行方差分析和相关性分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 不同菠萝种质果实外观性状比较分析
18 份菠萝种质的果实外观性状测量结果见表1,其中黑菠萝单果质量最大,达到1 992.07 g,其次为开英1号、N36、无刺卡因和上海2号,这些种质单果质量均超过1500 g,且黑菠萝、开英1号、N36的单果质量显著高于其他种质;Josapine单果质量最小,仅为377.44 g,显著低于除印度5Q、观赏类红果、Giant Kew 以外的其他种质。18 份种质中,黑菠萝果实横径最大,果实横径达到156.24 mm,显著高于其他种质;开英1号果实纵径为193.23 mm,是18个品种中最大,显著高于除黑菠萝、无刺卡因和N36外的其他品种;马来西亚沙捞越的果形指数为1.40,是18个菠萝种质中最大的,上海2号的果形指数最小,仅为1.11。Phetchaburi#2 果心直径为36.01 mm,果心直径最大且显著高于其他种质,Josapine 果心直径11.8 mm,为18 个种质中最小的。方差分析显示这几个性状在种质间存在着显著差异(表1)。
表1 菠萝种质果实外观性状
Table 1 Fruit external traits of pineapple accessions
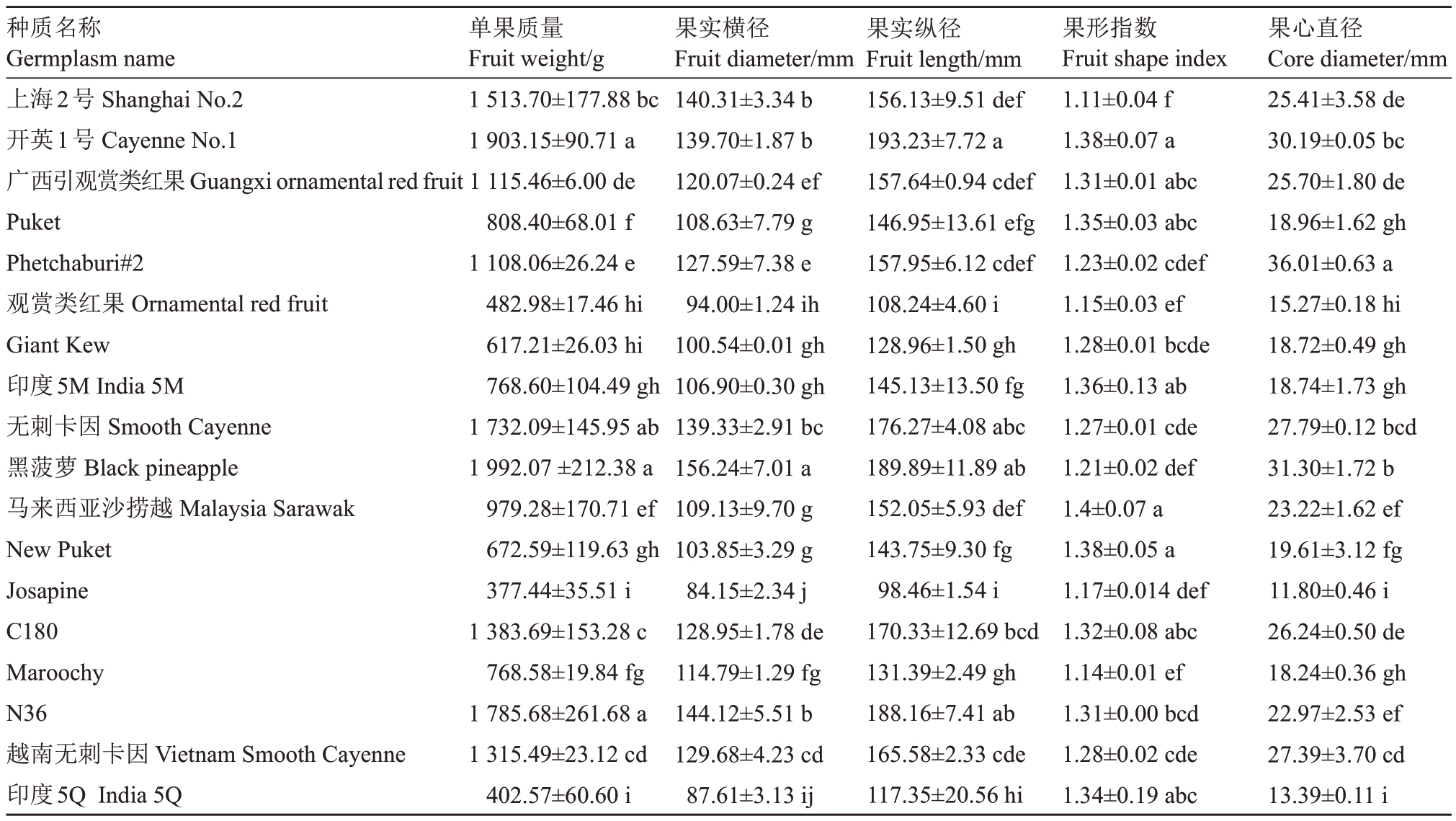
注:同列不同小写字母表示数据差异显著(p<0.05)。下同。
Note:Different lowercase letters in the same column represent significant difference(p<0.05).The same below.
种质名称Germplasm name上海2号Shanghai No.2开英1号Cayenne No.1广西引观赏类红果Guangxi ornamental red fruit Puket Phetchaburi#2观赏类红果Ornamental red fruit Giant Kew印度5M India 5M无刺卡因Smooth Cayenne黑菠萝Black pineapple马来西亚沙捞越Malaysia Sarawak New Puket Josapine C180 Maroochy N36越南无刺卡因Vietnam Smooth Cayenne印度5Q India 5Q果心直径Core diameter/mm 25.41±3.58 de 30.19±0.05 bc 25.70±1.80 de 18.96±1.62 gh 36.01±0.63 a 15.27±0.18 hi 18.72±0.49 gh 18.74±1.73 gh 27.79±0.12 bcd 31.30±1.72 b 23.22±1.62 ef 19.61±3.12 fg 11.80±0.46 i 26.24±0.50 de 18.24±0.36 gh 22.97±2.53 ef 27.39±3.70 cd 13.39±0.11 i单果质量Fruit weight/g 1 513.70±177.88 bc 1 903.15±90.71 a 1 115.46±6.00 de 808.40±68.01 f 1 108.06±26.24 e 482.98±17.46 hi 617.21±26.03 hi 768.60±104.49 gh 1 732.09±145.95 ab 1 992.07±212.38 a 979.28±170.71 ef 672.59±119.63 gh 377.44±35.51 i 1 383.69±153.28 c 768.58±19.84 fg 1 785.68±261.68 a 1 315.49±23.12 cd 402.57±60.60 i果实横径Fruit diameter/mm 140.31±3.34 b 139.70±1.87 b 120.07±0.24 ef 108.63±7.79 g 127.59±7.38 e 94.00±1.24 ih 100.54±0.01 gh 106.90±0.30 gh 139.33±2.91 bc 156.24±7.01 a 109.13±9.70 g 103.85±3.29 g 84.15±2.34 j 128.95±1.78 de 114.79±1.29 fg 144.12±5.51 b 129.68±4.23 cd 87.61±3.13 ij果实纵径Fruit length/mm 156.13±9.51 def 193.23±7.72 a 157.64±0.94 cdef 146.95±13.61 efg 157.95±6.12 cdef 108.24±4.60 i 128.96±1.50 gh 145.13±13.50 fg 176.27±4.08 abc 189.89±11.89 ab 152.05±5.93 def 143.75±9.30 fg 98.46±1.54 i 170.33±12.69 bcd 131.39±2.49 gh 188.16±7.41 ab 165.58±2.33 cde 117.35±20.56 hi果形指数Fruit shape index 1.11±0.04 f 1.38±0.07 a 1.31±0.01 abc 1.35±0.03 abc 1.23±0.02 cdef 1.15±0.03 ef 1.28±0.01 bcde 1.36±0.13 ab 1.27±0.01 cde 1.21±0.02 def 1.4±0.07 a 1.38±0.05 a 1.17±0.014 def 1.32±0.08 abc 1.14±0.01 ef 1.31±0.00 bcd 1.28±0.02 cde 1.34±0.19 abc
2.2 不同菠萝种质小果性状比较分析
不同菠萝种质小果性状测量结果见表2,N36、New Puket、Puket、Giant Kew和印度5M等种质的菠萝果眼深度显著高于其他菠萝种质,其中N36 的果眼最深,果眼深度达到10.68 mm,Josapine的果眼深度为7.72 mm,显著低于其他种质。上海2号和黑菠萝的小果高分别为31.93 mm和31.05 mm,显著高于其他种质,印度5Q 和New Puket 的小果高较小,分别为19.13 mm 和19.99 mm;上海2 号的小果宽为28.72 mm,显著高于其他种质,印度5Q 的小果宽最小,为16.26 mm。New Puket 的小果数最多,Josapine 的小果数最少。方差分析显示这几个性状在种质间存在显著差异(表2)。
表2 菠萝种质小果性状
Table 2 Fruitlets traits of pineapple accessions
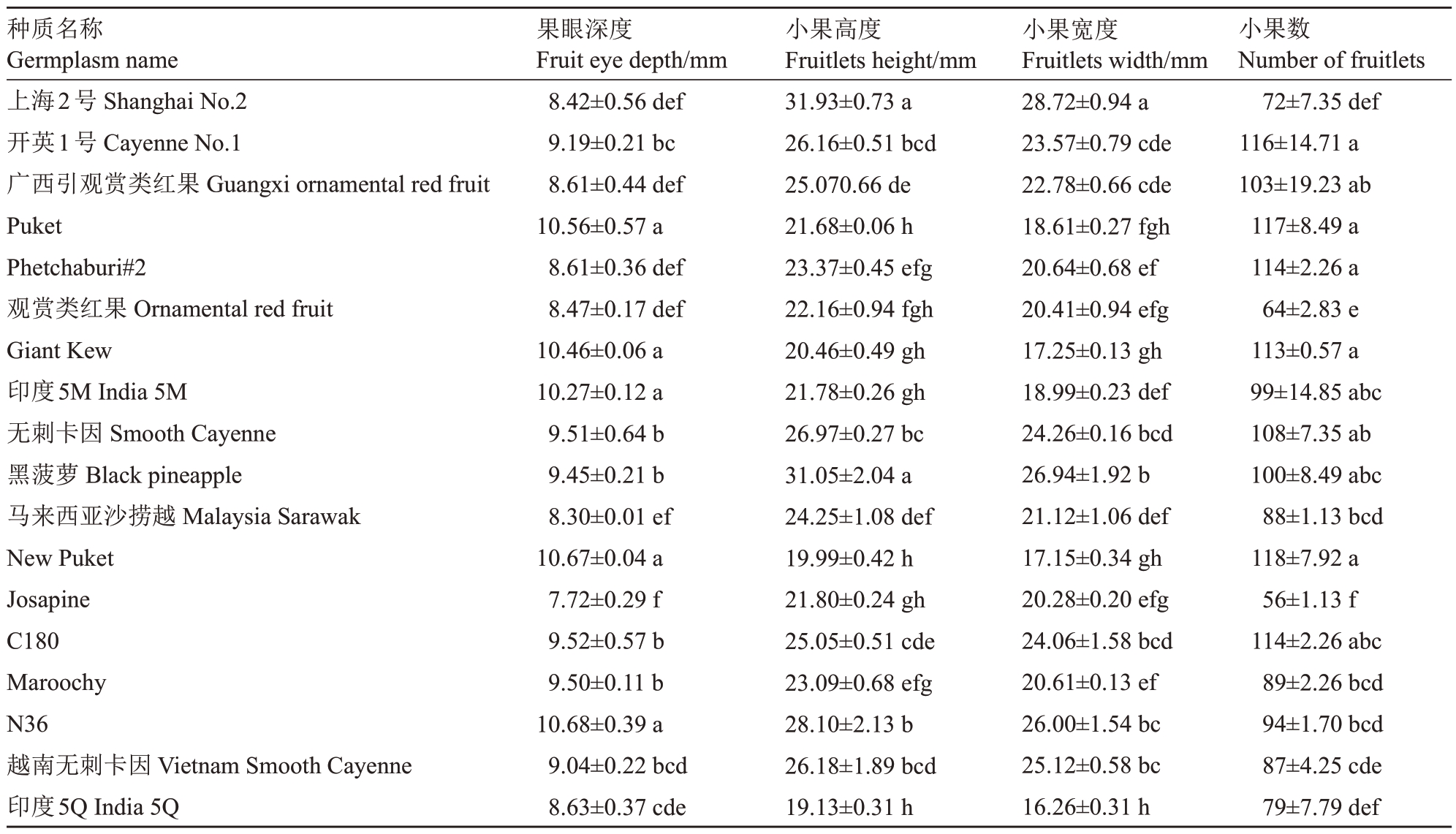
种质名称Germplasm name上海2号Shanghai No.2开英1号Cayenne No.1广西引观赏类红果Guangxi ornamental red fruit Puket Phetchaburi#2观赏类红果Ornamental red fruit Giant Kew印度5M India 5M无刺卡因Smooth Cayenne黑菠萝Black pineapple马来西亚沙捞越Malaysia Sarawak New Puket Josapine C180 Maroochy N36越南无刺卡因Vietnam Smooth Cayenne印度5Q India 5Q果眼深度Fruit eye depth/mm 8.42±0.56 def 9.19±0.21 bc 8.61±0.44 def 10.56±0.57 a 8.61±0.36 def 8.47±0.17 def 10.46±0.06 a 10.27±0.12 a 9.51±0.64 b 9.45±0.21 b 8.30±0.01 ef 10.67±0.04 a 7.72±0.29 f 9.52±0.57 b 9.50±0.11 b 10.68±0.39 a 9.04±0.22 bcd 8.63±0.37 cde小果高度Fruitlets height/mm 31.93±0.73 a 26.16±0.51 bcd 25.070.66 de 21.68±0.06 h 23.37±0.45 efg 22.16±0.94 fgh 20.46±0.49 gh 21.78±0.26 gh 26.97±0.27 bc 31.05±2.04 a 24.25±1.08 def 19.99±0.42 h 21.80±0.24 gh 25.05±0.51 cde 23.09±0.68 efg 28.10±2.13 b 26.18±1.89 bcd 19.13±0.31 h小果宽度Fruitlets width/mm 28.72±0.94 a 23.57±0.79 cde 22.78±0.66 cde 18.61±0.27 fgh 20.64±0.68 ef 20.41±0.94 efg 17.25±0.13 gh 18.99±0.23 def 24.26±0.16 bcd 26.94±1.92 b 21.12±1.06 def 17.15±0.34 gh 20.28±0.20 efg 24.06±1.58 bcd 20.61±0.13 ef 26.00±1.54 bc 25.12±0.58 bc 16.26±0.31 h小果数Number of fruitlets 72±7.35 def 116±14.71 a 103±19.23 ab 117±8.49 a 114±2.26 a 64±2.83 e 113±0.57 a 99±14.85 abc 108±7.35 ab 100±8.49 abc 88±1.13 bcd 118±7.92 a 56±1.13 f 114±2.26 abc 89±2.26 bcd 94±1.70 bcd 87±4.25 cde 79±7.79 def
2.3 菠萝果实外观性状变异情况
18份种质9个性状的总体变异系数能够体现不同菠萝种质间在这几个性状上的差异,其中单果质量变异系数最大,为48.62%,而果心直径(28.50%)、小果数(19.71%)、果实纵径(18.83%)、果实横径(17.54%)和小果宽(16.36%)变异系数也均高于15%,表明这几个指标在菠萝种质间具有较大差异。而果形指数和果眼深度在本研究中变异系数较小,低于15%,表明所试18 份种质在这二个性状上的变异相对前述性状较小(表3)。
表3 菠萝种质果实外观性状的变异情况
Table 3 Variation of appearance traits of pineapple fruit
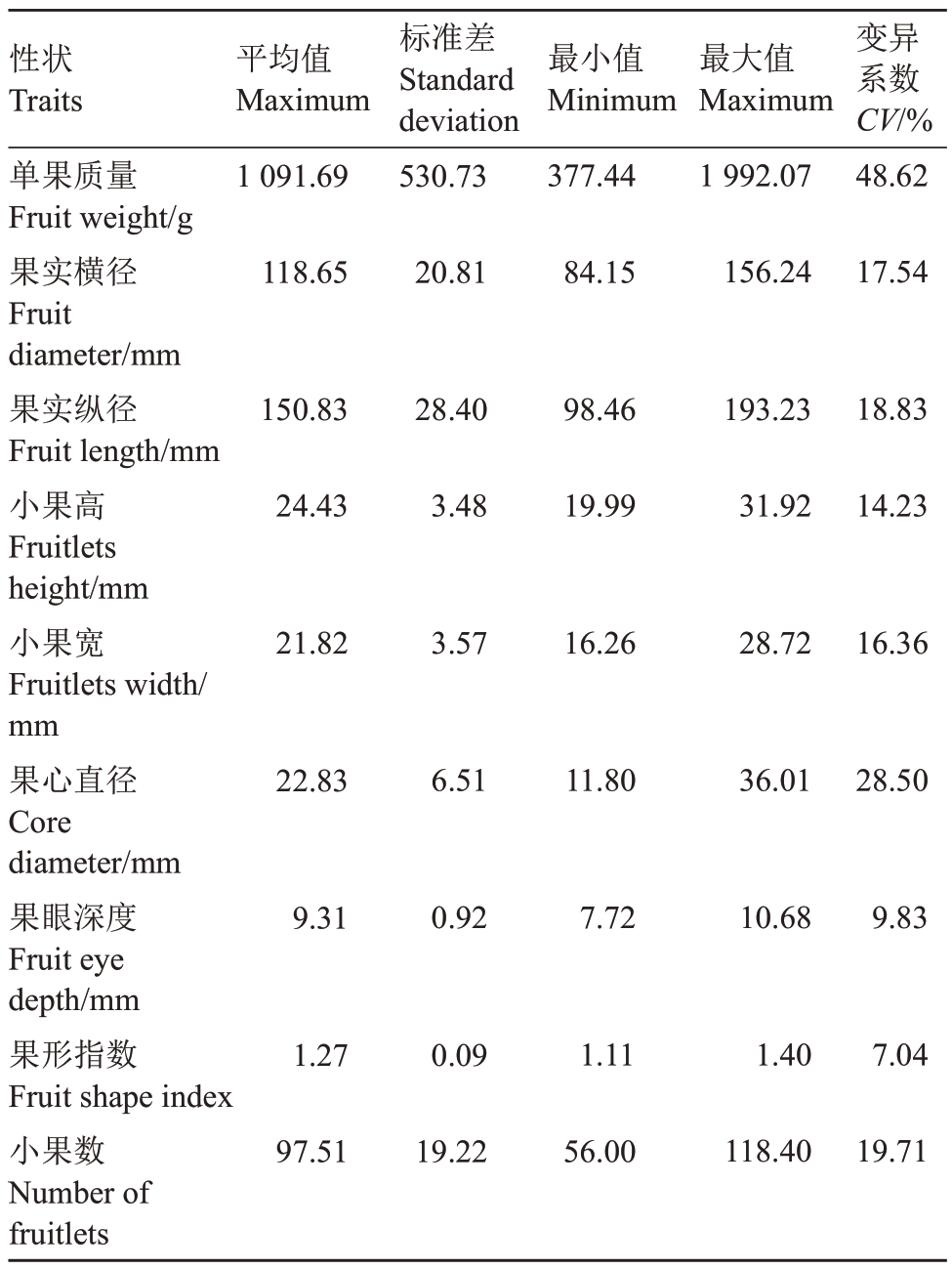
性状Traits单果质量Fruit weight/g果实横径Fruit diameter/mm果实纵径Fruit length/mm小果高Fruitlets height/mm小果宽Fruitlets width/mm果心直径Core diameter/mm果眼深度Fruit eye depth/mm果形指数Fruit shape index小果数Number of fruitlets平均值Maximum 1 091.69标准差Standard deviation 530.73最小值Minimum 377.44最大值Maximum 1 992.07变异系数CV/%48.62 118.65 20.81 84.15 156.24 17.54 150.83 28.40 98.46 193.23 18.83 24.43 3.48 19.99 31.92 14.23 21.82 3.57 16.26 28.72 16.36 22.83 6.51 11.80 36.01 28.50 9.31 0.92 7.72 10.68 9.83 1.27 0.09 1.11 1.40 7.04 97.51 19.22 56.00 118.40 19.71
各性状在不同菠萝种质内部的变异系数见表4,各性状种质内变异系数均小于种质间的变异系数。New Puket、马来西亚沙捞越、印度5M、印度5Q等的种质内单果质量变异系数均超过15%,比其他种质变异大,表明这些种质的单果质量受环境影响较大,有进一步通过改善环境增产的潜力,而广西引观赏类红果、越南无刺卡因等单果质量变异系数最小,表现出较高的稳产性能。另外广西引观赏类红果、Giant Kew 相对其他种质在小果数上具有较高的变异系数。New Puket 相对其他种质在果心直径上具有较高的变异系数,其他种质的各性状变异系数均小于15%,这些结果表明所试18份种质中多数种质在这些性状表现上受环境影响较小。
表4 菠萝种质果实各性状变异系数
Table 4 Variation coefficient of appearance traits of pineapple fruits %
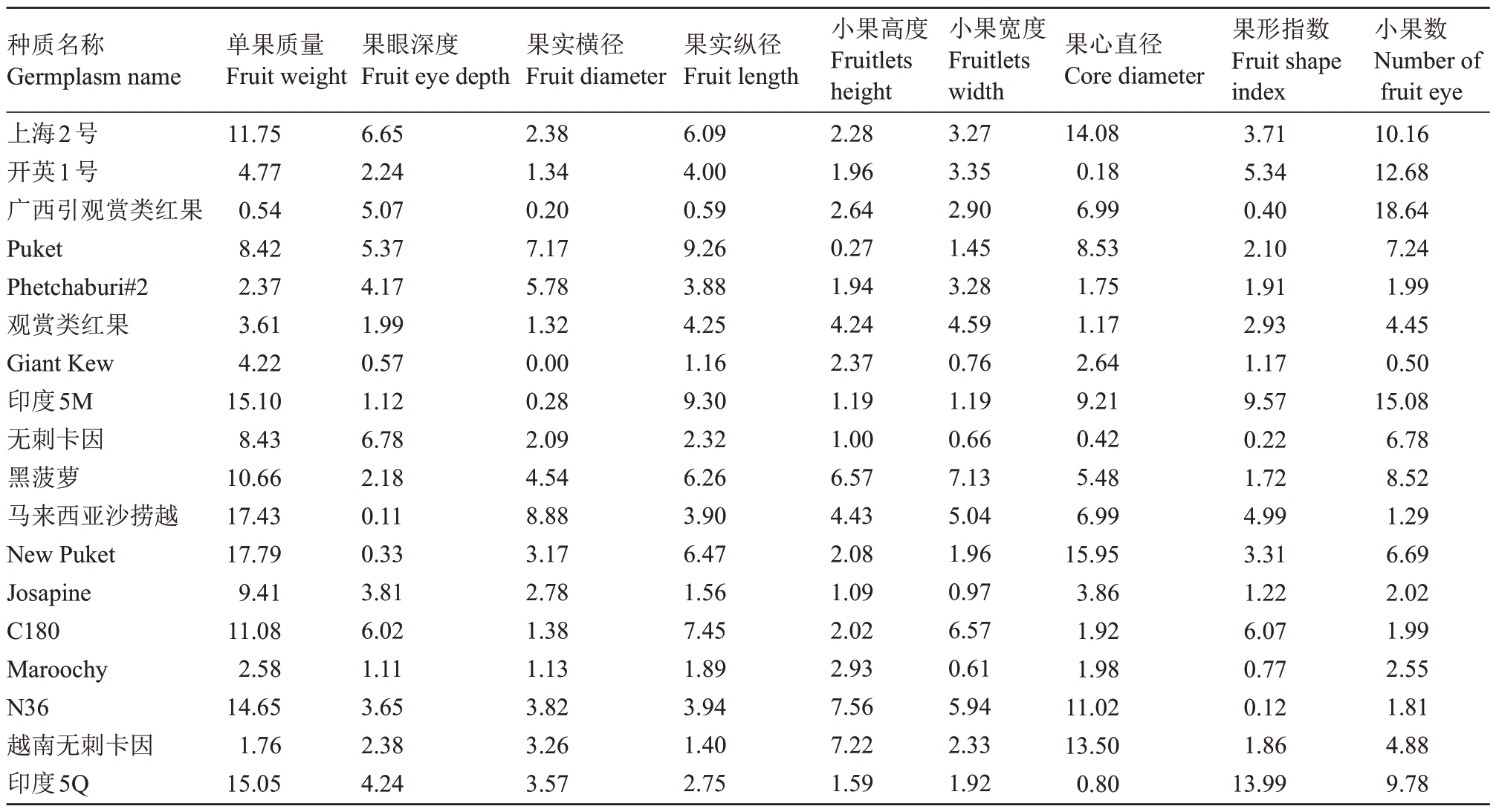
种质名称Germplasm name上海2号开英1号广西引观赏类红果Puket Phetchaburi#2观赏类红果Giant Kew印度5M无刺卡因黑菠萝马来西亚沙捞越New Puket Josapine C180 Maroochy N36越南无刺卡因印度5Q单果质量Fruit weight 11.75 4.77 0.54 8.42 2.37 3.61 4.22 15.10 8.43 10.66 17.43 17.79 9.41 11.08 2.58 14.65 1.76 15.05果眼深度Fruit eye depth 6.65 2.24 5.07 5.37 4.17 1.99 0.57 1.12 6.78 2.18 0.11 0.33 3.81 6.02 1.11 3.65 2.38 4.24果实横径Fruit diameter 2.38 1.34 0.20 7.17 5.78 1.32 0.00 0.28 2.09 4.54 8.88 3.17 2.78 1.38 1.13 3.82 3.26 3.57果实纵径Fruit length 6.09 4.00 0.59 9.26 3.88 4.25 1.16 9.30 2.32 6.26 3.90 6.47 1.56 7.45 1.89 3.94 1.40 2.75小果高度Fruitlets height 2.28 1.96 2.64 0.27 1.94 4.24 2.37 1.19 1.00 6.57 4.43 2.08 1.09 2.02 2.93 7.56 7.22 1.59小果宽度Fruitlets width 3.27 3.35 2.90 1.45 3.28 4.59 0.76 1.19 0.66 7.13 5.04 1.96 0.97 6.57 0.61 5.94 2.33 1.92果心直径Core diameter 14.08 0.18 6.99 8.53 1.75 1.17 2.64 9.21 0.42 5.48 6.99 15.95 3.86 1.92 1.98 11.02 13.50 0.80果形指数Fruit shape index 3.71 5.34 0.40 2.10 1.91 2.93 1.17 9.57 0.22 1.72 4.99 3.31 1.22 6.07 0.77 0.12 1.86 13.99小果数Number of fruit eye 10.16 12.68 18.64 7.24 1.99 4.45 0.50 15.08 6.78 8.52 1.29 6.69 2.02 1.99 2.55 1.81 4.88 9.78
2.4 菠萝果实性状间的相关性分析
菠萝果实数量性状之间的相关性分析结果见表5,菠萝单果质量与果实横径、果实纵径、小果高、小果宽、果心直径等性状均呈极显著正相关,其中菠萝单果质量、果实横径、果实纵径体现的是菠萝果实的大小相一致,果心直径的大小也在一定程度上与果实大小有关,小果高和小果宽体现菠萝果实组成的基本单元菠萝小果的大小。菠萝小果数与果眼深度、果形指数呈极显著正相关,有可能是小果数量增多时,小果发育相互拥挤,倾向纵向生长,使得小果的果眼也纵向发育,同时小果数增多形成更长的果实纵径,导致较高的果形指数。决定菠萝果实加工利用率的果眼深度、果形指数与单果质量、果实横径、果实纵径等体现菠萝果实大小的性状彼此不相关,表明选育品种时需要同时兼顾两类性状,才能选择到符合要求的个体。
表5 菠萝果实数量性状的相关性分析
Table 5 Correlation analysis of quantitative traits of pineapple fruit
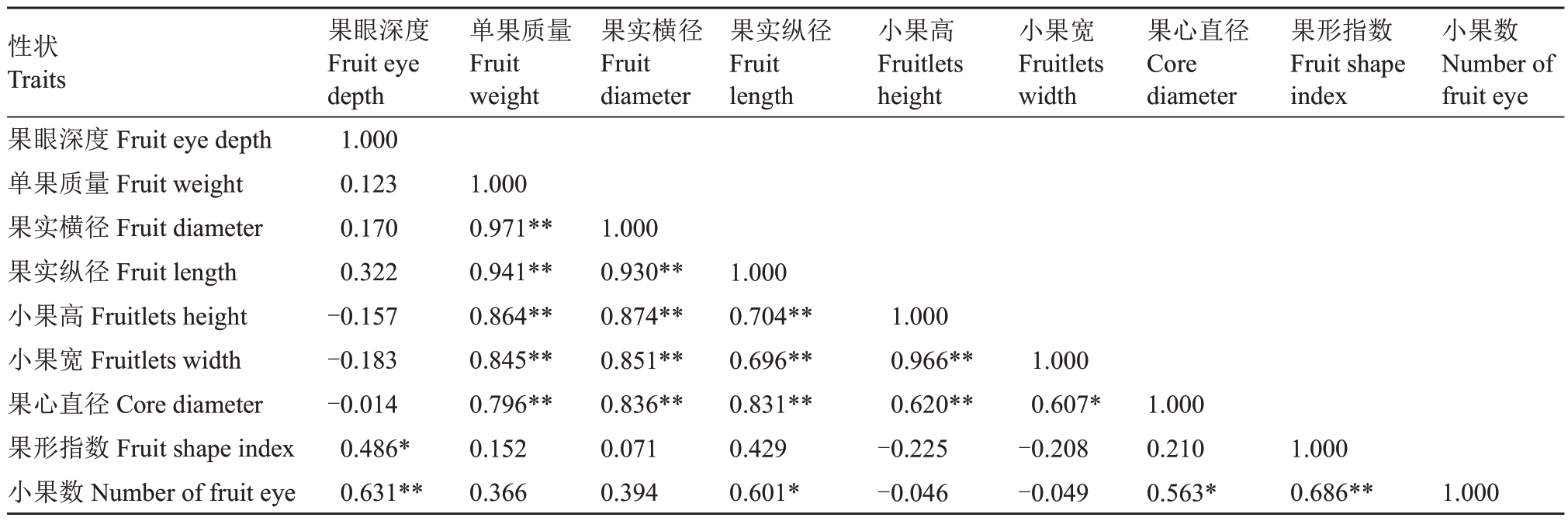
注:*表示差异显著(p<0.05),**表示差异极显著(p<0.01)。
Note:*means significant difference(p<0.05),**means extremely significant difference(p<0.01).
性状Traits果眼深度Fruit eye depth单果质量Fruit weight果实横径Fruit diameter果实纵径Fruit length小果高Fruitlets height小果宽Fruitlets width果心直径Core diameter果形指数Fruit shape index小果数Number of fruit eye果眼深度Fruit eye depth 1.000 0.123 0.170 0.322-0.157-0.183-0.014 0.486*0.631**单果质量Fruit weight果实横径Fruit diameter果实纵径Fruit length小果高Fruitlets height小果宽Fruitlets width果心直径Core diameter果形指数Fruit shape index小果数Number of fruit eye 1.000 0.971**0.941**0.864**0.845**0.796**0.152 0.366 1.000 0.930**0.874**0.851**0.836**0.071 0.394 1.000 0.704**0.696**0.831**0.429 0.601*1.000 0.966**0.620**-0.225-0.046 1.000 0.607*-0.208-0.049 1.000 0.210 0.563*1.000 0.686**1.000
3 讨 论
菠萝的小果统称为果眼[12],早期的行业标准也明确将果眼定义为头状花序发育成的复果上的小果[13-14]。因此《热带、南亚热带果树种质资源数据质量控制规范》、NY/T 2813—2015《热带种质资源描述规范 菠萝》、NY/T2750—2015《植物新品种特异性、一致性和稳定性测试指南凤梨属》等在描述果眼数量、外观和大小时均指小果的数量、大小和外观,而仅在果眼深度时指小果的花腔(宿存的花萼、果托、子房顶部包围而成的空腔,有的专家也称“果丁”[15])深度。因此,为了避免歧义直接采用了代表小果大小的小果高度和小果宽度,以及采用小果数代表果眼数。
上述规范或标准均给出了菠萝的单果质量、果实纵径、果实横径、果形指数等性状的测试方法,且方法一致。但这三者以及国际植物新品种保护联盟(UPOV)菠萝测试指南TG/295/1—2013等均未给出菠萝果眼深度、小果大小、果心直径等性状的具体测量部位。仅NY/T 2813—2015《热带种质资源描述规范菠萝》给出了果眼(实际指小果)大小的测量方法,即测量果眼(实际指小果)的纵径和横径。由于菠萝果实外形上中下各部位的宽度并不一致,因此,在测量果眼深度、小果大小、果心直径等性状时,采用果实纵向上果实1/4、1/2 以及3/4 处部位的小果、果心进行测量,然后求平均值。
单果质量是菠萝的重要商品性状[16],每株菠萝苗只结1个果实,种植密度一定时,单果质量决定菠萝最终产量[17]。目前市场上商品果单果质量要求超过620 g,适于加工制罐的菠萝单果质量要求超过1500 g[18]。18份种质中,Josapine、印度5Q、观赏类红果和Giant Kew 的单果质量未达到620 g,难作为目前市场上的大宗商品果销售;黑菠萝、开英1 号、N36、无刺卡因、上海2号的平均单果质量超过1500 g,达到加工制罐果单果质量的要求。同时本研究结果表明,黑菠萝、无刺卡因、上海2 号单果质量的变异系数均超过10%,受环境影响较大,这些种质有望通过改善条件进一步提高产量;而开英1 号单果质量最稳定,稳产性能较好。
菠萝果眼是宿存的花萼、果托、子房顶部包围而成的一个空腔,果眼深度影响到果实的可食用率和加工利用率[5]。18份菠萝种质中上海2号、广西引观赏类红果、观赏类红果、马来西亚沙捞越、Josapine和印度5Q 果眼深度较浅。种质内果眼深度变异系数均较小,遗传较为稳定,与吴竞等[19]果眼深浅遗传稳定的研究结果一致。其中马来西亚沙捞越果眼深度变异系数为0.11%,是18个种质中最小的,遗传最为稳定。多数菠萝加工去皮装置很难依据果实大小和形状自动调整刀具轨迹[20],因此菠萝果实横径变异程度大,会导致大果的果肉浪费。18份种质中单果质量超过1500 g的种质上海2号、无刺卡因、N36、开英1 号、黑菠萝果实横径变异系数均小于5%,果实大小较均匀,可用于加工制罐。
本研究中,菠萝单果质量与果实横径、果实纵径等体现菠萝果实大小的性状呈极显著正相关,这与龚雪[21]的研究结果一致,说明增加果实的纵径和横径可以提高单果质量。本研究中代表小果大小的小果高和小果宽与菠萝单果质量呈极显著正相关,表明小果大有利于单果质量增加;然而本研究中小果数和单果质量之间却未显著相关,说明小果大小对果实质量的贡献大于小果数量,因此在育种上应优先考虑增加小果的大小,其次才是小果数量。
本研究所试18 份菠萝种质在单果质量、果心直径、小果数、果眼深度、果实纵径等性状上存在较大的变异,证明菠萝种质在这些果实性状上具有丰富的遗传多样性。果实作为植物的重要定型器官,常用于品种鉴定识别,相比于采用果实的生理生化等指标的鉴定和分子DNA的鉴定,外观性状更为便捷,而且生化指标还受果实成熟度、采收季节等因素的影响,根据果实的外观形态对于进入流通和市场领域的果实进行初步的品种鉴定识别具有重要的意义。
4 结 论
所试18 份菠萝种质在单果质量、果心直径、小果数、果眼深度、果实纵径等性状上存在较大的变异,具有丰富的遗传多样性,可用于进入流通和市场品种果实的初步识别和鉴定。开英1 号、马来西亚沙捞越、N36等单果质量大、果眼浅的种质在果实外观性状上具有进一步开发利用的价值。
致谢:感谢国家热带植物种质资源库、农业农村部湛江菠萝种质资源圃对本研究的支持。
[1]刘海清.中国菠萝产业国际竞争力研究[D].北京:中国农业科学院,2016.LIU Haiqing.Study on international competitiveness of pineapple industry in China [D].Bejing:Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences,2016.
[2]孙伟生,吴青松,孙光明.我国菠萝产业发展现状及对策[J].中国热带农业,2013(3):22-24.SUN Weisheng,WU Qingsong,SUN Guangming.Present situation and countermeasures of pineapple industry in China[J].China Tropical Agriculture,2013(3):22-24.
[3]邓春梅,李玉萍,梁伟红,叶露.我国菠萝产业发展现状及对策[J].山西农业科学,2018,46(6):1031-1034.DENG Chunmei,LI Yuping,LIANG Weihong,YE Lu.Present situation and countermeasures of pineapple industry in China[J].Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences,2018,46(6):1031-1034.
[4]贺军虎,陈业渊,王芳,刘少芬,曾垂凤,赵小青.10 份菠萝种质资源的描述和评价[J].热带作物学报,2009,30(12):1731-1735.HE Junhu,CHEN Yeyuan,WANG Fang,LIU Shaofen,ZENG Chuifeng,ZHAO Xiaoqing.Description and evaluation of ten accessions of pineapple germplasm[J].Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2009,30(12):1731-1735.
[5]张阳梅,曾建生,赵志平,高世德,刘代兴.菠萝种质资源果实主要数量性状的主成分分析[J].热带农业科技,2016,39(2):10-13.ZHANG Yangmei,ZENG Jiansheng,ZHAO Zhiping,GAO Shide,LIU Daixing.Principal component analysis of main quantitative characters in pineapple germplasm[J].Tropical Agricultural Science&Technology,2016,39(2):10-13.
[6]严程明,张江周,刘亚男,马海洋,石伟琦.5 个品种菠萝果实品质比较与分析[J].广东农业科学,2012,39(19):42-44.YAN Chengming,ZHANG Jiangzhou,LIU Yanan,MA Haiyang,SHI Weiqi.The comparison and analysis of fruit quality for five different pineapple variety[J].Guangdong Agricultural Sciences,2012,39(19):42-44.
[7]陆新华,吴青松,刘胜辉,孙伟生,张秀梅,李运合,孙光明.菠萝种质果实可溶性糖组分及含量分析[J].热带作物学报,2012,33(5):936-940.LU Xinhua,WU Qingsong,LIU Shenghui,SUN Weisheng,ZHANG Xiumei,LI Yunhe,SUN Guangming.Analysis for components and contents of soluble sugars in pineapple germplasm[J].Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2012,33(5):936-940.
[8]陆新华,孙德权,吴青松,刘胜辉,张秀梅,孙光明.不同类群菠萝种质果实糖酸组分含量分析[J].果树学报,2013,30(3):444-448.LU Xinghua,SUN Dequan,WU Qingsong,LIU Shenghui,ZHANG Xiumei,SUN Guangming.Analysis of components and contents of soluble sugars and organic acids in pineapple germplasm[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2013,30(3):444-448.
[9]魏长宾,刘胜辉,陆新华,吴青松,孙光明.6 个菠萝品种香气成分及特征香气分析[J].广东农业科学,2015,42(24):111-117.WEI Changbin,SUN Weisheng,LU Xinhua,WU Qingsong,SUN Guangming.Analysis of aroma compounds and characteristic aroma in 6 pineapple varieties[J].Guangdong Agricultural Sciences,2015,42(24):111-117.
[10]李苗苗.菠萝果实维生素组分和含量变化的研究[D].海口:海南大学,2012.LI Miaomiao.Study on the changes of vitamins content in pineapple fruit[D].Haikou:Hainan University,2012.
[11]杨祥燕,蔡元保,孙光明.菠萝果肉颜色的形成与类胡萝卜素组分变化的关系[J].果树学报,2010,27(1):135-139.YANG Xiangyan,CAI Yuanbao,SUN Guangming.Relationship between color formation and change in composition of carotenoids in flesh of pineapple fruit[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2010,27(1):135-139.
[12]陈业渊,贺军虎.热带、南亚热带果树种质资源数据质量控制规范[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2006:8.CHEN Yeyuan,HE Junhu.Specification for quality control of tropical and southern subtropical fruit tree germplasm data[M].Bejing:China Agriculture Press,2006:8.
[13]华南热带农产品加工设计研究所,广西亚热带作物研究所.菠萝:NY/T 450—2001[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2001.South China Tropical Agricultural Products Processing and Design Institute,Guangxi Subtropical Crops Research Institute.Pineapple:NY/T 450—2001 [S].Beijing: Standards Press of China,2001.
[14]广西农科院园艺研究所,广西果品食杂公司.鲜菠萝:SB/T 10063—1992[S].北京:中国标准出版社,1992.Horticulture Research Institute,Guangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Guangxi Fruit and Grocery Company.Fresh pineapple:SB/T 10063—1992[S].Beijing:Standards Press of China,1992.
[15]广东省农业科学院果树研究所.菠萝及其栽培[M].北京:轻工业出版社,1987.Institute of Fruit Tree Research,Guangdong Academy of Agricultural Sciences.Pineapple and its cultivation [M].Beijing:Light Industry Press,1987.
[16]陆新华,孙德权,吴青松,刘胜辉,孙光明.12 个泰国菠萝品种的果实品质评价[J].热带作物学报,2011,32(12):2205-2208.LU Xinhua,SUN Dequan,WU Qingsong,LIU Shenghui,SUN Guangming.Principal component analysis of main quantitative characters in pineapple germplasm[J].Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2011,32(12):2205-2208.
[17]李运合,孙光明,吴青松.菠萝AcHMGR 基因的克隆与表达分析[J].热带作物学报,2016,37(12):2359-2365.LI Yunhe,SUN Guangming,WU Qingsong.Cloning and expression analysis of AcHMGR gene in pineapple[J].Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2016,37(12):2359-2365.
[18]孙伟生,吴青松,刘胜辉,孙光明.台农系列菠萝品种特性的比较分析[J].热带作物学报,2016,37(11):2050-2055.SUN Weisheng,WU Qingsong,LIU Shenghui,SUN Guangming.Comparative analysis of variety characteristics of Tainong series pineapple[J].Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2016,37(11):2050-2055.
[19]吴竞,何业华,谢桃,丁雅琦,栾爱萍,薛彪,张伟,李晶晶,刘朝阳.菠萝果眼发育相关基因AcCBL 超表达载体构建及其转化的研究[C]//中国园艺学会:中国园艺学会2019 年学术年会暨成立90 周年纪念大会论文摘要集.北京:中国园艺学会,2019:1.WU Jing,HE Yehua,XIE Tao,DING Yaqi,LUAN Aiping,XUE Biao,ZHANG Wei,LI Jingjing,LIU Chaoyang.Overexpression vector of AcCBL,a gene related to eye development research on construction and transformation [C]//Chinese Society for Horticultural Science:Abstracts of Papers of the 2019 Annual Conference of the Chinese Horticultural Society and the 90th Anniversary of the Founding Conference.Beijing:Chinese Society for Horticultural Science,2019:1.
[20]宋玲,史勇.菠萝去皮装置的研究现状及发展趋势[J].中国农机化学报,2017,38(6):109-113.SONG Ling,SHI Yong.Research status and development trend of pineapple peeling device[J].Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization,2017,38(6):109-113.
[21]龚雪.神湾菠萝主要性状调查与优株选择[D].广州:华南农业大学,2016.GONG Xue.Investigation on main characteristics of‘Shenwan’pineapple and selection of excellent individuals [D].Guangzhou:South China Agricultural University,2016.